Lecture 18 - Dopamine & Reinforcement Learning II
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
What is the learning signal in reinforcement learning? How do we represent the value of each state?
learning signal = RPE (TD error) in dopamine neurons
value of each state = discounted sum of future expected rewards
What signal do dopamine neurons encode in reinforcement learning models?
TD reward prediction error
reinforcement learning explains the activity of dopaminergic neurons
dopamine neurons encode RPE and project to striatum
What is credit assignment in temporal difference learning?
assigning value to states that are intrinsically not rewarding but that lead you to rewarding states
In temporal difference learning: What is the credit assignment problem? What is TD learning?
credit assignment → learning from delayed rewards
how can you assign credit to state and actions amongst the many past actions and states the agent has visited
TD learning: learning a guess from a guess
update the estimate based on the estimated value of other states (bootstrapping)
What does the RPE look like at the time of the reward (first trial → no learning)?
positive RPE
since a reward is not expected
RPE = rt + y(V^t+1) - V^t
RPE = rt + 0 + 0
RPE = rt
the reward state V^t now has value
What would the RPE look like if the reward had been omitted (first trial → no learning)?
no RPE
RPE = rt + y(V^t+1) - V^t
RPE = 0 + 0 + 0
RPE = 0

What is this showing?
since the previous trial had a reward, we give the step before it a value as well
the time step before has value since it leads us to getting the reward
What changes on the second trial of TD learning that causes the reward prediction error at the moment of reward to become smaller?
The reward time-step now has predicted value from the first learning experience, so the reward is less surprising, making the RPE smaller
Why does a positive RPE appear at the timestep before reward delivery on the second trial, and what does this accomplish?
Because the next time-step (the reward moment) now has future value, the RPE becomes γVt+1−Vt > 0
RPE is positive in prior state because you are just about to get a reward
What occurs for value during the third trial?
on the third trial, the time of reward delivery and the preceding time-step have value
at the 2 time steps preceding reward delivery, the future value contributes to the RPE
What occurs over time by learning the value step by step?
repeat across many episodes until the value converges
value all the way until the cue
prediction error response gets propagated backwards from the reward location to the reward prediction cue
no more prediction error at time of reward
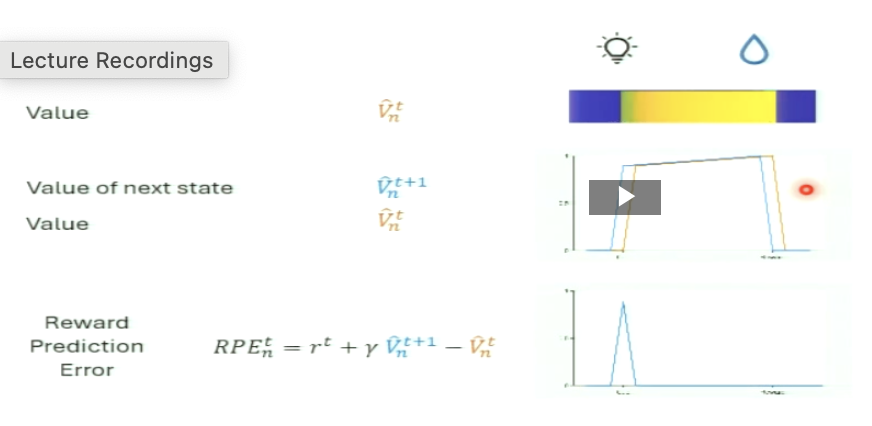
the system has experienced the cue → reward sequence many times.
Because of this, value has propagated all the way backward from the reward to the cue
This is what TD learning predicts and what dopamine neurons actually do
What is the evolution of value and RPE during learning?
value: as learning advances, value gets assigned to earlier and earlier moments until it reaches the reward predicting cue (no information before then)
RPE moves from reward time to time of cue

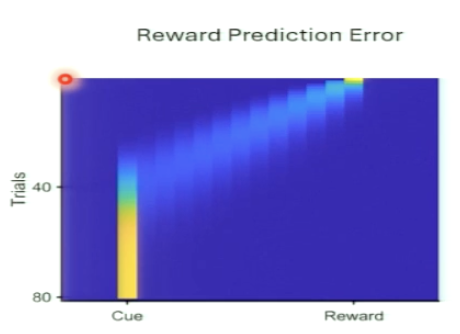
Why is there no RPE between cue and reward?
Before learning, the reward is surprising because nothing predicts it
As value propagates backward:
The moment right before the reward becomes predictable → no RPE
Then the moment two steps before becomes predictable → no RPE
This continues until the cue is the earliest predictor
Now:
The cue contains all available information
No new information shows up between the cue and reward
If nothing new is learned, there’s no prediction error
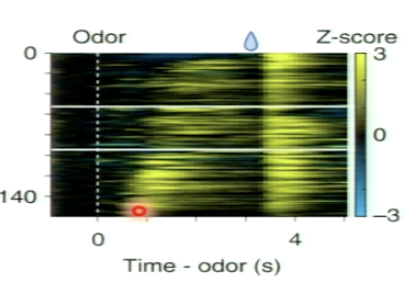
Do we see the backwards movement of value in experimental research?
yes!
experimental evidence reflects the model and shows the gradual shift from the reward time to cue time in dopamine neuron activity
thought to encode RPE
Is the same approach of value and policy networks used for advanced AIs playing games like ‘Go’?
yes!
build a value map of the different states of the world
bring the value back to events that predict rewards and assign value to these events and choose which events we want to do
Is the RPE an absolute value?
No! not an absolute value
instead a comparison between what we expect and what we receive
if things are better than expected → positive RPE
if things are worse than expected → negative RPE
Recap: What the is the value of each state? What does this mean?
discounted sum of future expected rewards
multiply the value of the future reward by a factor less than one (yt)
anything happening further in the future has less value than a current reward
value of state = value that can be reached from this state discounted by how far they are into future
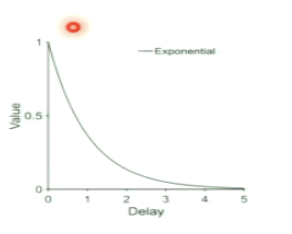
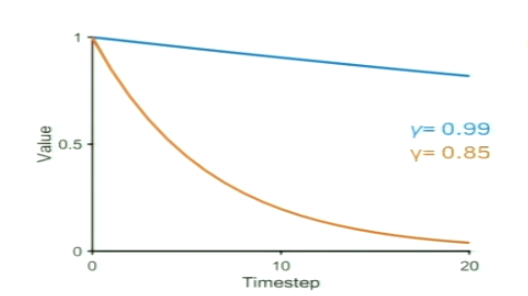
What is the discount factor in detail? What does larger discount rate vs. larger discount factor mean?
controls the value of future rewards
larger discount rate = future values are devalued faster (red)
larger discount factor = future values are devalued slower (blue)
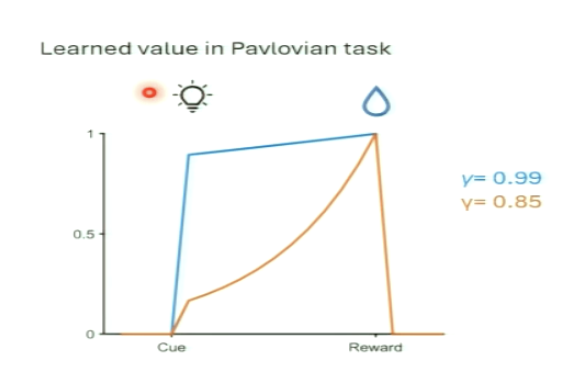
What do different discount factors mean for learned value in Pavlovian task?
the value at the time of the cue depends on the delay and the discount factor
larger factor → value stays high at cue (almost same as when it was at reward)
small factor/larger rate = value is low at cue compared to when it was at reward
What two factors determine how valuable cues are?
discount rate
delay between cue and reward
Describe example of comparing smokers and non smokers with delay discounting:
comparing smokers and non-smokers and whether they were adult or adolescent
adult smokers looking less at long term rewards and more at short term benefits
adolescent smokers might not be about delay discount
difference in delay discounting control populations have been measured in patients with pathological gambling or some addictions
behavioural measure that can be indicative of a change in brain processes
potential inability to match behaviour discounting to ecologically relevant timescale
ADULTS FOCUSING ON THE SHORT TERM GAINS OF SMOKING RATHER THAN ECOLOGICAL TIMELINE
steeper discount delay
if you get sick from smoking in the future (big loss in the future), matters less to you since value in future is lower
How do we decide which state to pick?
policy chooses action that maximizes future value
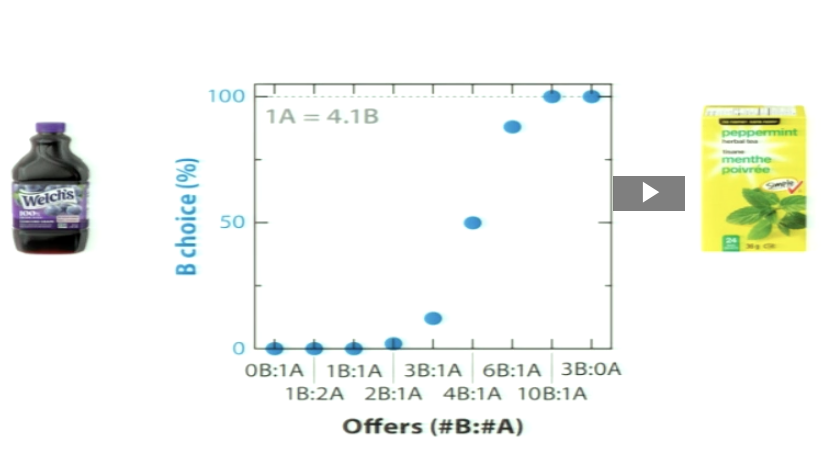
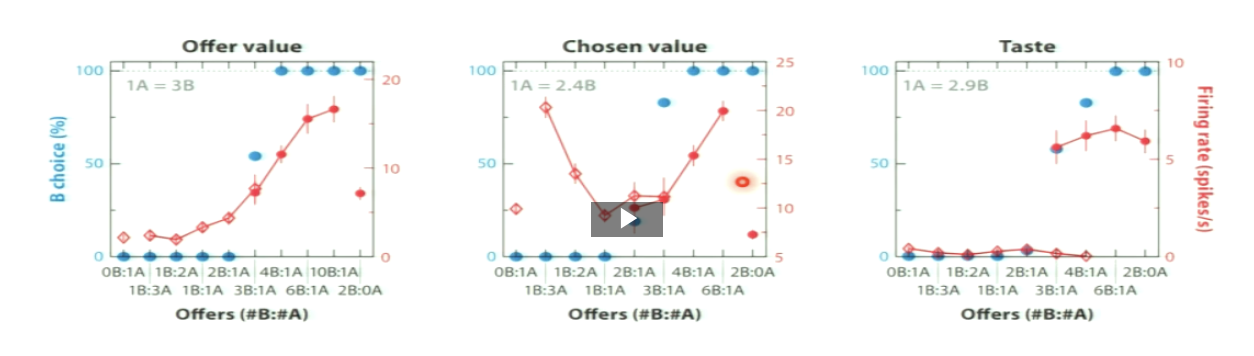
Recap: What was the exchange rate with different liquids?
monkey is presented with different offers by changing the relative amount of the two options
exchange rate is: How many units of Reward B does the monkey consider equal in value to 1 unit of Reward A
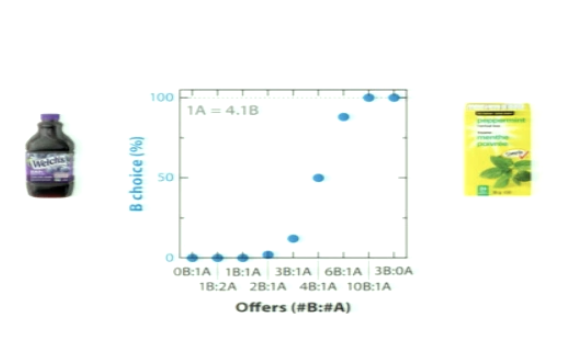
Why is there a smooth transition between the two juice offers?
the preferences for one or the other are not completely stable
if you already picked the peppermint tea, you might be keen to try the other
PREFERENCES ARE NOT STABLE
PREFERENCES ARE COMPLETELY FIXED
not exactly sure yourself what you prefer
you want to try both to see what you prefer!
What is the exploration-exploitation dilemma?
exploit: maximize the future reward given our current understanding of the world
explore: investigate less rewarding states to explore whether they can lead to potential higher future rewards
What factors can influences the exploration-exploitation tradeoff?
bias towards one
you always want to keep a small exploration bias
want for risk
personal curiosity
boredom (exploration)
What did this show regarding exploration vs. exploitation?
possible changes in preference across days
Recap the Bandit task? How does this version show the balance of exploration and exploitation? What does the optimal balance of exploration and exploitation depend on?
reward and there is a probability of getting reward if we pick an option, no reward for some options
here, you always get a reward but the value of the reward associated with each choice changes over time
it might be necessary to explore options that are thoughts to be non-optimal as their value might have changed
optimal balance depends on the volatility/uncertainty of the environment
What do VLPFC lesions cause for dynamic stimulus-outcome contingencies?
deficits in tracking dynamic contingencies
inability to use exploration update value preferences
Can confidence modulate exploration-exploitation?
yes
if more confident in value estimate, behaviour more exploitation (you’re sure that your option is the best)
if less confident, subject is more likely to explore suboptimal option
(more exploration)
How does the exploration-exploitation dilemma occur across cognitive domains?
general dilemma with many situations that are applicable
visual focus, problem solving, etc.
the act of balancing between exploiting current knowledge and exploring possible alternative futures occurs across cognitive domains both at individual and social levels
Recap: What is involved in learning signal, value of each state and choose action that maximizes future value?
learning signal: RPE (TD error) in dopaminergic neurons
value: discounted sum of future expected rewards
action: either exploit current knowledge or explore potential better alternatives