Clin Med L2 CBC - RBC portion
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
how do we examine blood?
through peripheral smears
how do you do peripheral smears?
you collect EDTA anticoagulated blood
place it on a glass slide
then the the blood is stained with Wright-Giemsa stain
what do peripheral smears allow you to identify and estimate?
identification and qualification % of WBC
identification and estimation of abnormal RBC morphology
estimation of platelet count
estimation for platelet clumping
what is CBC used for?
to evaluate
hematology parameters
white blood cell measures
platelets, and white blood cell parameters
what is in a CBC?
RBC count
Hemoglobin
Hematocrit
MCV
MCH
MCHC
RDW
Platelet Count
WBC count
Neutrophils % and absolute
Lymphocytes % and absolute
Monocytes % and absolute
Eosinophils % and absolute
Basophils % and absolute
what is fishbones?
its a shorthand way of displaying labs and memorizing normalized ranges for your facility
what does RBC provide?
a count of the number of RBCs present in the specimen
serves as an indirect estimate of the hemoglobin content of the blood
what does the Hemoglobin (Hgb) provide?
index of the oxygen carrying capacity of blood
what does the Hgb depend on?
on the number of RBCs as well as the amount of hemoglobin in each RBC
what does the Hemocrit (Hct) provide?
an indirect estimate of the number of RBCs and thus an indirect estimate of the amount of hemoglobin
what are the common abbreviations for hemoglobin and hemocrit?
H & H
Hgb & Hct
what does the Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV) provide?
the size of RBC
represents average RBC volume
what CBC value is helpful in diagnosing anemias as normocytic etc?
MCV
what does the Mean Corpuscular Hgb (MCH) provide?
the weight of Hgb per RBC
and color bc the cell will appear different after being stained due to hgb
what does the Mean Corpuscular Hgb Content (MCHC) provide?
concentration of Hgb per cell
if you have a smaller or large volume of blood this cocentration will change
what does the RBC Distribution Width (RDW) provide?
range of sizes of RBCs
ratio of immature and mature RBC cells
when do you order a CBC?
assessment for anemia
platelet dysfunction
monitoring blood loss
dehydration
-penia means
deficiency
-cytosis or –philia means
an increase in number of cells
what is anemia?
condition in which the oxygen carrying capacity of the blood is reduced
what values do we usually see for anemia?
decreased hemoglobin level
decreased hematocrit
decreased red blood cell count
AT LEAST TWO VALUES ARE DECREASED
what specific value determines the type of anemia the person has?
based on size of RBC
MCV
based on color of RBC
MCH
what does a normal MCV value mean?
MCV 80-100
normocytic
what does a high MCV value mean?
MCV >100
macrocytic (increased MCV)
what does a low MCV value mean?
MCV <80
microcytic (decreased MCV)
what are the differential diagnosis’s for Microcytic values?
"TALIS"
T – Thalassemias
A – Anemia of Chronic Disease (also called Anemia of Inflammation)
L – Lead poisoning
I – Iron Deficiency Anemia
S – Sideroblastic Anemia
what are the differential diagnosis’s for Normocytic values?
Hemolytic Intrinsic
"I Help People Get Proper Safe Hematology Care"
I – Intrinsic (category)
Help – Hereditary Spherocytosis
People – Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (PNH)
Get – G6PD Deficiency
Proper – Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency
Safe – Sickle Cell Anemia
Hematology – HbC Disease
Care – reinforces the clinical setting/context
what are the differential diagnosis’s for Normocytic values?
Hemolytic Extrinsic
Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia
Macroangiopathic hemolytic anemia
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia
what are the differential diagnosis’s for Macrocytic values?
Megalobastic
Folate deficiency (B9)
Cobalamin deficiency (B12)
Copper deficiency
Orotic acidura
Drug Induced (allopurinol)
what are the differential diagnosis’s for Macrocytic values?
Non-Megalobastic
Alcohol-use disorder
Liver Disease
Diamond-Blackfan anemia
what does this MCH value mean?
MCH ≥ 27
normochromic
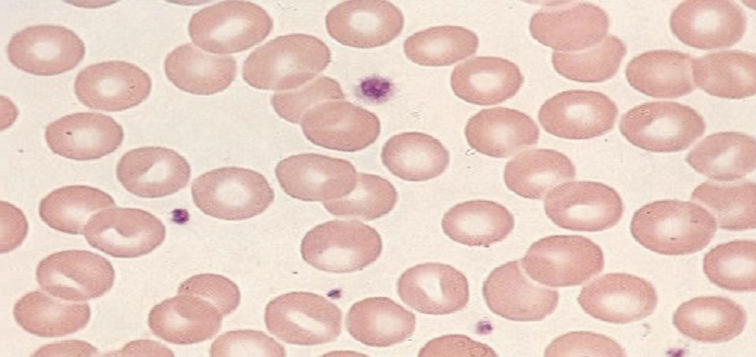
what does a low MCH value mean?
MCH <27
hypochromic
cells barely are seen after being stained and viewed in peripheral smear
what is aplastic anemia?
what is it caused by?
failure of an organ tissue to develop normally
caused by aplasia of bone marrow or its destruction by chemical agents (such as medications) or other physical factors
is anemia a isolated diagnosis?
NO, you need to also find the underlying reason for the anemia
how do you know when you should be concerned for anemia and complete a further work up?
the presence of poikilocytosis on peripheral smear merits further investigation
what is poikilocytosis?
>10% of the cells having a different shape such as teardrop shaped, crescent shaped, sickled, etc
what is schistocytes?
fragmented blood cells which may encompass a wide variety of cell shapes
what is anisocytosis?
a peripheral smear with a variety of cell sizes
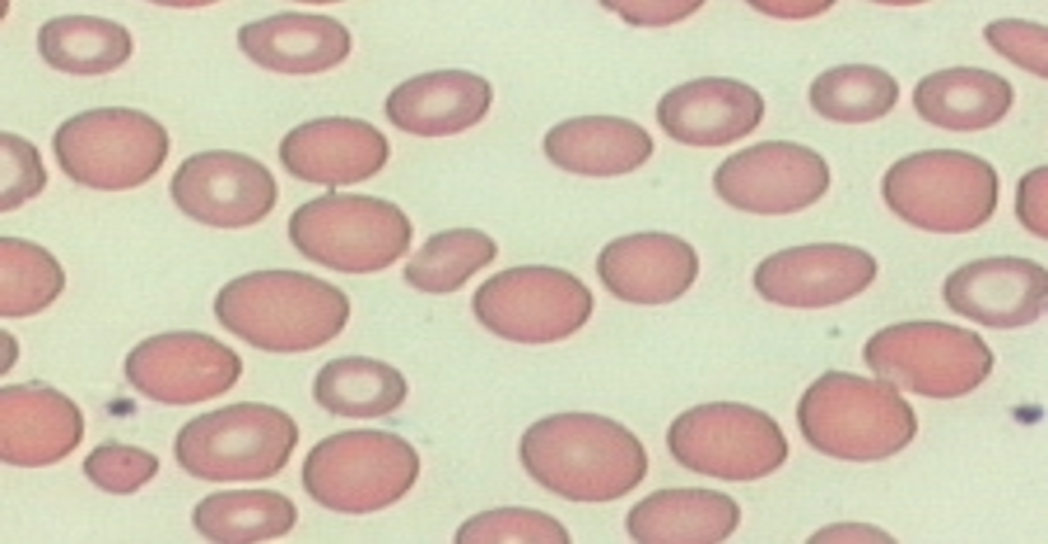
if ≤ 5% of cells vary from normal size, considered a ——
normal variation
what are spherocytes?
spherical cells with decreased surface membrane which appear microcytic and “hyperchromic” due to the loss of the central pale area
small and pigmented
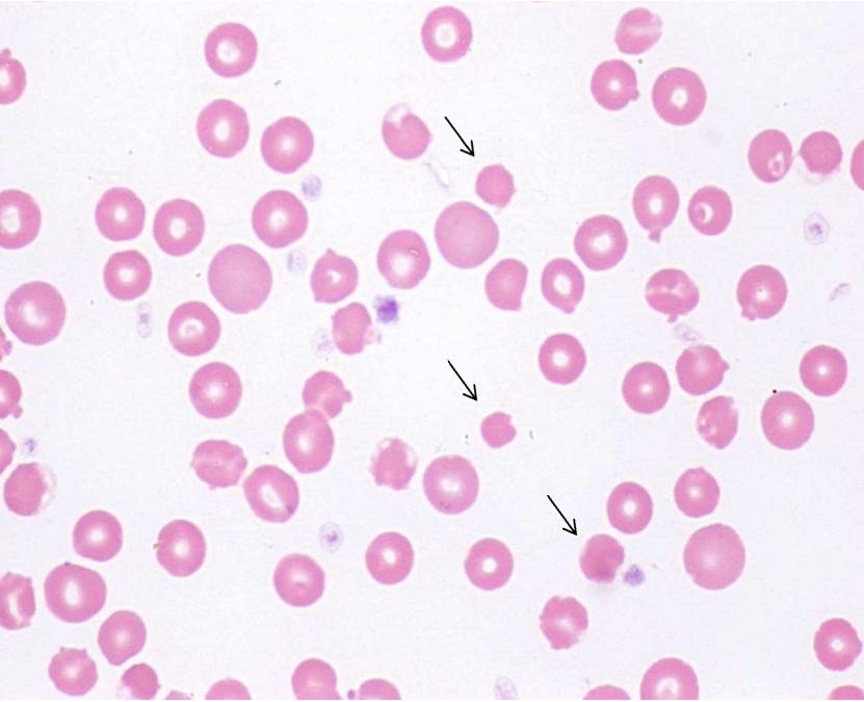
is shape change for spherocytes reversible?
irreversible
what is the clinical significance of spherocytes?
hereditary spherocytosis
immune hemolytic anemia
what are burr cells?
cells with 10-30 rounded spicules evenly spaced over surface of cell
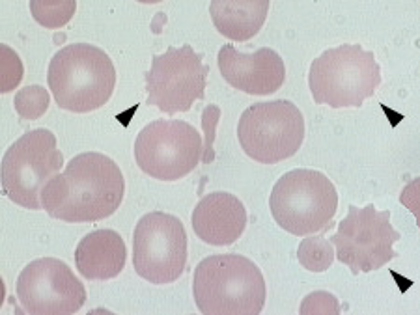
what is the clinical significance of burr cells?
renal disease, liver disease, or burns
what are helmet/bites cell?
cells with distinctive projections, usually two, surrounding an empty area of red cell membrane
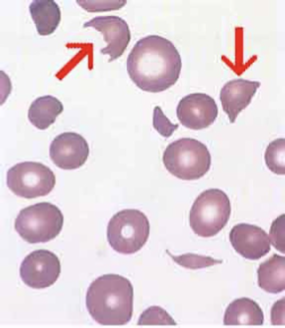
what is the clinical significance of helmet/bites cells?
glucose-6-Phosphate-Dehydrogenase (G6PD) Deficiency
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
mechanical heart valve or aortic stenosis
what are acanthocytes?
cell with normal or slightly reduced size possessing 3-8 finger-like projections distributed in an irregular manner along cell membrane
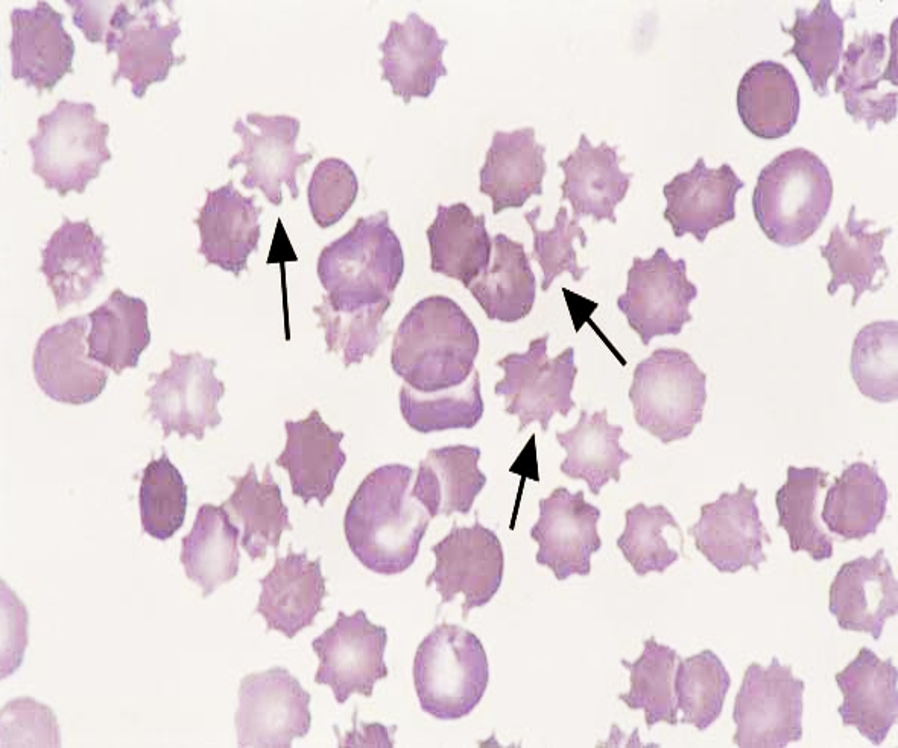
what is the clinical significance of acanthocytes cells?
severe liver disease
abetalipoproteinemia → spleen destroys RBCs
what are ovalocytes/elliptocytes?
oval, egg-shaped, or elongated shape cells
may be normocytic or macrocytic and normochromic or hypochromic
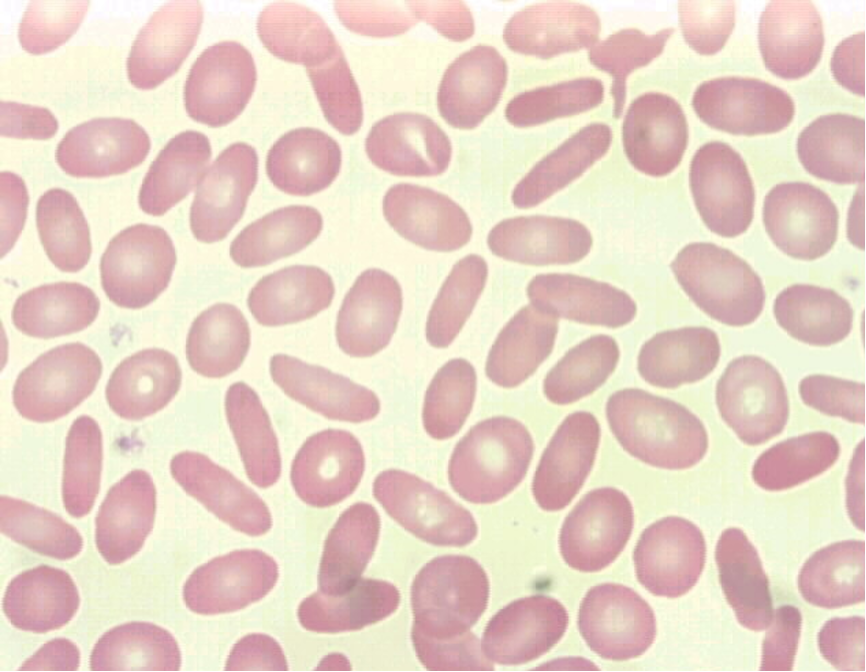
what is the clinical significance of ovalocytes/elliptocytes cells?
thalassemias
myelodysplastic syndrome
megaloblastic anemias
iron deficiency anemia
what are target cells?
cells with large portion of hemoglobin displayed at the rim of the cell and a portion of hemoglobin either central, eccentric, or banded
Always hypochromic
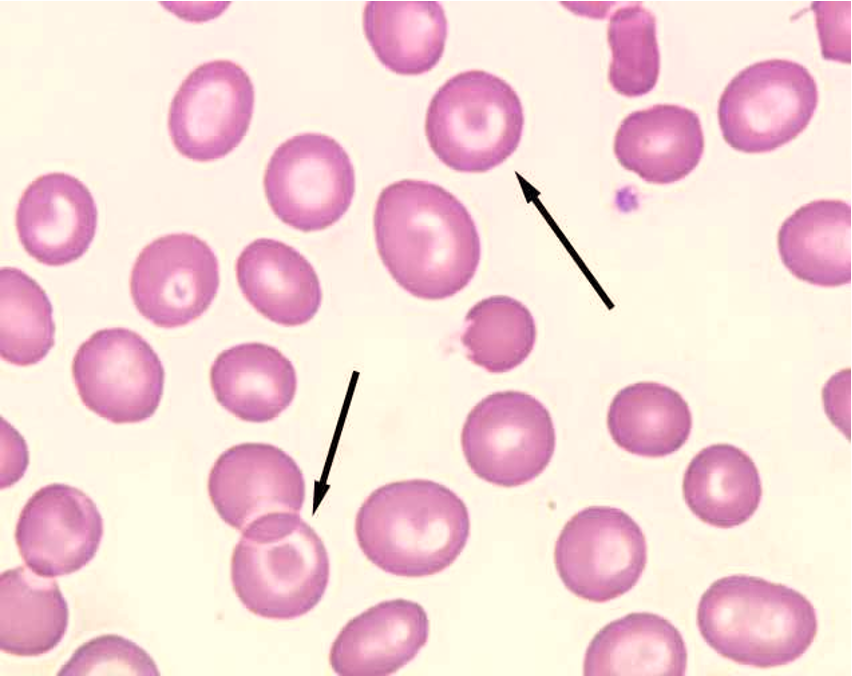
what is the clinical significance of target cells?
liver disease (increased red cell membrane cholesterol) Hemoglobin C Disease
Iron def anemia
Thalassemias (decreased intracellular hemoglobin)
what are tear cell?
cell which look as if one end has been pulled out to a tail while the other is still rounded
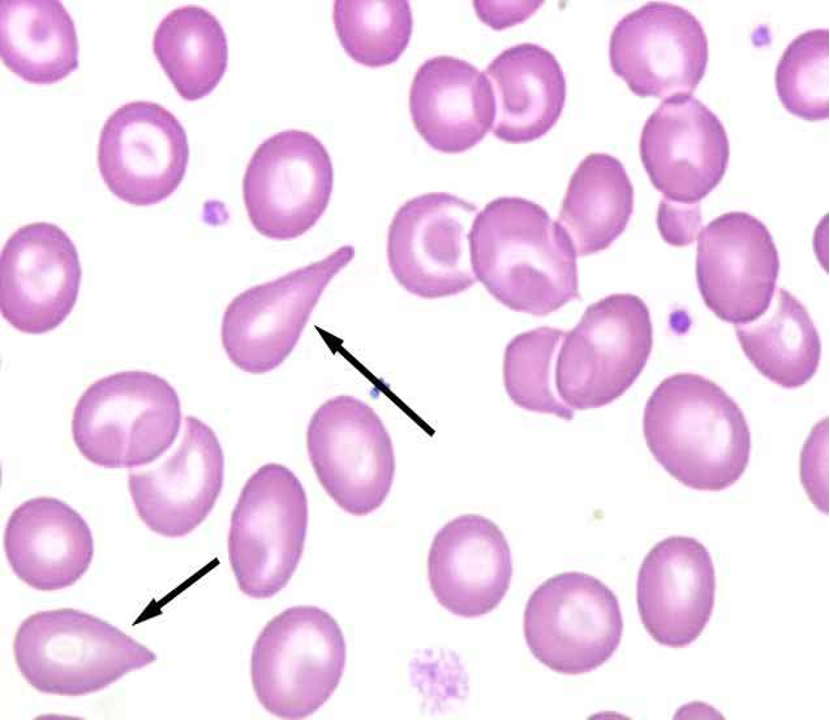
what is the clinical significance of tear cells?
idiopathic myelofibrosis
Thalassemia
Iron Def Anemia
what are stomatocytes cells?
cells that have a rectangular or slit-like central pale area
what is the clinical significance of stomatocytes cells?
hereditary spherocytosis
hereditary stomatocytosis
acute alcoholism
what are rouleaux cells?
cells partially adhering to each other, microscopically have the appearance of a stack of coins
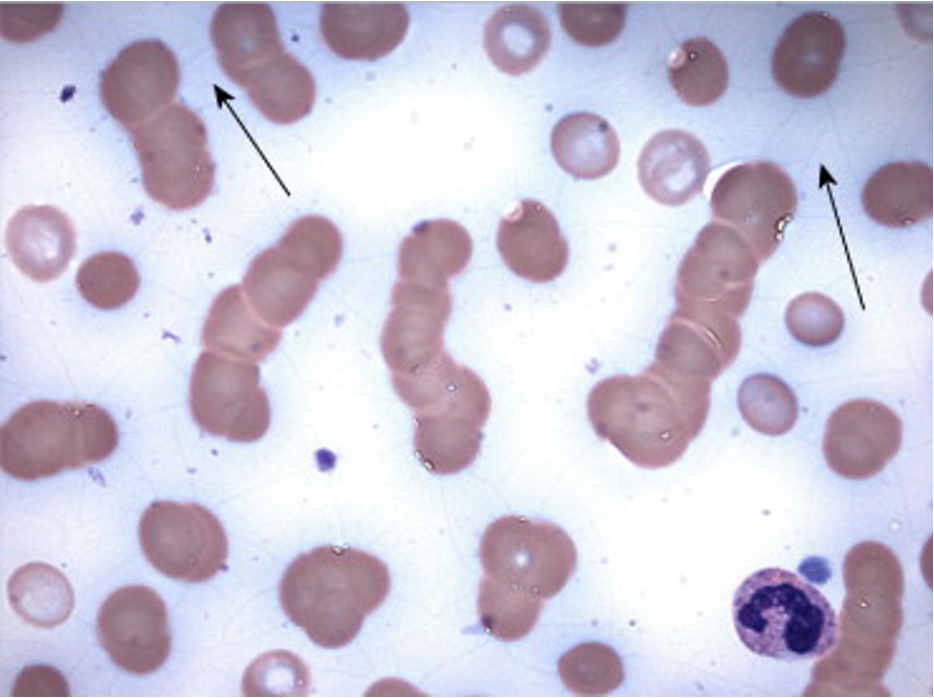
what is the clinical significance of rouleaux cells?
occurs in disease states with abnormal protein levels such as multiple myeloma
what are Basophilic Stippling (Inclusions)?
Small dark blue dotlike structures scattered fairly uniformly throughout the RBC
Derived from ribonucleoprotein and mitochondrial remnants
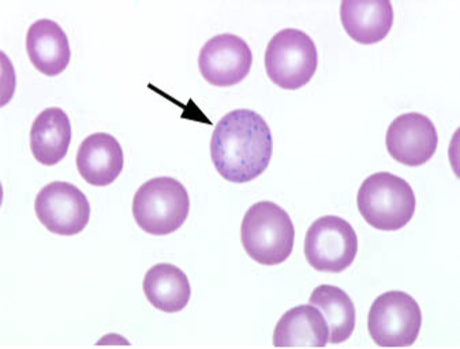
what is the clinical significance of Basophilic Stippling (Inclusions)?
conditions with defective or accelerated heme synthesis such as lead poisoning or Thalassemias
what are Howell-Jolly Bodies (Inclusions)?
Small, round, blue-black inclusions that occur singly or doubly in an eccentric position
Derived form DNA remnants
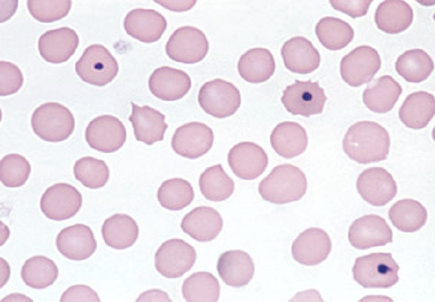
what is the clinical significance of Howell-Jolly Bodies (Inclusions)?
seen s/p splenectomy or in Thalassemias
hemolytic anemias, or megaloblastic anemias
what are Pappenheimer Bodies (Inclusions)?
Small, irregular magenta-colored granules that usually occur in small groups
Derived from hemosiderin granules (non-heme iron deposits)
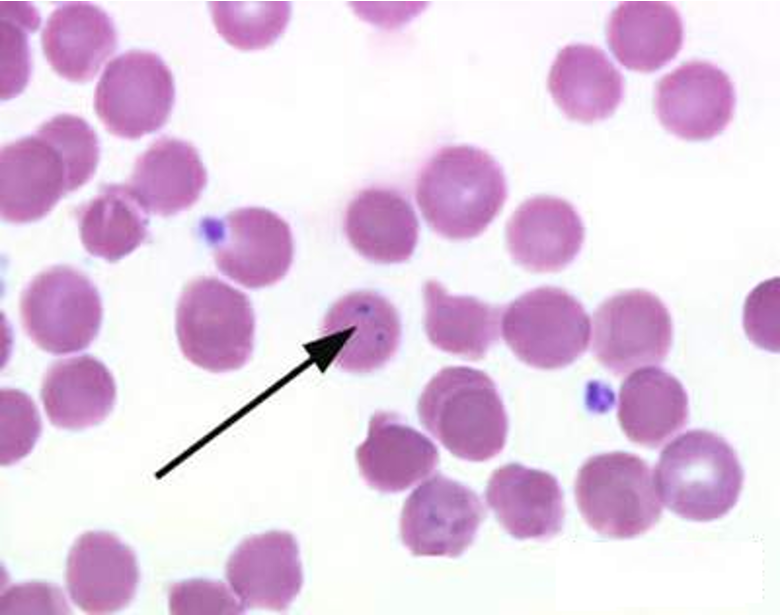
what is the clinical significance of Pappenheimer Bodies (Inclusions)?
sideroblastic anemias
hemochromatosis
iron overload disorders
hemoglobinopathies
s/p splenectomy
what are Heinz Bodies (Inlcusions)?
Small scattered blue dot-like structures of varying size in the RBC – stained with supravital stain
If 1-4 found, considered normal, 5 or more/cell is considered pathogenic
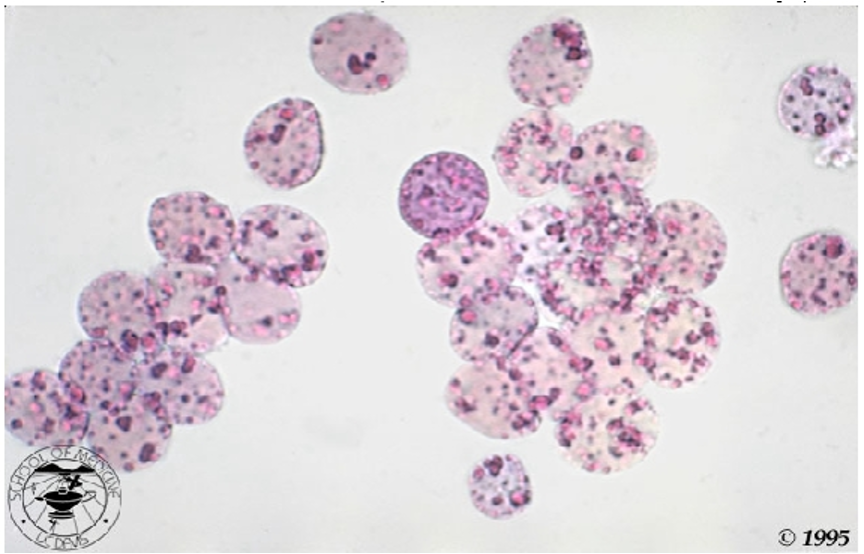
what is the clinical significance of Heinz Bodies (Inlcusions)?
G6PD deficiency
alpha-thalassemia
drug-induced hemolytic anemias
when there is an increase in the RBCs, H&H, and sometimes WBCs what does this mean?
there is a decrease amount of fluid in the blood, concentrating the RBCs, creating an increase in the H&H
-good indication of dehydration