UWORLD Infectious Dz Step 2 CK
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
Most common cause pneumonia in HIV patients.
Encapsulated bacteria, Strep Pneumococcus
Majority of human infectious with ___ asx but hydatid cysts can be found any part of the body including the liver (2/3 pts) and lungs.
Echinococcus granulosus
- Sheep are raised, dogs
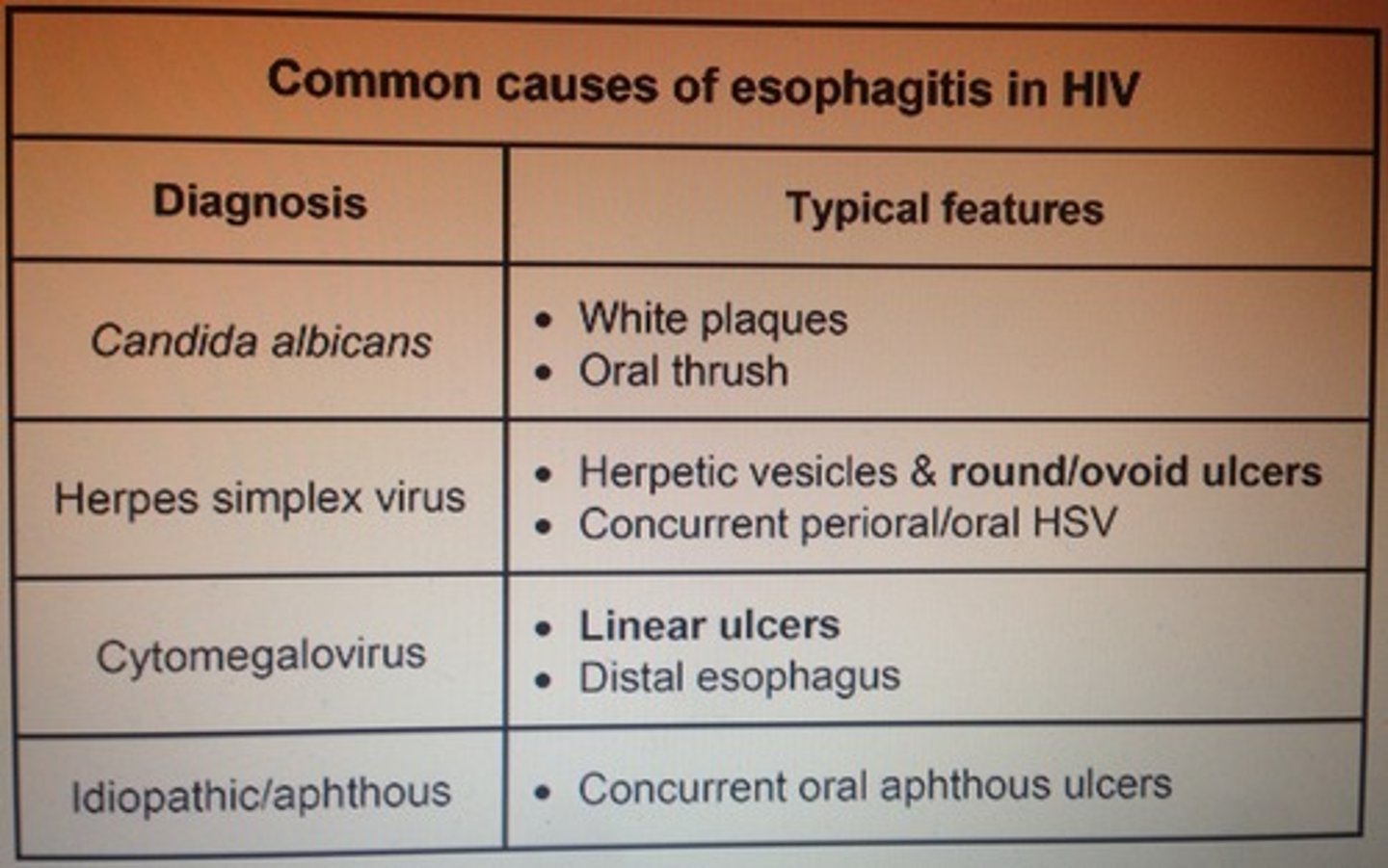
Common causes of esophagitis in HIV
Pill esophagitis causes.
KCl
Tetracycline
Bisphosphonates
NSAIDs
Acute odynophagia due to direct effects of a med on esophageal mucosa
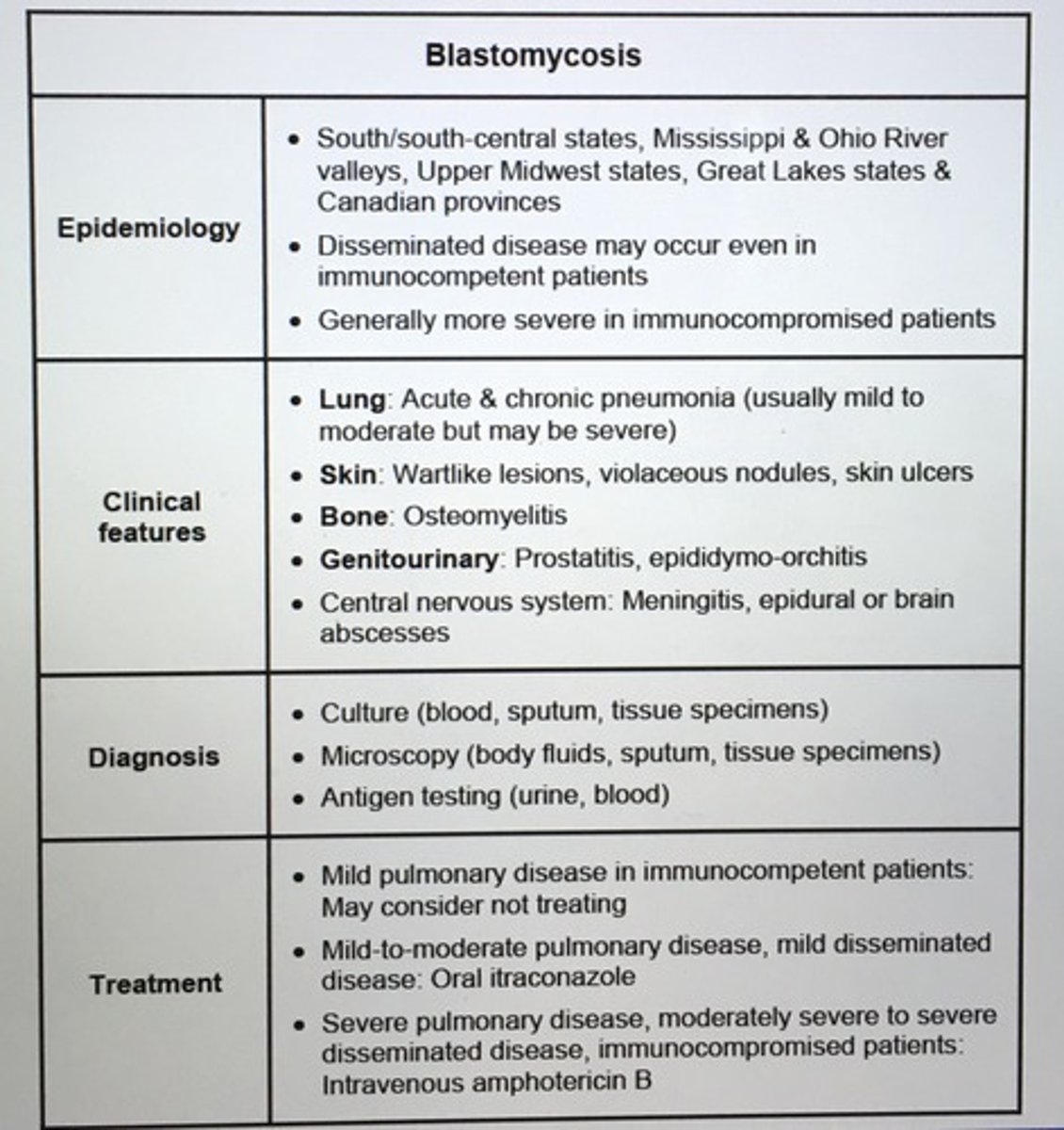
Blastomycosis epidemiology, clinical feats, dx, tx.
In DM pt, the pathogenic mechanism of osteomyelitis adjacent to a foot ulcer is ___ spread of infection.
Contiguous (spread of infection to bone from adjacent soft tissue and joints)
What is an effective measure to reduce risk of UTI in pts with neurogenic bladder?
Intermittent catheterization
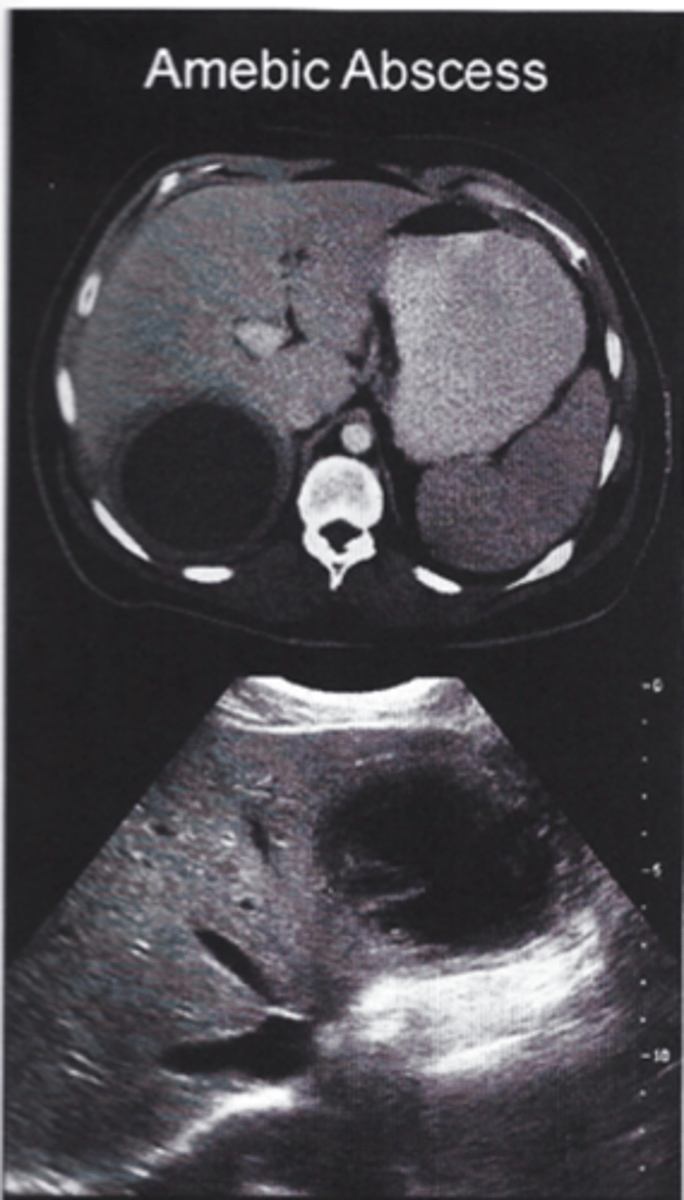
___ is a protozoan, which can cause amebic liver abscess single located in the right lobe liver.
Entamoeba hystolytica
- travel to Mexico, dysentery + RUQ pain with single cyst
- stool exam trophozoites, serology, liver imaging
- tx: Metronidazole
Consider __ as a late complication of post-bone marrow transplant recipient who present with pneumonitis and colitis.
CMV

Rubella (German measles)
Tx febrile neutropenia.
Cefepime
Meropenem
Piperacillin-tazobactam
ANC < 1500 = neutropenia
Infective endocarditis due to E. corrodens is usually seen in setting of?
Poor dentition and/or periodontal infections (gram - anaerobe)
Enterococcus faecalis are a common cause of endocarditis associated with nosocomial ___.
UTIs
___ presents with erythema and swelling, severe pain out of proportion to the PE, signs tissue crepitus, purulent drainage, or X-ray evidence of gas in the deep tissues.
Necrotizing fasciitis
- hypotension
- strep pyogenes, staph, clostridium perfrinegens
- extremities & perineal region
- surgical debridement
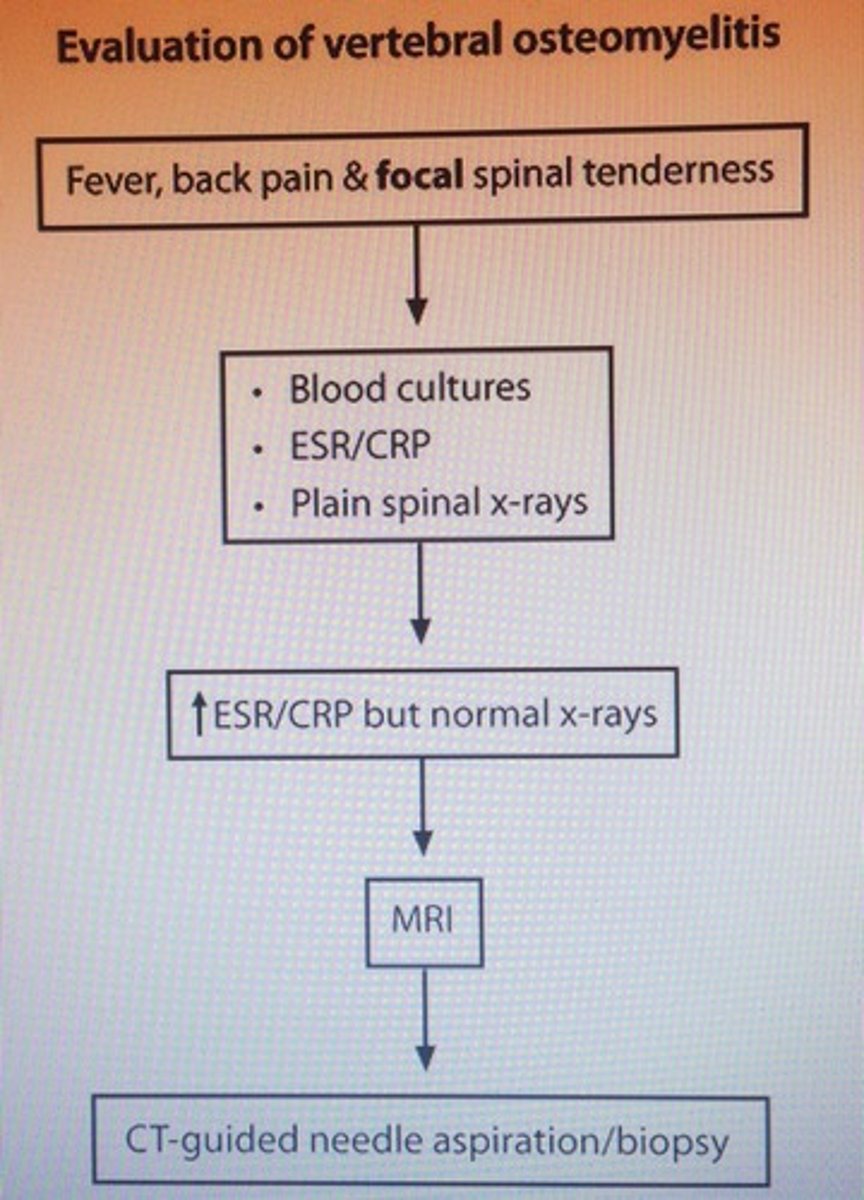
Evaluation of vertebral osteomyelitis
- Staph aureus 50% pyogenic spinal osteomyelitis
- Exquisite focal tenderness
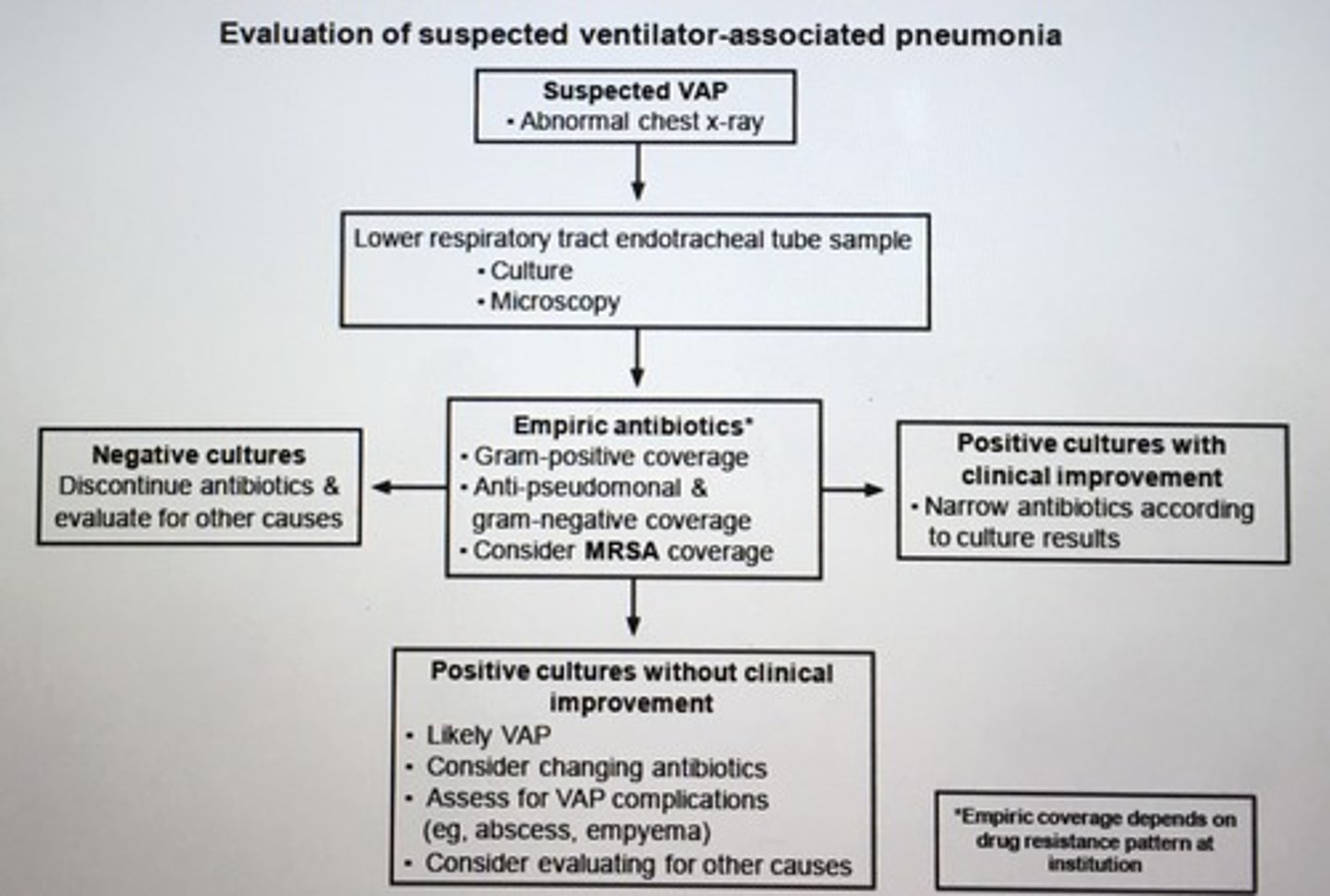
Evaluation of suspected ventilator-associated pneumonia
- tracheobronchial aspiration -> lower respiratory tract sampling
__ is the tx of choice for pregnant and lactating patient with early localized Lyme disease.
Amoxicillin
- Doxycycline contraindicated in young children < 8 as well as pregnant and lactating women because causes permanent discoloration of teeth and retardation of skeletal development
What confirms the dx of E. histolytica?
Serologic testing for E. histolytica antibodies
Infectious mononucleosis

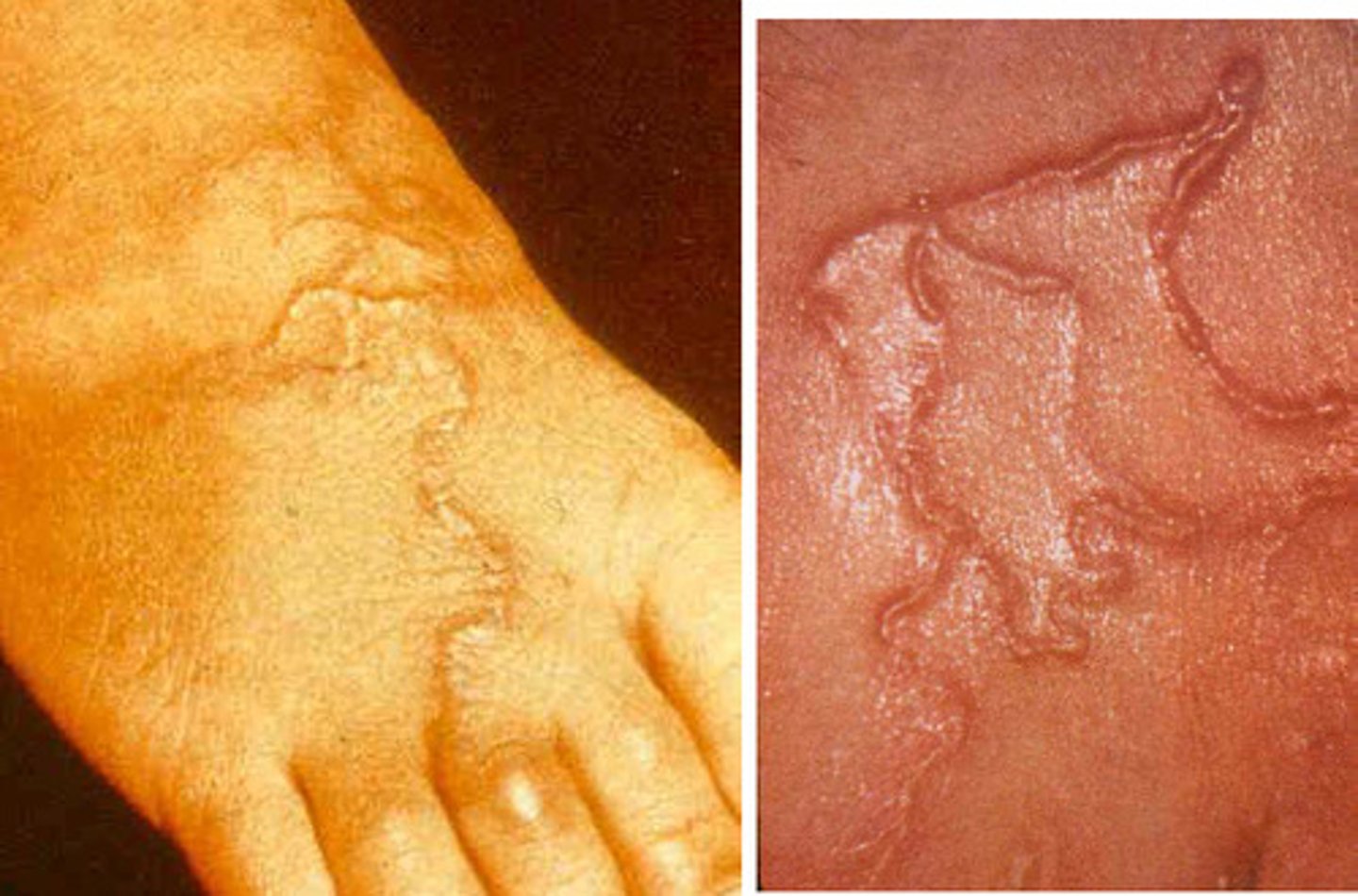
___ is common in travelers in tropical regions, and is characterized by pruritic, elevated, serpiginous lesion on the skin. Contact through sand.
Cutaneous larva migrans
- Ancylostoma braziliense, dog and cat hookworm
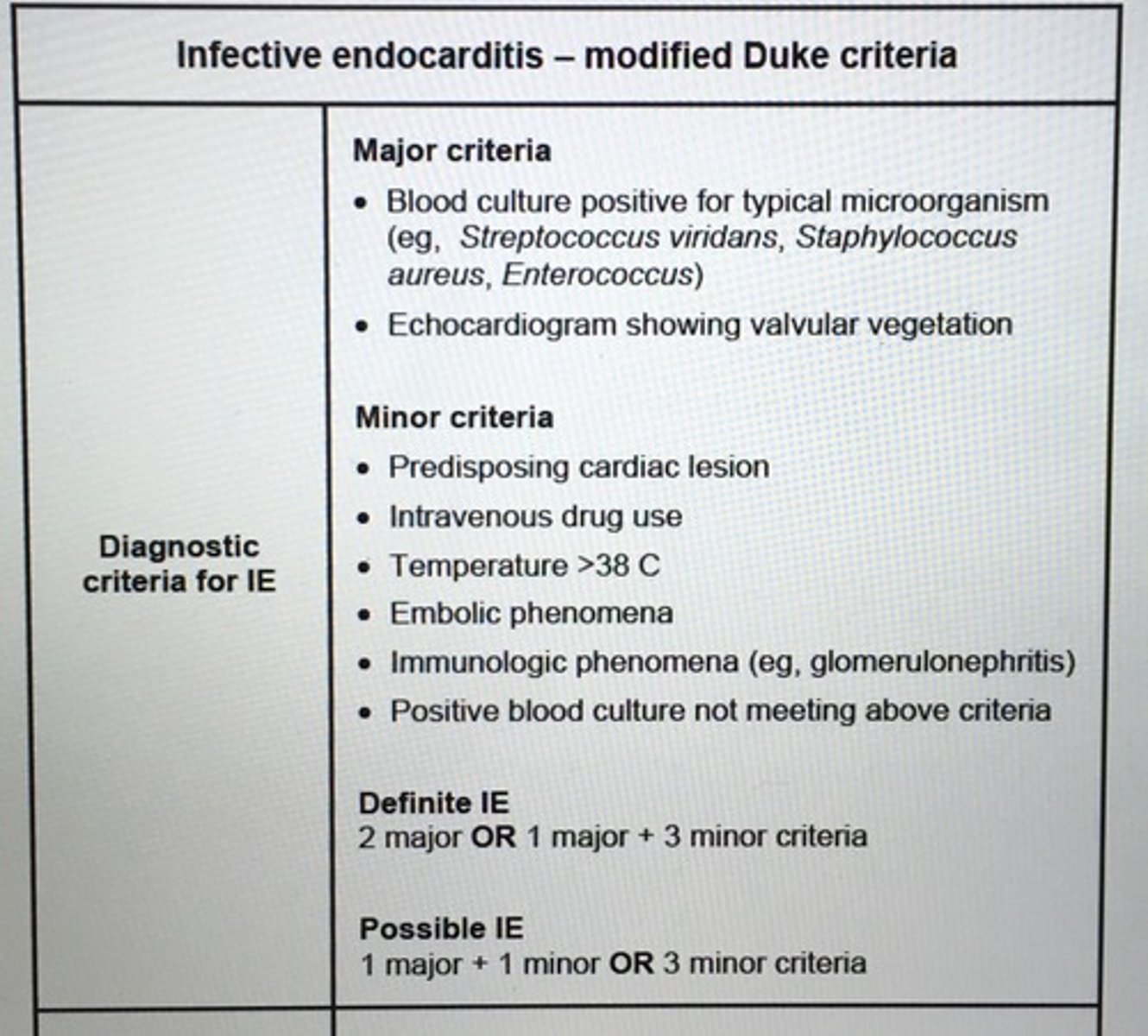
What should be obtained in suspected Infective endocarditis pt prior to initiating abx therapy?
Blood cultures from separate venipuncture sites over a specific period
Recommended vaccines for adults
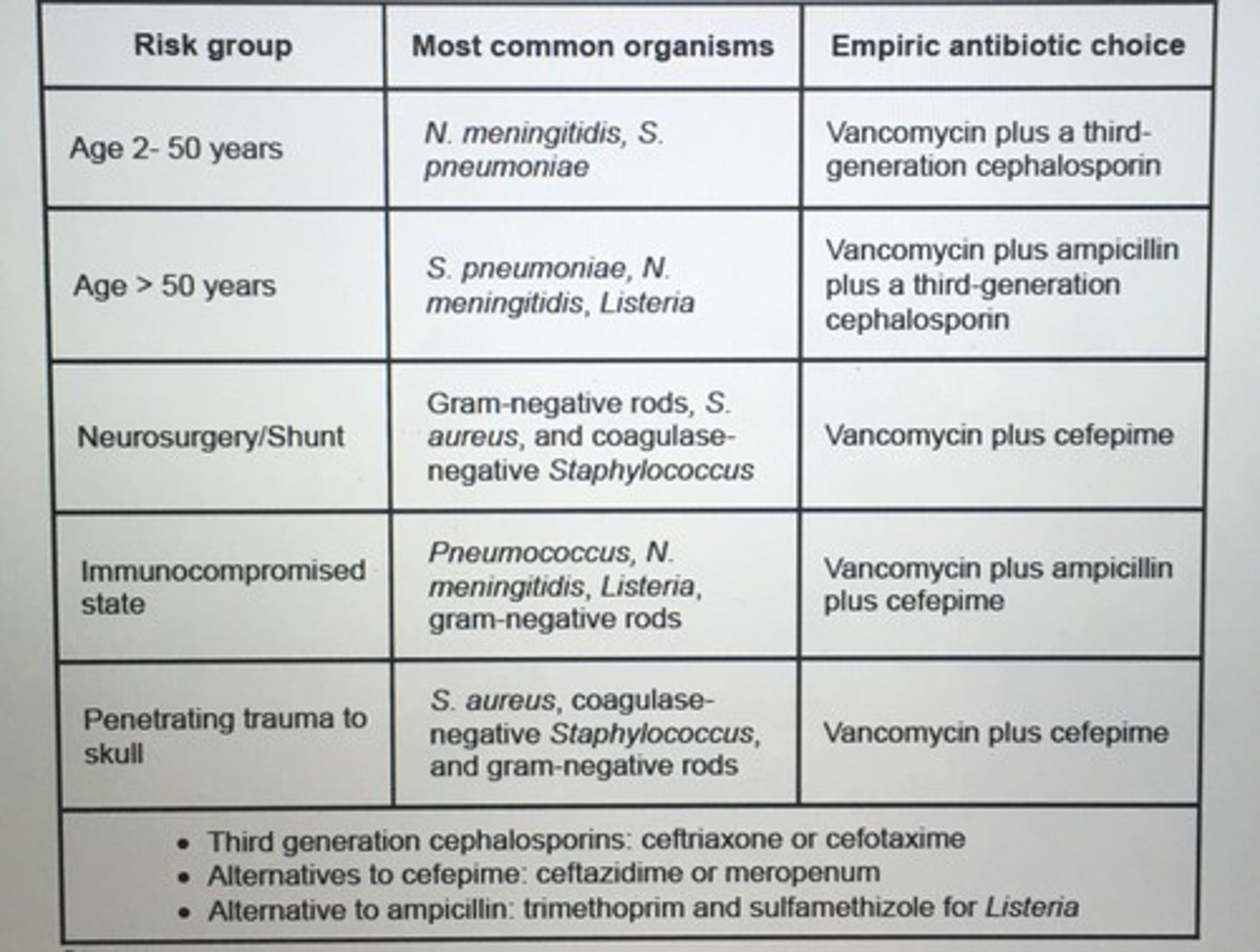
Abx of choice for each age group suspected acute bacterial meningitis.
Adults who presents with suspected bacterial meningitis should also be given Dexamethasone with first dose Abx (helpful for S. pneumoniae 4 days D/C if another organism shown in cx)
___ mimics the presentation of sarcoidosis and should be considered when a patient with suspected sarcoidosis (hilar adenopathy) deteriotes after immunosuppressive tx.
Histoplasmosis
- Mississipi
- mold in soil and in bird/bat droppings
- urinary antigen testing dx
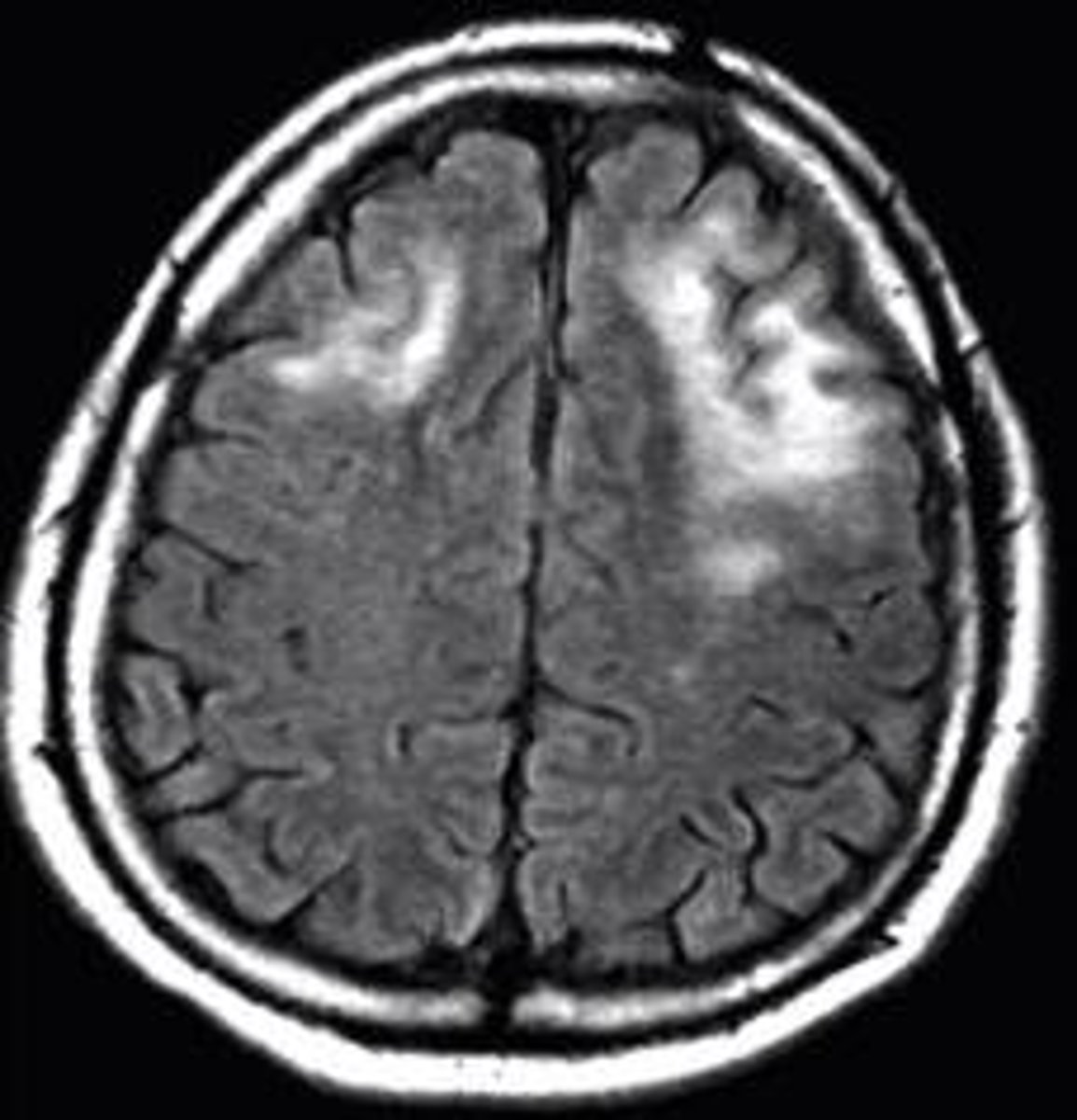
MRI shows multiple demyelinating, non-enhancing lesions with no mass effect seen in immunocompromised pt that has hemiparesis and disturbed speech.
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML)
- JC virus, human polyomavirus
- cortical white matter
- survival 6 mo. post dx.
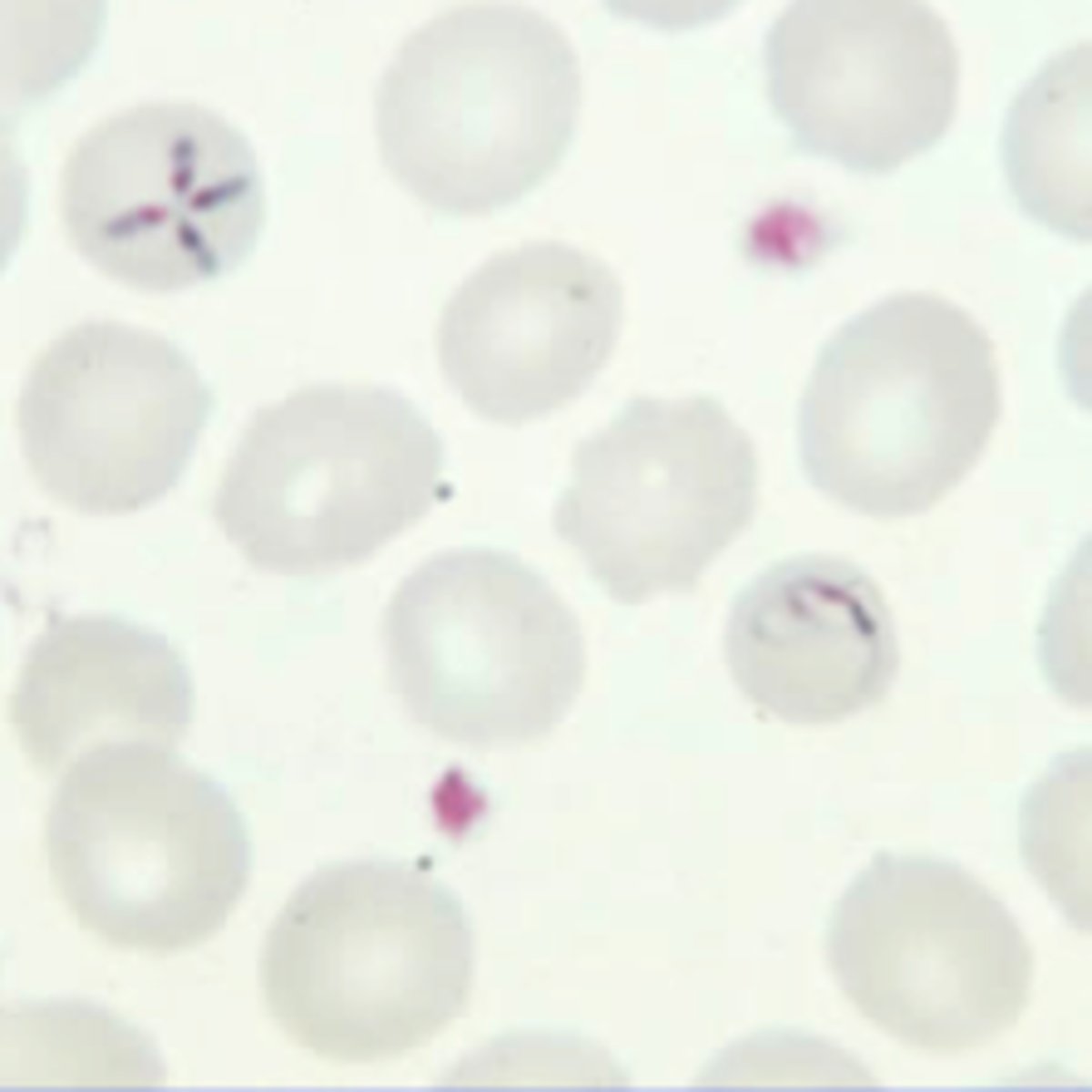
Pt presents with tick bite from northeast US, hemolysis, pt jaundiced, age > 40, no spleen/immunocompromised. Dx.
Babesiosis
- Ixodes tick
- hemolytic anemias: jaundice, hemoglobinuria, renal failure, death
- Giemsa stain
- Tx: Quinine-clindamycin and Atovaquone-azithromycin
Main source of infection are infected cattle, goat, sheep. People at risk include meat processing workers and vets. Flu-like syndrome, hepatitis, or pneumonia.
Q fever
- Coxiella burnetii
All patients who are started on anti-tubercular therapy should also be started on vitamin ____ to avoid ___.
pyridoxine (10 mg/day)
peripheral neuropathy if already developed then dose 100 mg/day pyridoxine
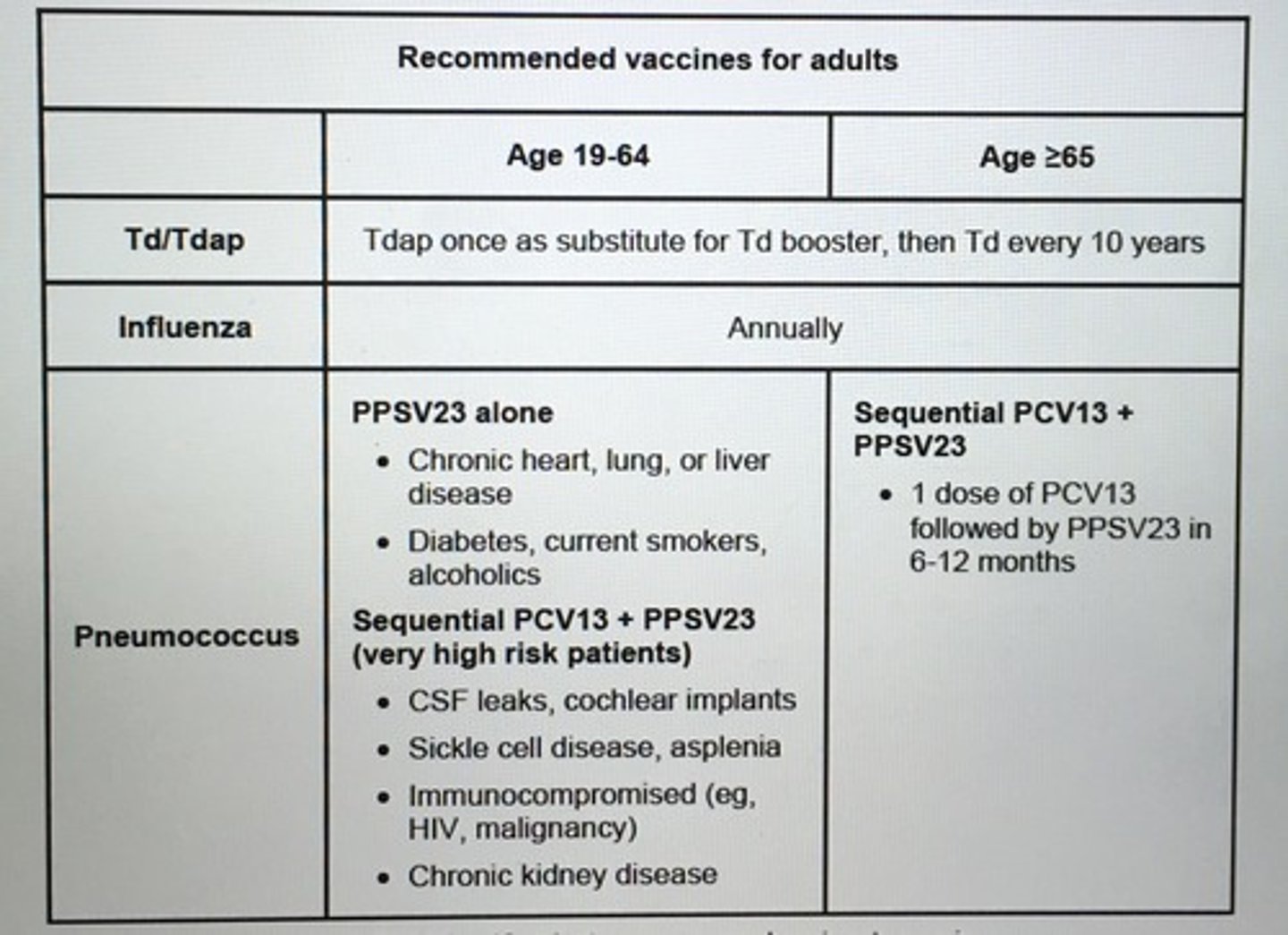
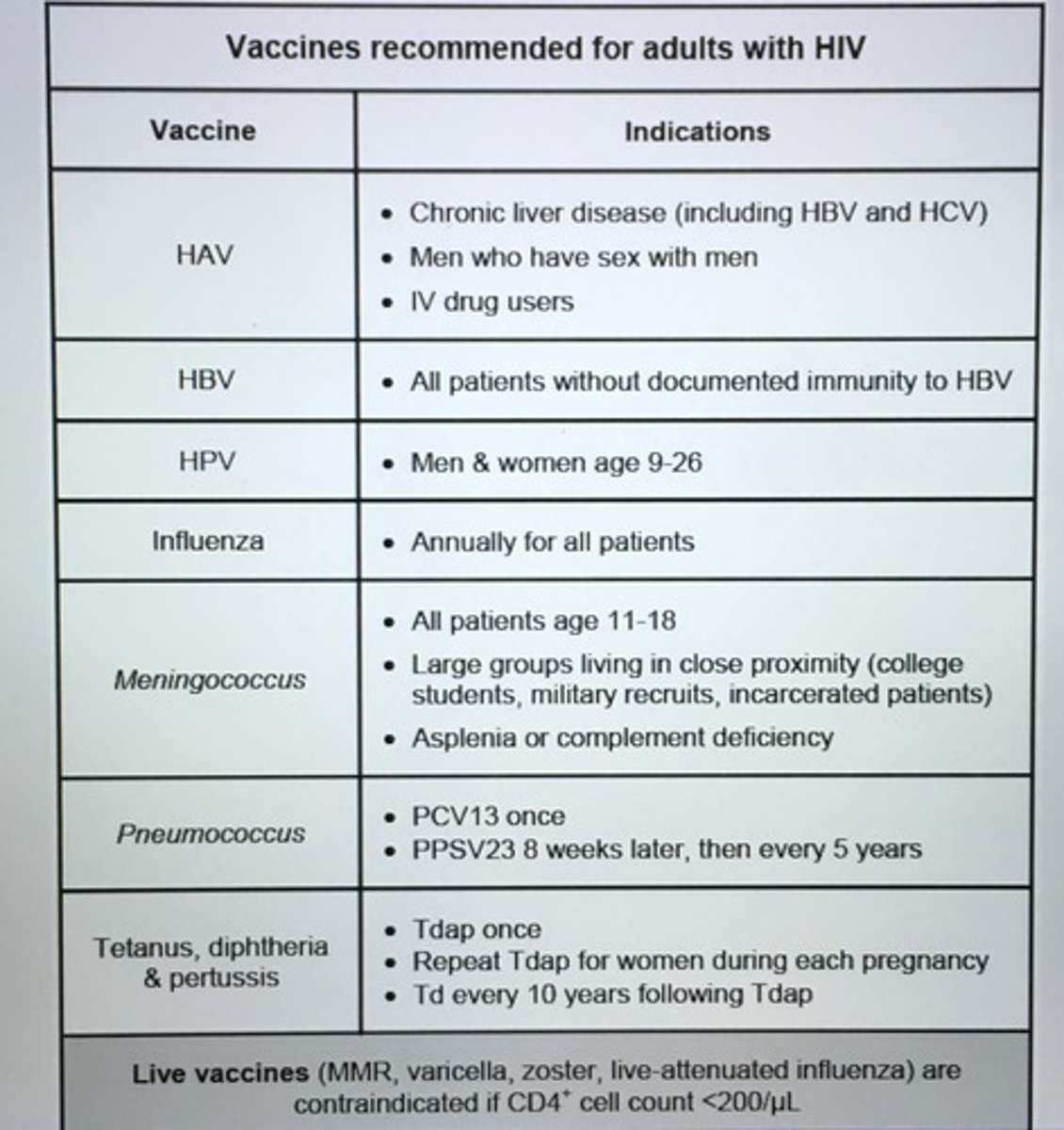
Vaccines recommended for adults with HIV.
When should meningococcal vaccine be given?
All adolescents age 11-12
Booster age 16-21 (if vaccinated prior to 16)
Military recruits
College students living in dorms
Travelers to sub-Saharan Africa
Muslim hajj pilgrimage to Mecca, Saudi Arabia
___ treatment of choice for cellulitis with systemic signs.
IV nafcillin or cefazolin
oral dicloxacillin -> mild cellulitis
cellulitis (beta-hemolytic step/staph aureus generalized swelling erythematous, warm, tender, and less-demarcated than erysipelas)
systemic signs: high fever, rigors, chills, malaise, fatigue, confusion
High fever with relative bradycardia, HA and confusion, watery diarrhea
Hyponatremia, sputum gram stain showing many neutrophils, but few organisms.
Dx and Tx.
Legionella urine antigen test
Respiratory FQ's or newer macrolides
B/L lung infiltrates, confusion, and diarrhea following travel
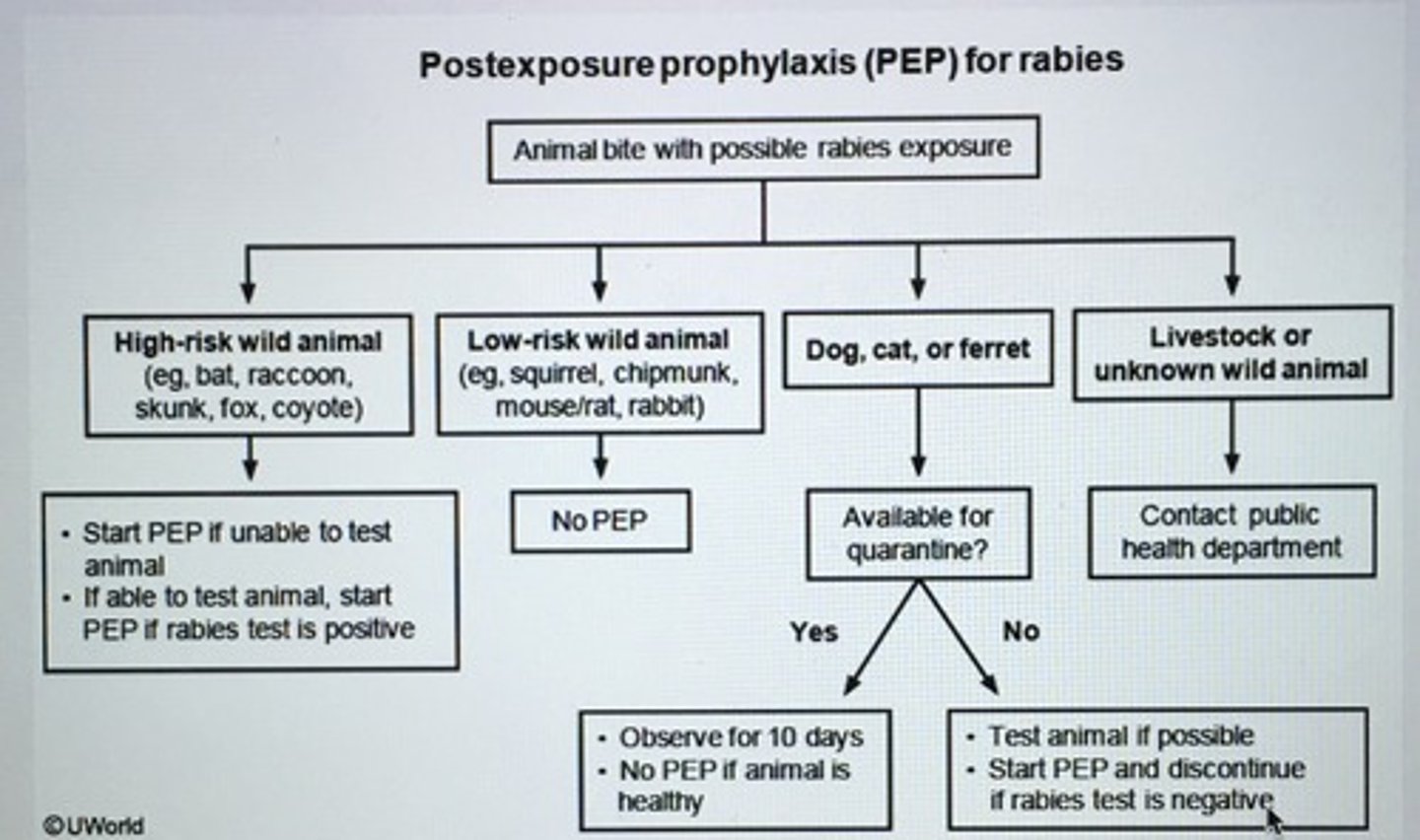
Postexposure prophylaxis (PEP) for rabies
Rabies presents with motor weakness, paresthesias, and encephalitis that can progress to coma and death
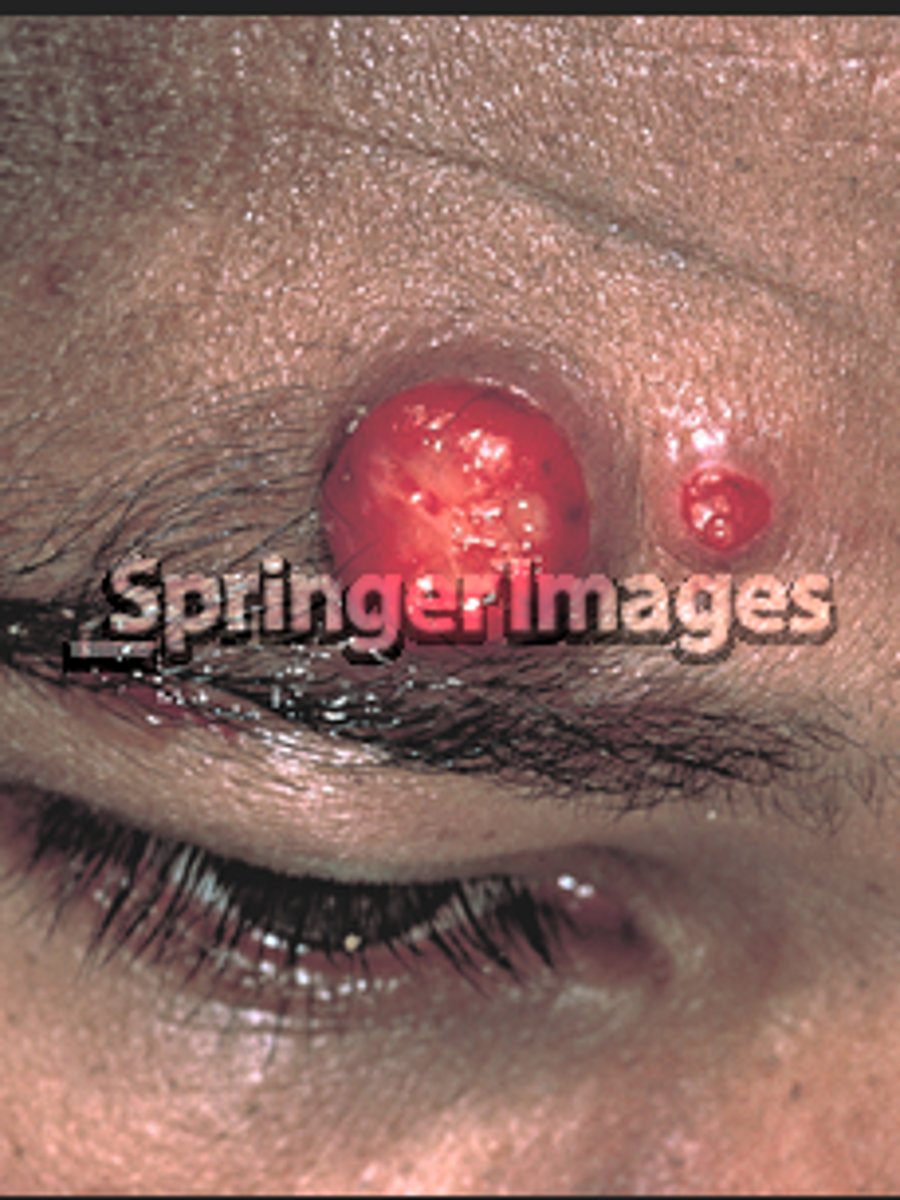
Bright red, firm, friable, exophytic nodules in an HIV infected patient most likely ___.
Bacillary angiomatosis
- Bartonella, gram negative bacillus
Oral erythromycin
___ is used in HIV positive patient to prevent opportunistic infections caused by Pneumocystis jiroveci and Toxoplasma gondii.
Trimethoprim/sulfathoxazole
Microbiology of infective endocarditis
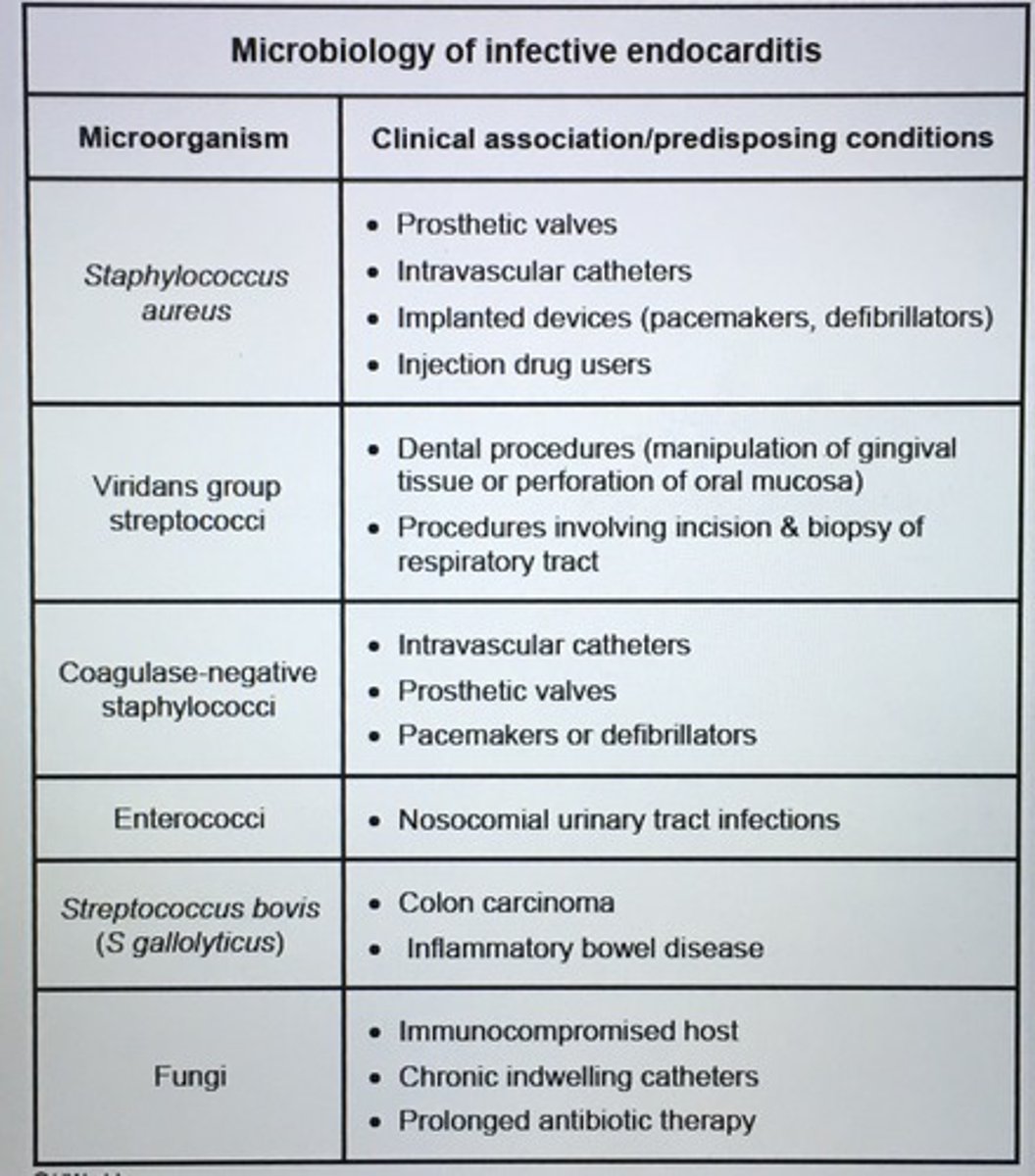
Strep viridans includes which organisms?
S. sanguinis
S. mitis
S. mutans
S. sobrinus
S. milleri
IE with viridans group is commonly encountered after dental procedures and procedures involving incision and bx of respiratory tract
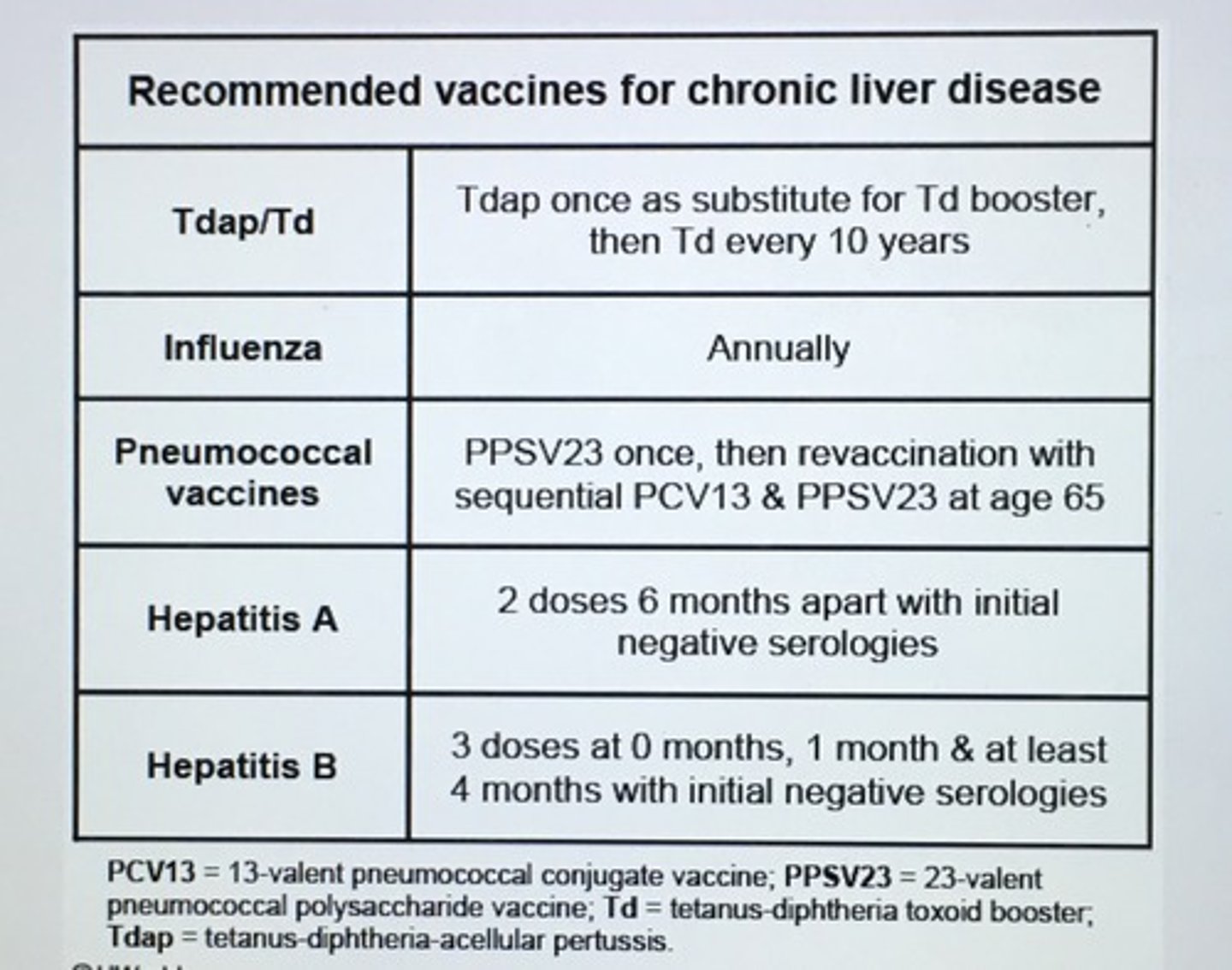
Recommended vaccines for chronic liver disease.
Clinical features of trichinellosis

Postherpetic neuralgia tx.
TCA such as amitriptyline or nortriptyline with acute antiviral therapy (valacyclovir or acyclovir)
When is CT imaging done in pyelonephritis?
- Persistent clinical sxs despite 48-72 hours of therapy
- Hx nephrolithiasis
- Unusual urinary findings (gross hematuria, suspicious urinary obstruction)
Complicated pylo (progression to renal corticomedullary abscess, perinephric abscess, papillary necrosis) occurs in DM, kidney stones, immunosuppression, anatomic abnormalities
Fever, leukocytosis, and LUQ abdominal pain. L sided pleuritic chest pain with L pleural effusion. Splenomegaly.
Splenic abscess (staph, strep, salmonella)
- abd CT scan diagnostic
- broad spectrum abx and splenectomy
- percutaneous drainage in poor surgical candidates
Risk factors for splenic abscess
- Infection (infective endocarditis) with hematogenous spread
- Hemoglobinopathy (sickle cell disease)
- Immunosuppression
- IV drug use
- Trauma
Large basophilic lymphocytes with vacuolated appearance. Pt has fatigue, fever, muscle aches, and arthralgias. Splenomegaly. Heterophiles antibody negative.
CMV
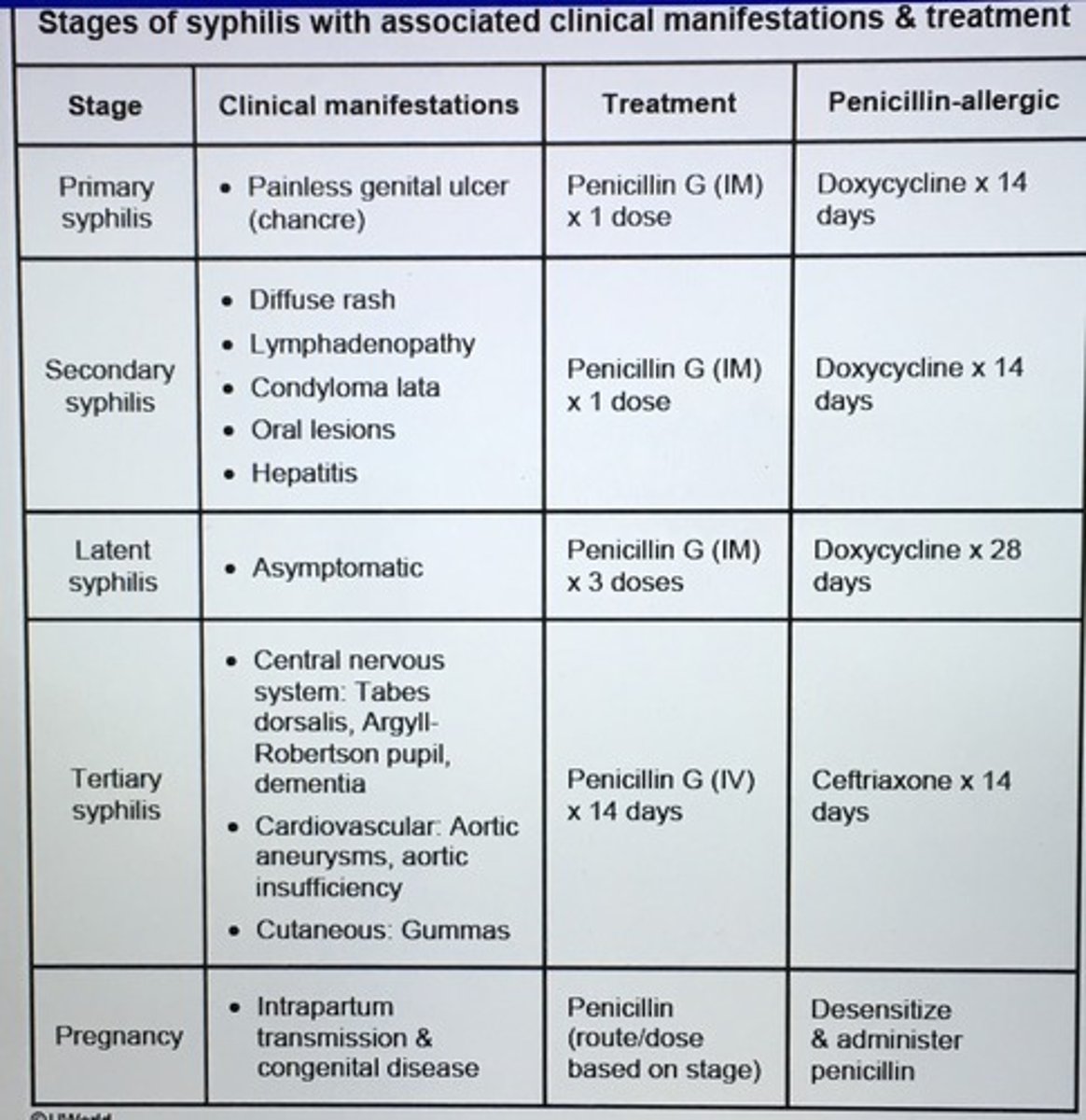
A single dose of ___ is the tx of choice for primary syphilis. In non pregnant patients with penicillin allergy can use ___. Pregnant patients with penicillin allergy use ___.
Single dose IM benzathine penicillin G
Allergy: 2 week course Doxycycline
Pregnant with allergy: desensitization before penicillin therapy
Mucormycosis caused by Rhizopus treatment.
Surgical debridement plus amphotericin B
Post exposure prophylaxis for HIV treatment which drugs are preferred due to low SE profile.
Tenofovir-emtrictabine-raltegravir for 4 weeks
- HIV testing initial, 6 weeks, 3 months, 6 months
Eggshell calcification of hepatic cyst on CT scan is suggestive of ___.
Hydatid cyst
- Echinococcus granulosus
- dogs
- unilocular cystic lesions
- sx resection under the cover of albendazole
- aspiration risk of anaphylactic shock due to cyst content spillage
___ is defined as hepatic encephalopathy that develops within 8 weeks of onset of acute liver failure.
Fulminant hepatic failure
- high priority for liver transplant
General contraindications for liver transplant.
- Irreversible cardiopulmonary disease causing prohibitive risk
- Incurable or recent (<5 years) malignancy external to liver
- Active alcohol or drug abuse
Tx for patient with fever and cough productive foul-smelling sputum after an upper GI endoscopy and any other instrumentation of the upper airway or esophagus suspect ___.
Anaerobic lung infection
- Clindamycin
__ is diagnosed by the presence of branching, beaded, gram +, partially acid fast filaments in gram stain and culture. Tx.
Norcardiosis
- soil
- Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
Usefulness of bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL).
Evaluation of suspected malignancy and opportunistic infection
> 90% sensitive and specific for PCP
___ is chronic granulomatous disease that primarily affects the peripheral nerves and skin.
Leprosy
- Mycobacterium leprae
- early part of the disorder may present as insensate, hypopigmented plaque
- resulting muscle atrophy
- dx made by acid-fast bacilli on skin bx
Pt has Pneumocystis jirovecii with worsening pulmonary fxn what is the tx?
Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole and corticosteroids
- minimize the initial antibiotic induced worsening of respiratory function
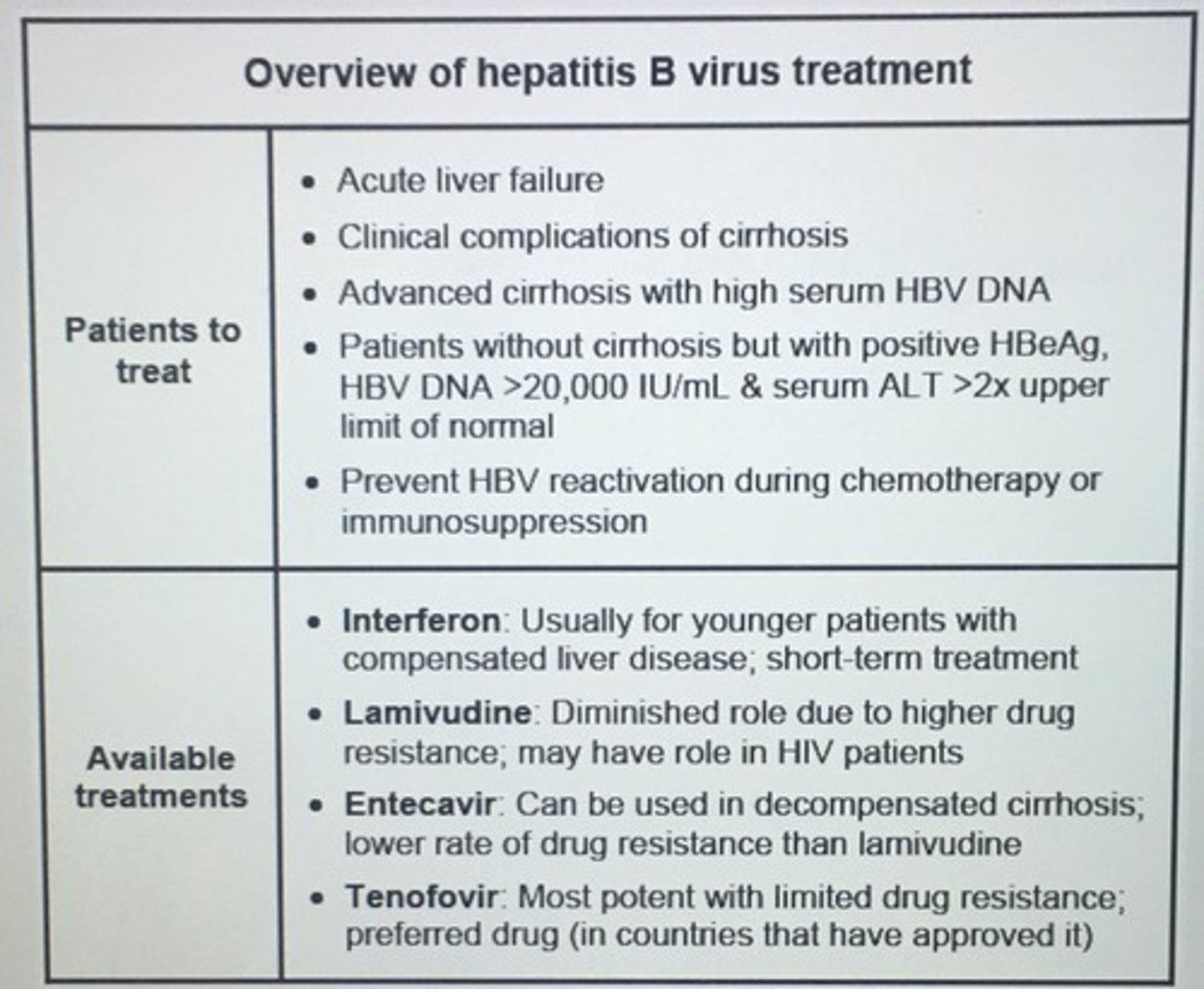
Tx Hep B
Interferon
Lamivudine
Entecavir
Tenofovir
What are the chemoprophylaxis options for travels to endemic regions of chloroquine-resistant malaria?
Mefloquine
Atovaquone-proguanil
Doxycycline
(Sub-Saharan Africa, Amazon basin, Southern and Southeast Asia)
Primaquine for P.ovale and P.vivax in (Korean peninsula, Mexico)
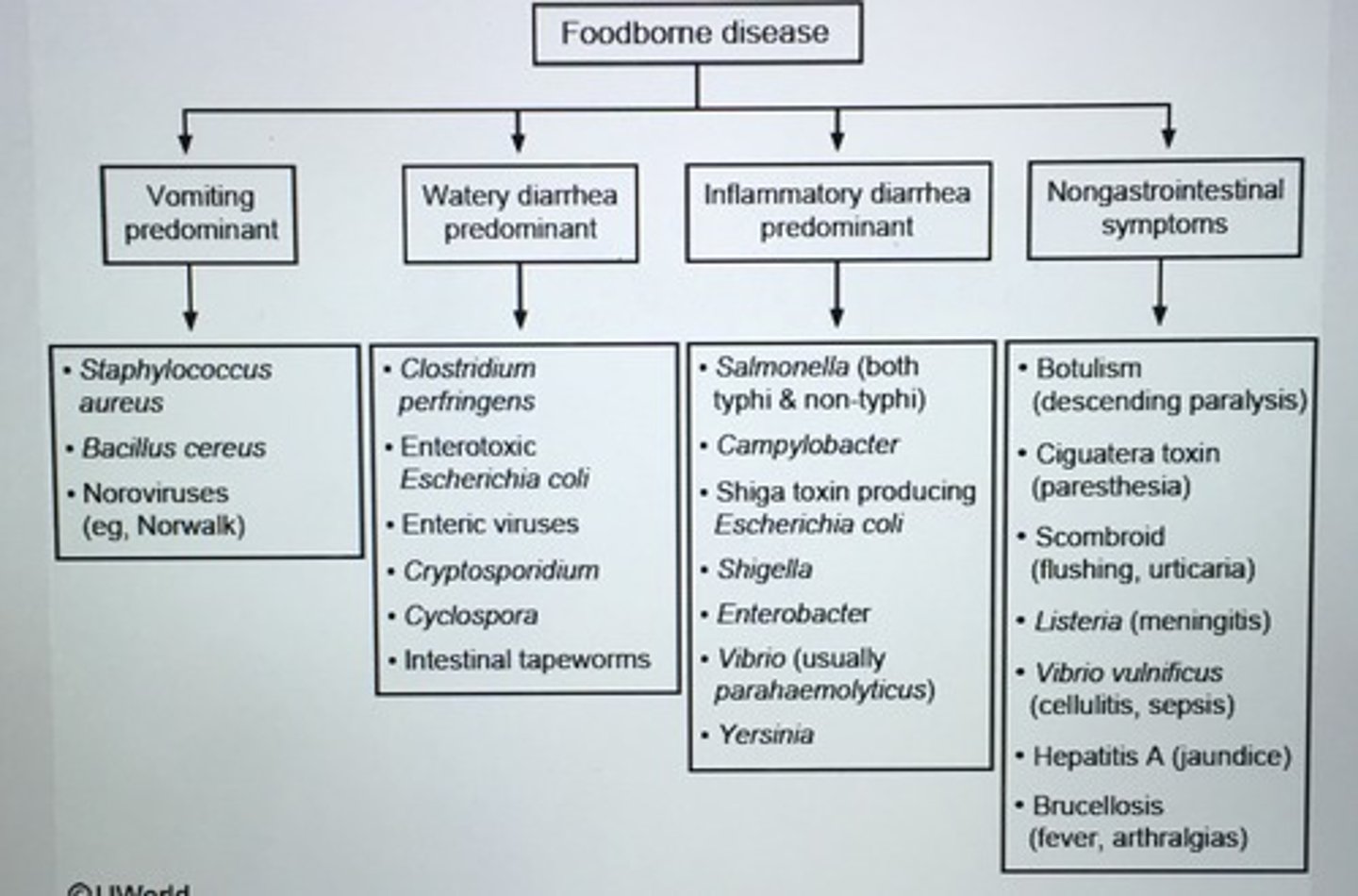
Foodborne disease causes
Tx multiple ring enhancing lesions on CT in HIV patient.
Toxoplasmosis
- Sulfadiazine and pyrimethamine
TMX-sulfamethoxazole for prophylaxis
Human monocytic ehrlichiosis

___ are a common cause of endocarditis associated with nosocomial UTI.
Enterococci
When to give vaccines for splenectomy patients?
14 days before scheduled splenectomy OR 14 days after
- PCV13, then 8 week later PCV23
- Meningococcal
- Hib
Dx Chlamydia trachomatis in sexually active male with dysuria, pyuria, urinary discharge.
Nucleic acid amplification test of a first-catch urine
tx: azithromycin or doxycycline
__ is infection of the submandibular and sublingual glands. source infection is teeth, second or third mandibular molar.
Ludwig's angina
- asphyxiation common cause of death
Sudden onset of sharply-demarcated, erythematous, edematous, tender skin lesion with raised border in a febrile patient suggests ___. MCC.
Erysipelas
- group A beta-hemolytic strep
__ is a frequent cause of osteomyelitis in adults with Hx of nail puncture wound.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- puncture occurs through rubber-soled footwear
Tx: FQs and aggressive surgical debridement
children: staph aureus MCC osteomyelitis
__ is a serious complication of influenza pneumonia.
Staph aureus
- pt presents with influenza improves with oseltamivir then develop pneumonia 2 weeks after presentation
- gram + cocci in clusters
- can cause post-vital URI necrotizing pulmonary bronchopneumonia with multiple nodular infiltrates that can capitate to cause small abscesses
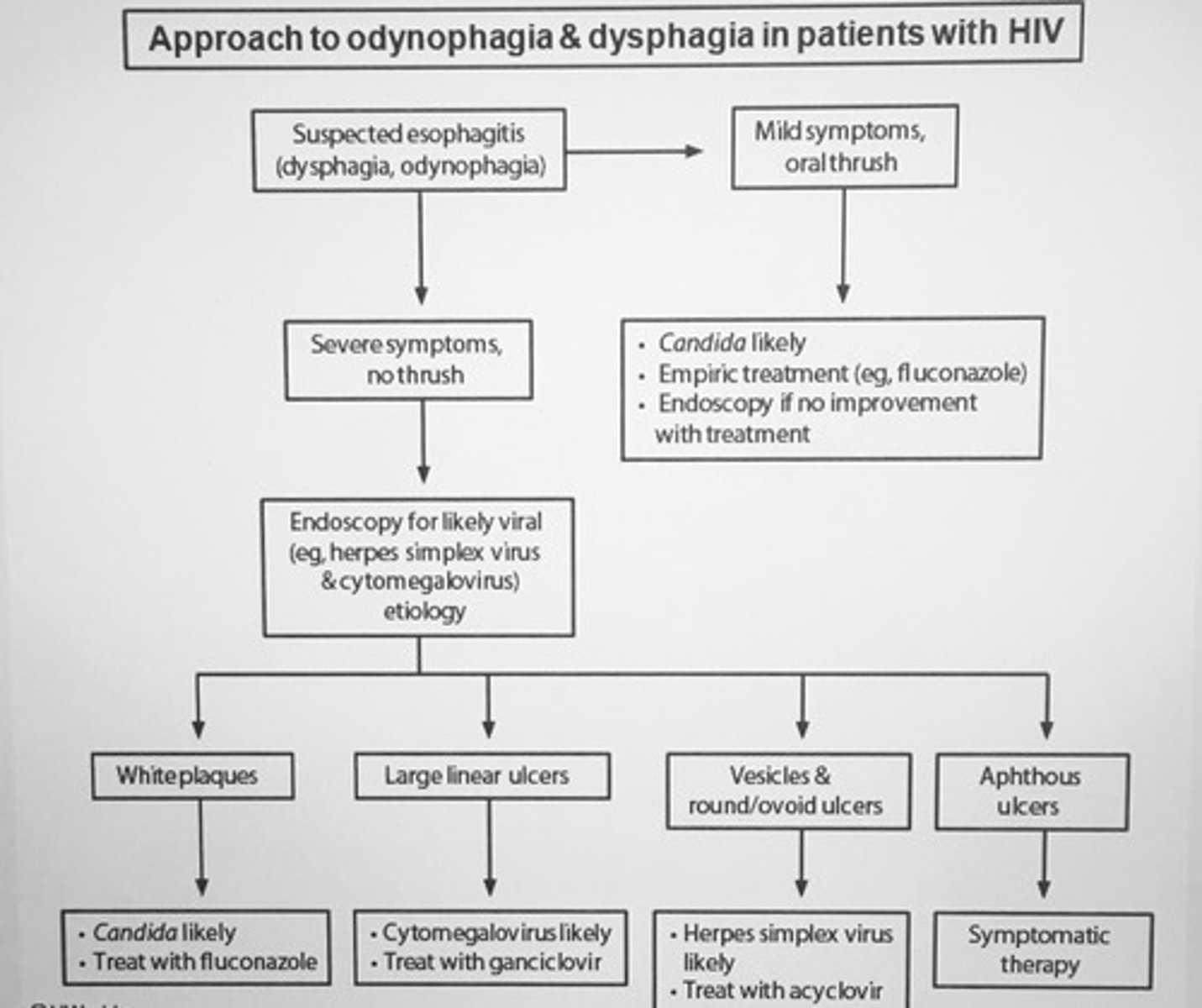
Approach to odynophagia and dysphagia in patients with HIV.
Clinical features of cervical actinomycosis
Tx PCN for 12 weeks
Allergy PCN: Clindamycin

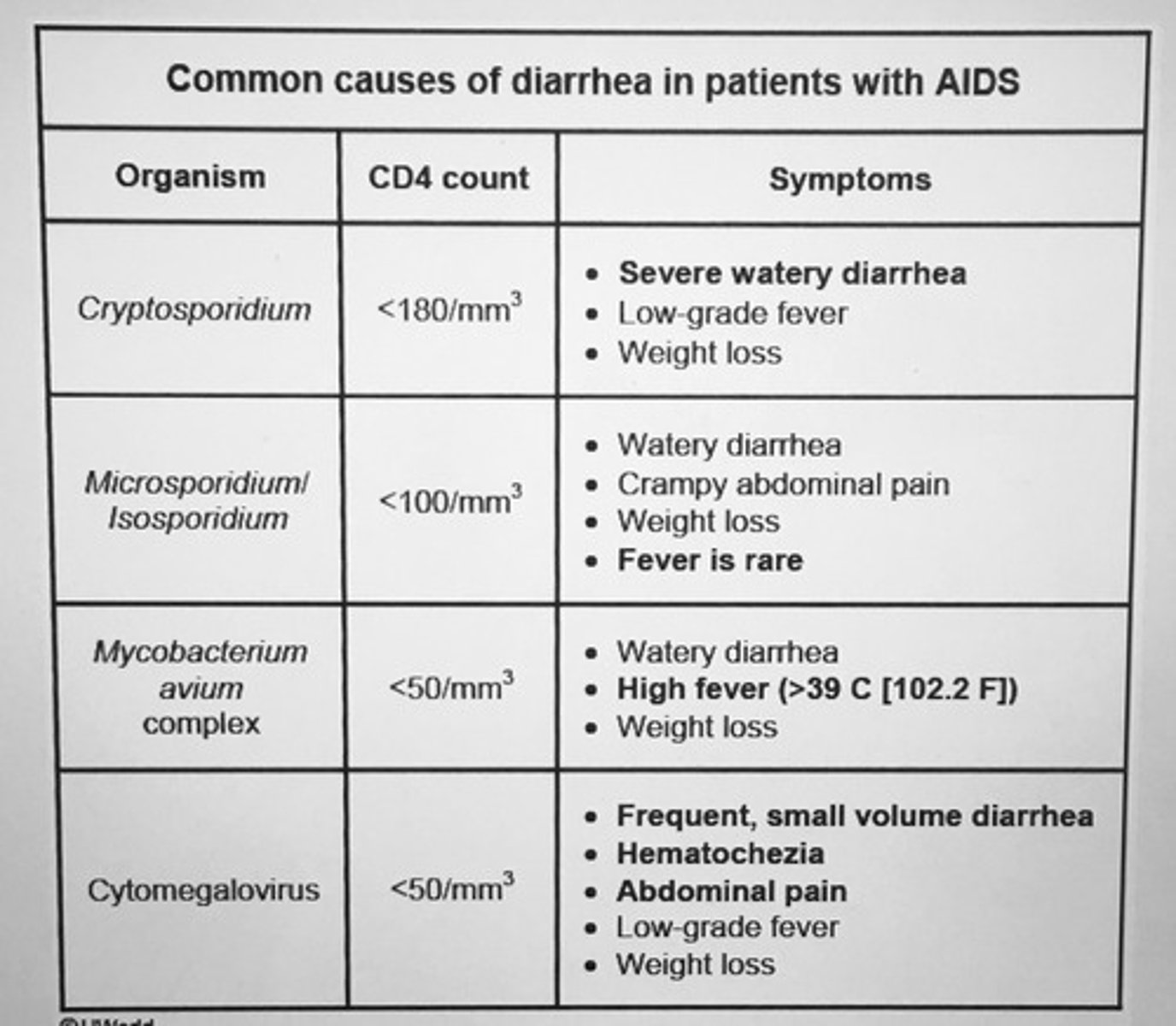
Common causes of diarrhea in patients with AIDS
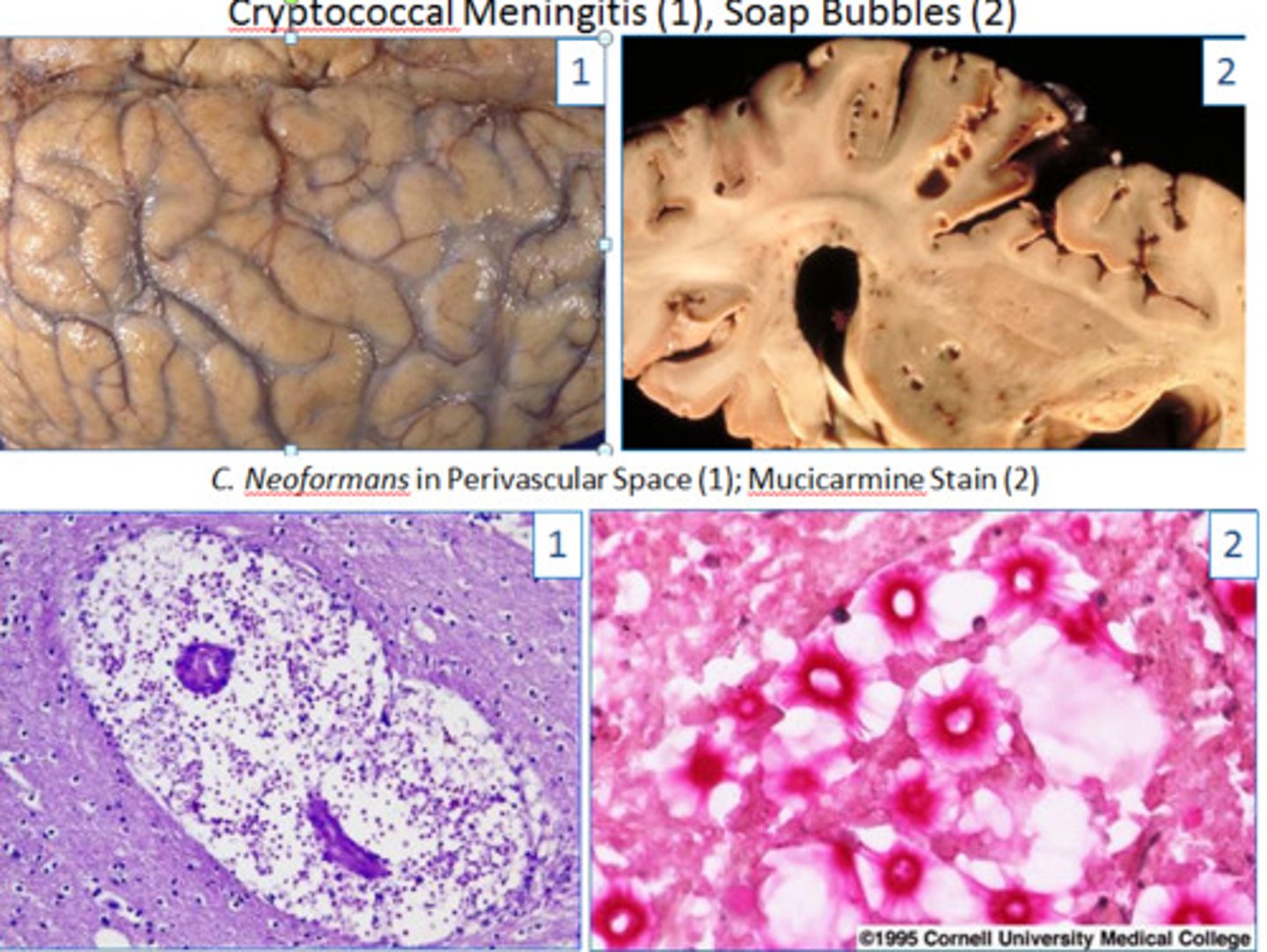
HA, Fever, malaise, HIV patient. Dx.
Cryptococcal meningoencephalitis
- Cryptococcus neoformans
- CSF: high opening pressure, low glucose, high protein, WBC < 50, transparent capsule seen with india ink stain, cryptococcal antigen +, culture on Sabouraud agar
Tx: Initial amphotericin B with flucytosine
Maintenance: fluconazole
Most sensitive and rapid test for detection of disseminated histoplasmosis.
Histoplasma antigen immunoassay of the serum or urine
___ treatment for histoplasmosis.
Itraconazole
severe disease: IV amphotericin B for 2 weeks followed by itraconazole for 1 year
Tx lyme disease nonpregnant and > 8 years old.
___ is indicated for children < 8 and pregnant woman.
Doxycycline
Amoxicillin for pregnant and < 8 since doxycycline can cause permanent tooth discoloration and skeletal problems in exposed children and fetuses
What are the signs and symptoms of necrotizing surgical site infection?
1. Pain, edema, or erythema spreading beyond the surgical site
2. Systemic signs such as fever, hypotension, or tachycardia
3. Paresthesia or anesthesia at the edges of the wound
4. Purulent, cloudy-gray discharge (dishwater drainage)
5. SQ gas or crepitus
* common in patients with diabetes and are polymicrobial
-> surgical exploration and debridement
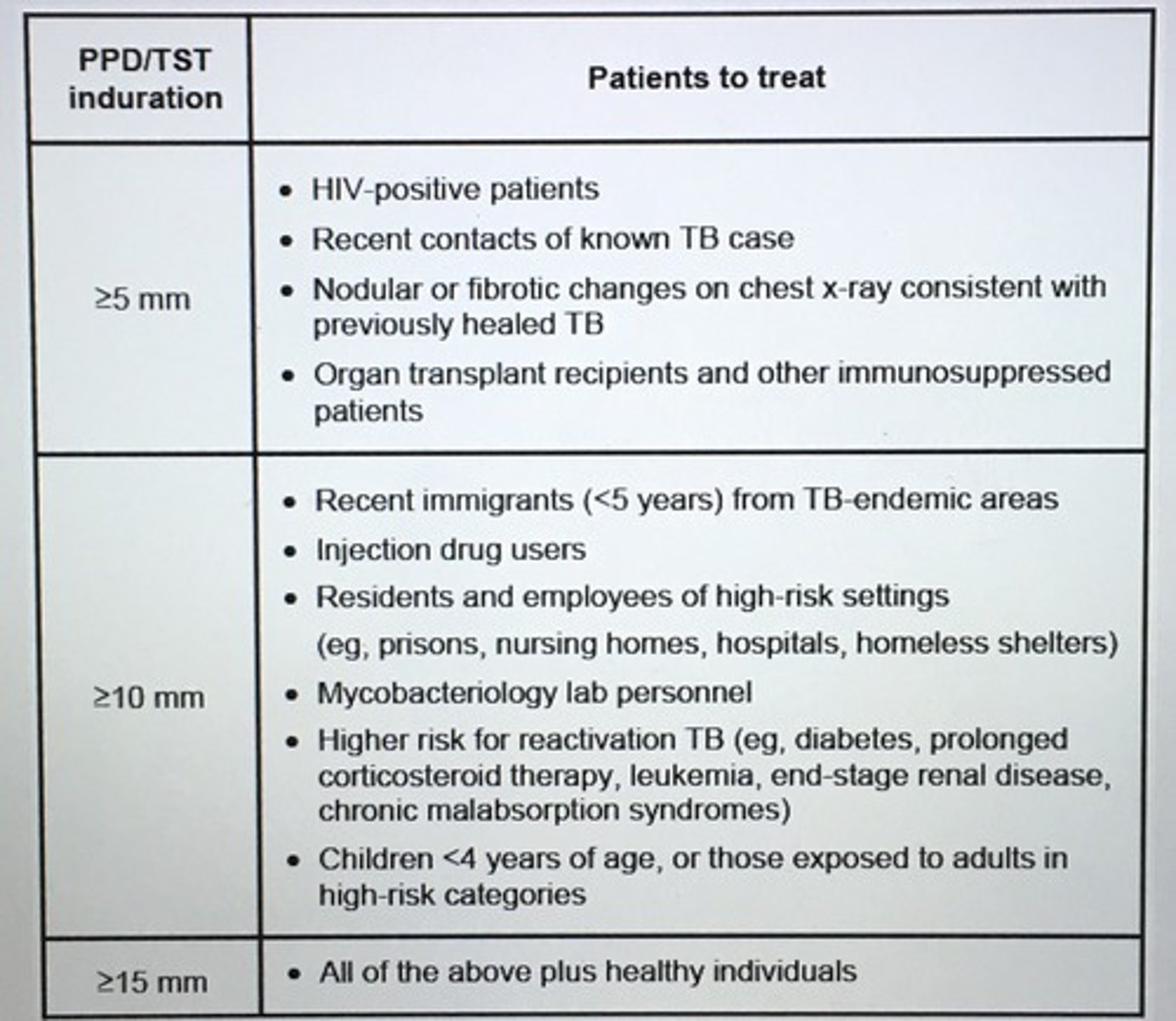
Preferred HIV testing as screening.
HIV p24 antigen and antibody testing
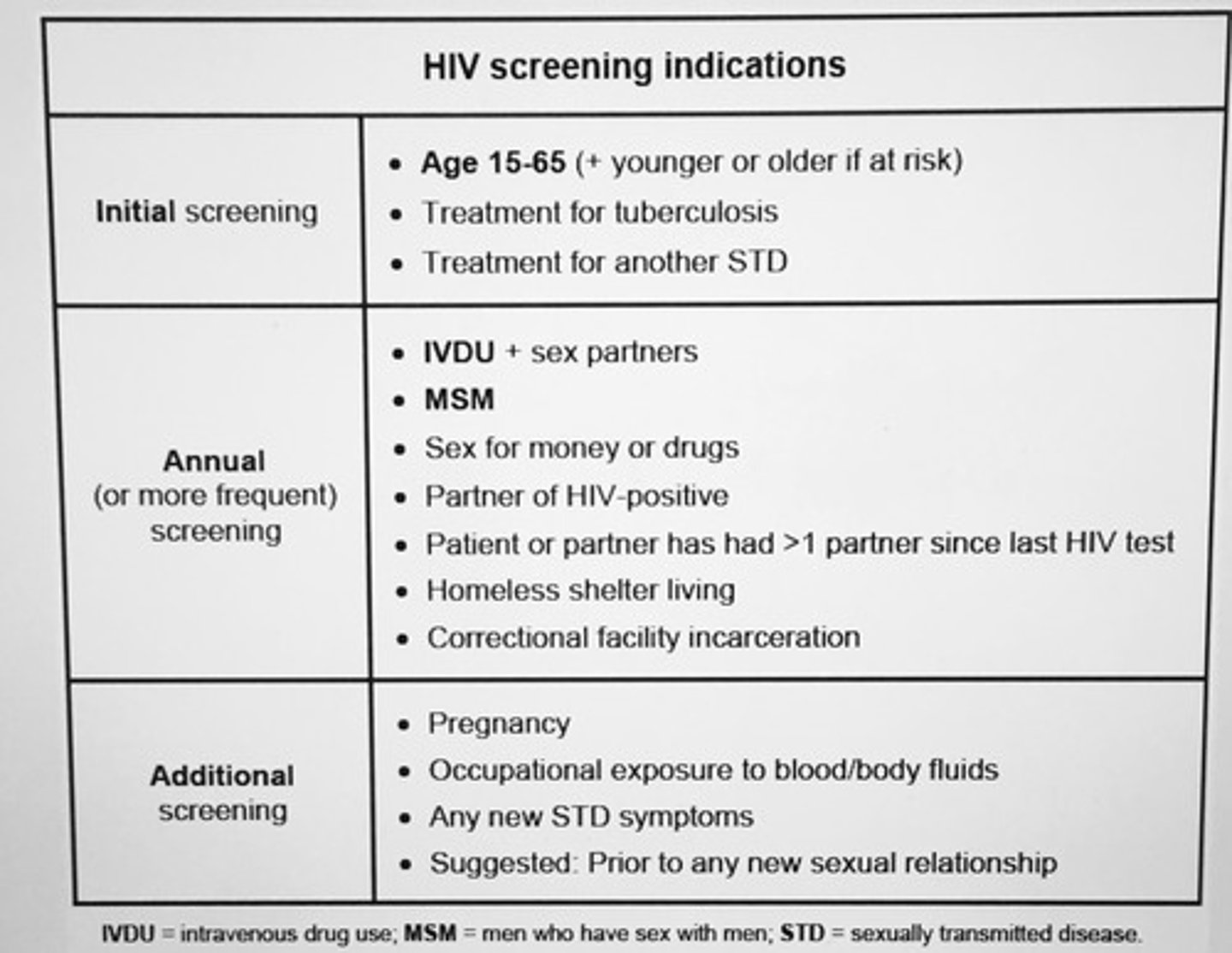
Clinical features of parvovirus B19 infection.
___ most likely cause of UTI in patients with alkaline urine.
Proteus mirabilis
- secretes urease to alkalinize the urine, leading to the formation of struvite stones
Urease producing bacteria.
Proteus
Klebsiella
Morganella morganii
Pseudomonas
Providencia
Staph aureus
Ureaplasma urealyticum
Most common organisms responsible for epiglottis in adult population.
H. influenzae
Steph pyogenes
Triad:
Tenosynovitis
Dermatitis
Migratory asymmetric polyarthralgia without purulent arthritis
Disseminated gonococcal infection
- purulent arthritis w/o skin lesions
OR
- TRIAD: tenosynovitis (wrist, ankles, fingers, knees), dermatitis (pustules, macules, papules, bullae), arthritis
Dx disseminated gonoccal infection
- Blood cx negative 2 sets
- Synovial fluid show 50,000 cells
- Urethral, cervical, pharyngeal or rectal cx (nuclear acid amplification)
- Recommended HIV and syphilis screen
- Recurrent DGI: check terminal complement activity
Tx Disseminated gonococcal infection
IV ceftriaxone 1g/day for 7-14 days switch to po (cefexime) when clinically improved
Joint drainage for purulent arthritis
Empiric Azithromycin OR doxycycline for concomitant chlamydial infection
tx sexual partners
___ is the most frequent cause of malignant otitis externa.
Pseudomonas
- diabetic patients with severe ear pain, otorrhea, and evidence of granulation tissue in the ear canal
Common acute life-threatening reactions associated with HIV therapy.
1. Didanosine: pancreatitis
2. Abacavir: hypersensitivity syndrome
3. Lactic acidosis 2/2 NRTIs
4. Steven Johnson syndrome 2/2 NNRTIs
5. Nevirapine: liver failure
___ is well-known SE of indinavir therapy.
Crystal induced nephropathy
- protease inhibitor
- periodic monitoring of UA and serum creatinine every 3-4 months
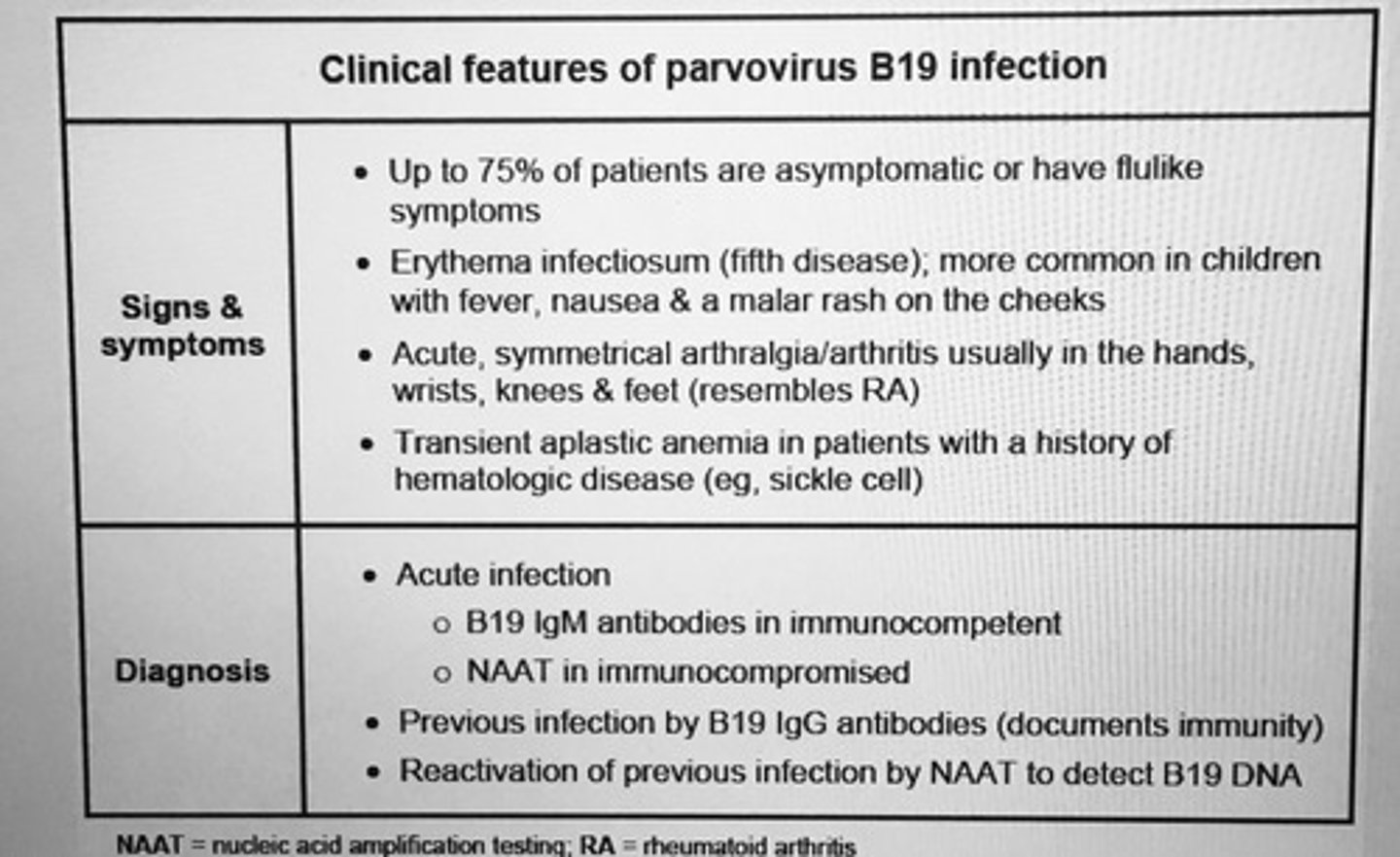
Features of Clostridium difficile colitis
IVDU are prone to ___ caused by ___. Fragments of the vegetation can embolize to the lungs, causing characteristic nodular infiltrate with cavitation.
Tricuspid endocarditis
Staph aureus
___ is the most cammon valvular abnormality detected by patients with infective endocarditis.
MVP with coexisting MR
___ occurs in immunocompromised patients, who may presents with fever, cough, dyspnea, and hemoptysis. CXR show cavitary lesion, and CT scan shows pulmonary nodules with a halo sign or lesions with an air crescent.
Invasive aspergillosis
Dx test viral encephalitis.
viral DNA by PCR in CSF
- empiric tx with IV acyclovir
Patients with infectious mononucleosis possible complications.
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia 2-3 weeks after the initial sxs
Splenic rupture - avoid contact sports 3-4 weeks
High fevers, severe polyarthralgias. HA, myalgia, conjunctivitis. Travel to Central & South America, South Asia, Caribbean islands.

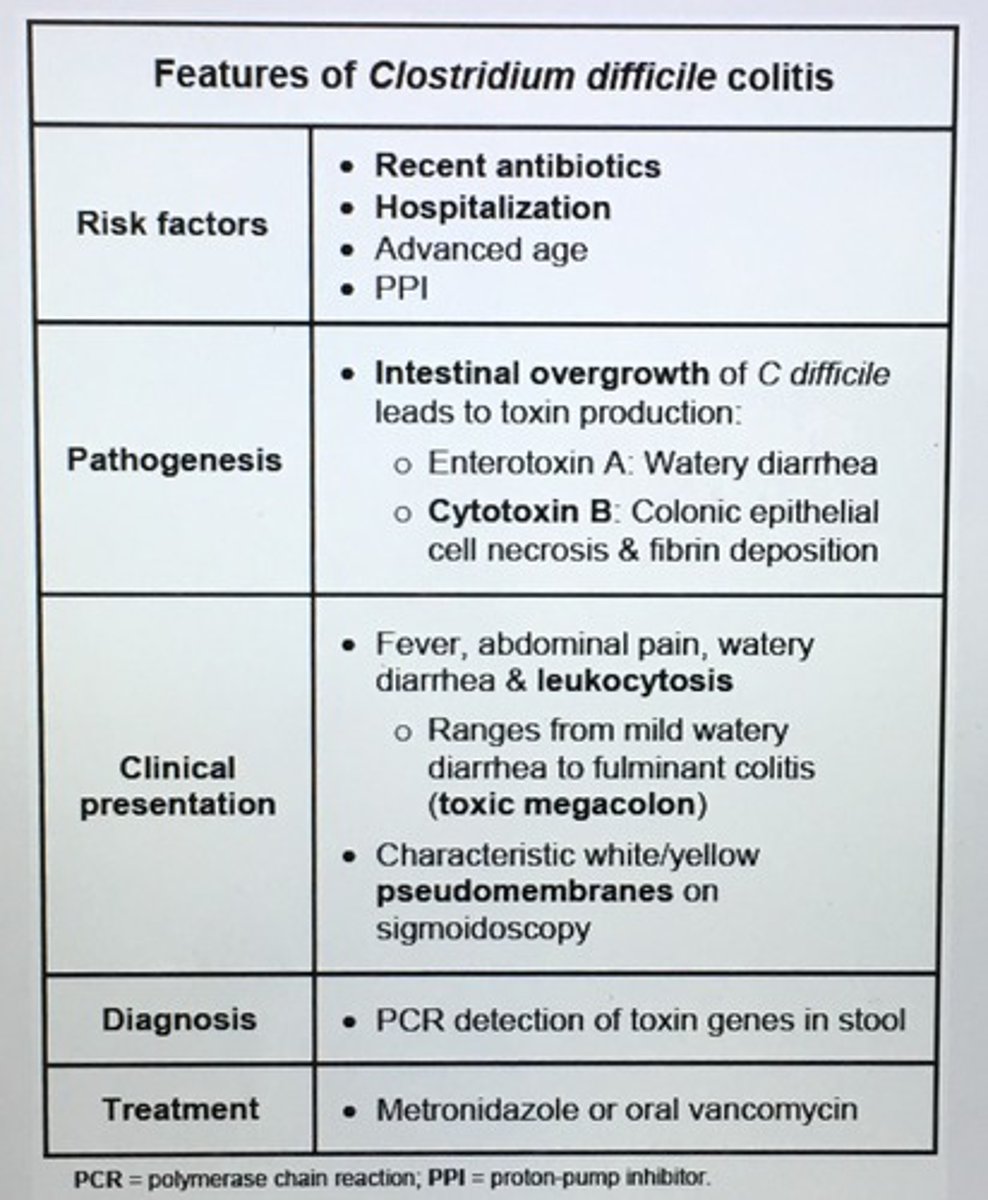
PPD/TST induration and patients to treat
Indications for corticosteroid use in PCP include PaO2 < ___ or Aa gradient > __.
PaO2< 70
Aa > 35 mm Hg
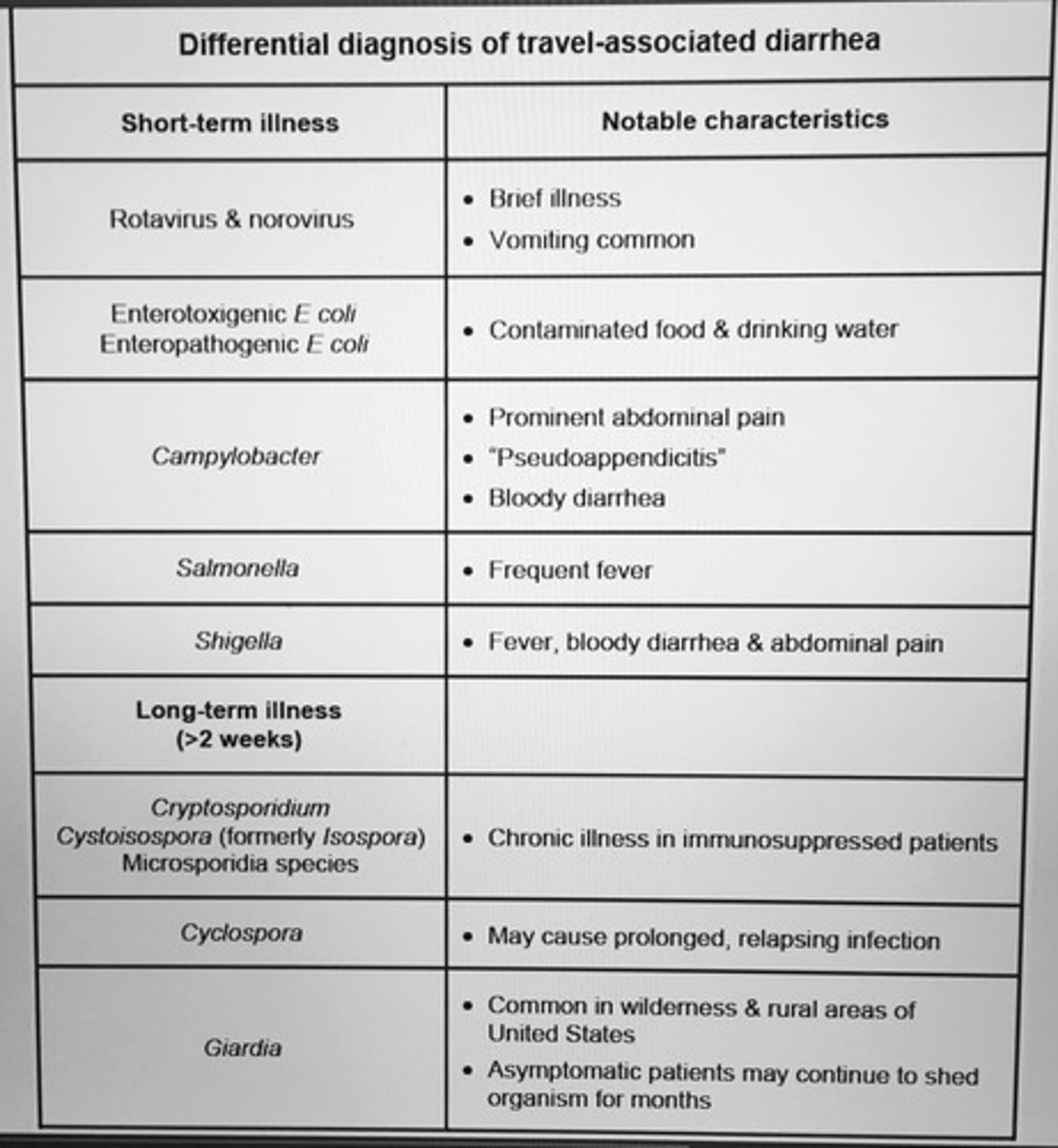
Differential diagnosis of travel-associated diarrhea