Pulse Modulation
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Pulse Modulation
A type of modulation in which the message signal (analog or digital information) is transmitted using a train of pulses. Instead of continuously varying the amplitude, frequency, or phase of a carrier (as in analog modulation). It represents the information by modifying characteristics of discrete pulses in time.
Types of Pulse Modulation
I. Analog Pulse Modulation
II. Digital Pulse Modulation
Pulse Amplitude Modulation (PAM)
Pulse Width/Duration Modulation (PWM/PDM)
Pulse Position Modulation (PPM)
Types of Analog Pulse Modulation
Analog Pulse Modulation
The message signal is analog, and the pulses carry continuous amplitude or time variations.
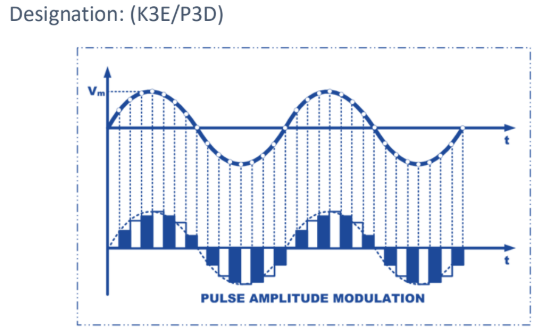
Pulse Amplitude Modulation (PAM)
A method of converting information wherein the amplitude of a constant width, constant position pulse is varied in accordance to the instantaneous amplitude of the modulating signal.
Pulse Time Modulation (PTM)
It is a class of signaling technique that encodes the sample
values of an analog signal onto the time axis of a digital signal
It is analogous to angle modulation (FM/PM).
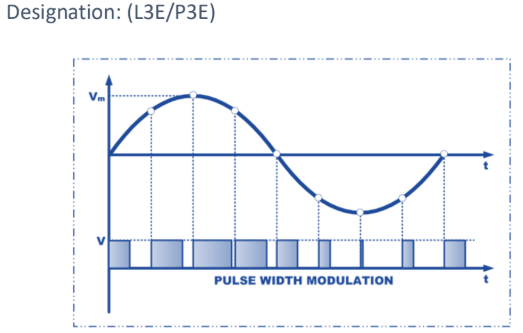
Pulse Width/Duration Modulation (PWM/PDM)
A process where the pulse width of a fixed amplitude pulse varies proportionally to the amplitude of the analog signal.
The width (duration) of each pulse changes according to the message signal.
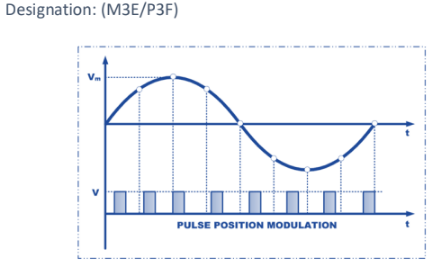
Pulse Position Modulation (PTM)
A form of pulse modulation where the position of a constant width pulse within a prescribed timeslot is varied according to the amplitude of the modulating signal.
The position of each pulse (relative to a reference time) varies according to the message signal.
Digital Pulse Modulation
The analog signal is first sampled and then quantized into binary form.
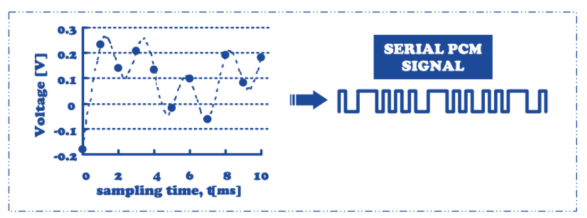
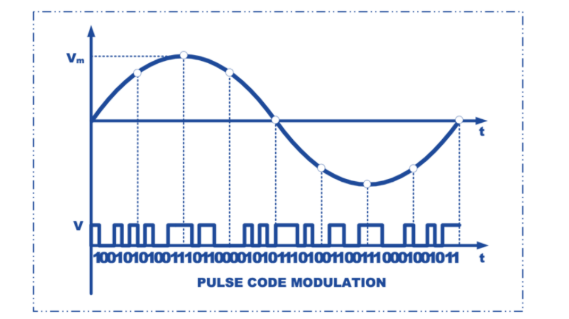
Pulse Code Modulation (PCM)
Essentially analog-to-digital conversion of a special type where the information contained in the instantaneous samples of an analog signal is represented by digital words in a serial bit stream.
The amplitude of the sampled signal is represented as a binary code.
Widely used in digital telephony and audio systems.
I. Band Limiting
II. Sampling
III. Quantization
IV. Encoding
BSQE
Band Limiting
It limits the frequency of the input analog signal to the standard voice frequency band of 0 to 4 kHz. The purpose is to eliminate any unwanted signal that will result to fold-over distortion at the receiver.

Sampling
The act of periodically holding a value of the continually changing analog input signals.

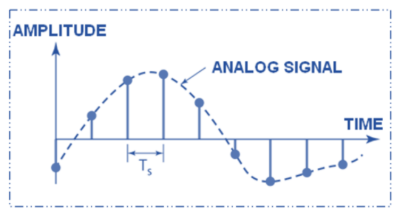
i. Ideal Sampling
ii. Natural Sampling (Gating)
iii. Flat-top Sampling (Instantaneous sampling)
Types of Sampling (INF)
Ideal Sampling
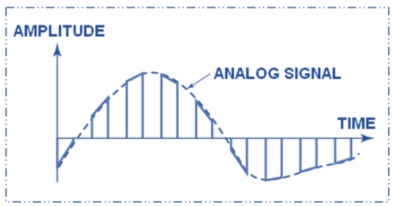
Natural Sampling (Gating)
This method retains the natural shape of the sample analog waveform.
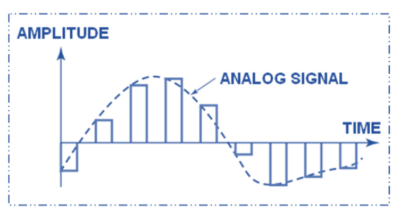
Flat-top Sampling (Instantaneous Sampling)
The most common method used for sampling voice signals in PCM where the sample-and-hold circuit convert those samples to a series of constant-amplitude PAM levels.
Aperture Error
Flat-top sampling alters the frequency spectrum and introduces an error
Quantization
The process of assigning discrete level to a time-varying quantity in multiples of some fixed unit, at a specified instant or specified repetition rate.
Encoding
The process of converting the quantized discrete-signal (PAM samples) to parallel PCM codes.