Pneumonia
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Aaaa my lungs are filled with juice
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Definition of pneumonia
Infection of lungs that causes inflammation of the alveoli
Caused by microbial organisms (bacterial, viral, fungal)
Alveolar consolidation → Alveoli become filled with fluid, pus, etc
Most common cause of bacterial pneumonia
Streptococcus penumoniae
Viral pneumonia can be caused by
Often influenza and RSV
What often causes walking pneumonia?
Mycoplasma pneumonia
Types of pneumonia origins
Community acquired pneumonia (CAP)
Hospital acquired pneumonia (HAP)
Ventilator associated pneumonia (VAP)
Community acquired pneumonia
Infection is acquired outside of the hospital
Can be bacterial, viral, fungal
Hospital acquired pneumonia
Onset of symptoms 48 hours or more after admission
Often caused by bacteria
Ventilator Associated Pneumonia
Onset of symptoms 48 hours or more after intubation
Often caused by bacteria
What are the various ways that the lungs can be infected by pneumonia-causing pathogens?
Aspiration of normal flora from nasopharynx or oropharynx
Decreased cough/epiglottis reflexes
Decreased LOC
Inhalation
Increased secretions in the lungs + Impaired clearance
Smoking, post-viral, cystic fibrosis, COPD/asthma
Hematogenous spread
Primary infection in another area of the body → Travels to lungs via the blood stream
What risk factors increase the chances of developing pneumonia>
Abdominal or thoracic symptoms
Elderly
Altered LOC
Bedrest and immobility
Chronic conditions
Immunosuppression
Intestinal/gastric tubes
Malnutrition
Smoking
Tracheal intubation
Upper respiratory infection (cold, flu) and Altered oropharyngeal flora (mouth/throat infection)
Clinical manifestations of pneumonia
Tachypnea and Dyspnea
Adventitious lung sounds over affected area
Pleural rub, crackles, rhonchi
Tachycardia
Fever. Might have chills
Cough (productive or dry)
Sputum → Green, yellow
Rust colored → might be bloody!
General malaise
Pleural chest pain
Dull percussion (from fluid)
Decreased SpO2
How might pneumonia present in geriatric populations?
Altered mental status, confusion, stupor
Hypothermia
Diaphroetic
Anorexia
Fatigue
Myalgia (muscle aches)
Headaches
What imaging study is often used to diagnose pneumonia?
Chest X-ray
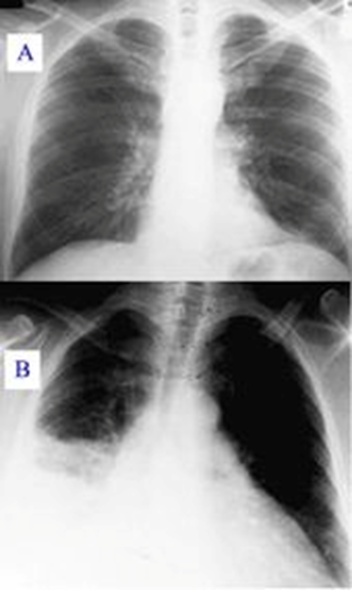
What diagnostic studies might be used to diagnose pneumonia?
Chest x-ray
Sputum
Gram stain and cultures
CBC
Elevated WBCs
CRP
Elevated → presence of inflammation (nonspecific)
Procalcitonin
Elevated → Bacterial inflammatory stimulus
SpO2 and ABGs
Hypoxemia
What diagnostic study indicates the presence of inflammation in response to bacterial infections?
CRP
Sputum culture
Procalcitonin
Procalcitonin → Lab value, rises in response to inflammatory stimulus from bacteria (specific!)
Wrong answer:
CRP → General inflammatory marker
Sputum culture → Determines what specific bacteria is infecting the lungs. It’s close, but doesn’t detect the presence of inflammation
What possible nursing diagnoses might be used to describe a patient with pneumonia?
Ineffective airway clearance
Impaired gas exchange
Risk for infection
Activity intolerance
Deficient knowledge
What goals are appropriate to have when caring for a patient with pneumonia?
Maintain effective airway clearance
Improve oxygenation and respiratory function
Prevent complications such as sepsis and respiratory failure
Educate on prevention strategies (especially for those with chronic/lifestyle risk factors)
What medication is used to prevent a patient at risk from getting pneumonia?
Pneumococcal vaccine
True or false:
For a patient with pneumonia, antibiotics aren’t given until the results of a sputum culture are obtained to determine the specific organism causing the illness.
FALSE.
Empiric antibiotics (broad spectrum based on clinical presentation) are started immediately
At least 2 medications
Take a culture before administering antibiotics, BUT start antibiotics before receiving results.
Empiric antibiotics
Started immediately before specific pathogen causing the infection is known
Based on the most likely cause and risk factors for multidrug resistant organisms
At least 2 meds are given
Often levoquin, vancomycin, zosyn
Medications that are given to patients with pneumonia
Preventative - pneumococcal vaccine
Empiric antibiotics - broad spectrum, at least 2
Bronchodilators - albuterol, anticholinergics
Mucolytics
Antipyretics
Analgesics - morphine is preferred
True or false:
Dilaudid is the preferred analgesic for patients with pneumonia
FALSE
It’s not bad, but when given the choice, morphine is preferred
“Relaxes the muscles in the lungs”
Nursing interventions for patients with pneumonia
Administer prescribed medications
Supplemental oxygen
Chest physiotherapy
Fluids
Rest, but ensure patient mobilizes themselves
Position - High/semi-fowlers if BP tolerates
Suction PRN
Coughing, deep breathing, and incentive spirometer
Assess vitals, breath sounds, skin color Q4 hours
What to assess/monitor in patients with pneumonia?
Q4 hours - Respiratory status, vital signs, breath sounds, skin color
Cough and sputum (consistency, color)
ABGs, report abnormal values
Pain, administer analgesia if needed
Complications of pneumonia
Pleura
Pleurisy (inflammation of pleura)
Pneumothorax
Pleural effusion
Systemic / Organs other than Lungs
Bacteremia (can lead to sepsis)
Sepsis, septic shock
Pericarditis, endocarditis
Meningitis
Strep. pneumoniae, haemophilus influenzae
Atelectasis
Lung abscess (not common)
Empyema
Respiratory failure → DEATH!
What is the leading cause of death in patients with pneumonia?
Respiratory failure
What pathogens increase the risk of developing meningitis secondary to pneumonia infection?
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Haemophilus influenzae
Types of pleural effusion
Transudative — watery
Exudative — high amount of WBCs and proteins → Purulent
What is a pleural effusion?
Buildup of fluid in the pleural space
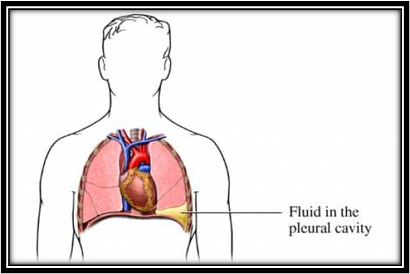
Clinical manifestations of pleural effusion?
Possible complication of pneumonia
Dyspnea
Pleuritic pain
Decreased breath sounds
Chest x-ray!!!!
True or false:
A chest tube might be required for a pleural effusion
True
What are signs that a patient with pneumonia is improving?
Decreased work of breathing
Normalized vital signs
Clearer lung sounds
Wha
What are signs that a patient with pneumonia is experiencing complications?
Worsening respiratory distress
Signs of sepsis
Worsening ABGs and pulse oximetry
Worsening dyspnea
Reduced lung capacity and elasticity
Methods of preventing ventilator-associated pneumonia
Hand washing
Check tubing, drain away from the patient
Don’t instill normal saline through the endotrach tube
Suction every 2 hours instead to loosen mucus!
For patients with altered LOC
Position to prevent aspiration
Turn every 2 hours
VAP bundle
Methods to prevent VAP specific to patients with altered level of consciousness
Positioning to prevent aspiration (elevated HOB)
Turn and reposition → Every 2 hours
VAP Bundle
Elevated HOB - 30-45 degrees
Daily Sedation Vacations
Trying to see if patient can tolerate being off of sedation
Prophylaxis for
Peptic ulcer disease (PPIs) → reduce GI stress
Venous thromboembolism (DVT) → prevent pulmonary embolism
Q2 hours CARE
Suction (+ PRN)
Oral care Chlorohexidine (2-4 hours)
Oral moisturizer (2-4 hours)
Brushing teeth Q12 hours
How often should patients on a ventilator and altered LOC be repositioned?
Q 2 hoursH
What do patients on a ventilator receive as prophylaxis in order to prevent VAP?
Prophylaxis for Peptic ulcer disease and DVT/VTE (thromboembolism)
How often should these actions be performed as indicated by the VAP bundle?
Suctioning
Oral care with chlorohexidine
Oral moisturizer
Teeth brushing
Sedation vacation
Suctioning — Q2 hours and PRN
Oral care with chlorohexidine — Q2-4 hours
Oral moisturizer Q2-4 hours
Teeth brushing — Q12 hours
Sedation vacation — Daily
Severe covid-19 infection is characterized by
SpO2 < 94% on room air
Respiratory rate > 30 BPM
Lung infiltrates >50% of lung tissue
Ratio oxygen pressure to fraction of inspired oxygen: PaO2/FiO2 < 300 mmHg
Overall — Gas exchange is BAD
When covid-19 progresses to critical illness in individuals, this can cause…
Respiratory failure
Septic shock
Multiple organ dysfunction
Severe Covid-19 is higher in people who…
Aged >65 years
Living in nursing homes, long-term care facilities
Chronic medical conditions

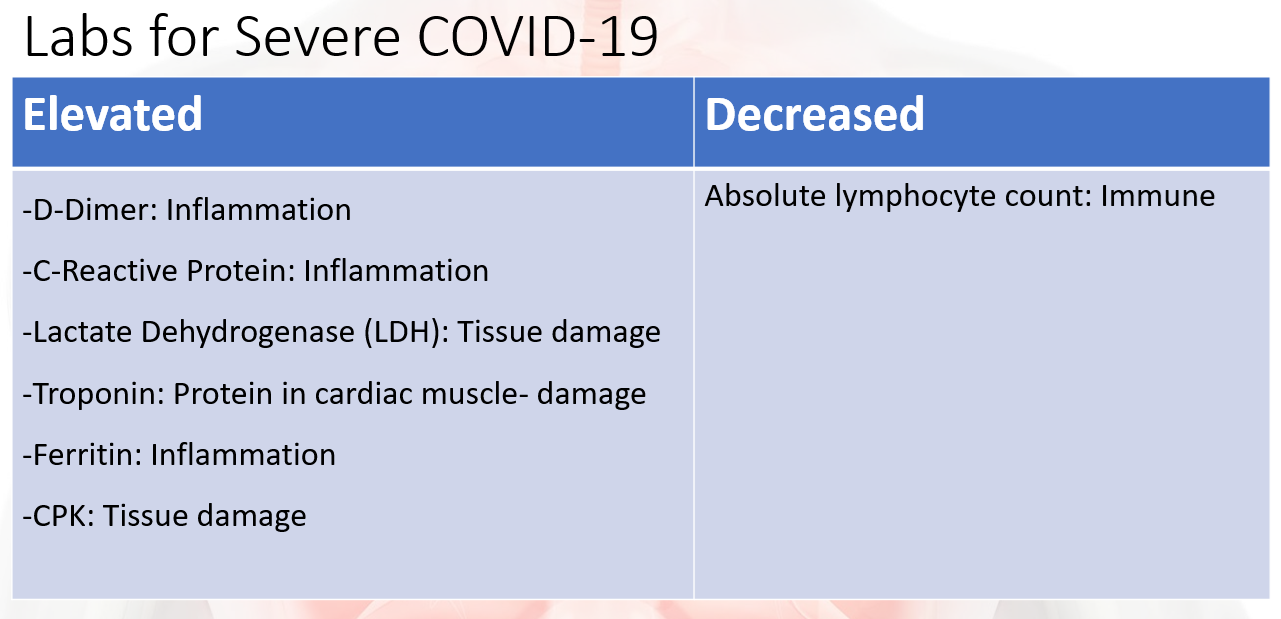
Lab values and what they indicate in patients with severe covid-19
** Lymphocytes may be increased in infections, but decreased in severe infections
Treatment for severe Covid-19 infections
Corticosteroids
Reduces inflammatory response, lowers temperature
Baricitinib
Inhibits virus infxn and cytokine signalling (inhibits excessive inflammation)
Albumin
Oxygen and ventilation
Guidelines for Acute Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure (ARDS)
VTE prevention - Heparin
Antibiotics for other respiratory infxns