Business Analysis </3
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Explain why analysis is the first step toward a successful project.
Analysis is the first step because it forms the foundation of the project by identifying stakeholder needs and defining requirements. Poor analysis can lead to wrong decisions and project failure.
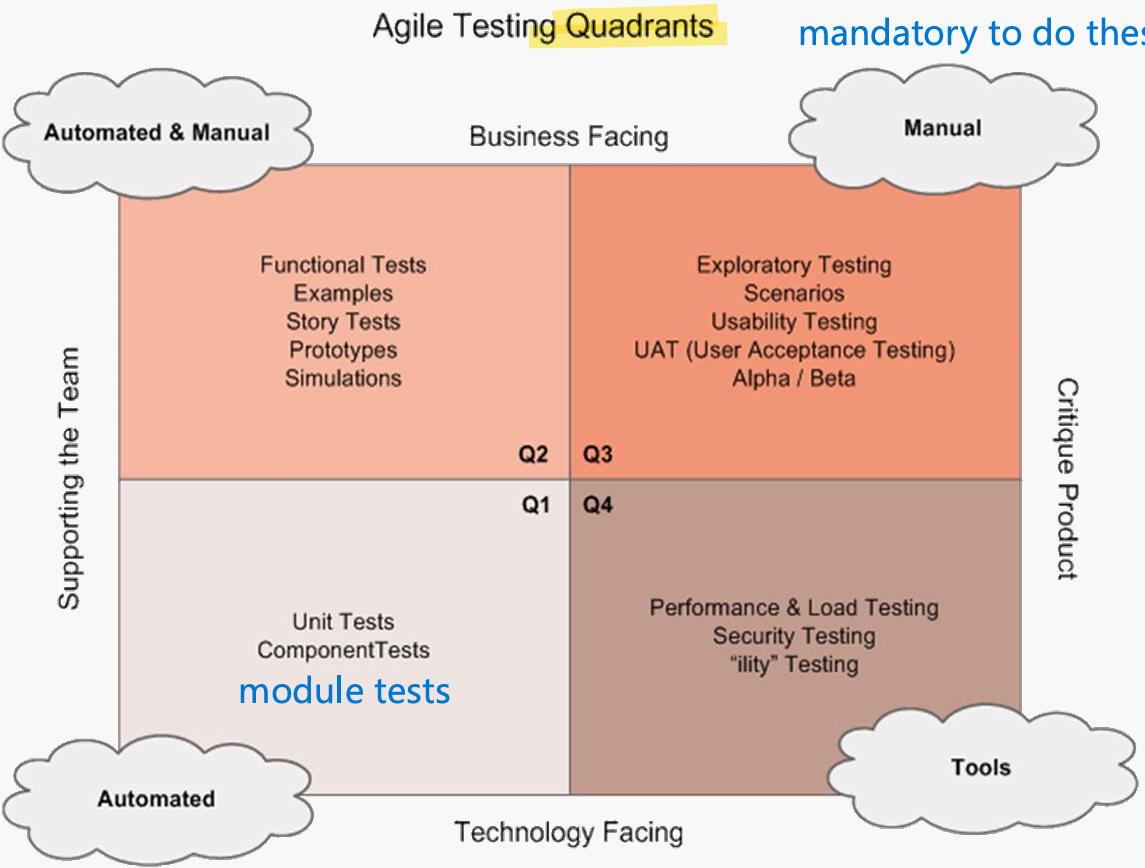
Complete and explain the Agile testing quadrants.
Q1 Automated: unit and component tests. Q2 Automated & Manual: functional tests, examples, story tests, prototypes, simulations. Q3 Manual: exploratory, scenario, usability, and user acceptance testing. Q4 Tools: performance, load, security, and non-functional testing.
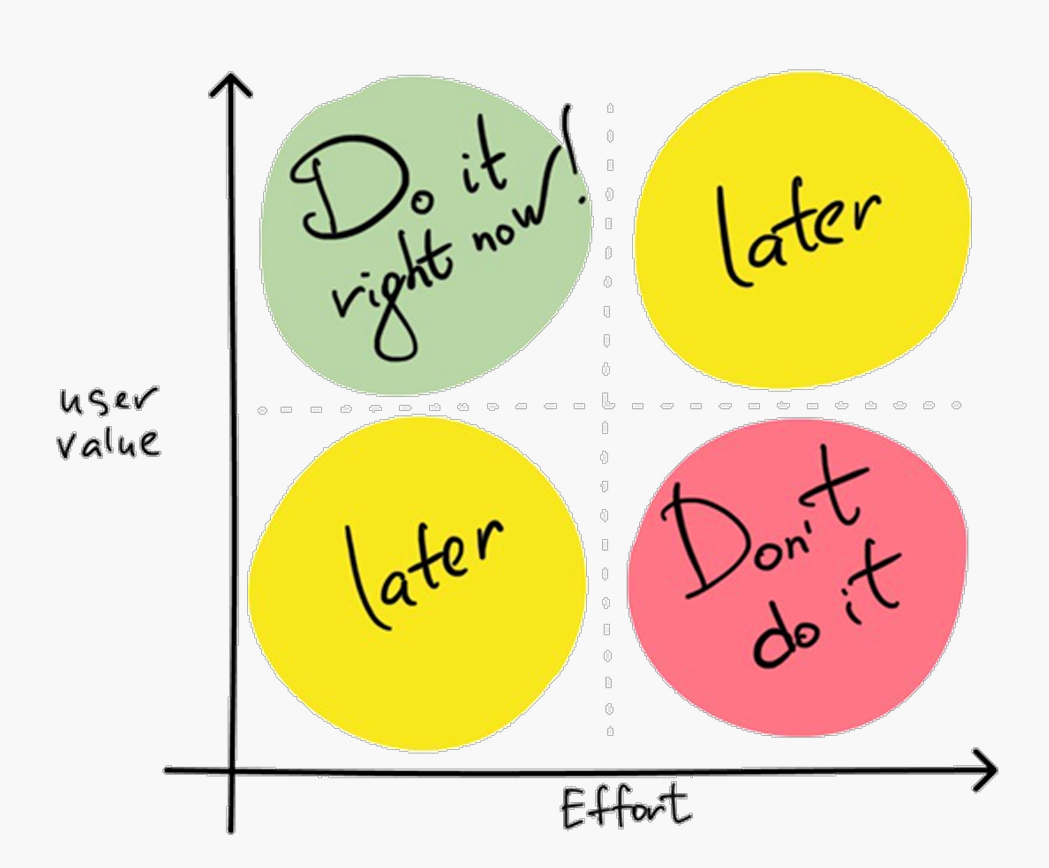
Explain the value/effort matrix.
It is used to prioritize work based on customer value and required effort. High value–low effort items are prioritized; low value–high effort items are not.
What is the difference between brainstorming and brainwriting?
Brainwriting involves writing ideas down instead of sharing them verbally like in brainstorming.
Explain user stories in detail.
A user story is a short, simple description of a feature describing what the user wants and why. (WHO? WHAT? WHY?)
=> everyday language, not too technical (communication IT <=> business)

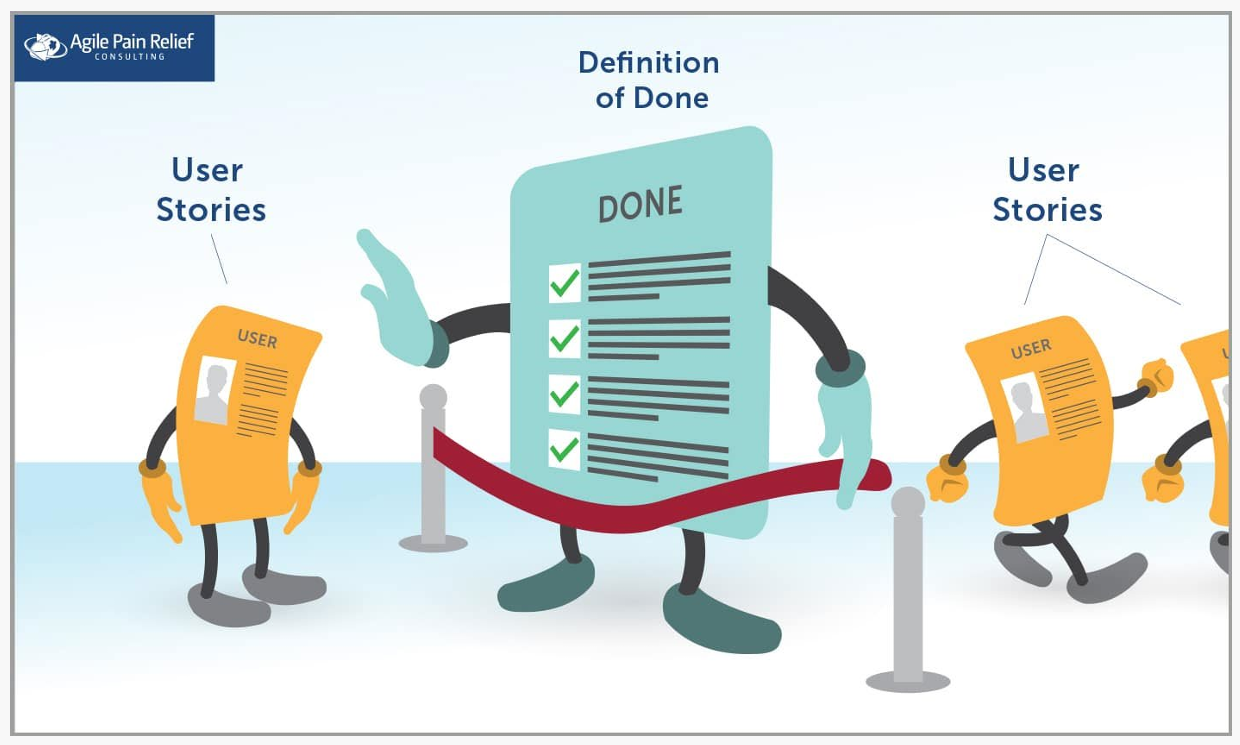
How can a definition of done improve a development team?
It clarifies when work is finished, ensures shared understanding, and prevents misunderstandings.
Why is testing not easy?
It requires
General knowledge of information technology
Knowledge of infrastructure, tools and development environments
Social skills
Tester must be able to:
Give a good assessment of the quality of SW
Demonstrate added value in the life cycle of IT systems
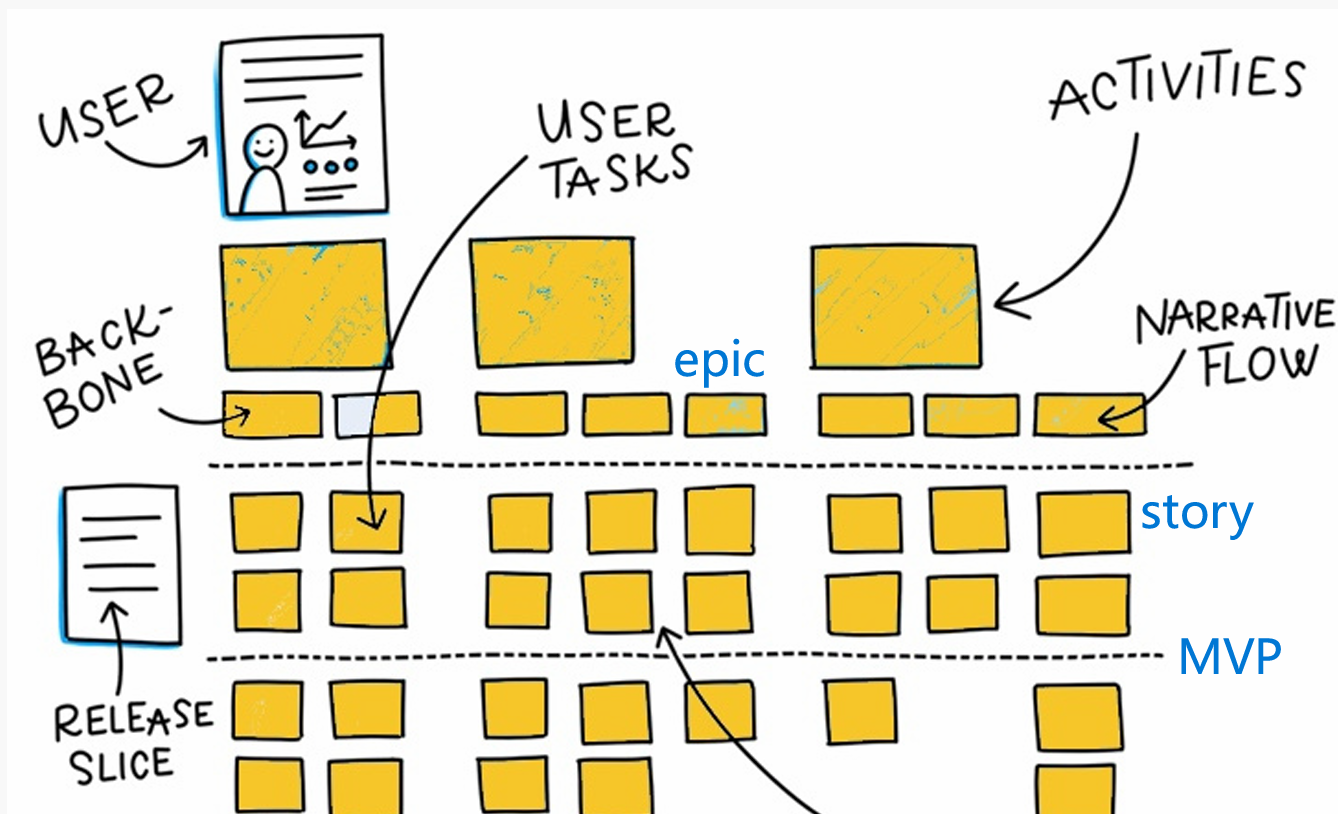
What is story mapping?
A visual technique to create shared understanding, organize and prioritize user stories, with story told horizontally/chronologically and each activity is further elaborated vertically in details + priority
= start of product backlog
Why is testing necessary?
Every change entails a risk; early defect detection is cheaper and prevents damage.
(early) testing: limits risks, increases flexibility

Explain the difference between output and outcome in Scrum teams.
Output is what the team delivers (=story points); outcome is the customer value or impact created for stakeholders.
What are acceptance criteria and how are they related to user stories?
They are testable conditions a user story must meet to be considered done, often written in Given-When-Then format.
How can a Scrum Master speed up an Agile team?
By enforcing the definition of done, improving communication, applying Agile techniques, tracking processes, and managing Scrum events.
What are MVPs (Minimum Viable Products)?
Products with the minimum features needed to launch and collect user feedback.
How is value determined in a user story?
Business value through higher revenue, lower costs, increased customer satisfaction, efficiency, or effectiveness.
=> easier if a financial advantage can be linked to user story
How does company culture influence elicitation techniques?
Dynamic start-ups or open work cultures prefer creative techniques like workshops so everyone can express their ideas
<=> strictly hierarchical organizations prefer structured methods like interrogation or documentation techniques (interviews/survey/..)
Can Agile work with fixed time and fixed budget? Why?
Yes, by keeping scope flexible and delivering the highest-value features within constraints.
What does an analyst do in a business process?
Defines projects and teams, gathers information, supports modeling, and ensures quality.
Understanding the problem domain and organization
Solving problems top-down approach
Modelling skills
What are the advantages of the V-model and how is regression testing included?
Testing happens in parallel with development, enabling early defect detection
Regression testing verifies existing functionality after changes.
= type of test which allows us to check if previous code continues to work when we integrate new functionalities in that system
How does an interview differ depending on the stakeholder role?
Sponsor: Leadership perspective, Insight into vision and ultimate goal, What is success?
Managers and responsible: Impact on their specific environment (operations, product, system, people), Concerns and ideas that fit within the sponsor's vision
End users: Direct insight into problems/opportunities, Current frustrations, Ideas for improvements
Process knowledge is fragmented across an organization:
no single stakeholder understands the entire system or process
=> interviews must focus on what each stakeholder knows best.
What types of questions can be asked in an interview?
Main questions with follow-ups, open questions, and closed questions for clarification.
Which elicitation techniques suit a start-up and a government institution?
open dynamic start-up: creative techniques, because they're a new and emerging company, also small company not much hierarchy so everyone can express their own ideas
= brainstorming, mind mapping, story mapping.
<=> more hierarchical government: interrogation techniques, survey to get info about all those stakeholders aka citizens and documentation techniques
= interviews, surveys, observations.
Explain creative, interrogation, and observational elicitation techniques.
Creative generate ideas; interrogation collects information; observational seeks insight into real behavior.
How do you choose an elicitation technique?
Based on
human aspects (communication, experience),
organizational aspects (availability, budget/time)
professional aspects (required level of detail, experience)
company/corporate culture.
What are the steps of an interview?
Preparation: Determine the goal. Which roles/people do I want to interview? Prepare questions
Execution: bond, expectations, active listening + closing
Follow-up: thanks, plan of action/next steps
What is the difference between an interview and a survey?
Interviews are personal, resource-intensive and in-depth; surveys are anonymous and structured.
Are preparation steps alone sufficient for an interview?
No, active listening, follow-up, and processing information are also required.
What types of tests exist?
Module and integration tests, system tests, acceptance tests (FAT, UAT, PAT - functional, user, production), chain test, pilot test, regression test
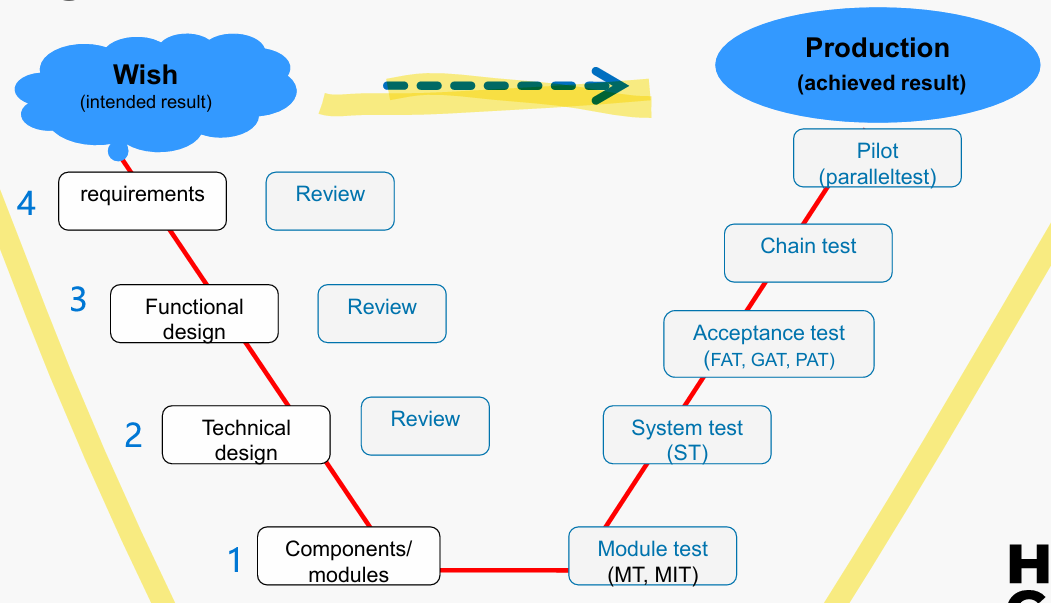
Where do regression tests fit in test stages?
After changes, often following module or system testing.
(regression test: type of test which allows us to check if previous code continues to work when we integrate new functionalities in that system)
What is the difference between regression testing and integration testing?
Regression testing checks existing features after changes; integration testing checks module interaction and collaboration with the adjacent systems
What is Continuous Integration and why is it important?
Frequent code integration and testing to detect defects early and improve quality.
Why is testing throughout the IT lifecycle important?
It prevents late defect discovery and improves software quality.
How has testing evolved over time?
From end-phase testing to continuous testing throughout development.
Why distinguish UAT, FAT, and PAT?
Each acceptance test serves a different validation purpose.
Functional Acceptance Test (FAT) – Testing a whole system, Client, Verification based on system requirements and functional design
User Acceptance Test (UAT) – Validating test, Representative scenarios from the daily work of the users, User-friendliness, usability,…
Production Acceptance Test (PAT) – formal validation of application = final test before deployment
Why are user stories useful even without direct business value?
????
They support tasks, requirements, and communication between stakeholders.
What are story points and how do they affect sprint planning?
They estimate effort using Fibonacci numbers and guide sprint capacity planning.
take into account: Amount of work, Complexity, Risk, Dependency
What is Yesterday’s Weather in Agile?
Using past performance to predict future sprint capacity.
How many Story Points were delivered last sprint?
=> Gives an indication of how much work can be included in the next sprint
(often an average is taken of x last sprints)
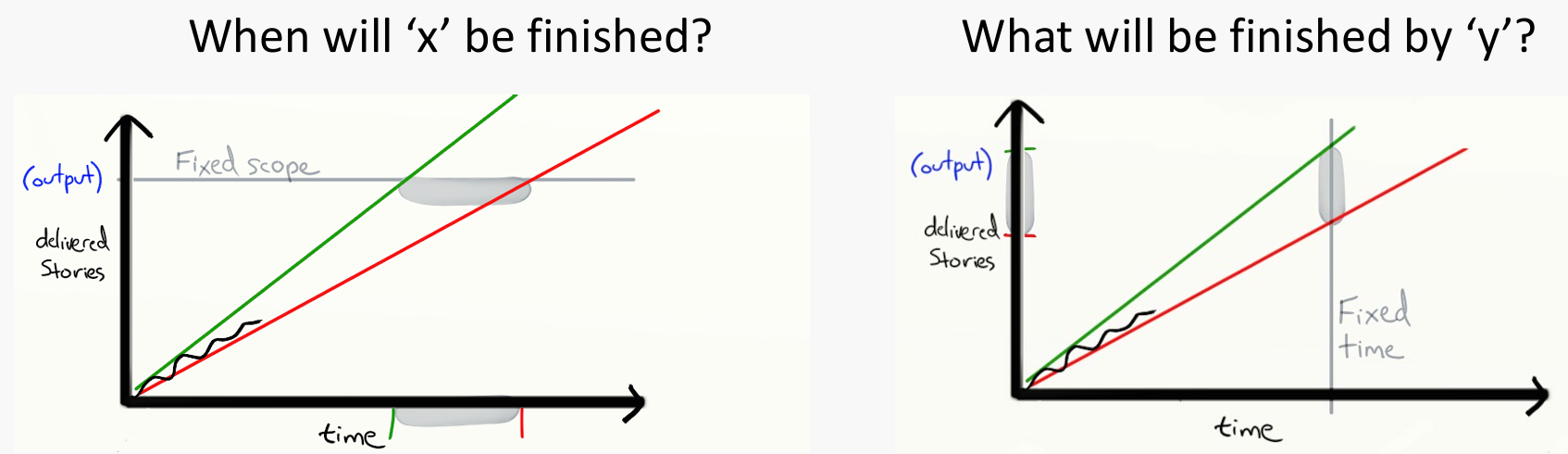
What is a burn-up chart?
A chart showing project progress and forecasting completion.
By keeping track of the velocity we can forecast:
What is a walking skeleton?
A minimal working product released to test and prod, and then used as a foundation for further development.
Who are the 3 Amigos?
Business analyst, developer, and tester.
What is the difference between a product backlog and a team backlog?
Product backlog contains all work items; team backlog contains sprint-assigned items.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of product and team backlogs?
Product backlog gives long-term vision but can be abstract; team backlog gives short-term focus but may lose strategic alignment.
How do story mapping and prioritization help determine value?
They create a prioritized backlog focused on customer value and effort.
How do you determine what to test from a user story?
By defining acceptance criteria.
Explain the MoSCoW method.
Must, Should, Could, Won’t categorization of requirements.
What is INVEST?
Independent, Negotiable, Valuable, Estimable, Small, Testable.
What are the three Agile Product Owner circles?
Build it right, build the right thing, build it fast.
What does “building the wrong thing right” mean?
Correctly implementing the wrong features due to poor understanding.
Why are fixed scope and fixed time problematic in Agile?
They limit flexibility and responsiveness to change.
What is a walking skeleton in project development?
A minimal functional product used to gain early feedback.