Nervous System Lecture Overview
1/159
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
160 Terms
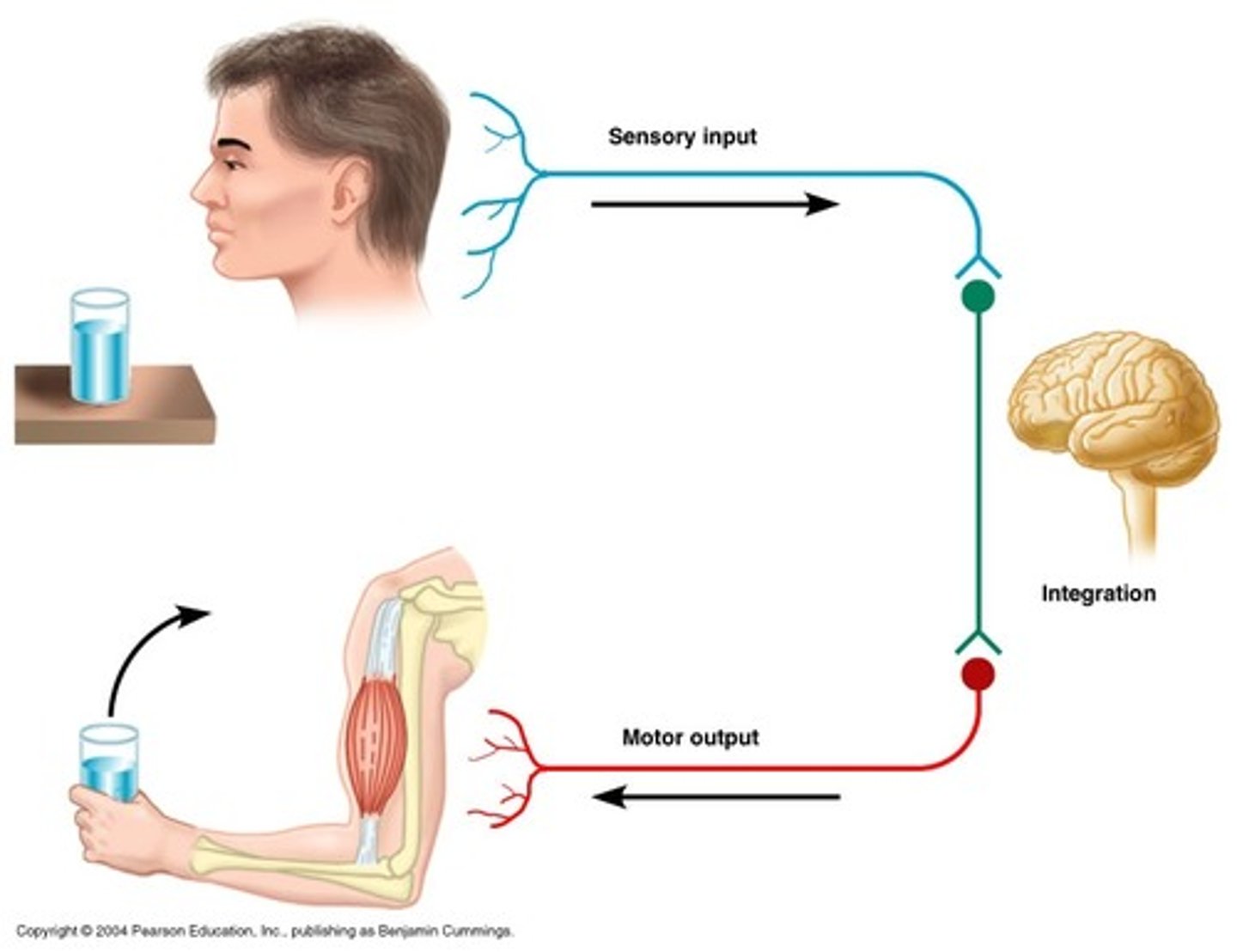
what are the three vital steps within the nervous system?
1. perception
2. integration
3. motor output
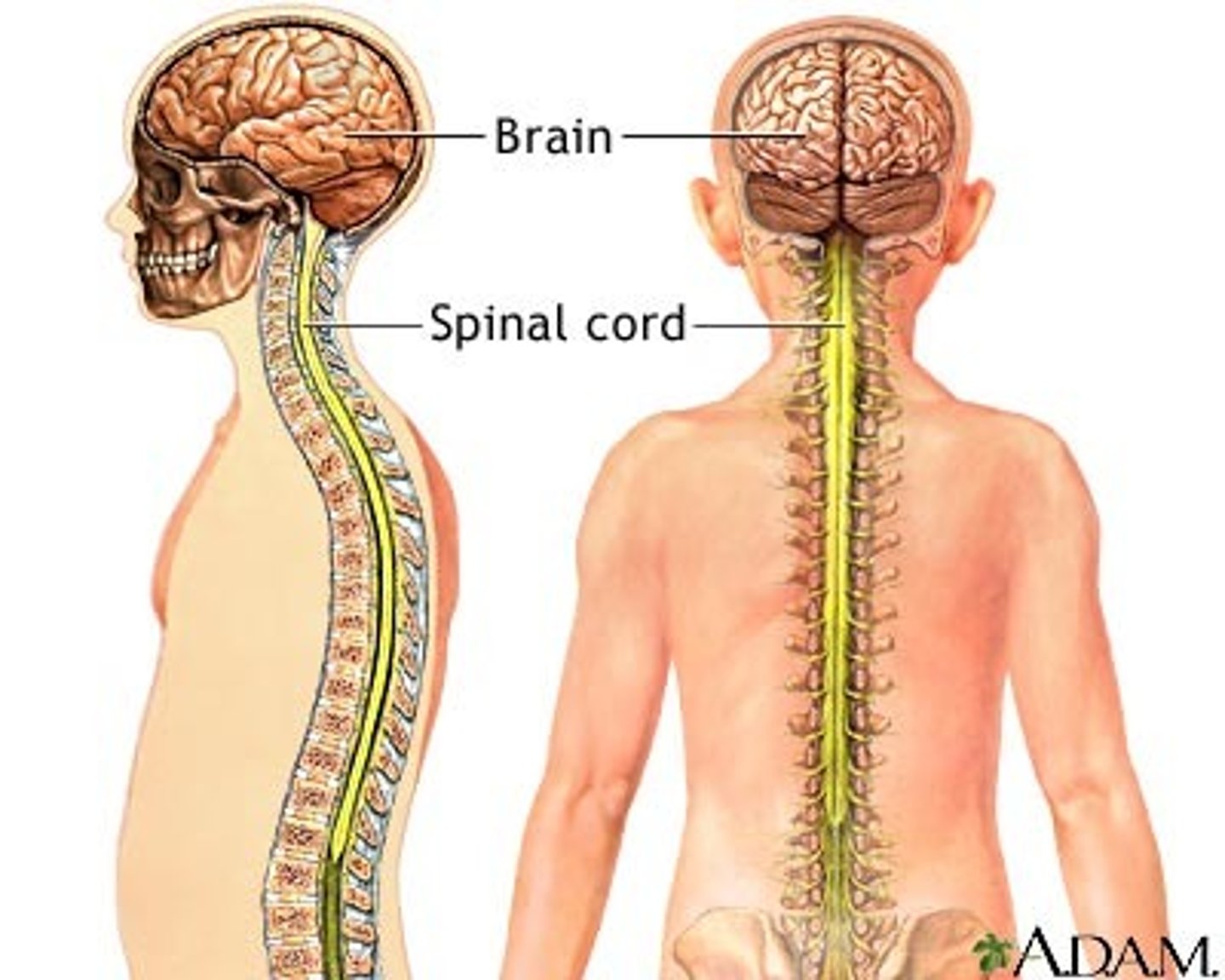
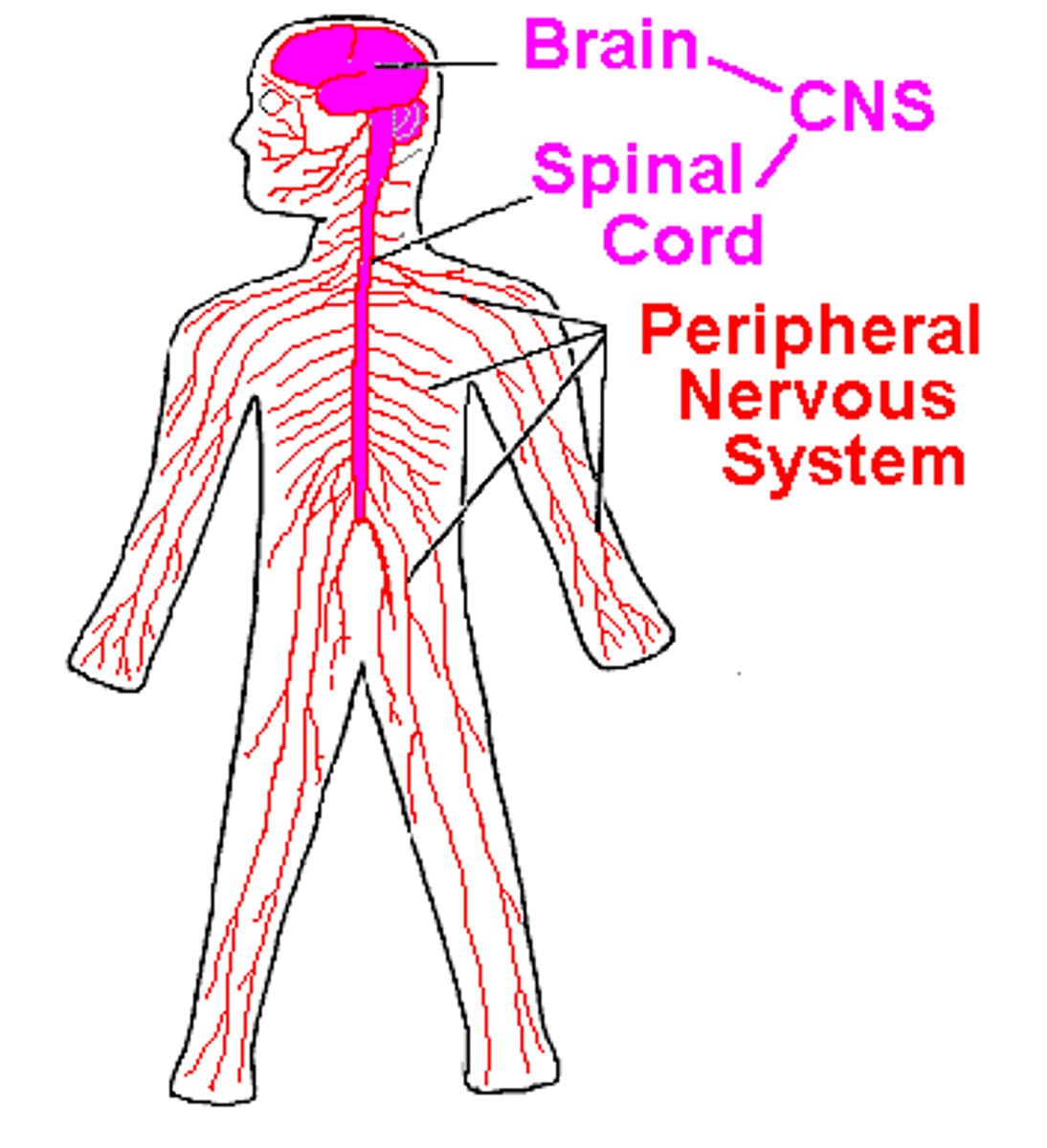
central nervous system (CNS)
brain and spinal cord
peripheral nervous system (PNS)
-the sensory and motor divisions that connect the CNS to the rest of the body
-cranial and spinal nerves
visceral sensory division
carries signals from the viscera (heart, lungs, stomach, and urinary bladder)
somatic sensory division
carries signals from receptors in the skin, muscles, bones, and joints
visceral motor division
-carries signals to glands, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle
-can be sympathetic or parasympathetic
-involuntary
somatic motor division
-carries signals to skeletal muscles
-voluntary
sympathetic division
accelerates respiration, inhibits digestion
parasympathetic division
reduces respiration, stimulates digestion
function of CNS
integration and command center
function of PNS
communication lines between the CNS and the rest of the body
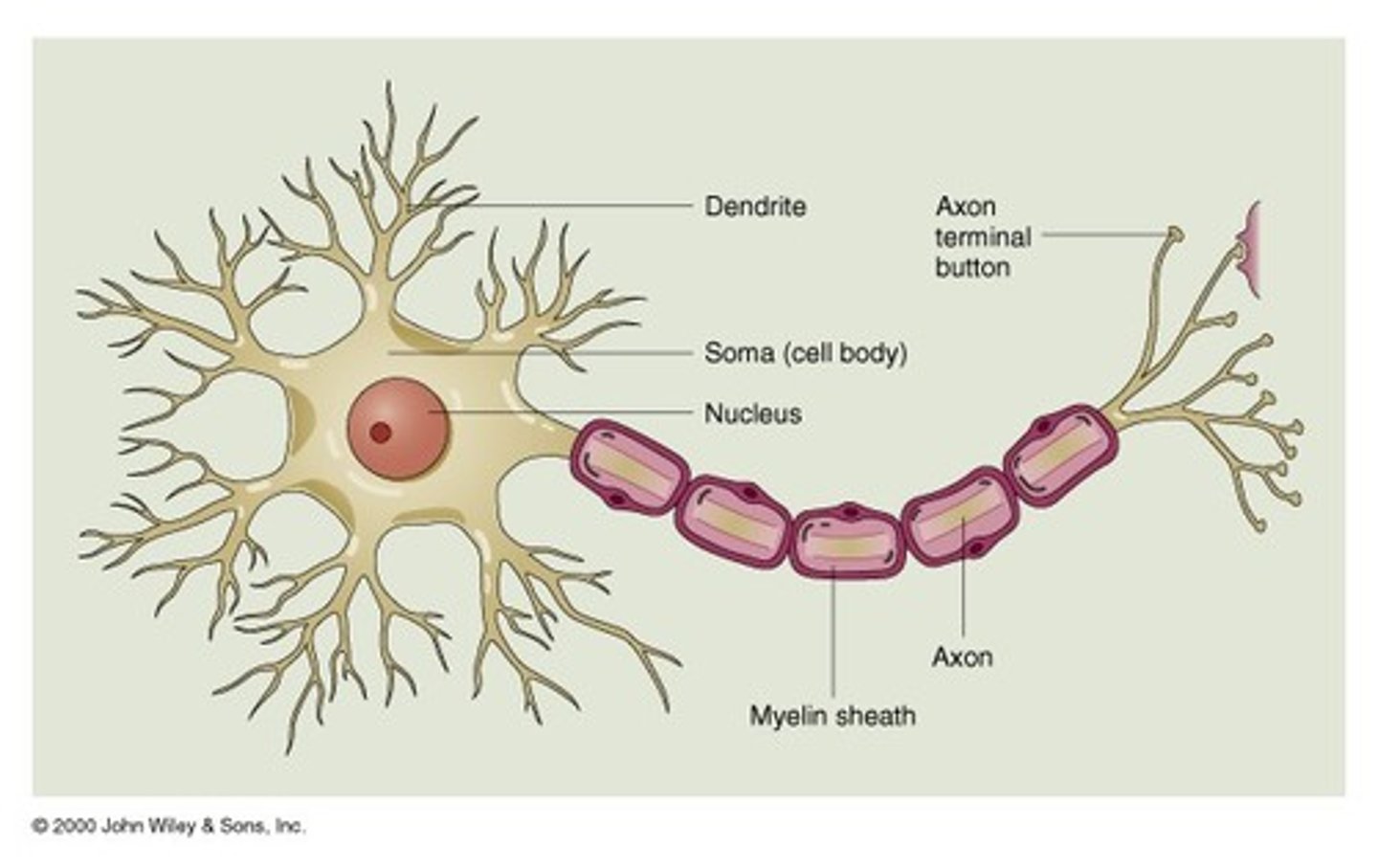
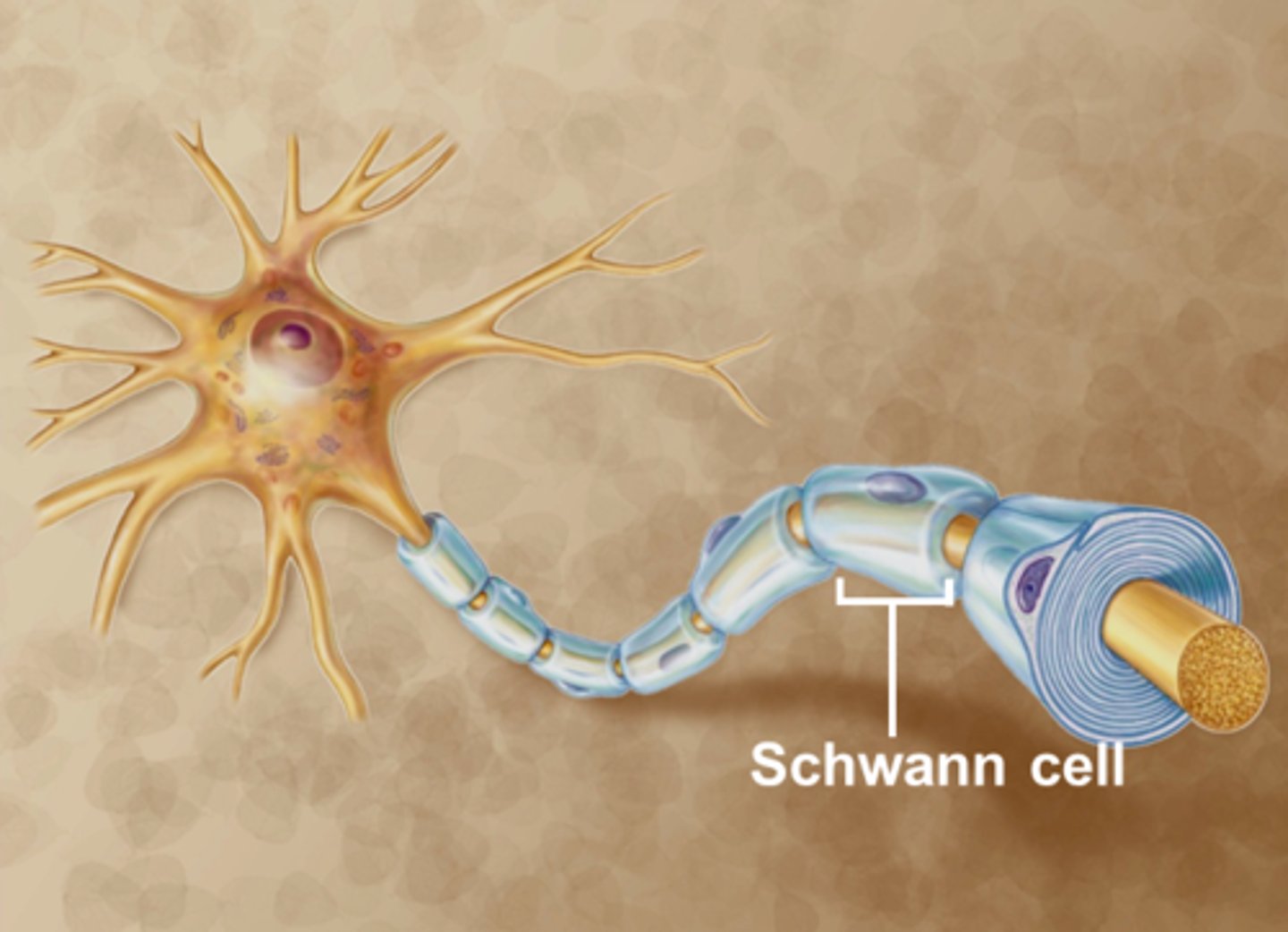
axon
part of the neuron that sends action potentials
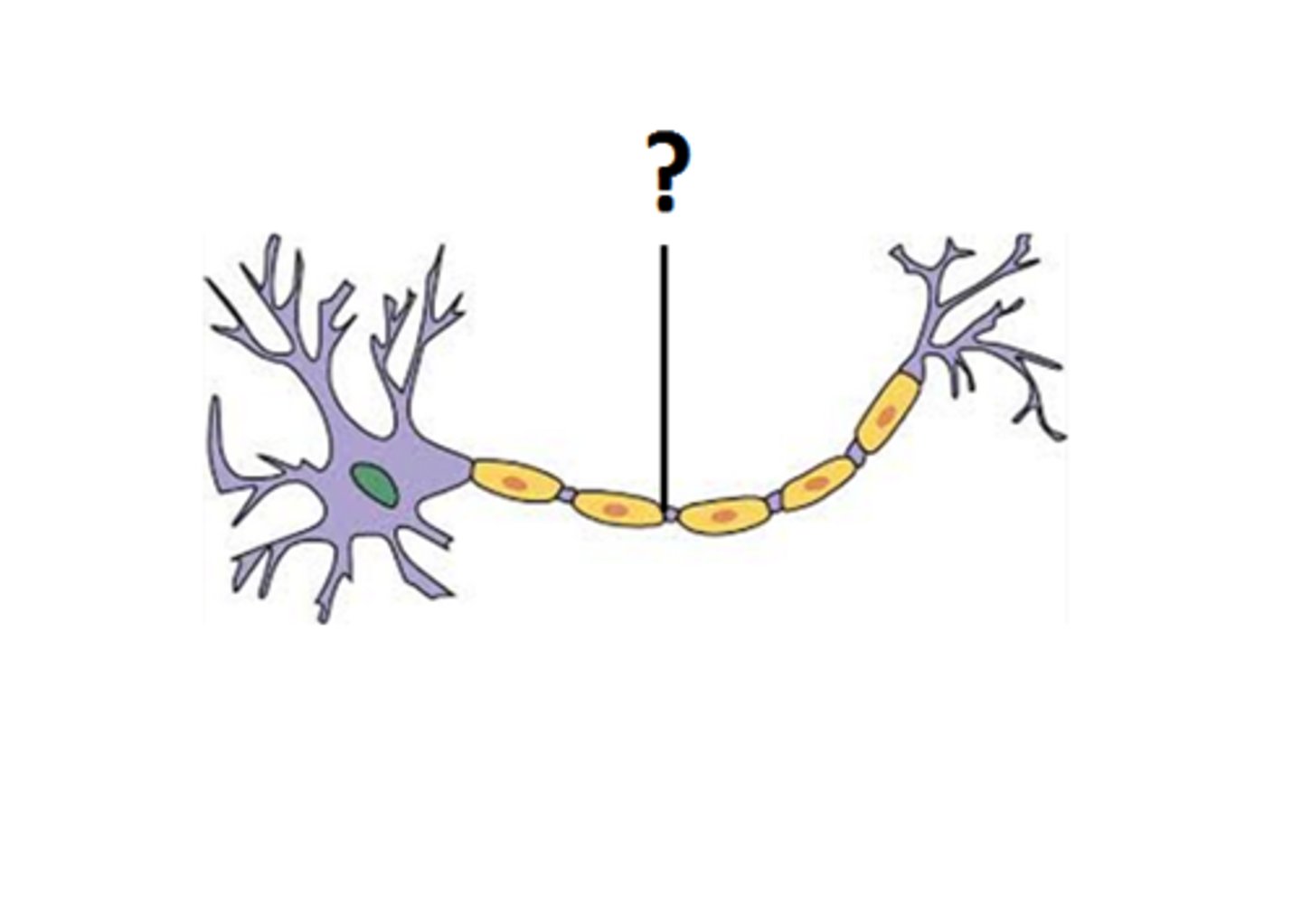
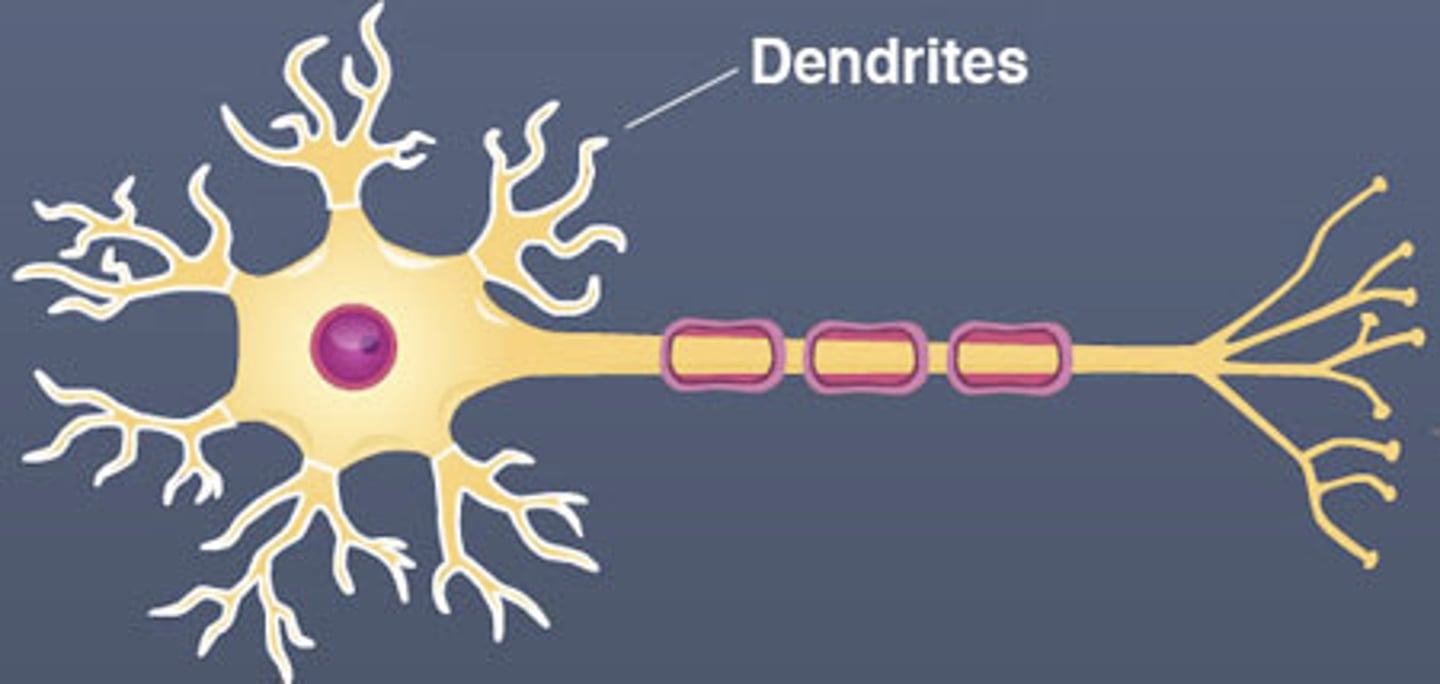
dendrite
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive signals
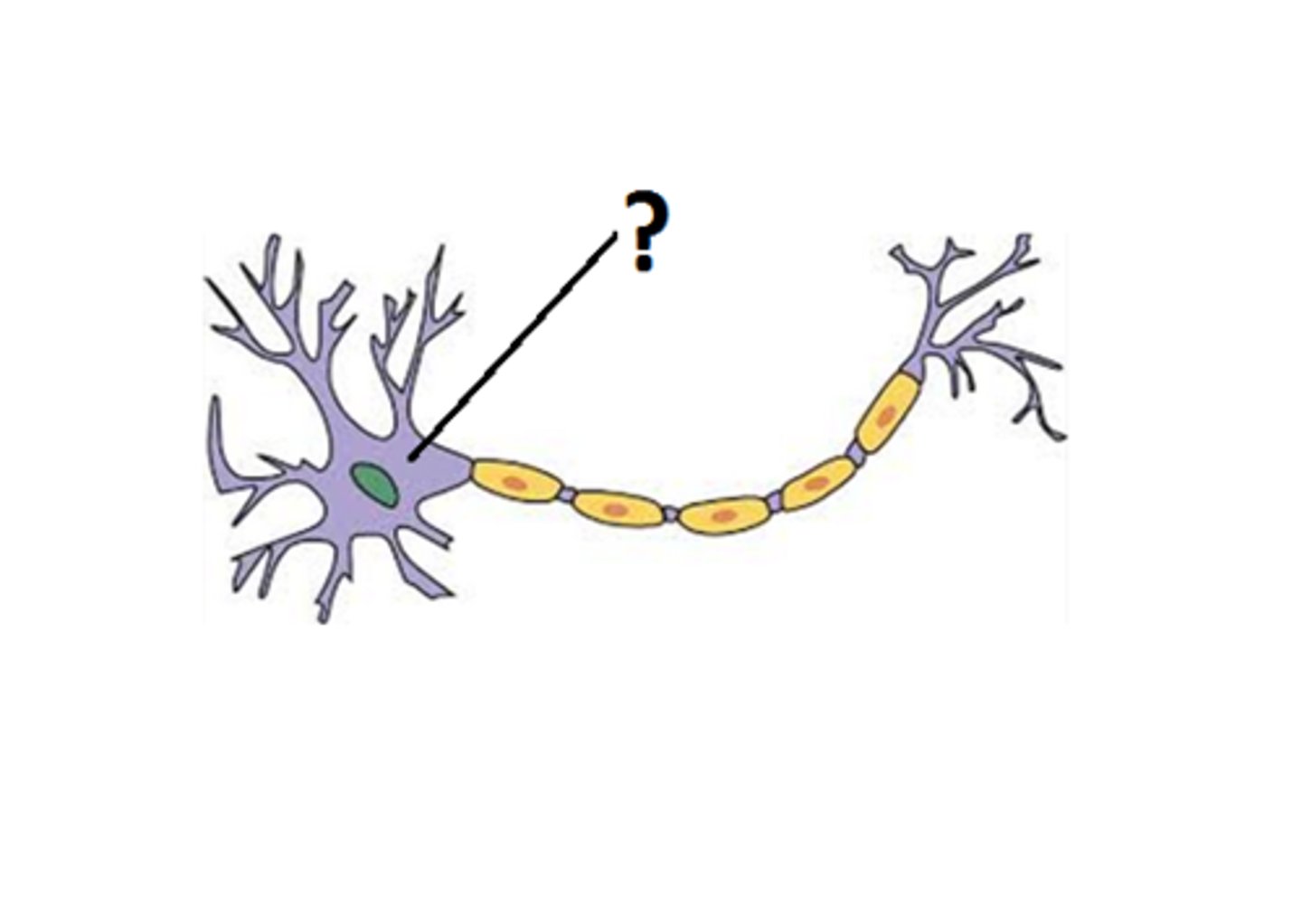
cell body of neuron
contains nucleus and organelles
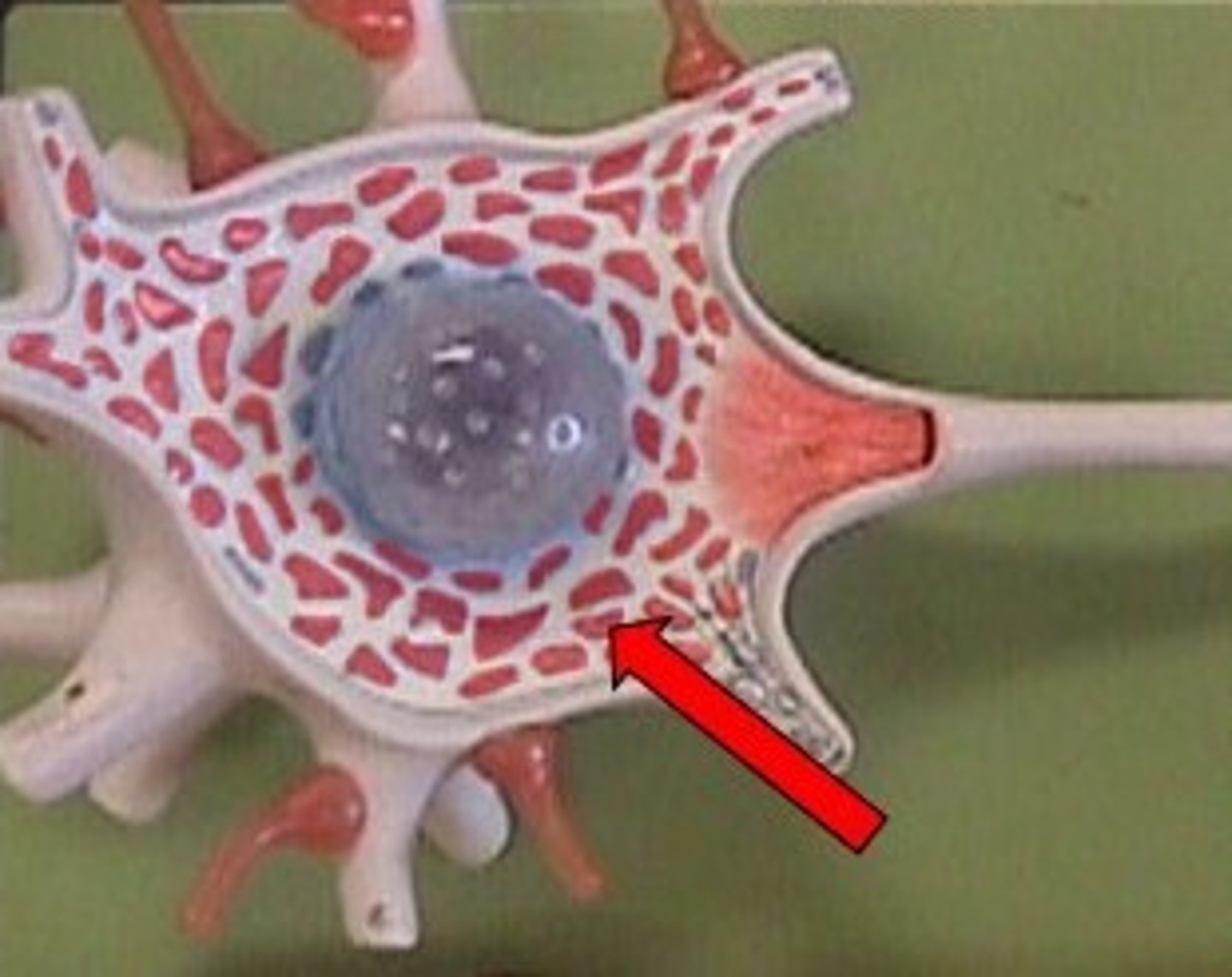
nissl bodies
Rough endoplasmic reticulum in neuron
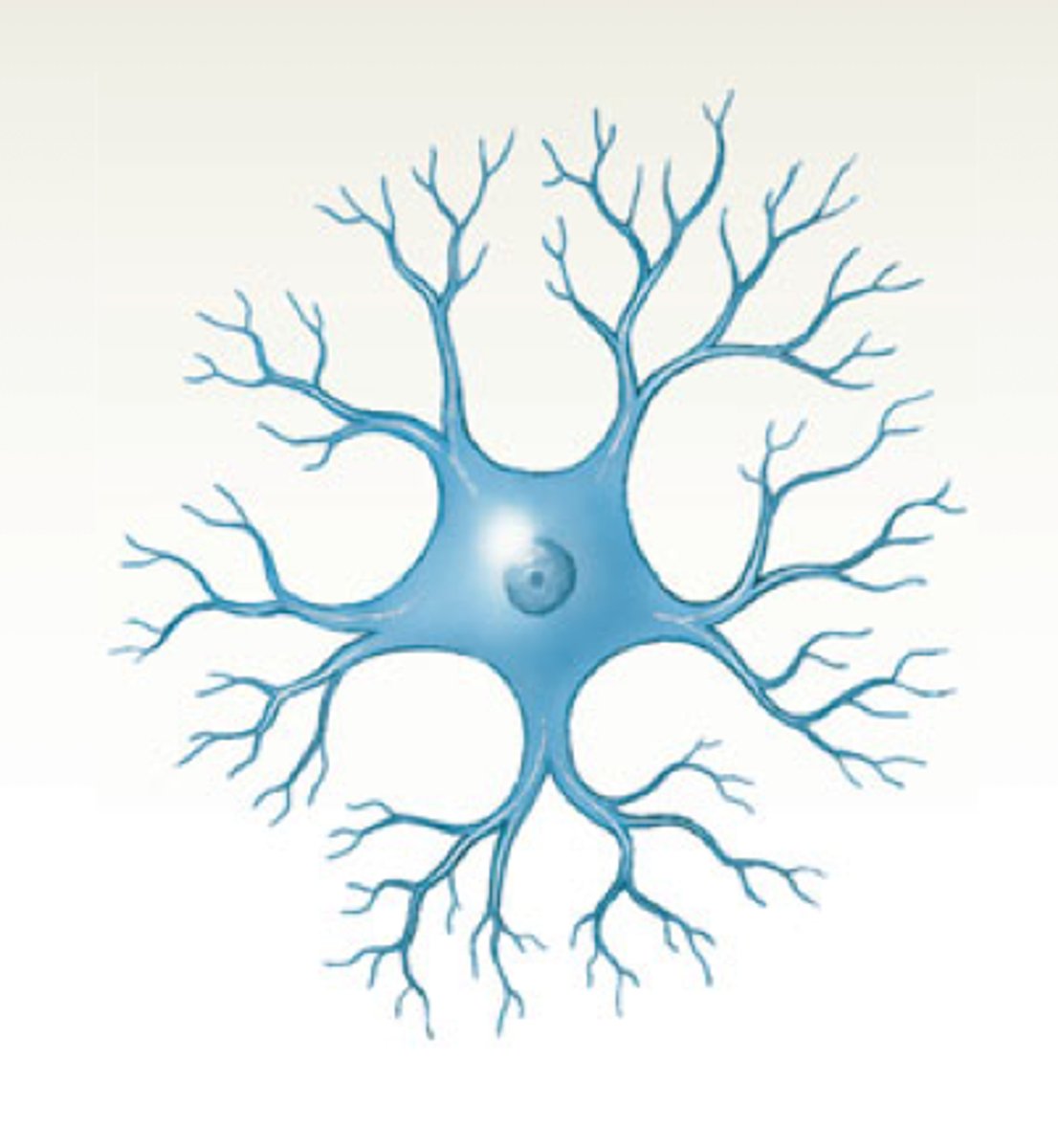
multipolar neuron
a nerve cell that has many dendrites and a single axon
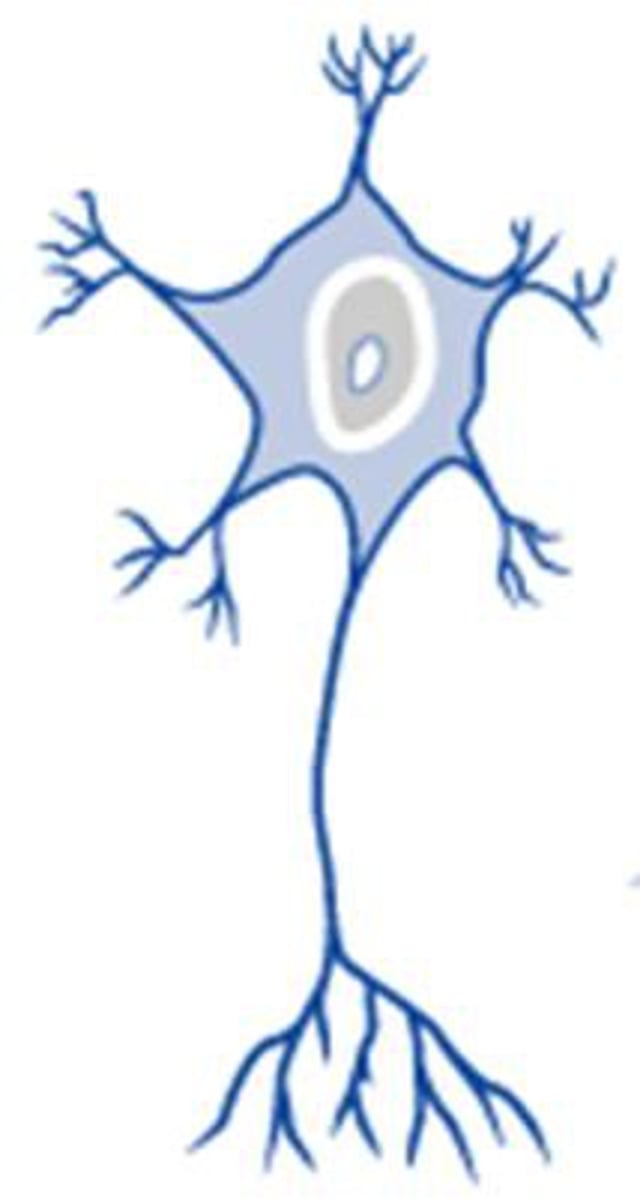
bipolar neuron
nerve cell with one axon and one dendrite
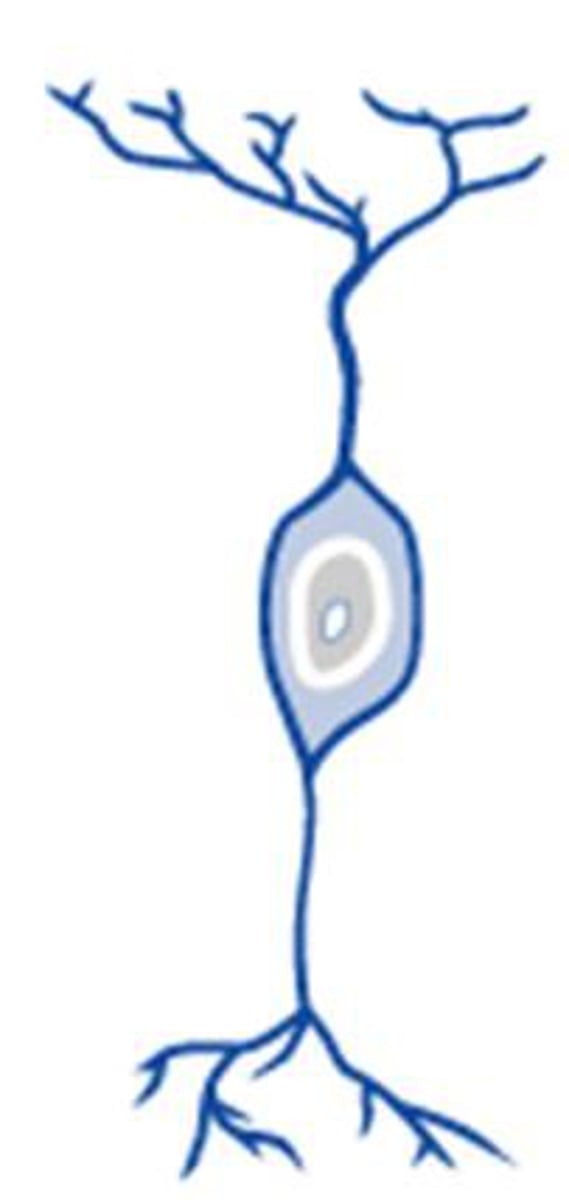
unipolar neuron
nerve cell with no dendrites, one axon
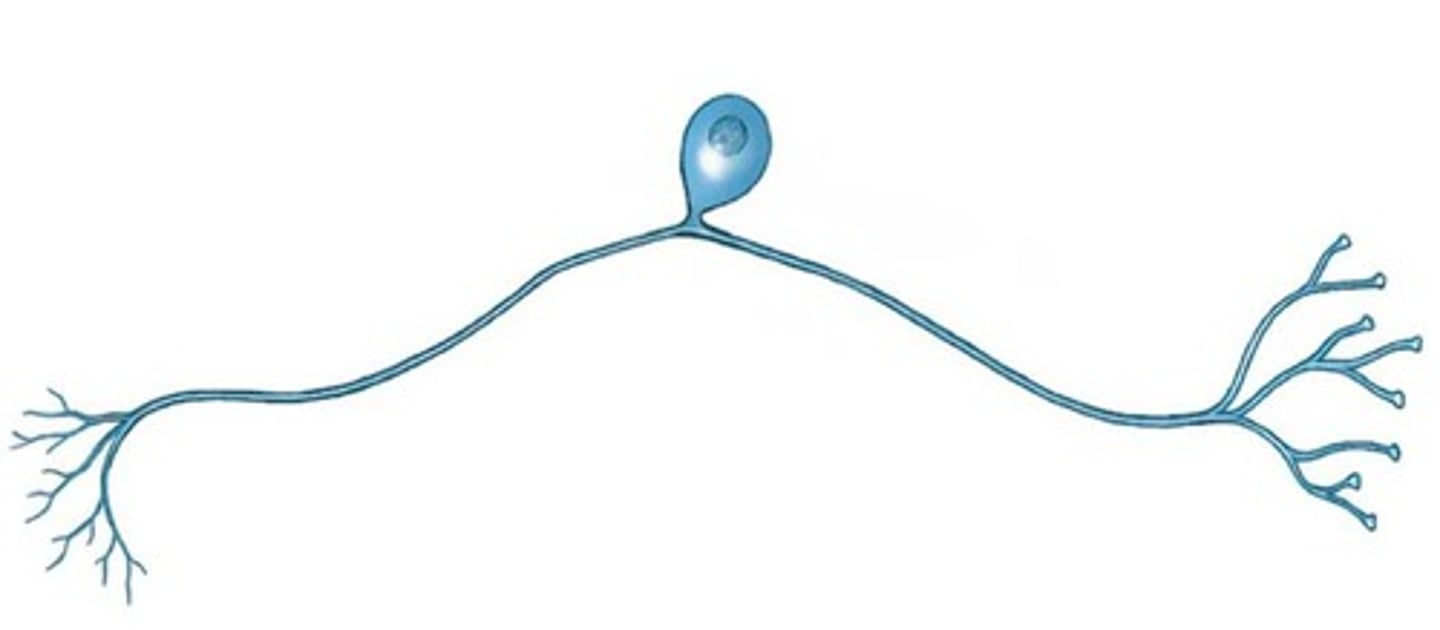
anaxonic neuron
many dendrites but no axon
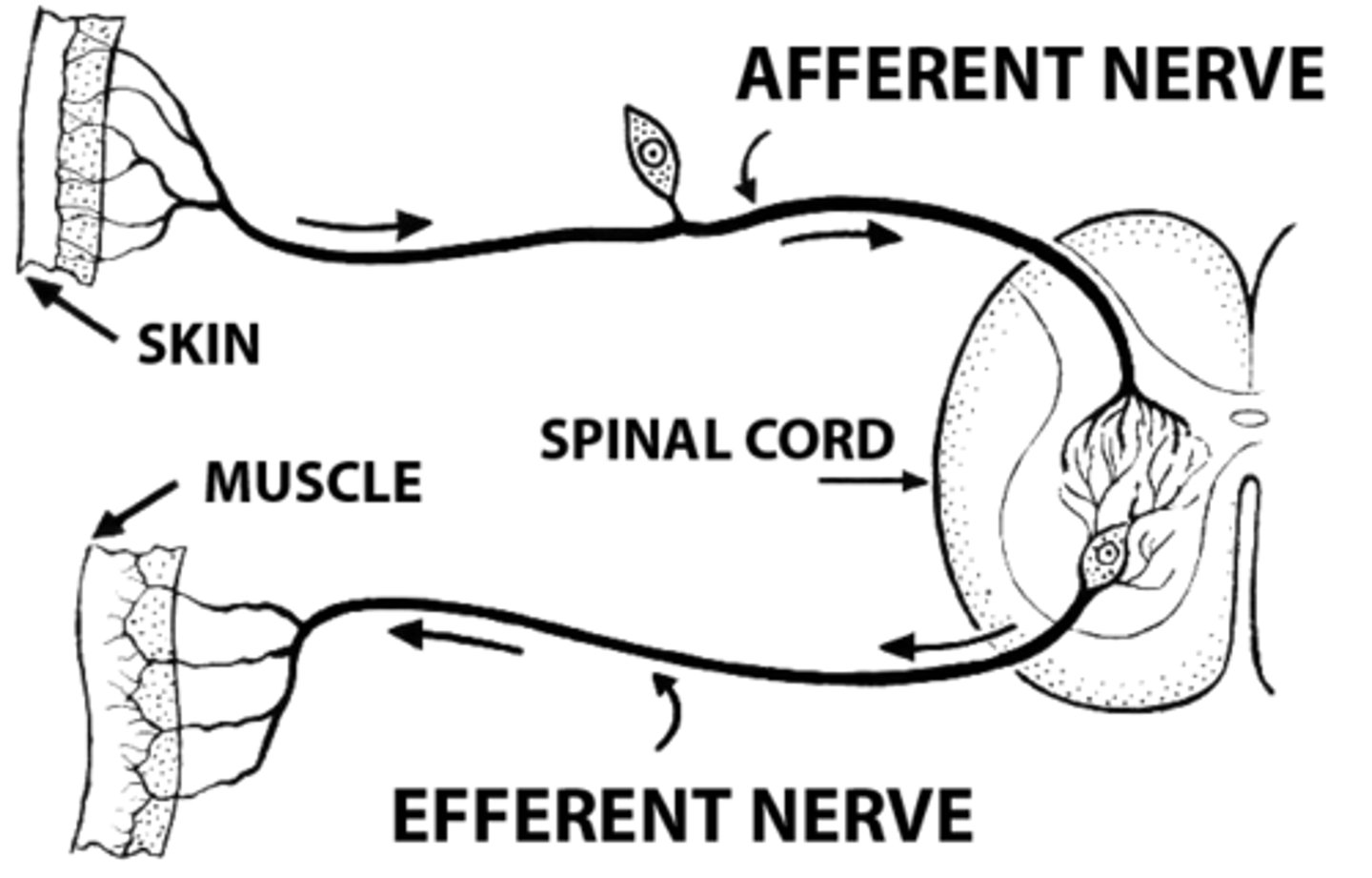
afferent
-sensory; carry information TOWARDS the CNS
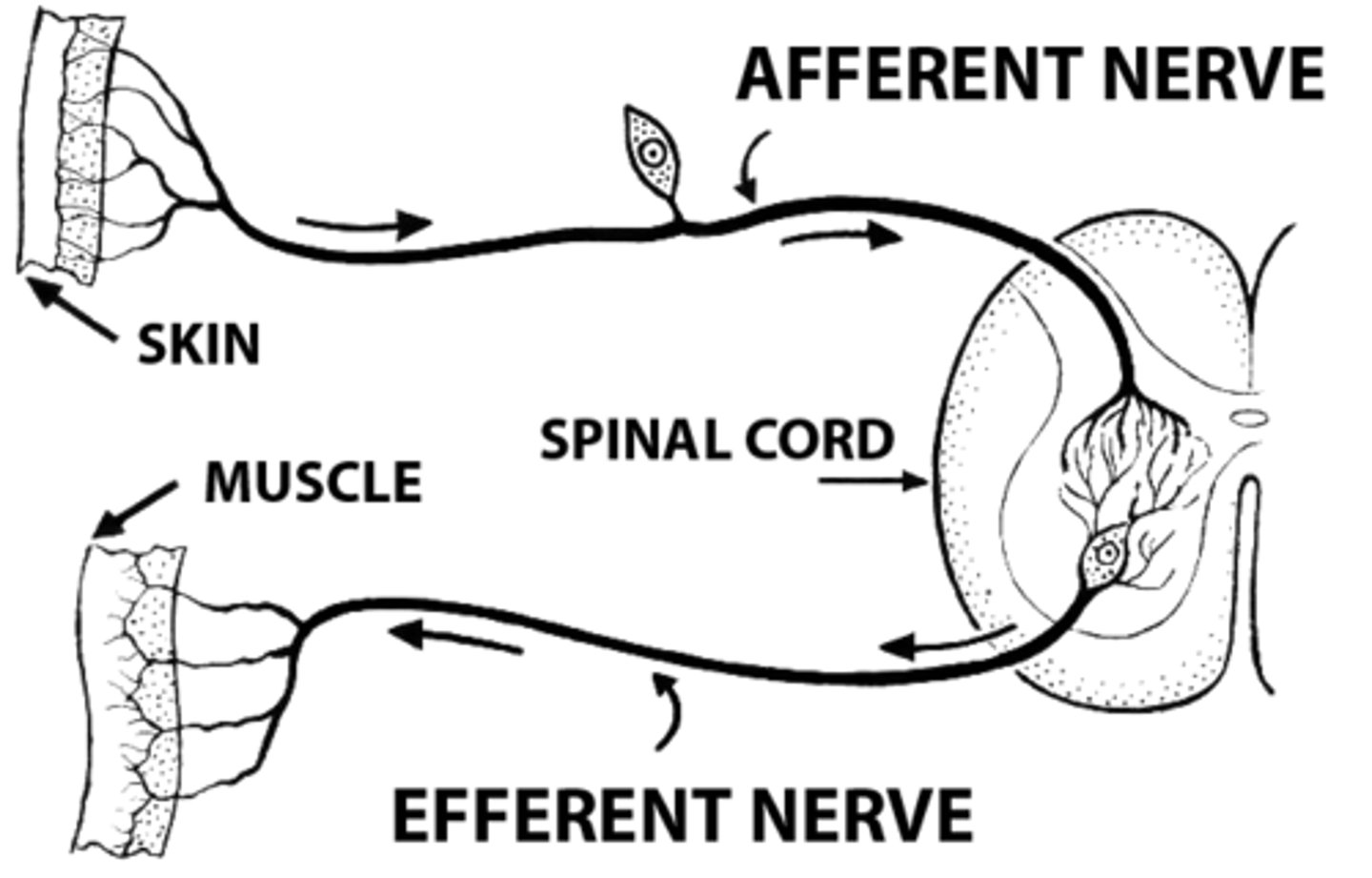
efferent
-motor; carry information AWAY from the CNS
ascending tracts
carry information from body up the spinal cord and towards the brain
descending tracts
carry nerve impulses away from the brain
pathways
a bundle of axons that connects 2+ neurons for communication
nerve
A bundle of nerve fibers
plexus
large, interlacing network of nerves
ganglion
A cluster of nerve cell bodies, often of similar function, located in the PNS.
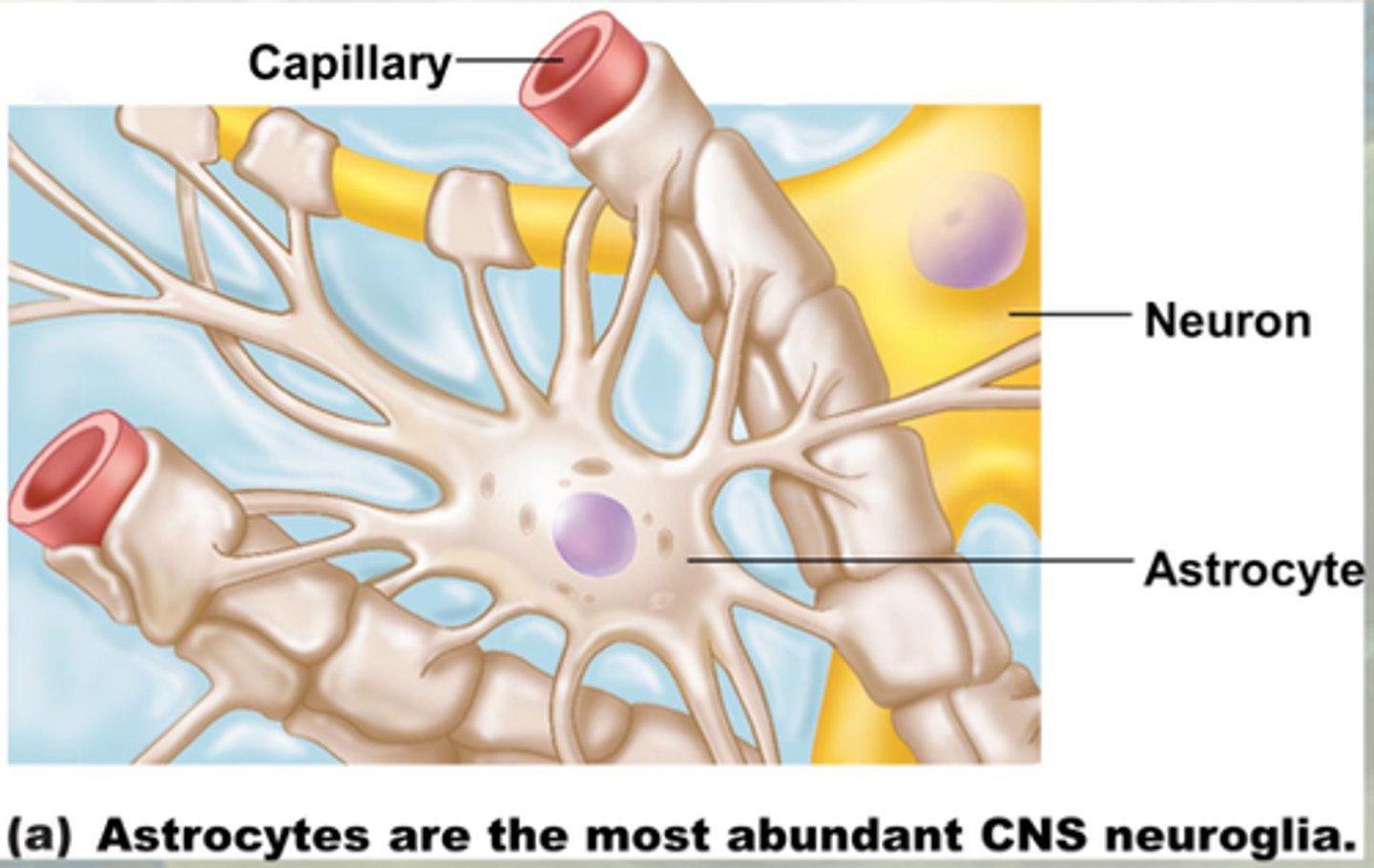
neuroglial cells
supportive cells and make up about half of all neural tissue
astrocytes
brace neurons
form blood-brain barrier
oligodendrocytes
Form myelin sheath in CNS
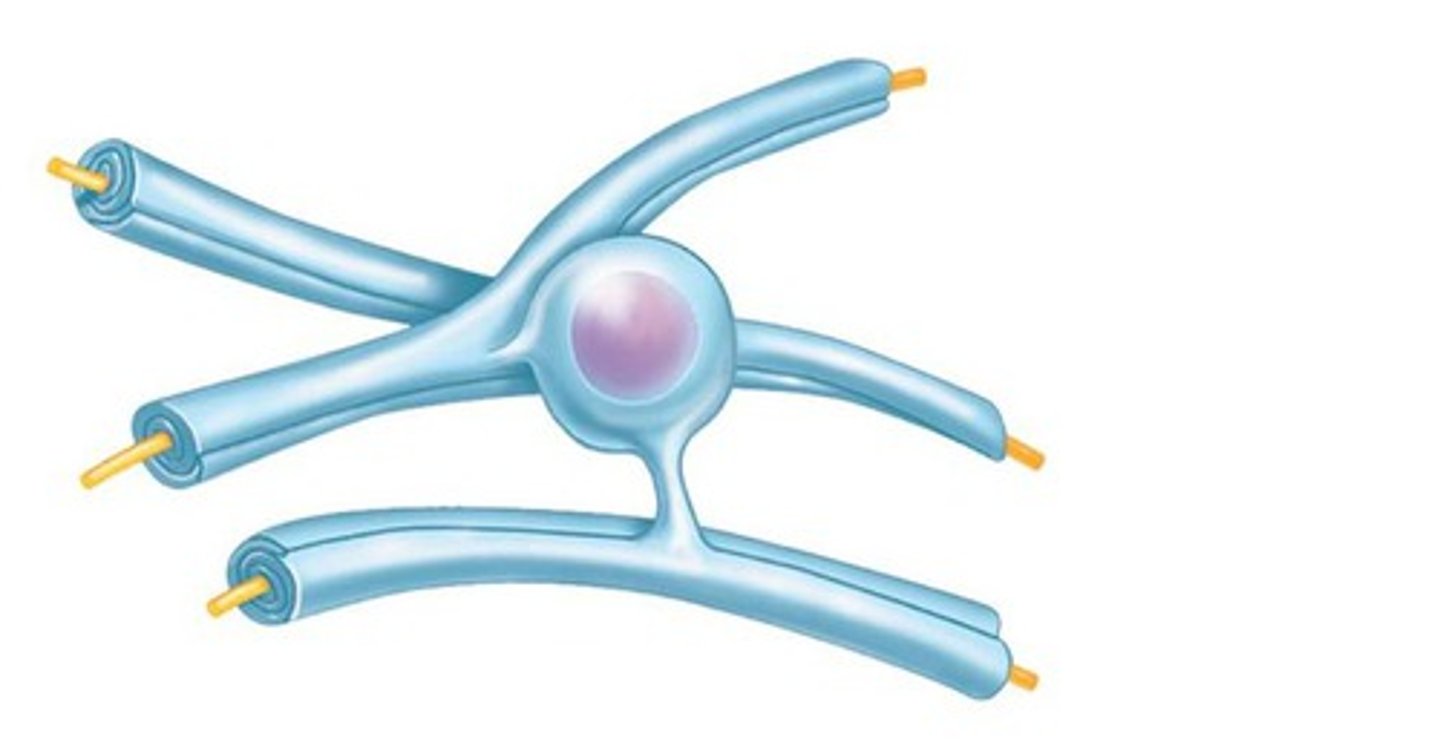
myelin sheath function
-insulates myelin
-prevents electrical charge from leaking across membrane
-speeds up nerve transmission; allows charge to travel faster down axon
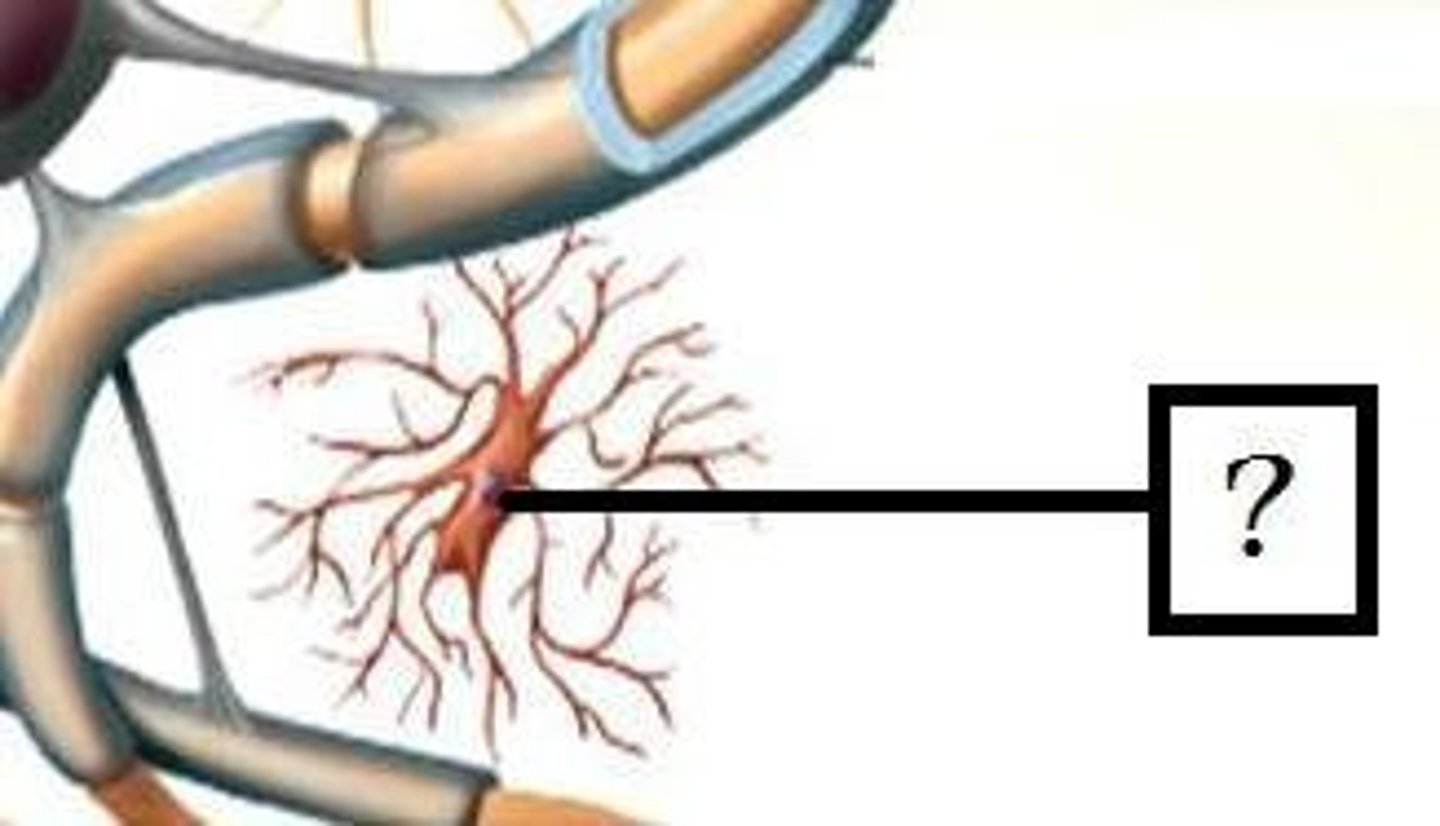
microglia
CNS phagocytes
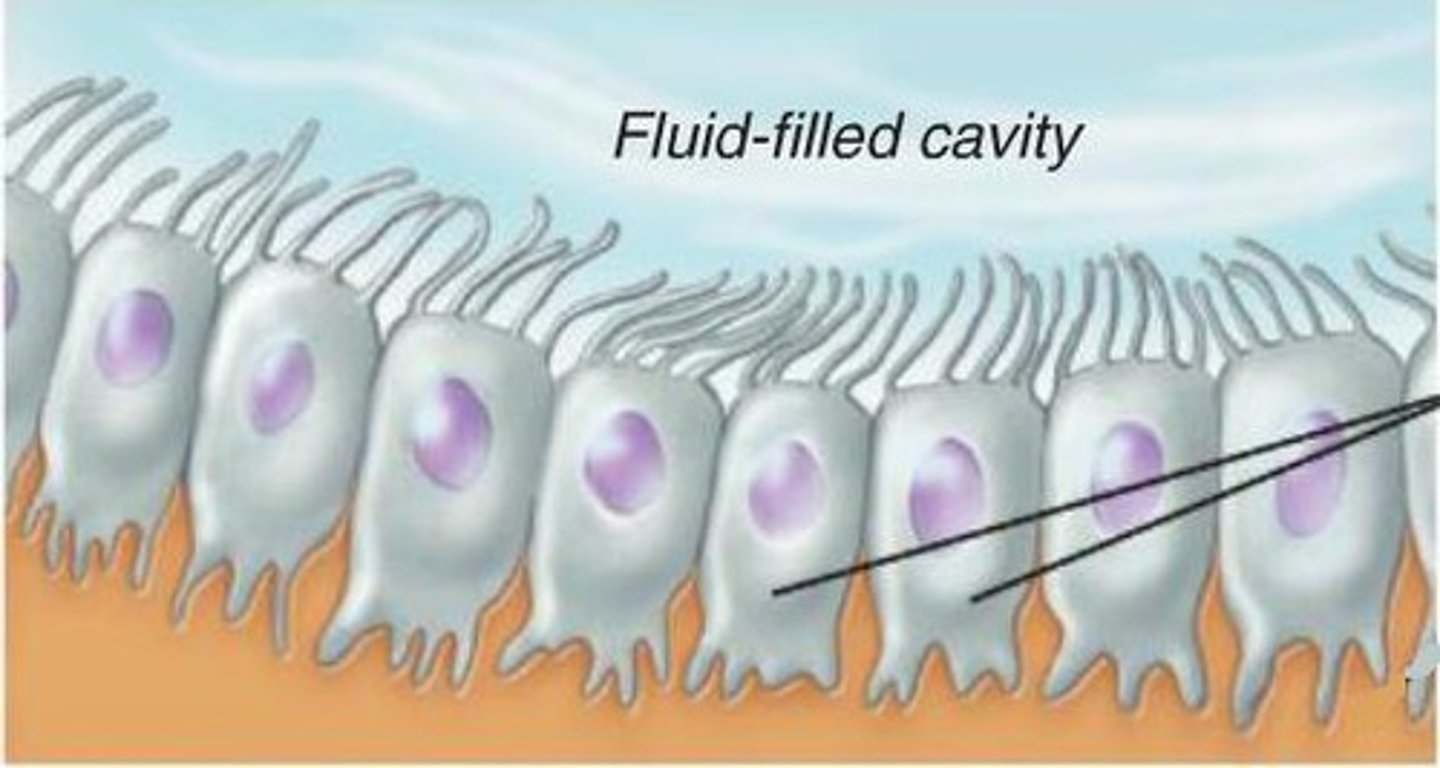
ependymal cells
line cavities of the brain and spinal cord, circulate cerebrospinal fluid
satellite cells
surround + protect neuron cell bodies in PNS
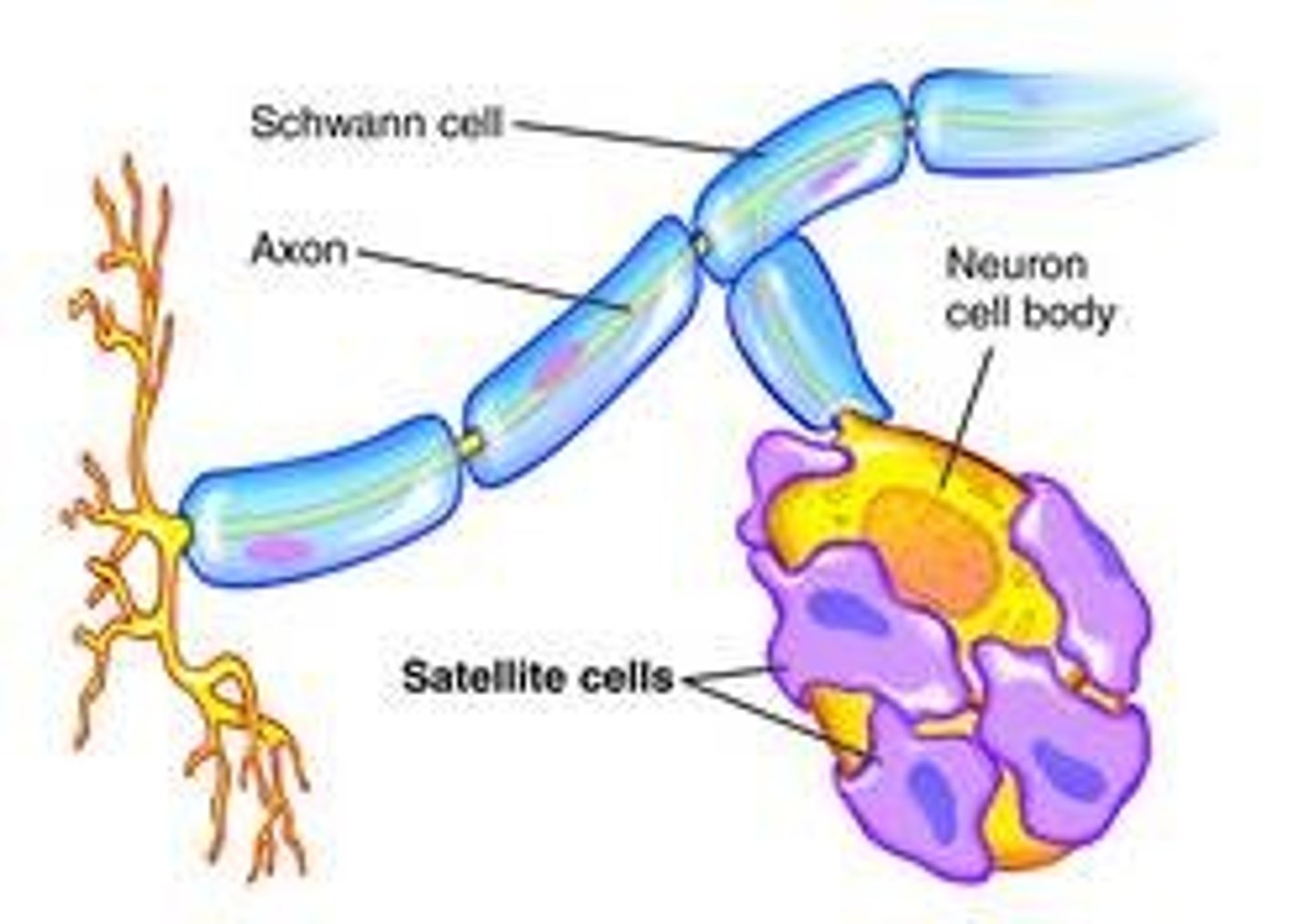
schwann cells
produce myelin in PNS
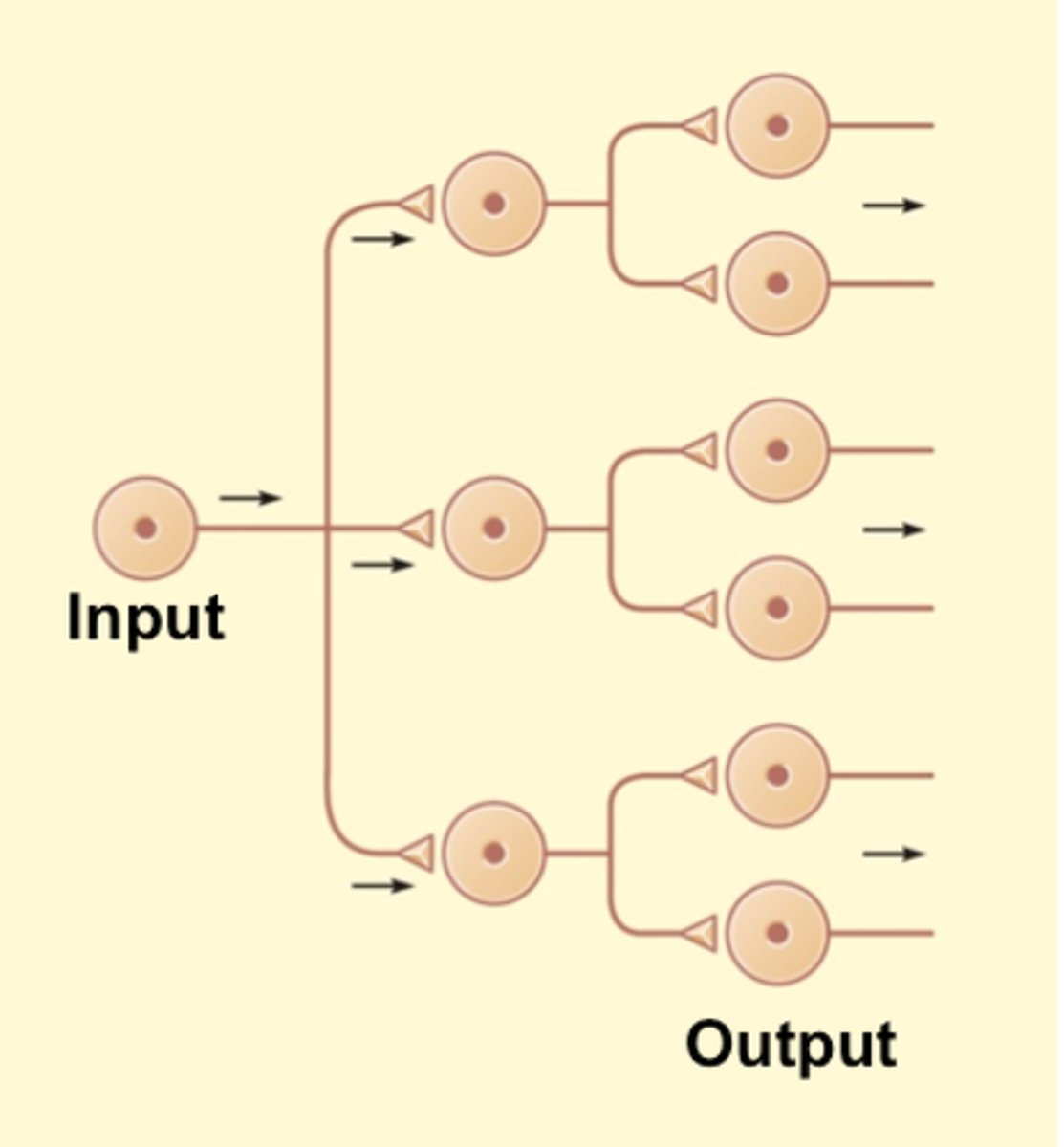
diverging circuit
one input, many outputs
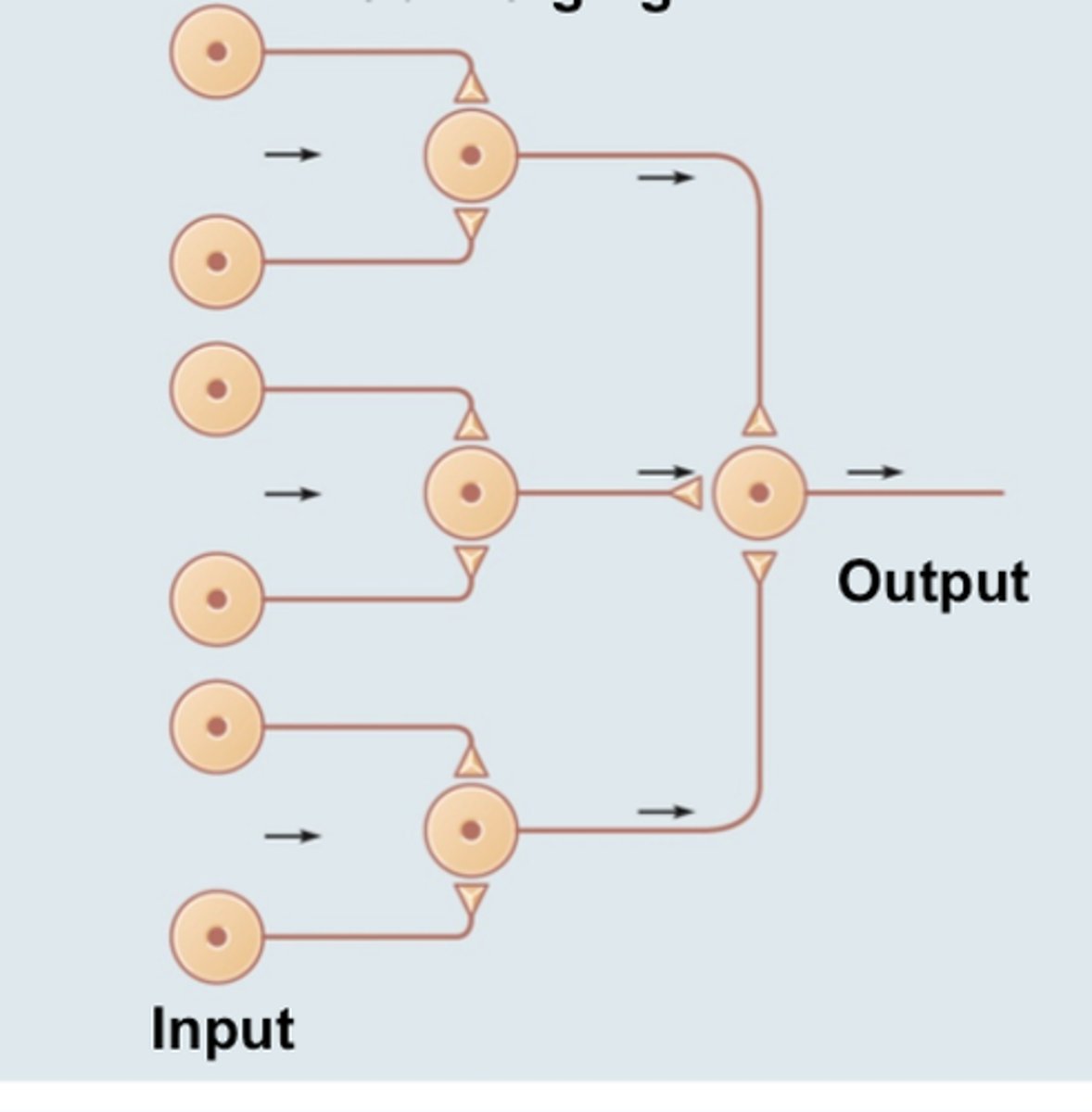
converging circuit
many inputs, one output
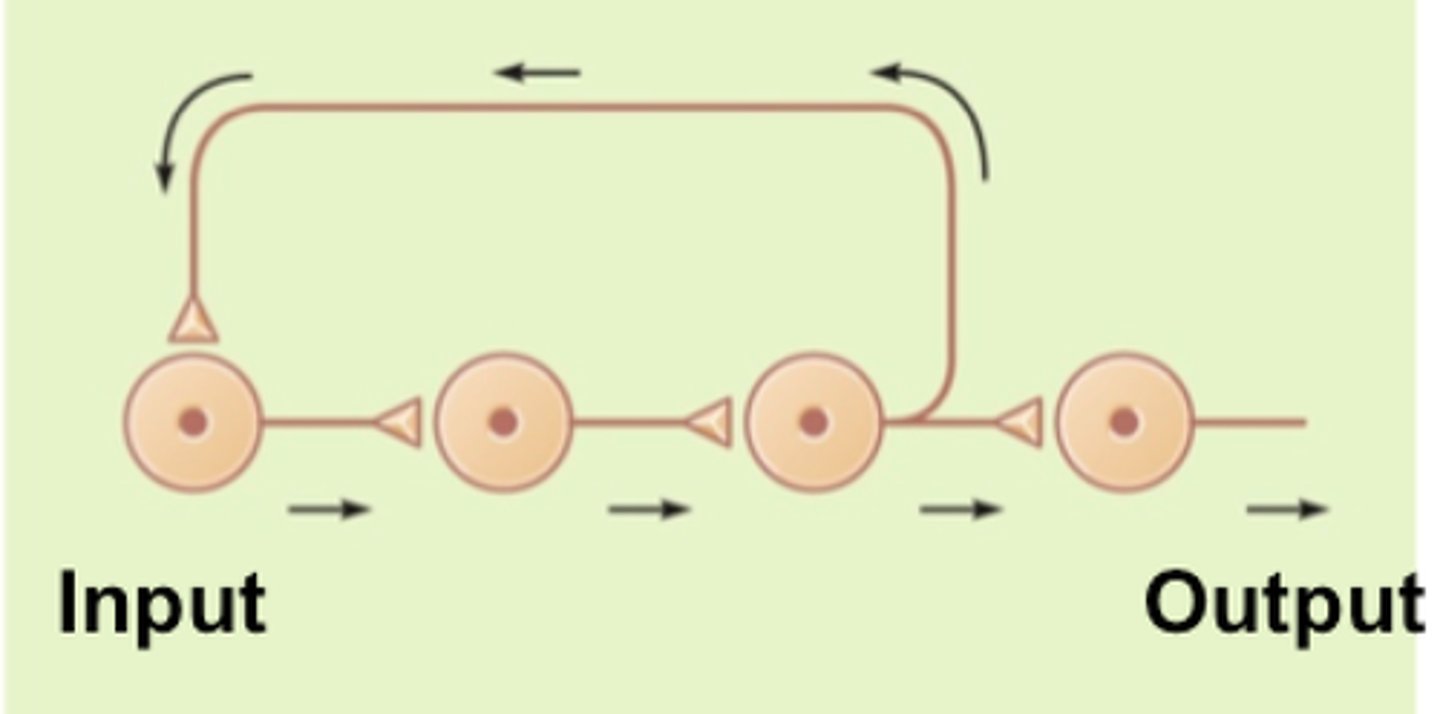
reverberating circuit
neurons stimulate one another in a sequence
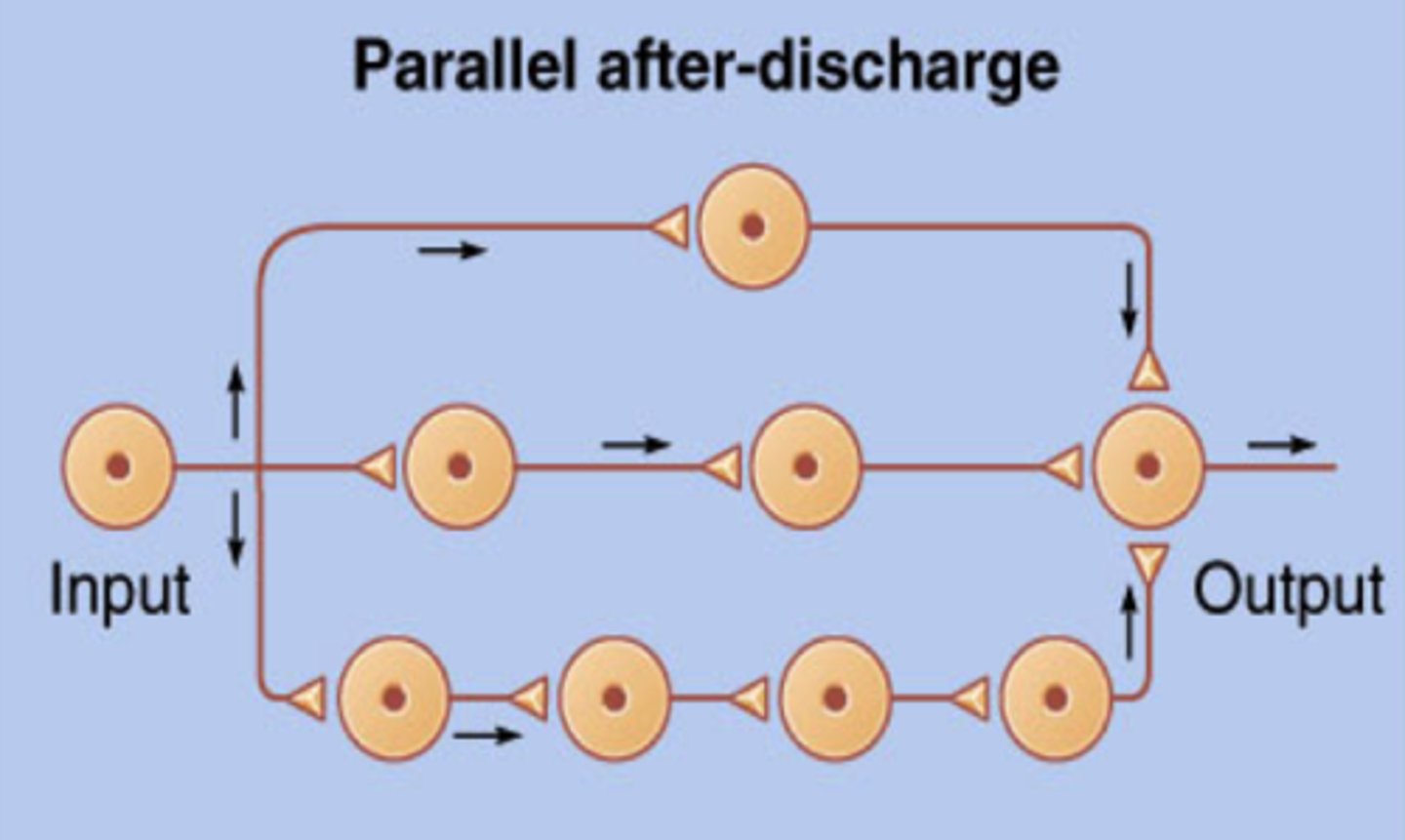
parallel after-discharge circuit
input neuron diverges into multiples chains to eventually reconverges
structural function of spinal cord
-begins at foramen magnum, ends at 1st/2nd lumbar
-provides 2 way conduction path for the braindi
How many pairs of spinal nerves are there?
31
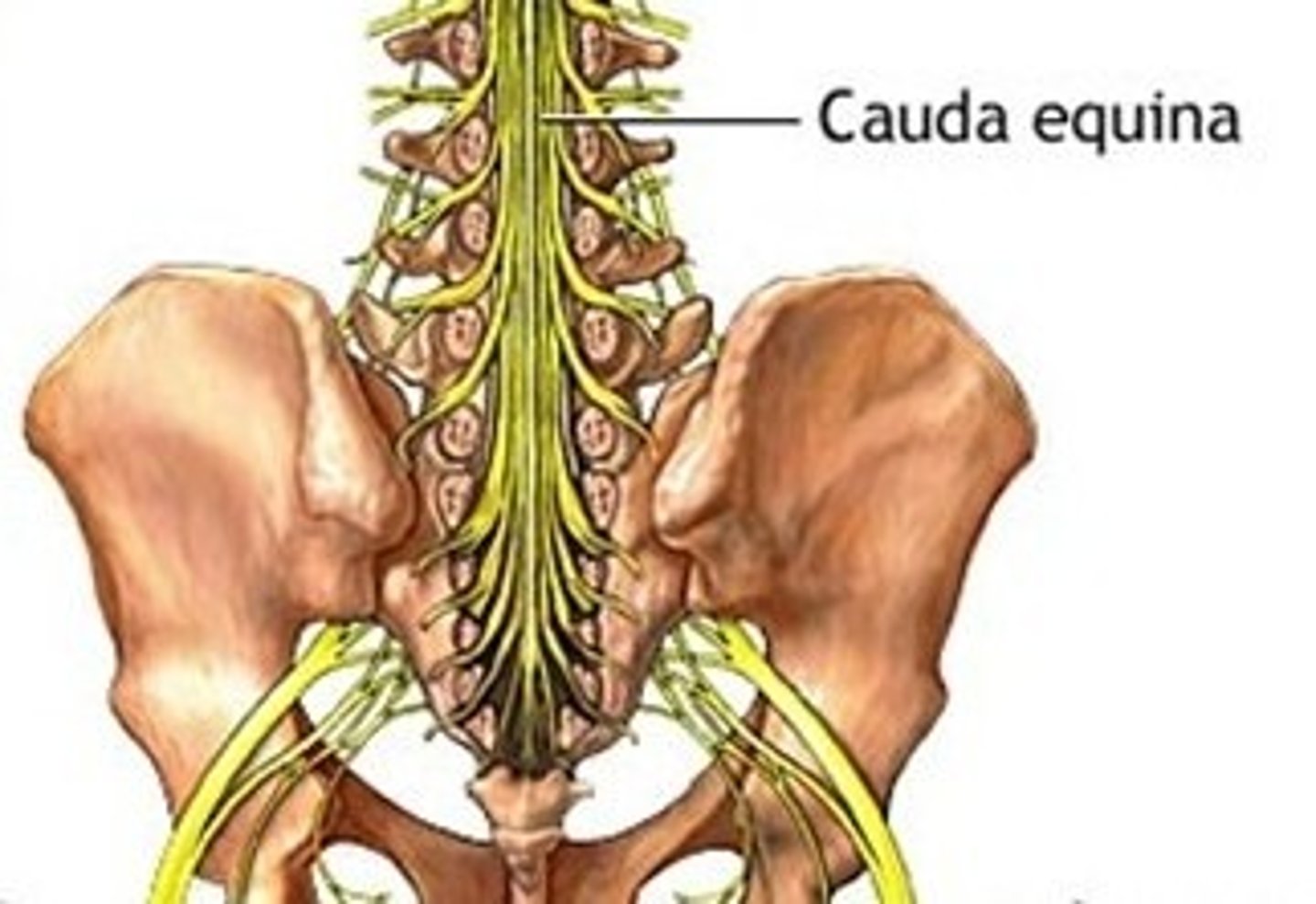
Cauda equina
collection of spinal nerves below the end of the spinal cord
spinal cord functions
conduction, neural integration, locomotion, reflexes
internal gray matter
mostly cell bodies (dorsal horns and anterior horns)
dorsal horns house
interneurons
ventral horns house
motor neurons
exterior white matter
conduction tracts; dorsal, lateral, ventral columns
spinal meninges
dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater
dura mater function
-tough outer layer
-protection of brain and spinal cord
arachnoid mater
-middle layer
-subarachnoid space filled with cerebral spinal fluid
pia mater
-thin, delicate, inner layer
-Coccygeal and denticulate ligaments: AKA give spinal cord horizontal support
ascending pathway
carry sensory info to the brain
descending pathway
carry motor info from brain
decussation
where many tracts cross the midline
tract origin ____ to its destination
contralateral
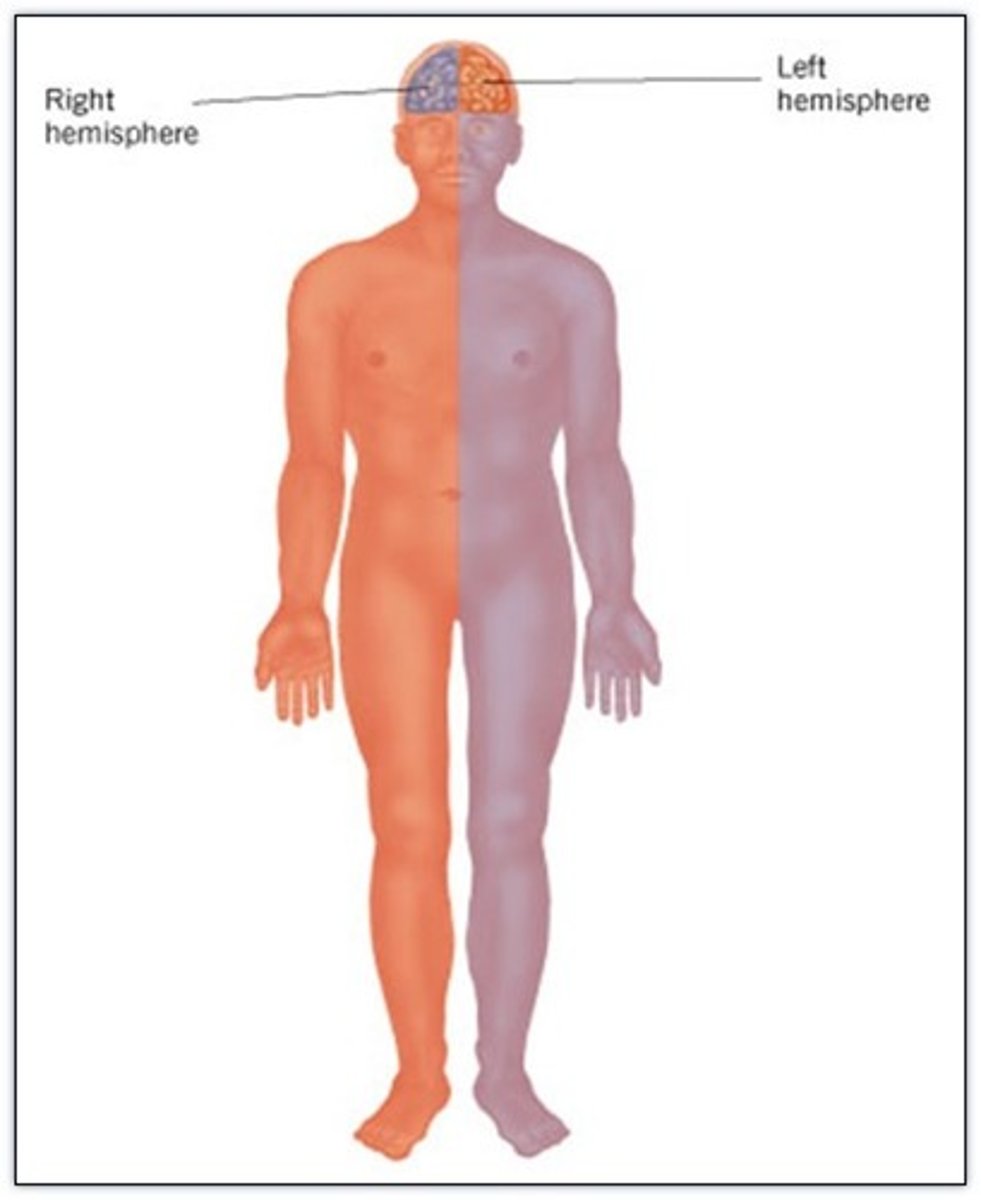
Ipsilateral
on the same side of the body
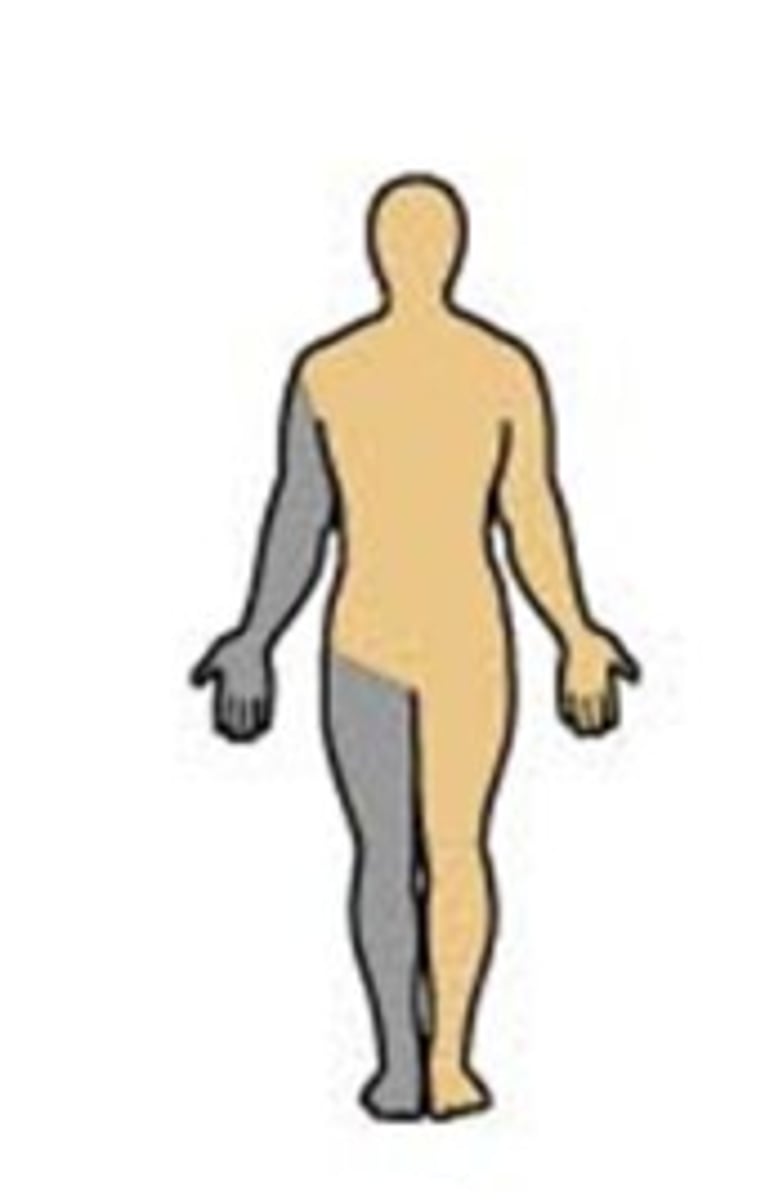
gracile fasciculus
carries signals from lower body to brain
cuneate fasciculus
ascending tract that carries sensory information from upper extremities to brain
spino____
ascending tract
_____spino
descending tract
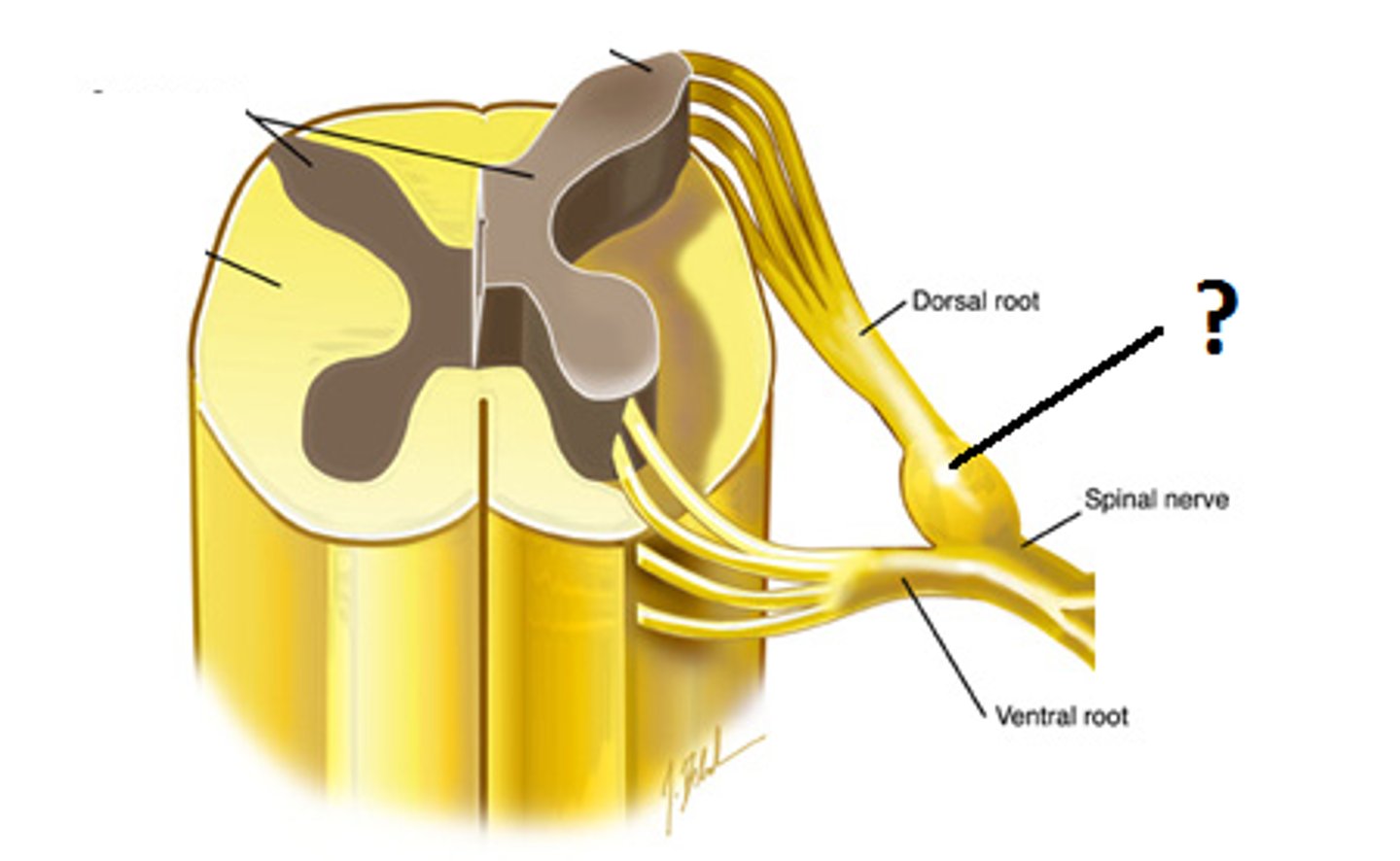
ramus
branch of a spinal nerve with both sensory and motor fibers
dorsal rami
serve the skin and muscles of the posterior trunk
ventral rami
form a complex of networks (plexus) for the anterior
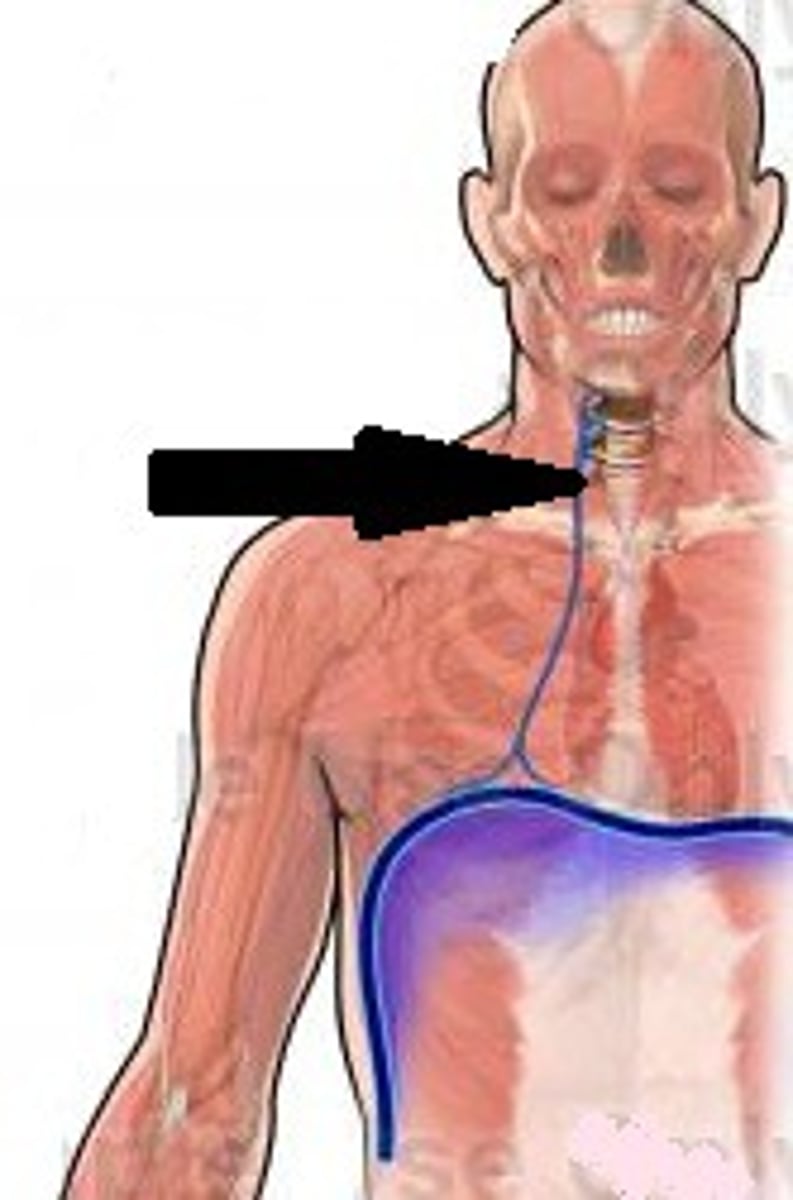
phrenic nerve
Carries impulses to the diaphragm from the brain.
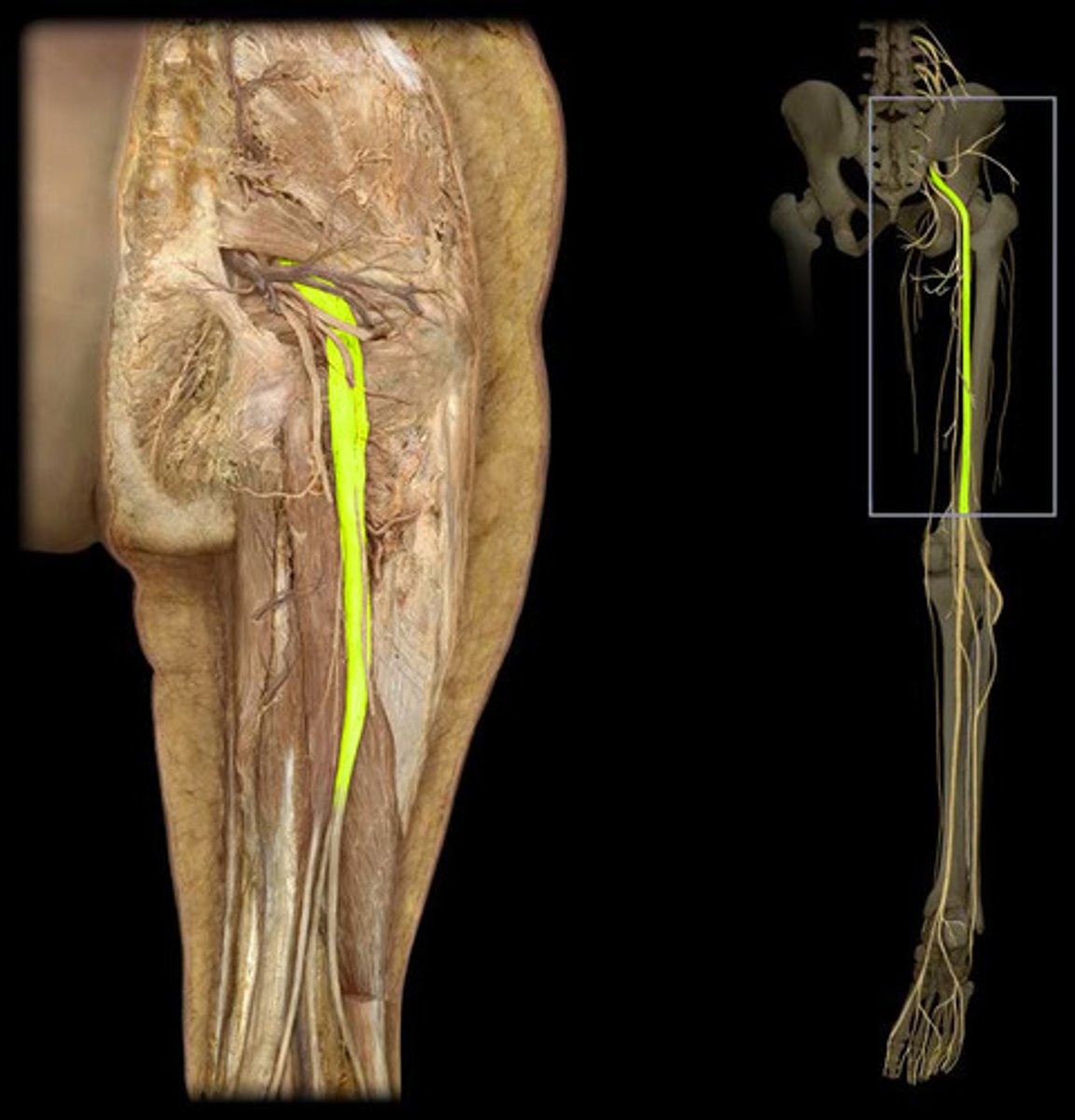
sciatic nerve
nerve extending from the base of the spine down the thigh, lower leg, and foot
femoral nerve
innervates quadriceps and skin of anterior thigh and medial surface of leg
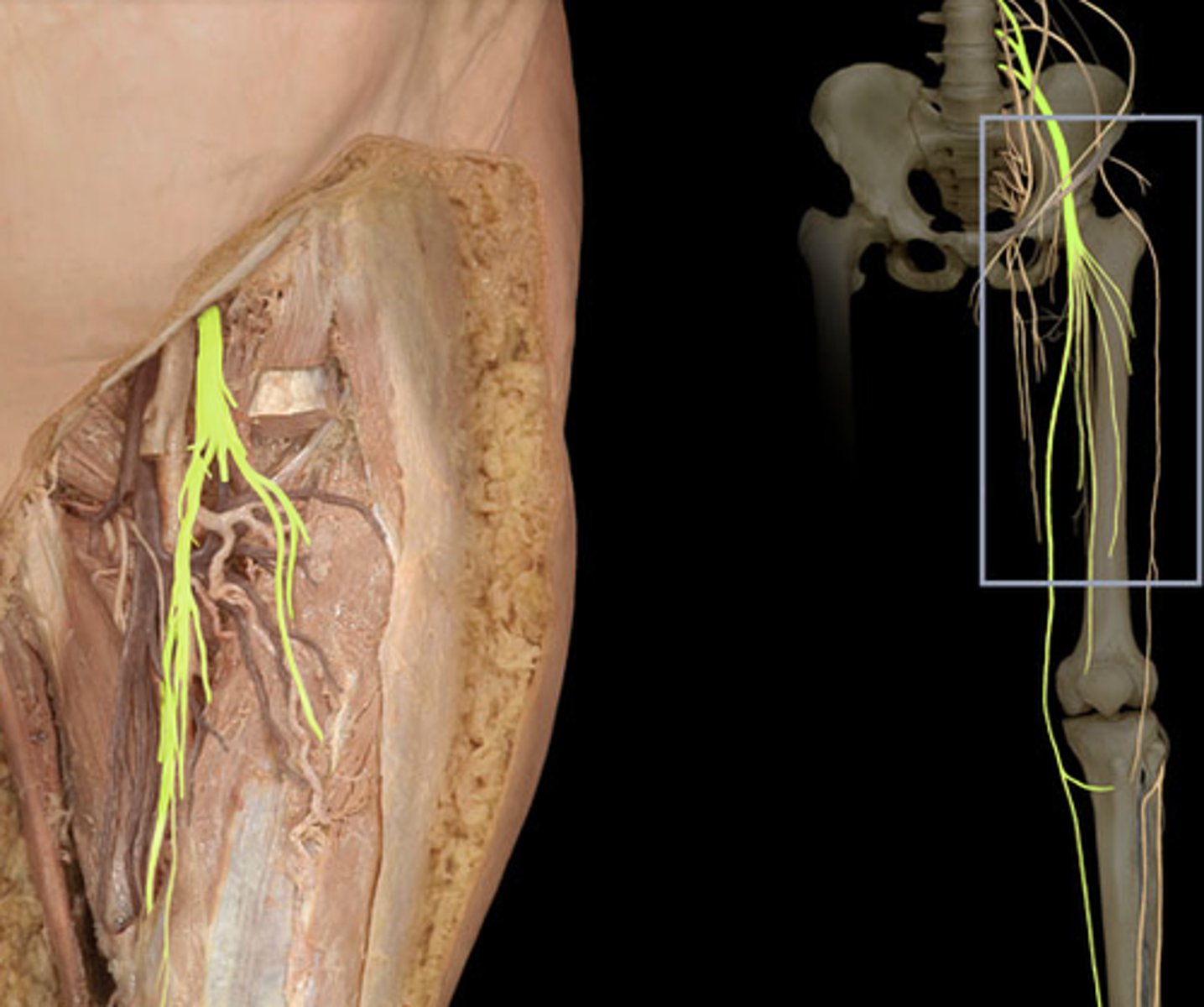
Musculocutaneous nerve
coracobrachialis, biceps brachii, brachialis
innervates upper arm
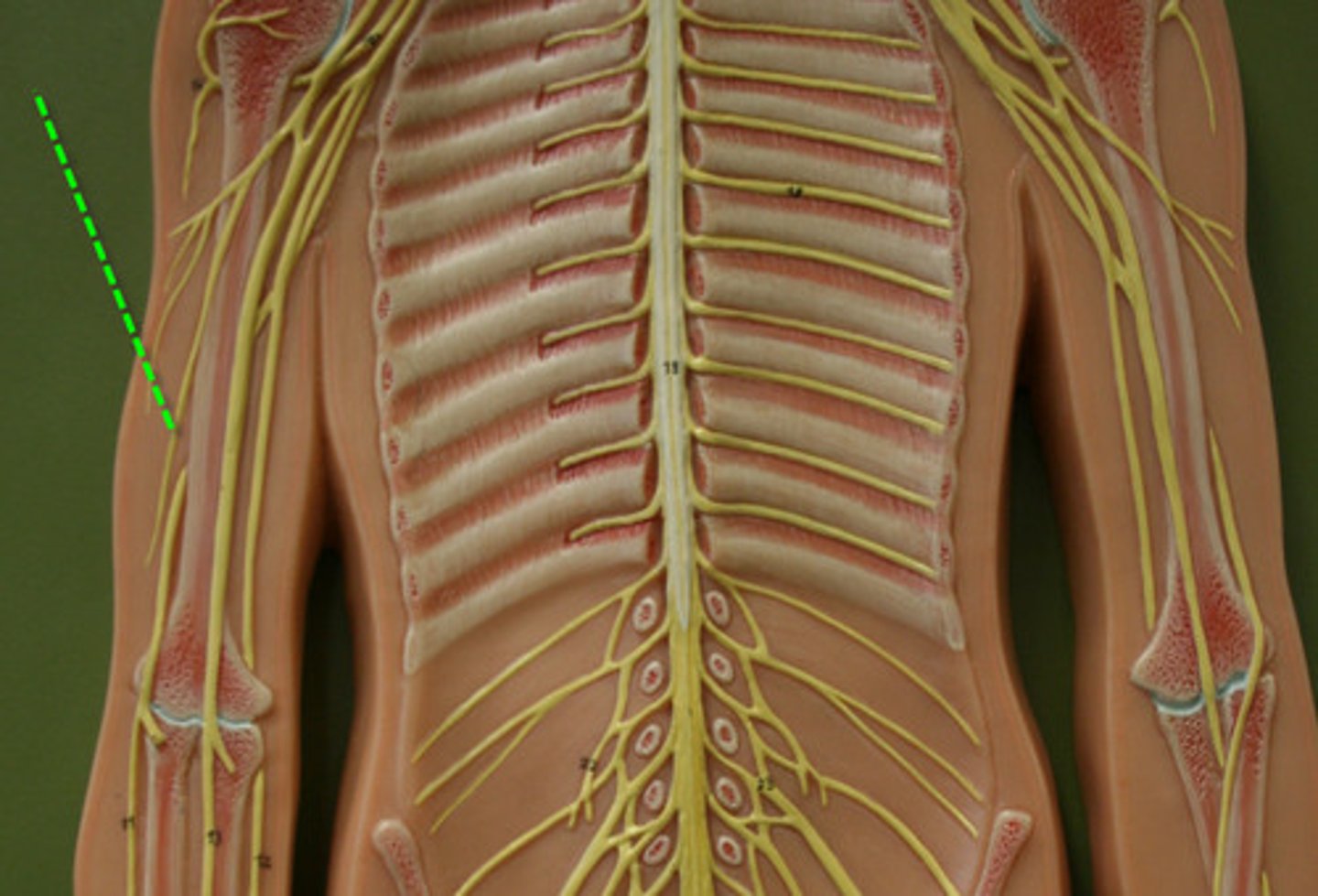
cutaneous innervation
refers to area of skin which is supplied by a specific cutaneous nerve
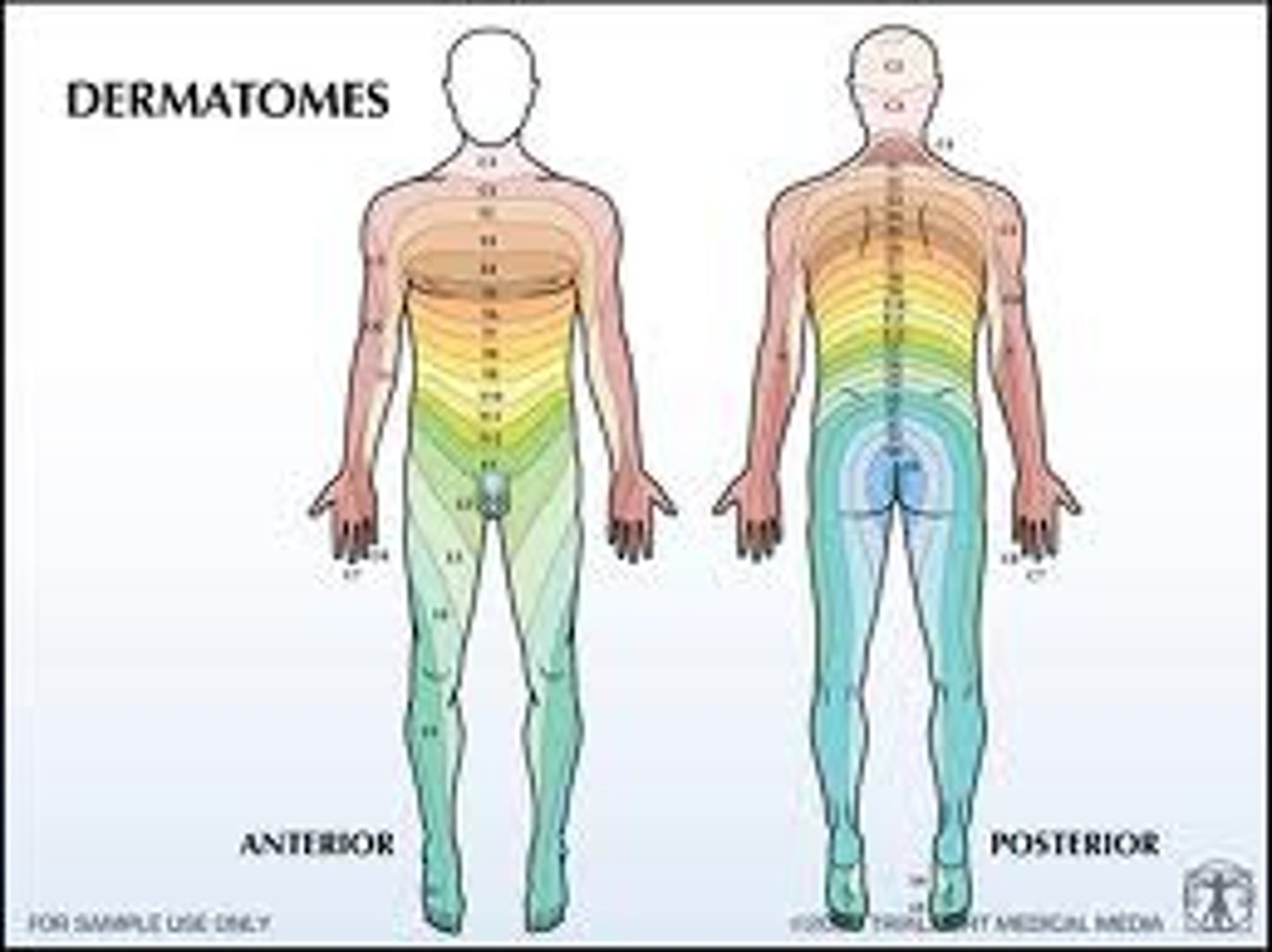
dermatomes
Skin areas innervated by specific spinal nerves.
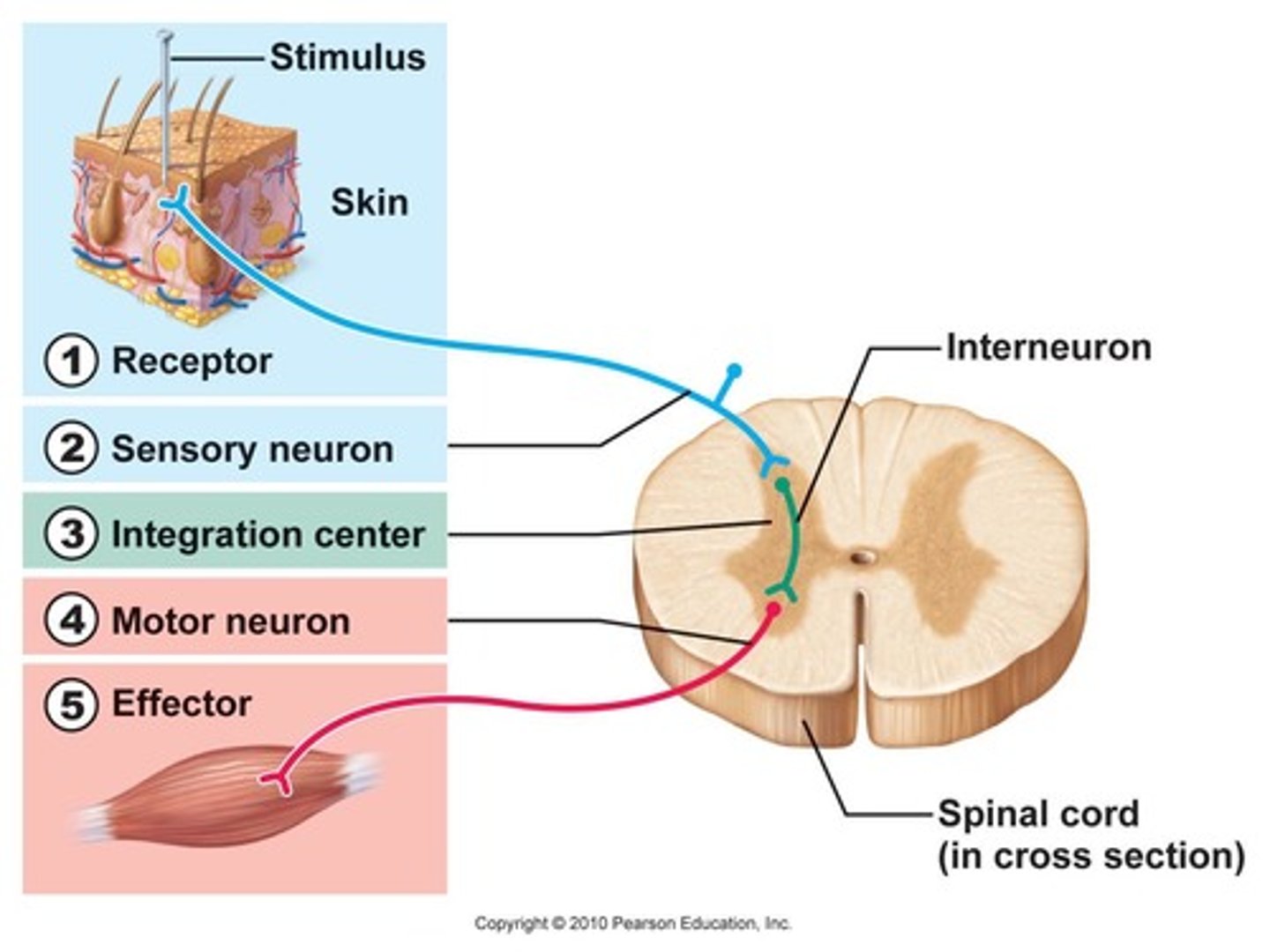
reflex arc
sensory receptor, sensory neuron, motor neuron, and effector that are involved in a quick response to a stimulus
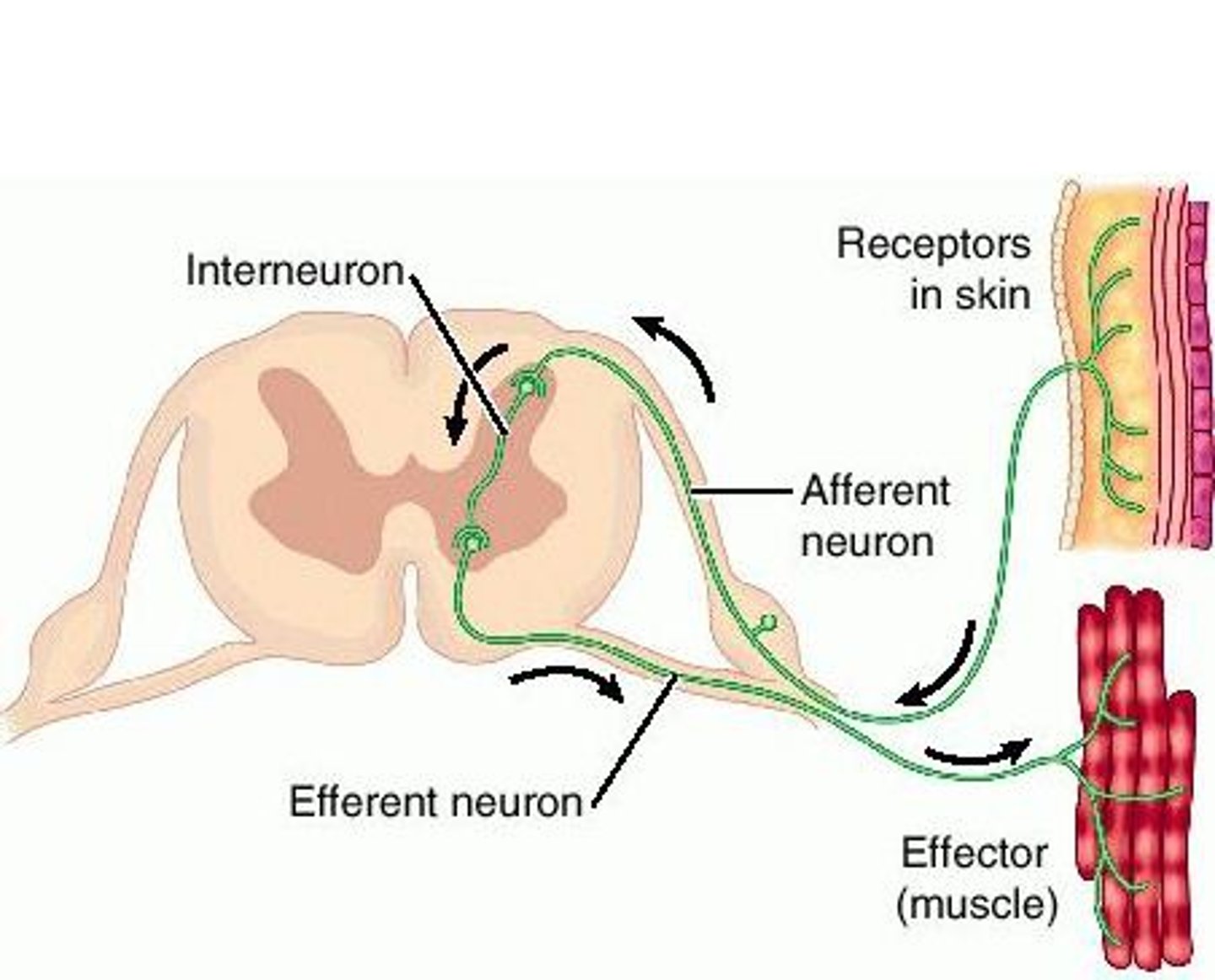
what are the 5 components of a reflex arc?
1. receptor
2. sensory neuron
3. integration center
4. motor neuron
5. effector
somatic reflexes
activate skeletal muscle, voluntary
visceral reflexes
Reflex of the autonomic nervous system affecting organs; involuntary
ANS sympathetic division
"Fight or flight"
-causes body to respond to stress
ANS parasympathetic division
"rest and digest response"
-digestion and brings back to homeostasis
ANS autonomic tone
balance between sympathetic and parasympathetic
spinal shock
syndrome of paralysis and absence of reflexes after transection of cord
Neurogenic shock
dangerous drop in blood pressure due to lack of sympathetic nervous system activity
paraplegia
paralysis of both lower limbs due to lesions from T1 to L1
quadriplegia
paralysis of all four limbs due to lesions above C5
hemiplegia
paralysis on one side of body usually due to stroke or brain lesions
cerebrum
Area of the brain responsible for all voluntary activities of the body
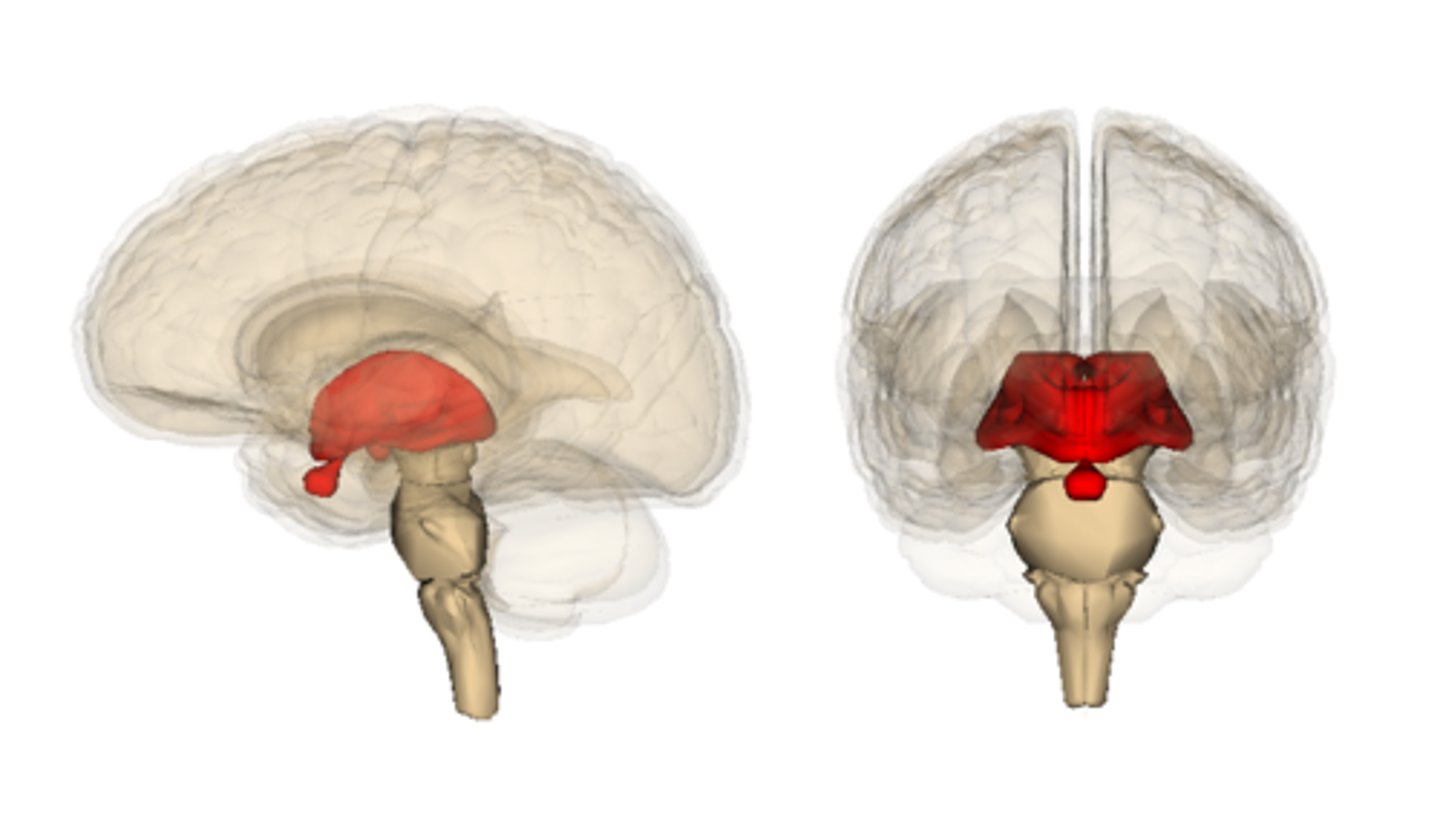
diencephalon
Contains thalamus and hypothalamus
midbrain
A small part of the brain above the pons that integrates sensory information and relays it upward.
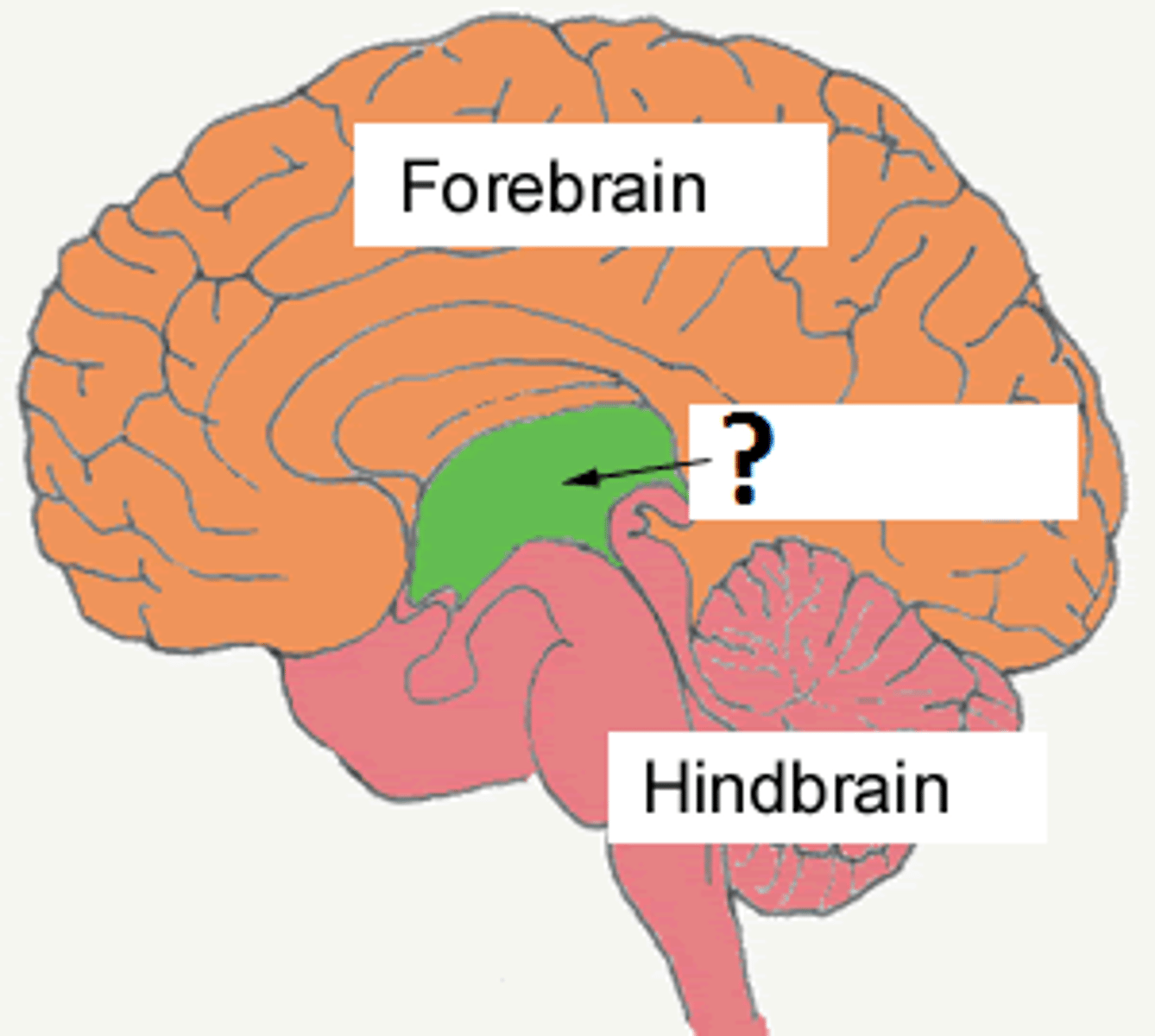
pons
the part of the brainstem that links the medulla oblongata and the thalamus.
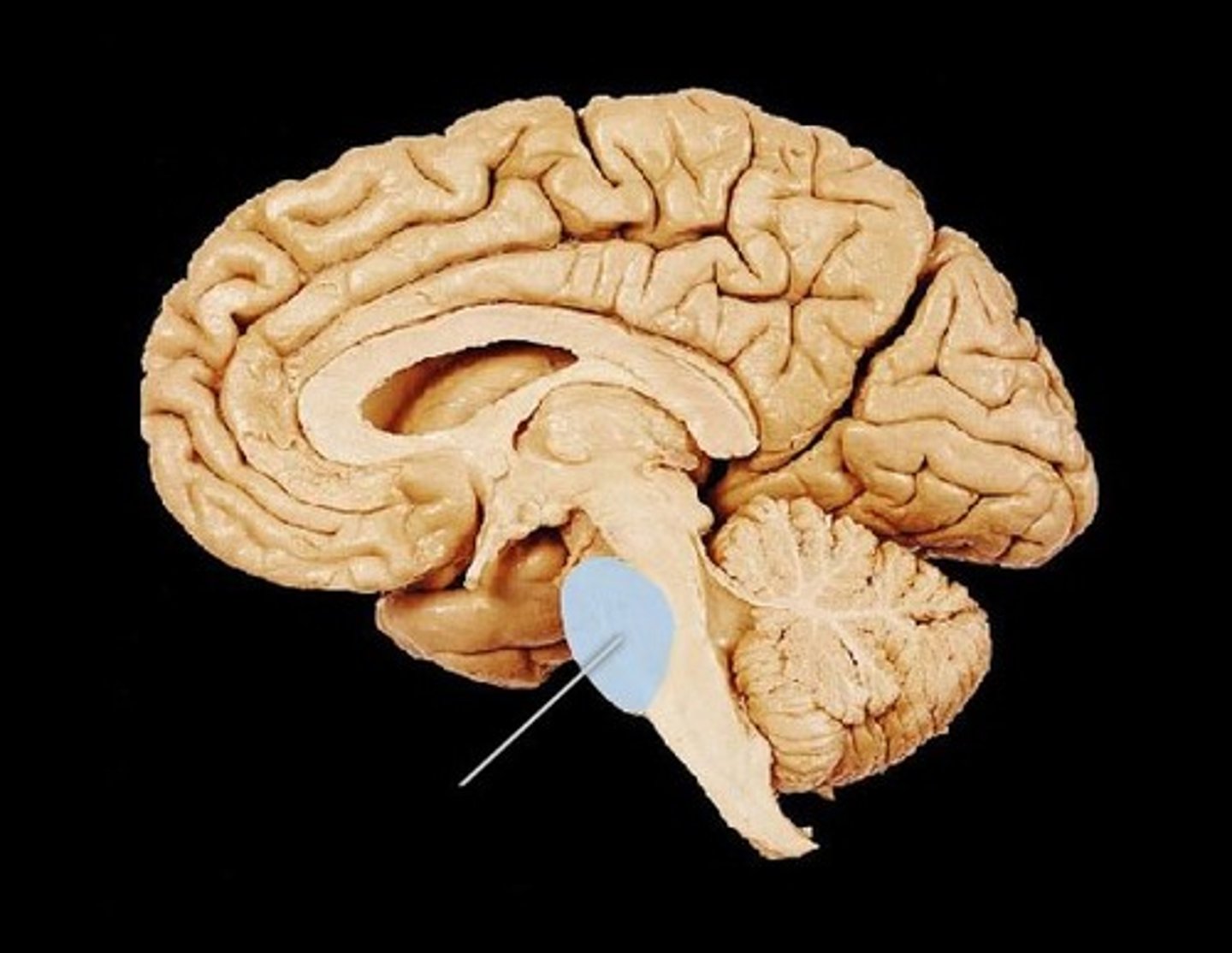
cerebellum
A large structure of the hindbrain that controls fine motor skills, AKA balance and coordination
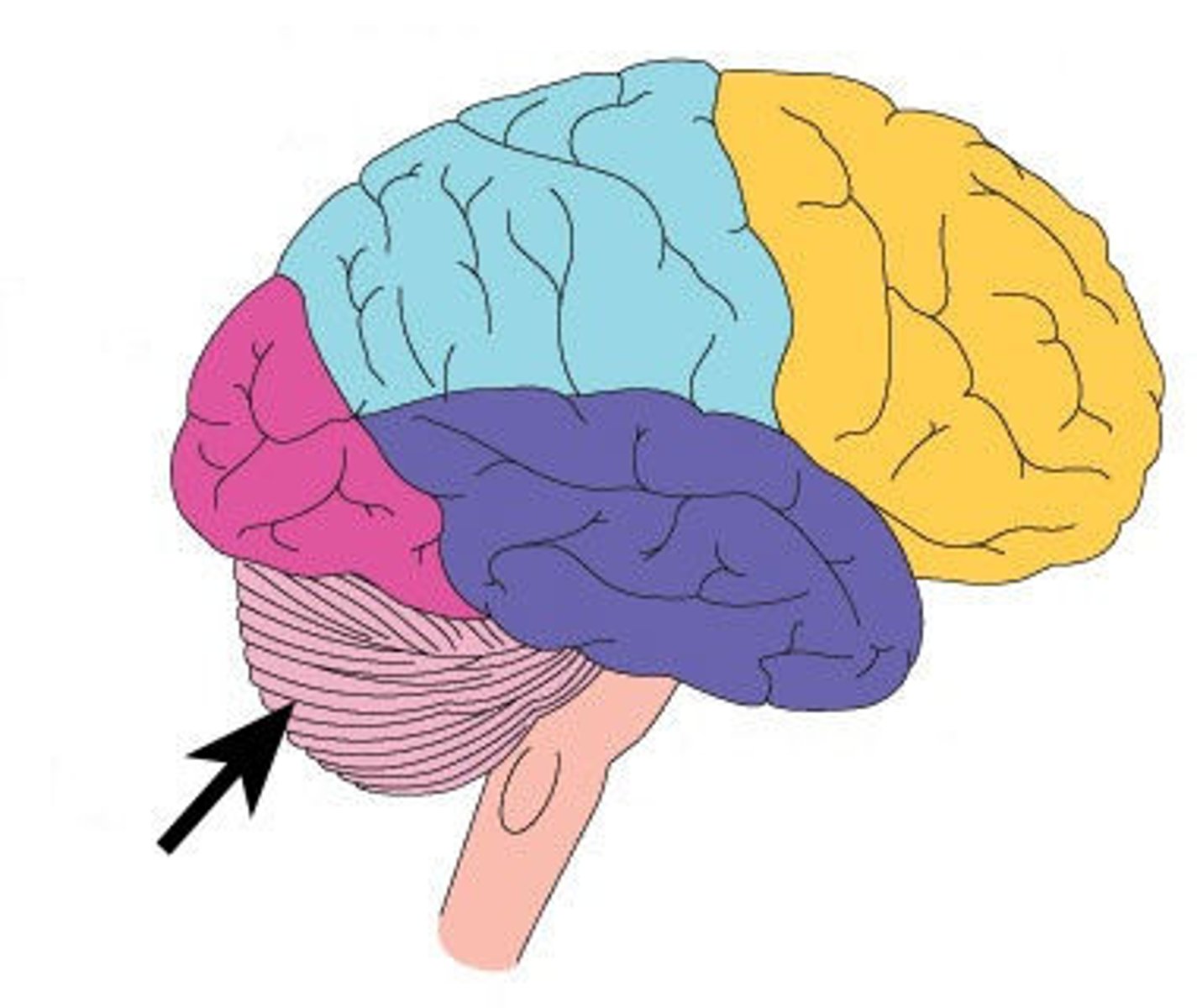
brain stem
midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata
connects brain and spinal cord
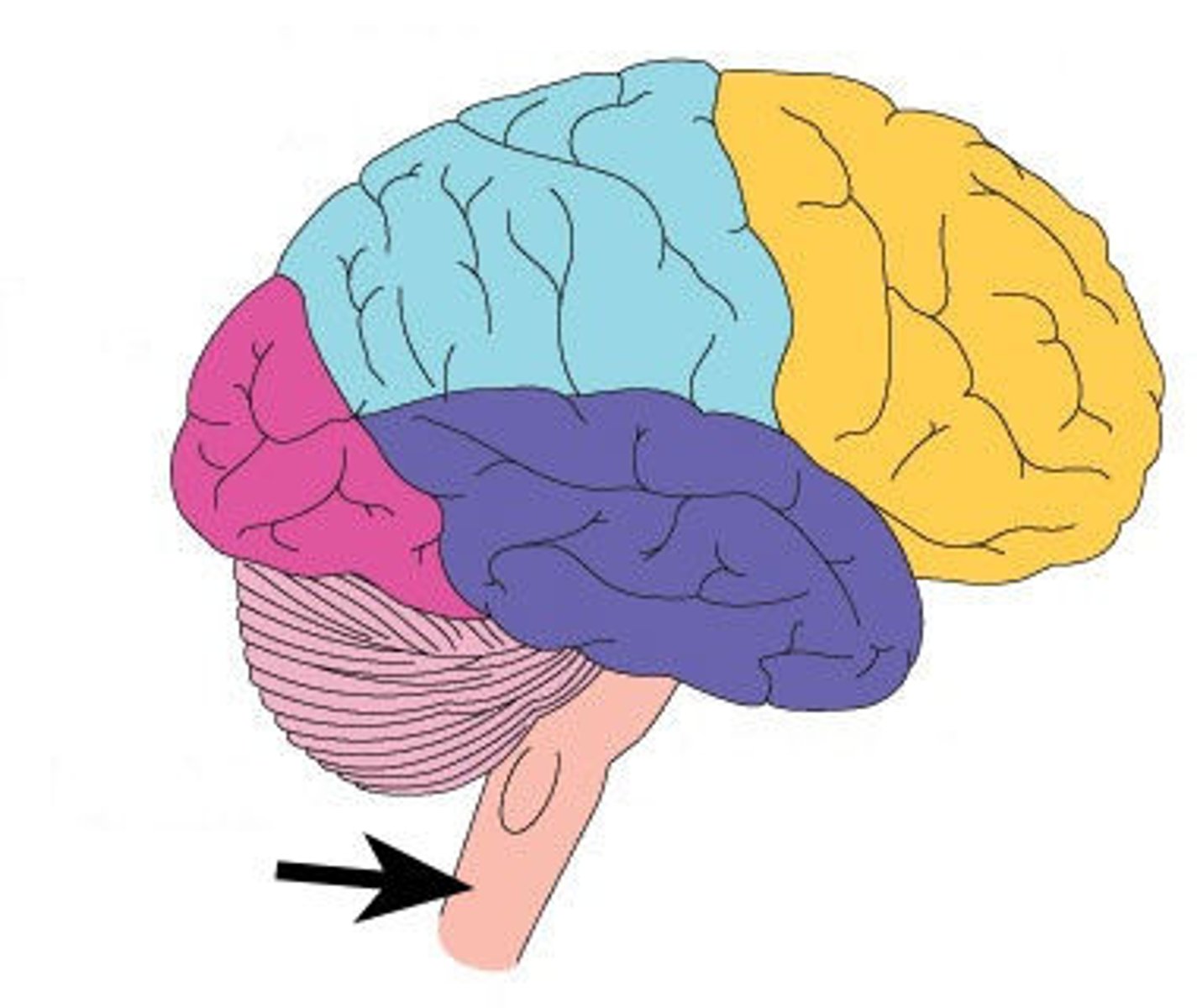
gray matter
Outer part (cortex) of cerebrum and of cerebellum
white matter
myelinated axons, deep in brain
cerebrospinal fluid function (CSF)
buoyancy, protection, chemical stability
what structure makes CSF?
choroid plexus
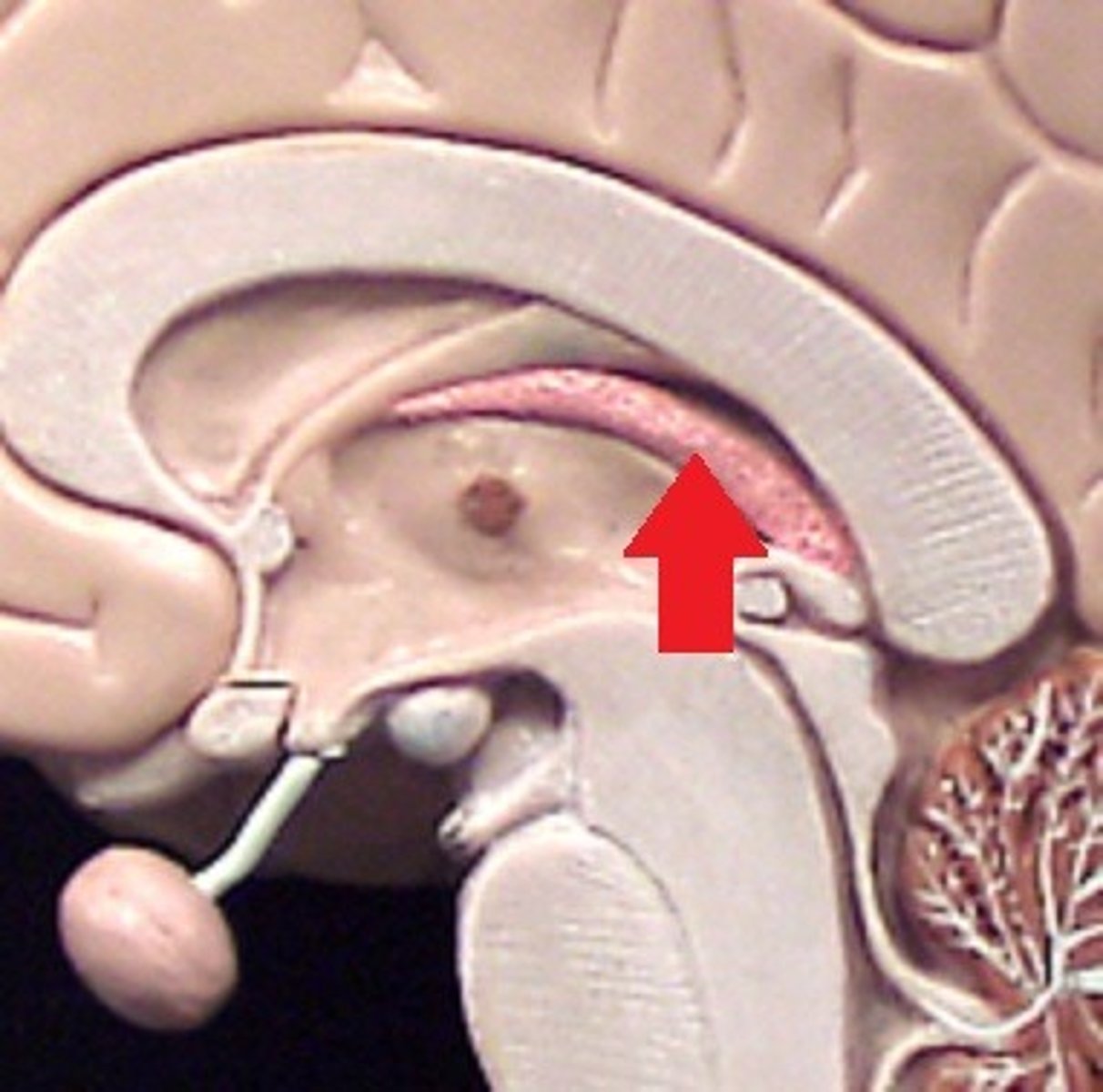
medulla oblongata nuclei
cardiac center
vasomotor center
respiratory center
pons nuclei
cranial nerves V, VI, VII, VIII
reticular formation function
-Somatic motor control
-Cardiovascular control
-Pain modulation
-Sleep and consciousness
-Habituation
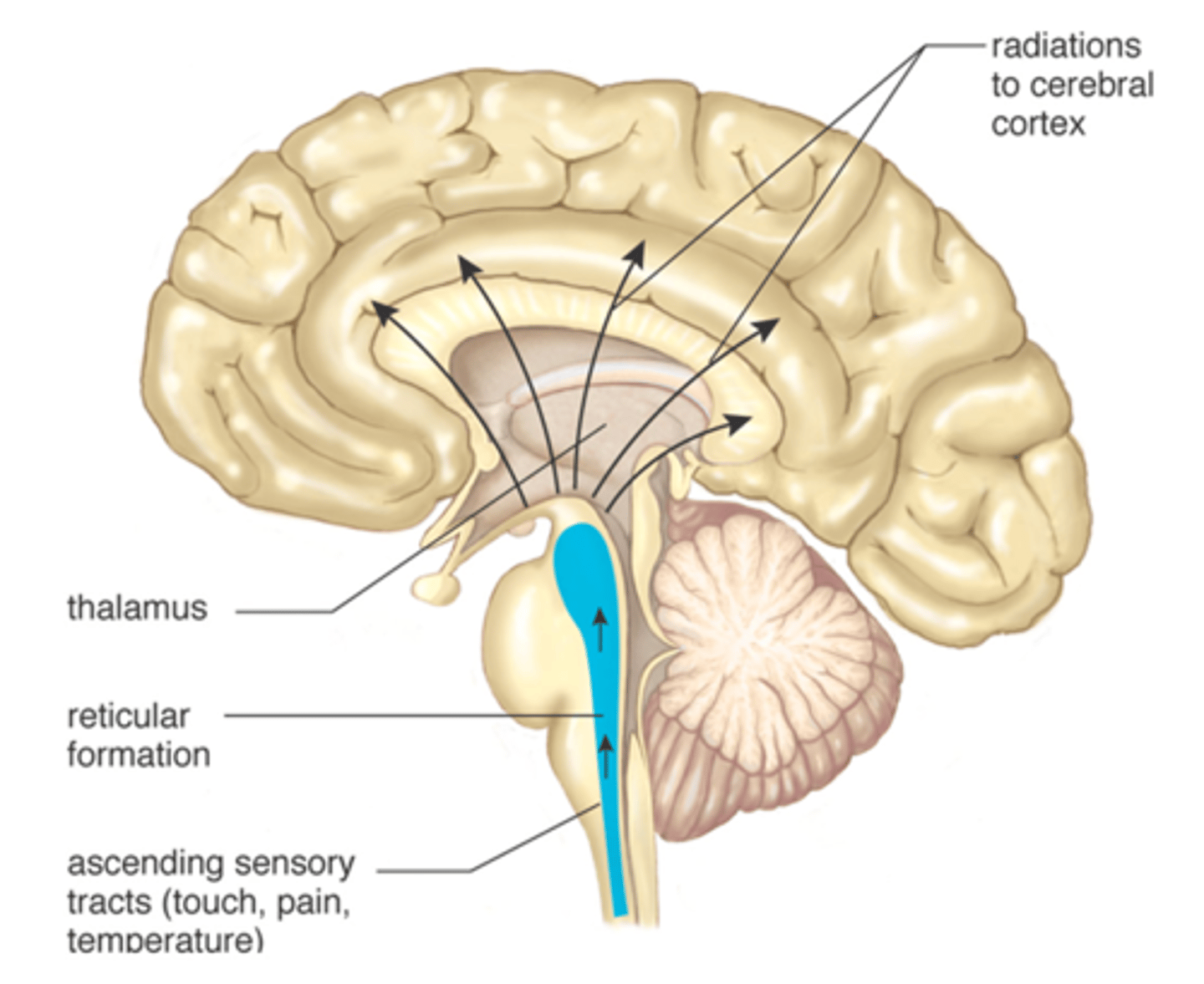
reticular formation clinical impact
Injury to the reticular formation can result in irreversible coma
hypothalamus function
-Hormone secretion
-Autonomic effects
-Thermoregulation
-Food and water intake
-Sleep and circadian rhythms
-Emotional responses
Memory
medullar oblongata function
-Centers for circulatory and respiratory control
-Sensory and motor functions for head and neck
insula function
Taste
visceral sensation
language
cerebellum function
Balance and coordination
longitudinal fissure
separates cerebral hemispheres