HISTOLOGY
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
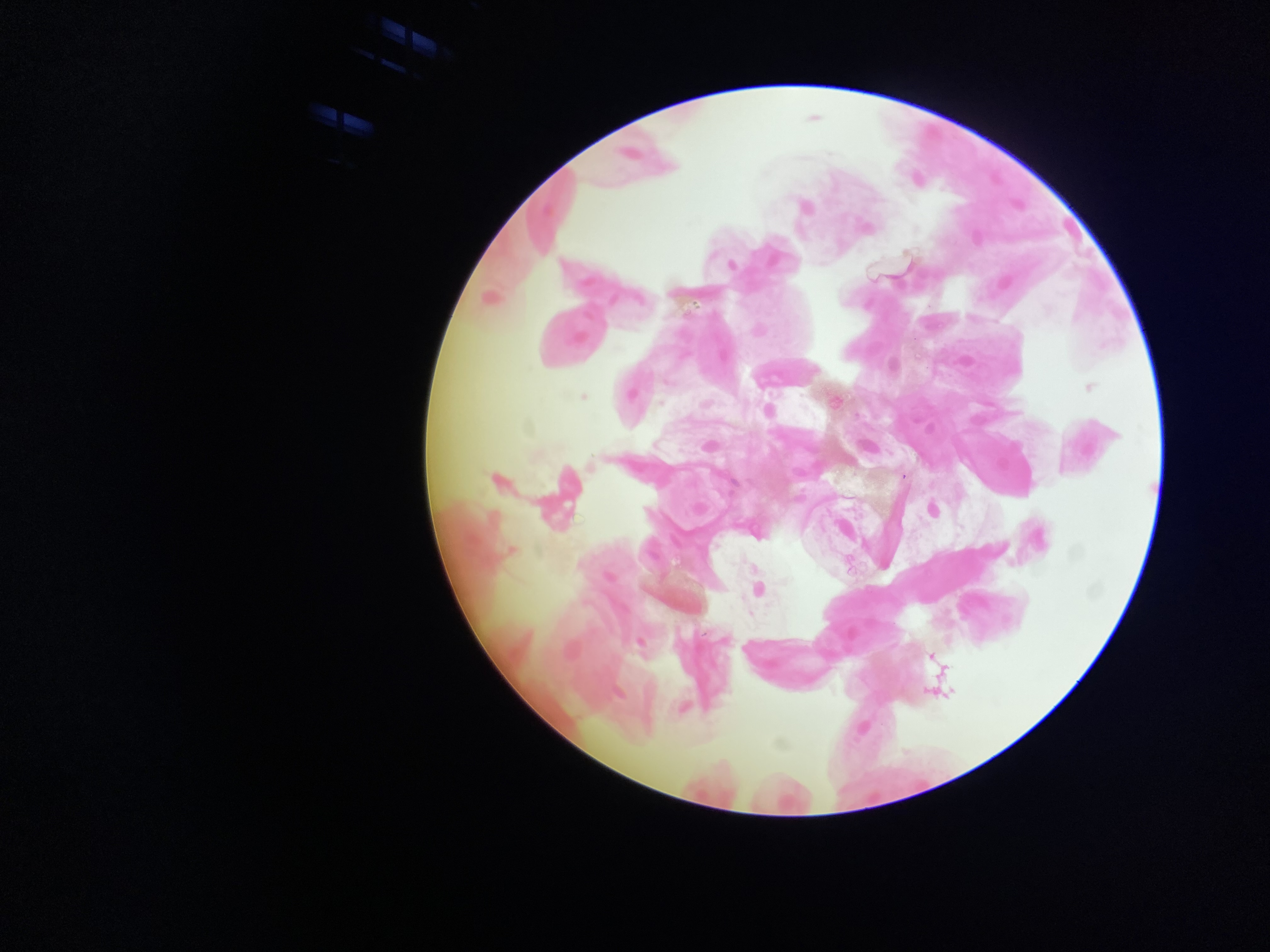
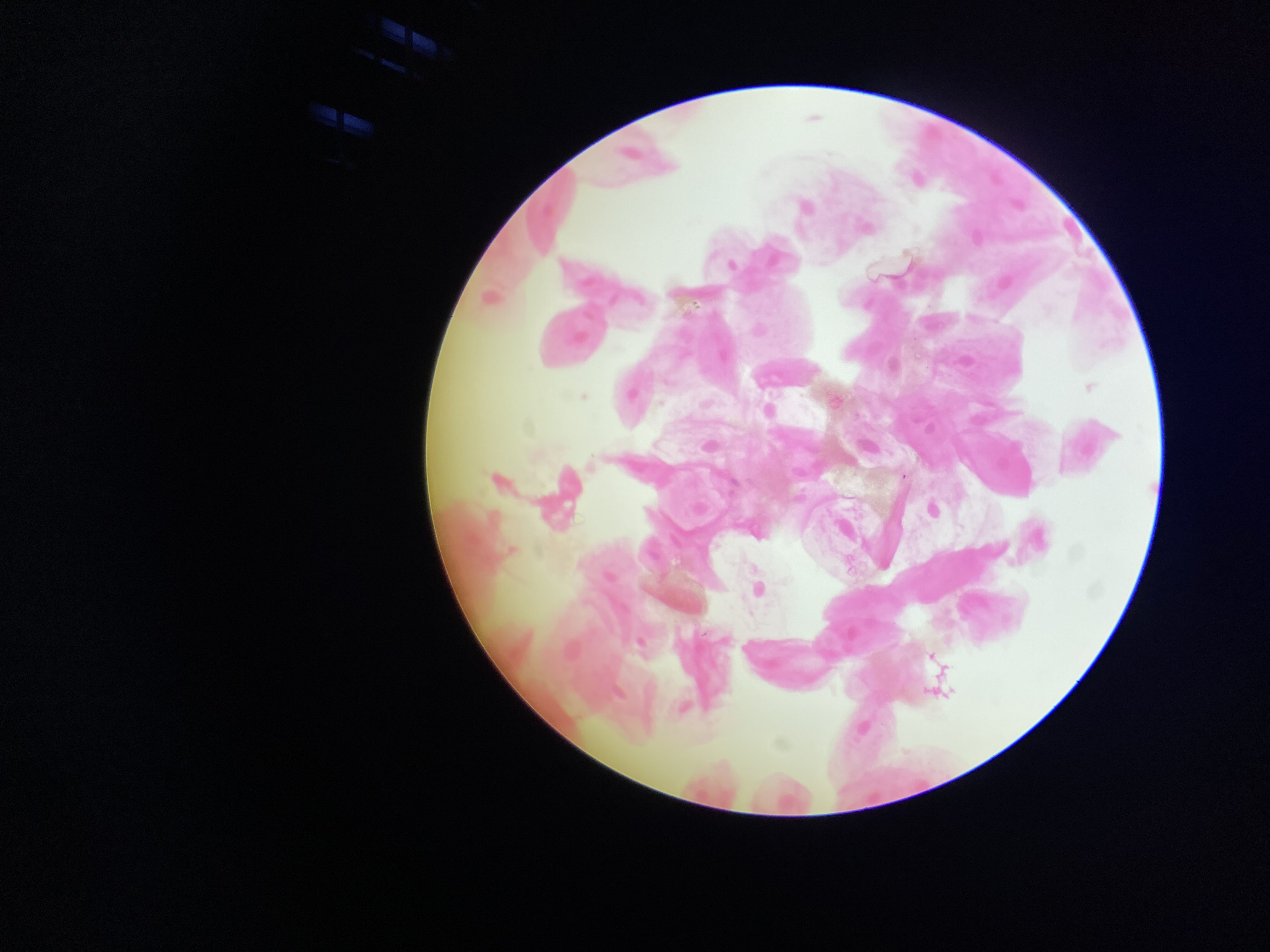
What tissue is this?
simple squamous epithelium
What is the function of this?
Allows passage of materials by filtration and diffusion.
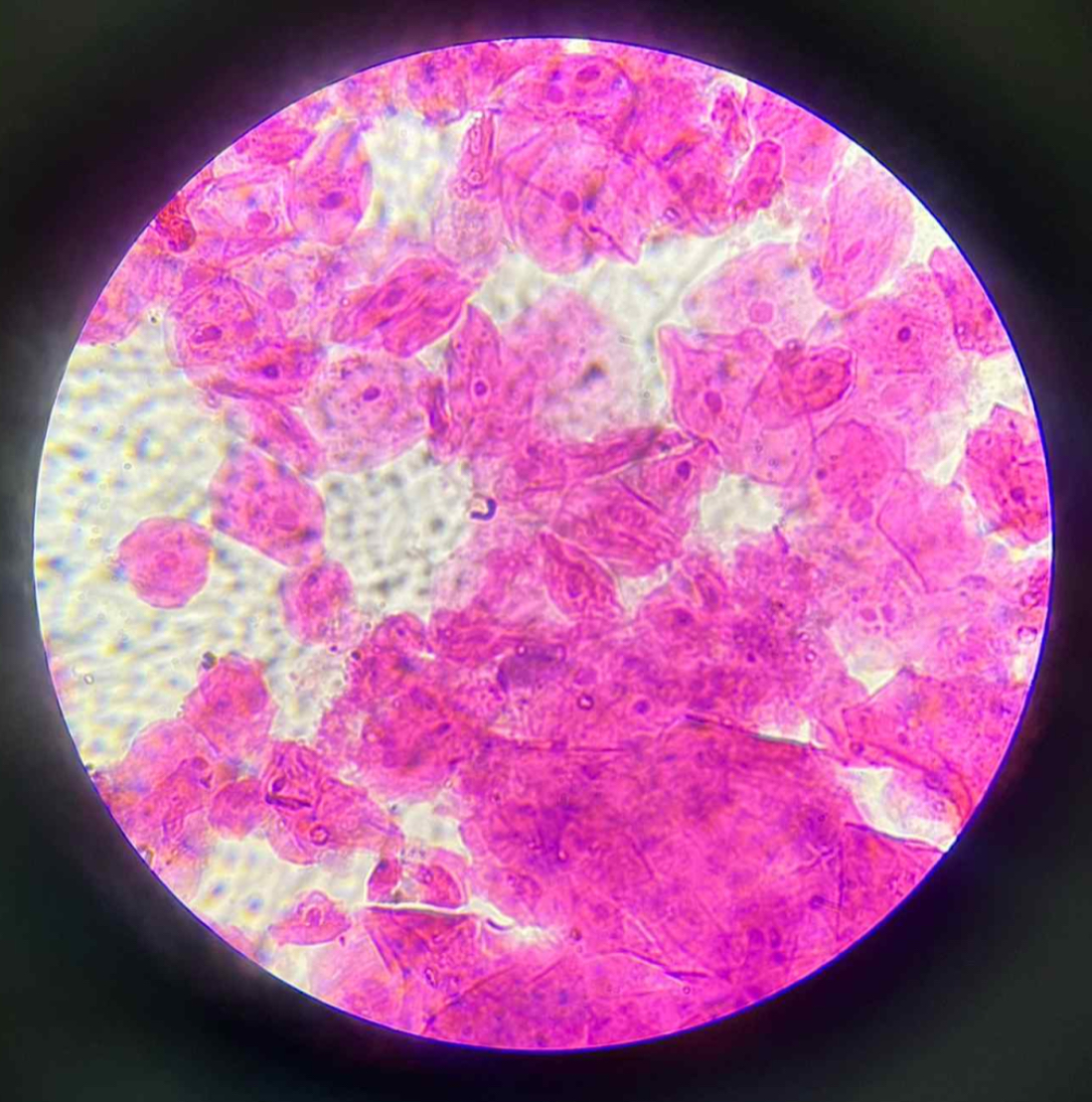
Where is this located?
Forms the very thin lining in areas where thin membranes are required.
Alveoli of lungs
Lining of blood and lymphatic vessels
Surface layer of pleura, pericardium, and peritoneum
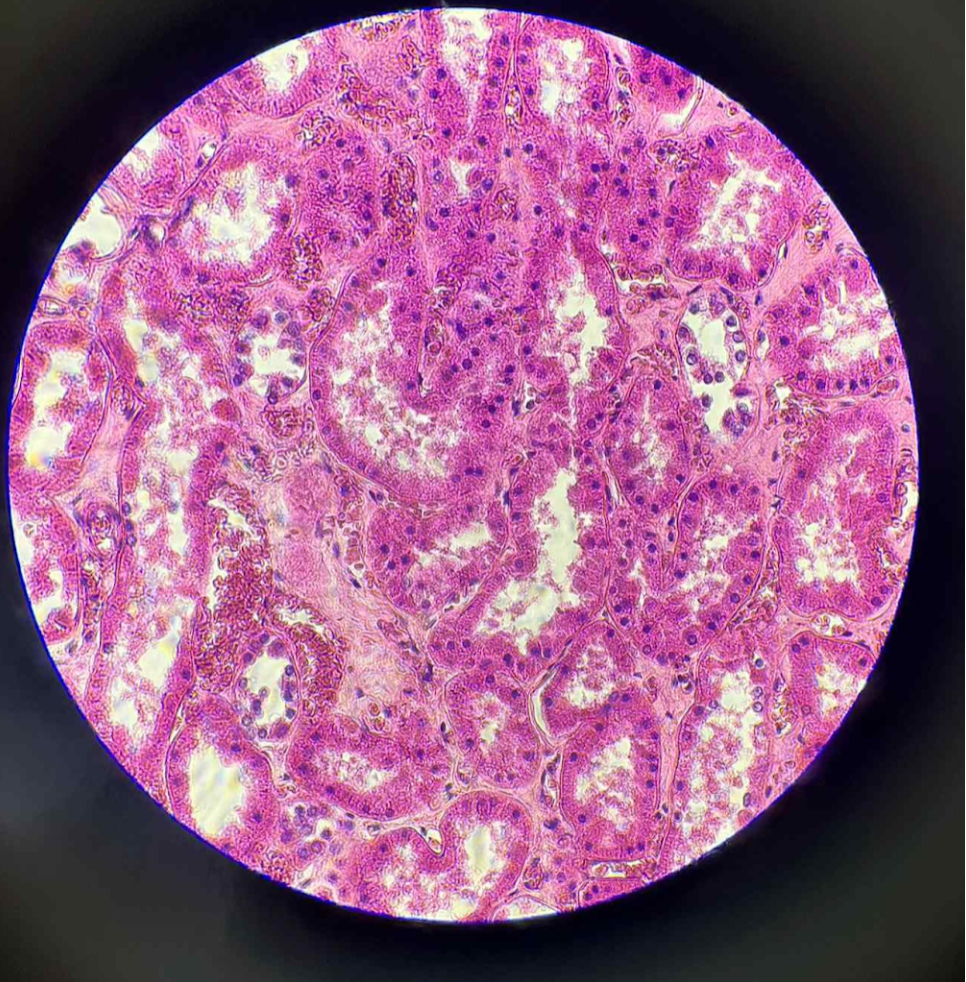
What tissue is this?
simple cuboidal epithelium
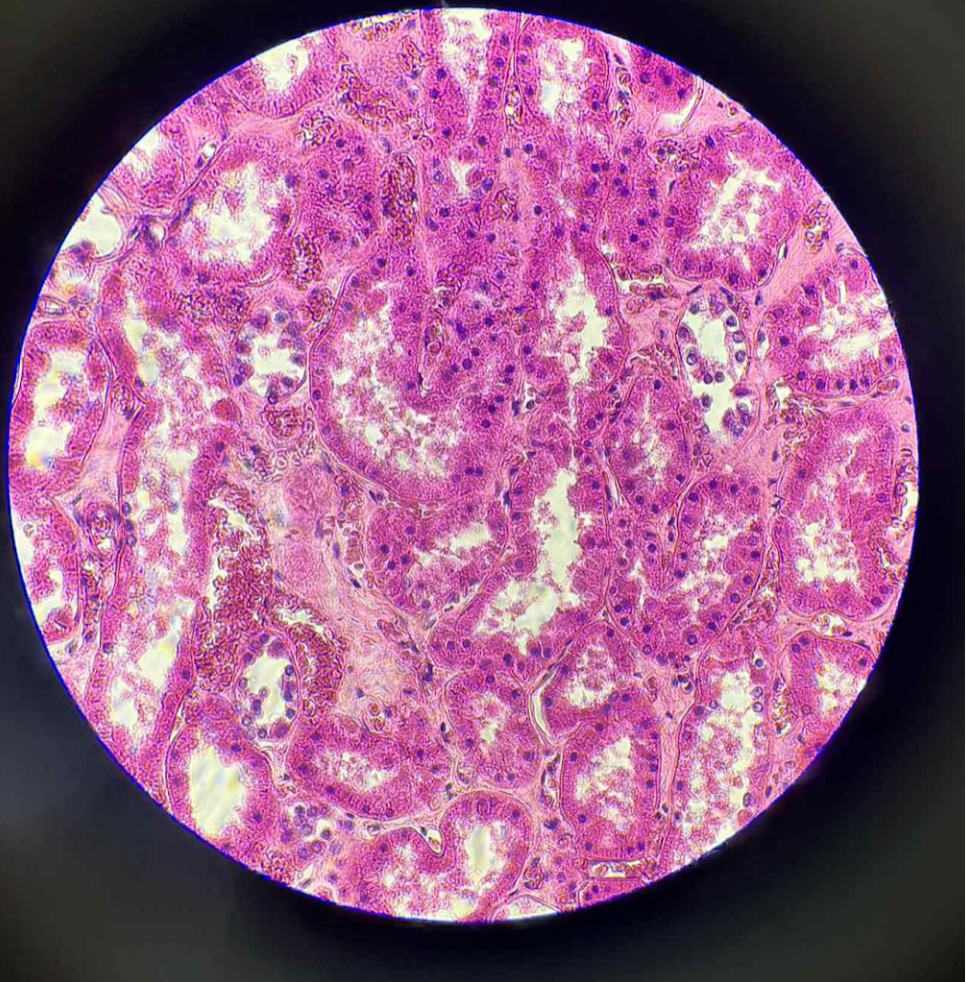
What is the function of this?
Secretion
Absorption
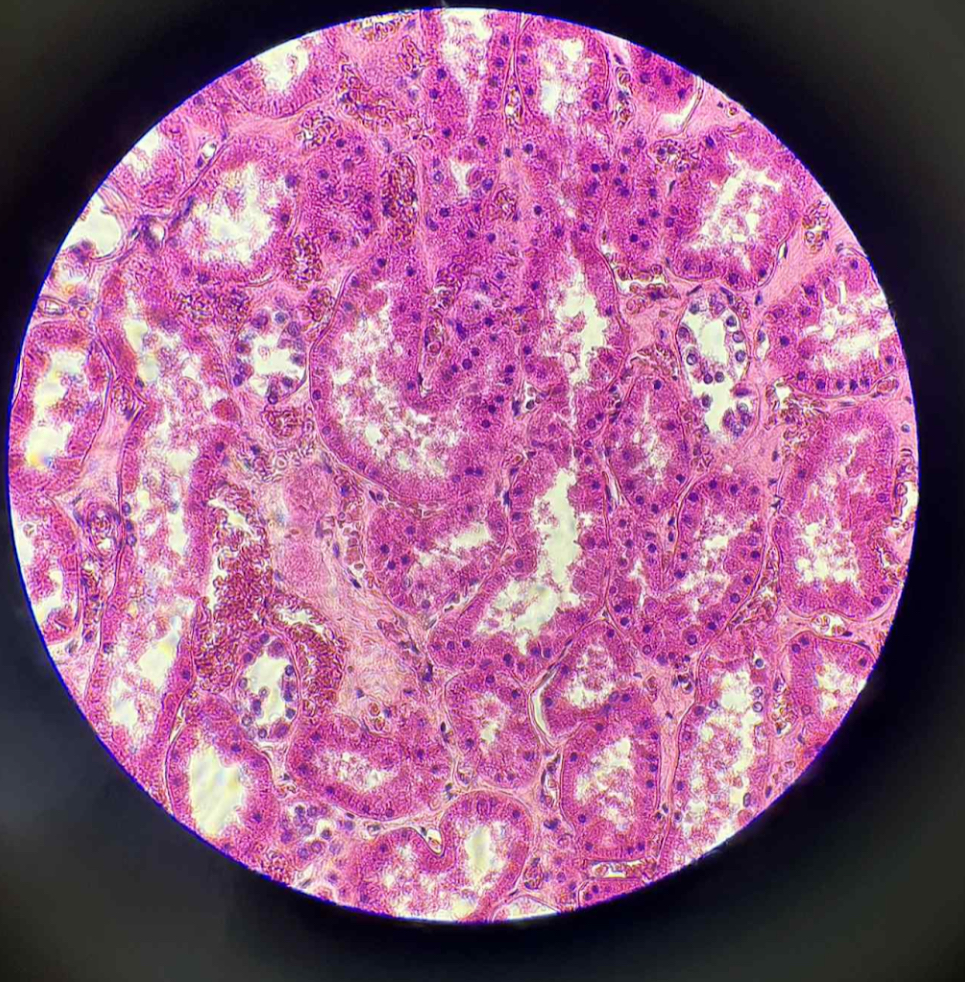
what organ is this?
human kidney
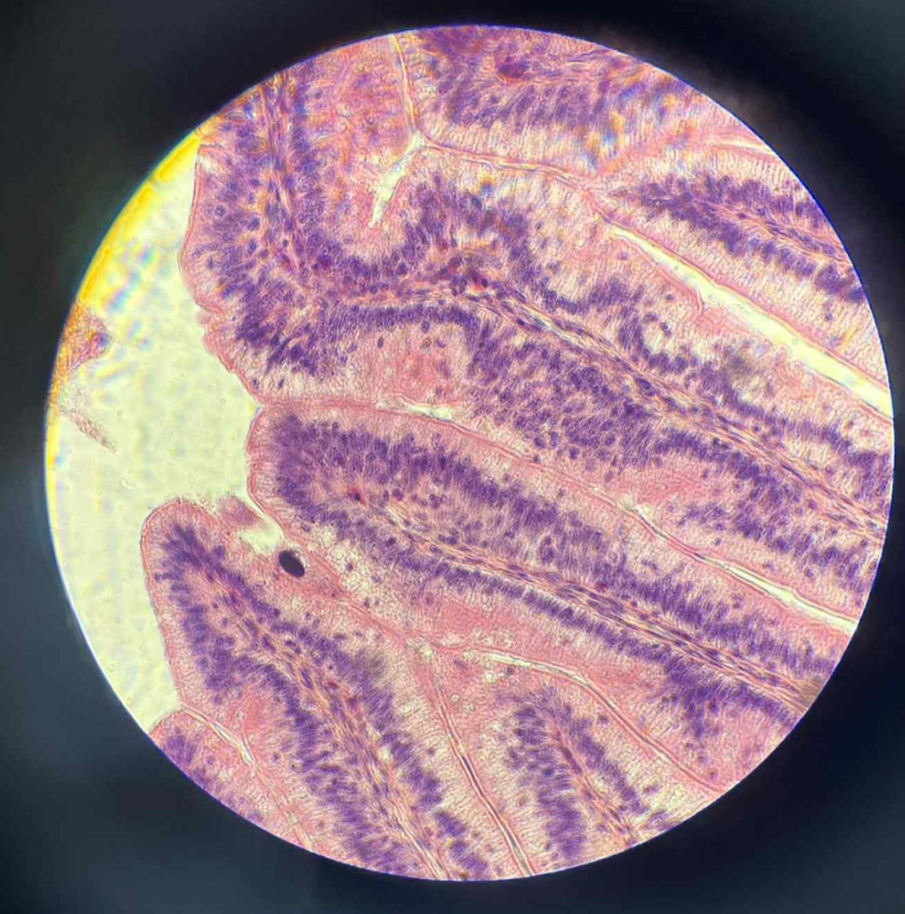
What tissue is this?
simple columnar epithelium
What is the function of this?
Protection
Absorption
Secretion
Form linings specialized for absorption and secretion.
Often line cavities with deeply folded or grooved walls.
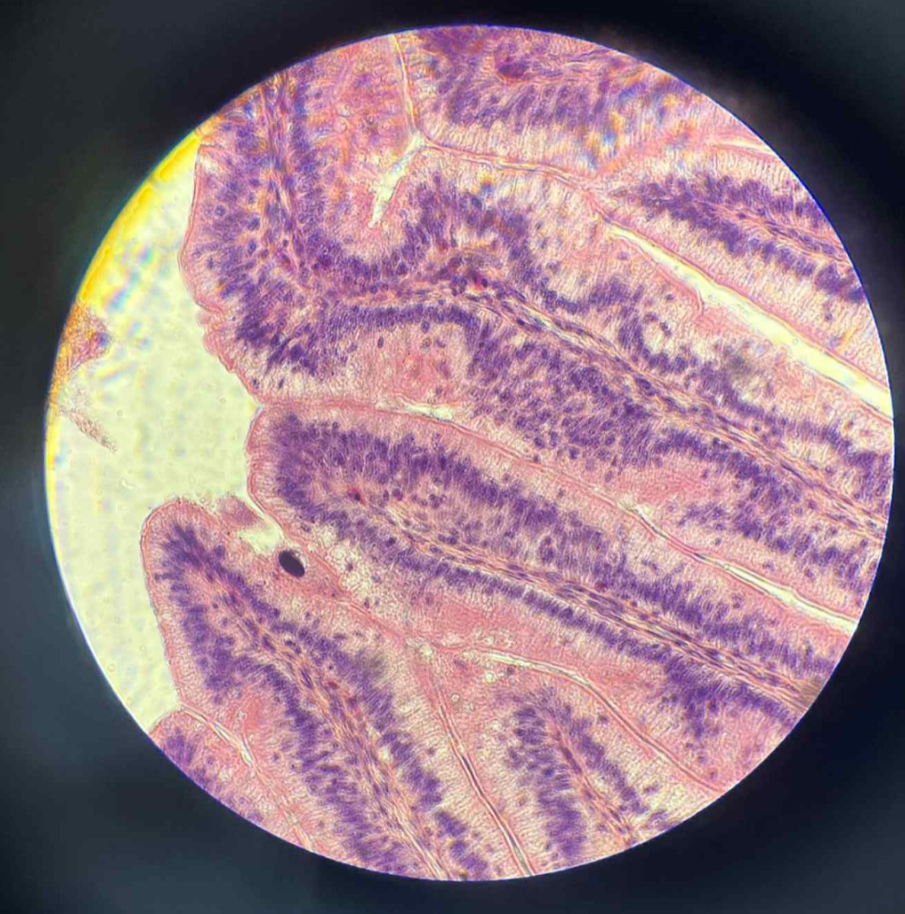
what organ is this?
small intestine
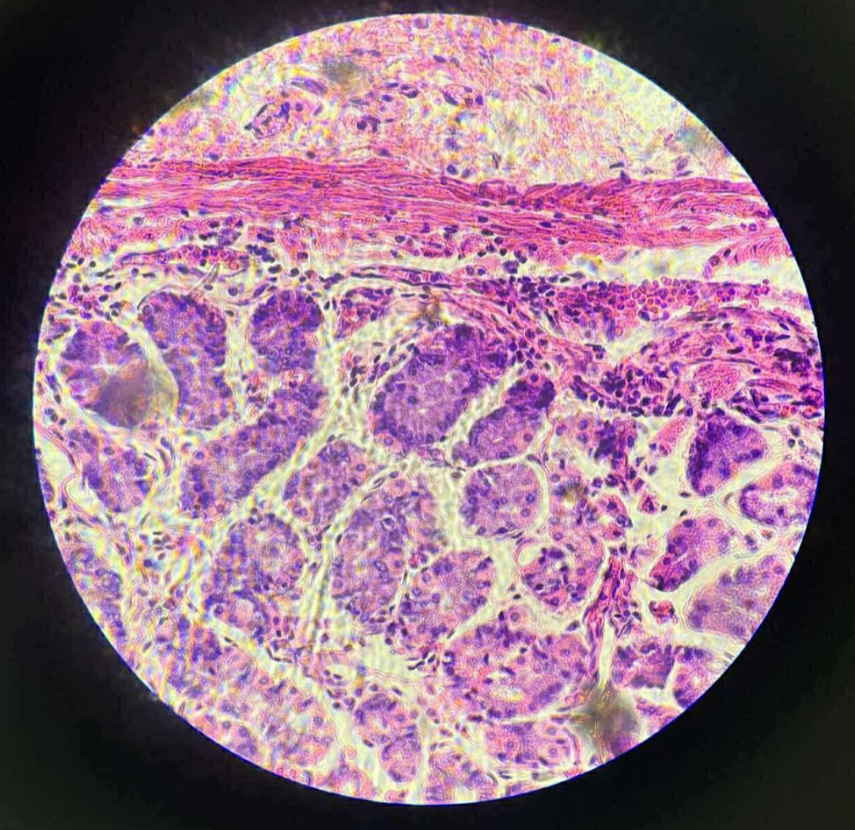
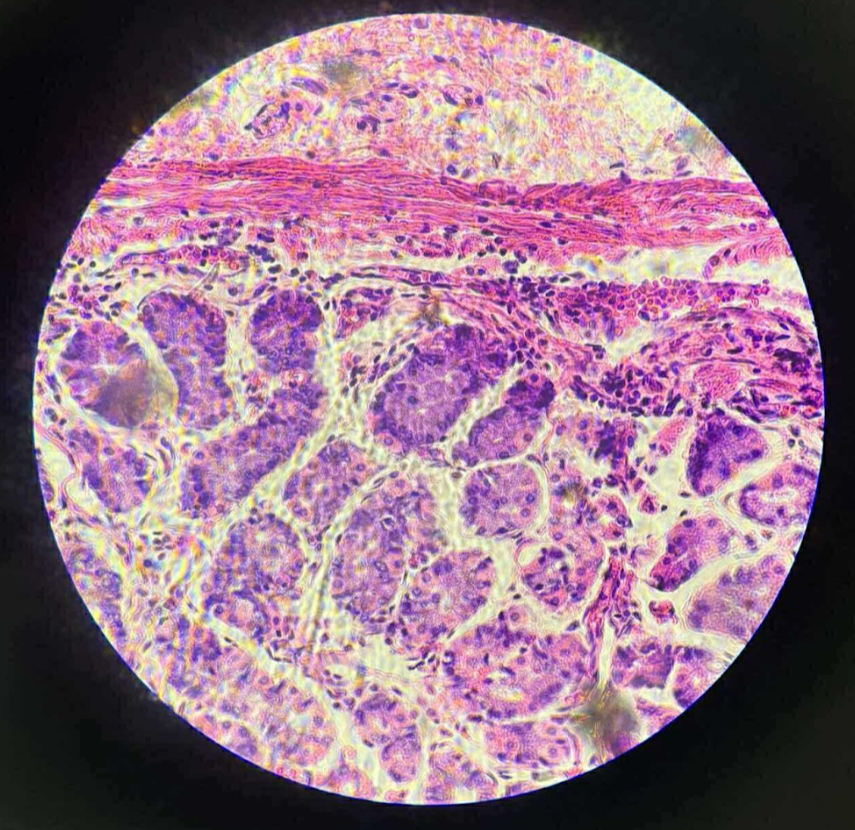
what organ is this?
human fundic-stomach
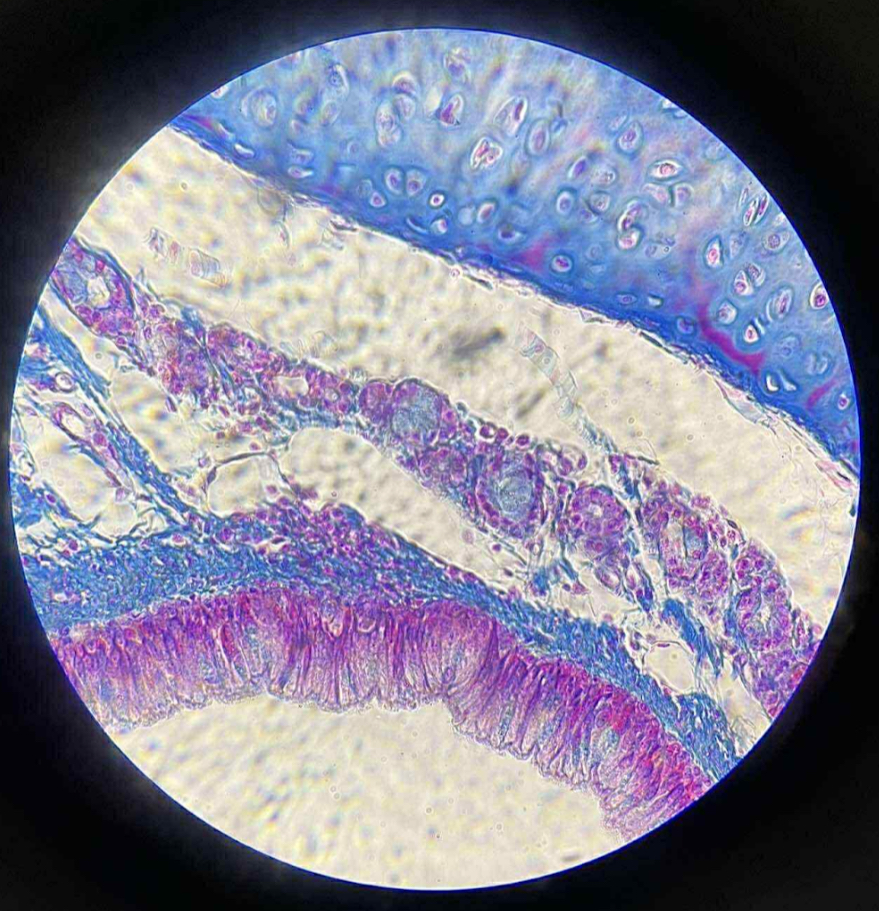
what tissue is this?
pseudostratified columnar epithelium
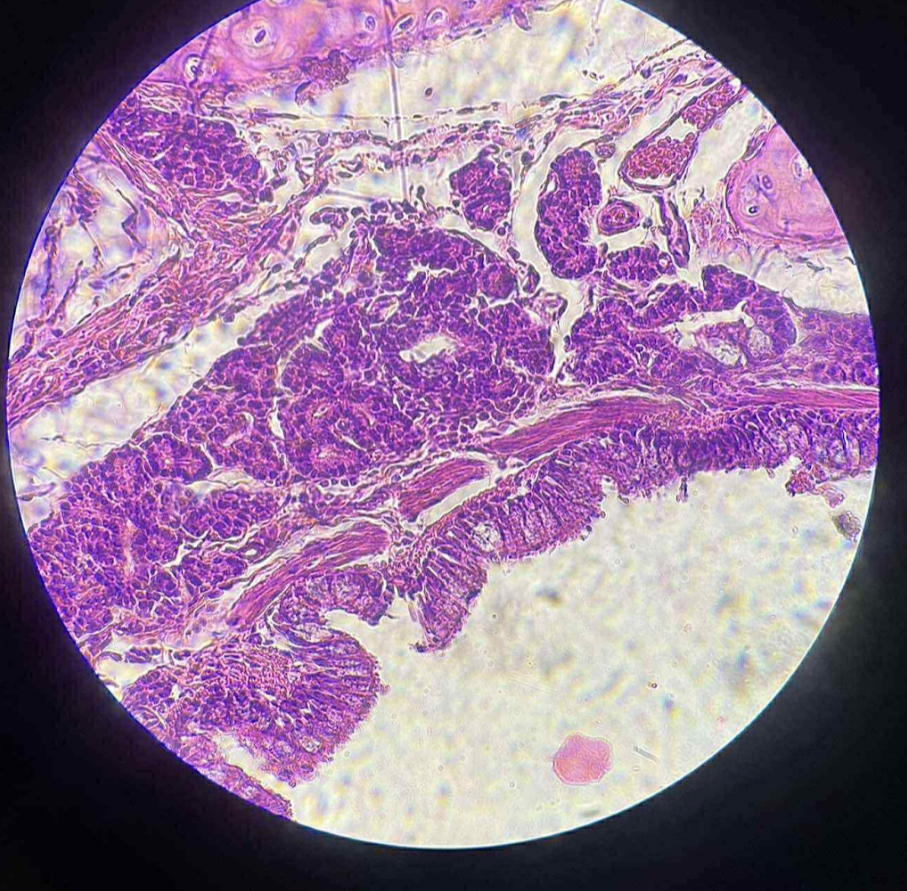
what is the function of this?
Secretion of mucus (by goblet cells)
Propulsion of mucus by ciliary action
Protection
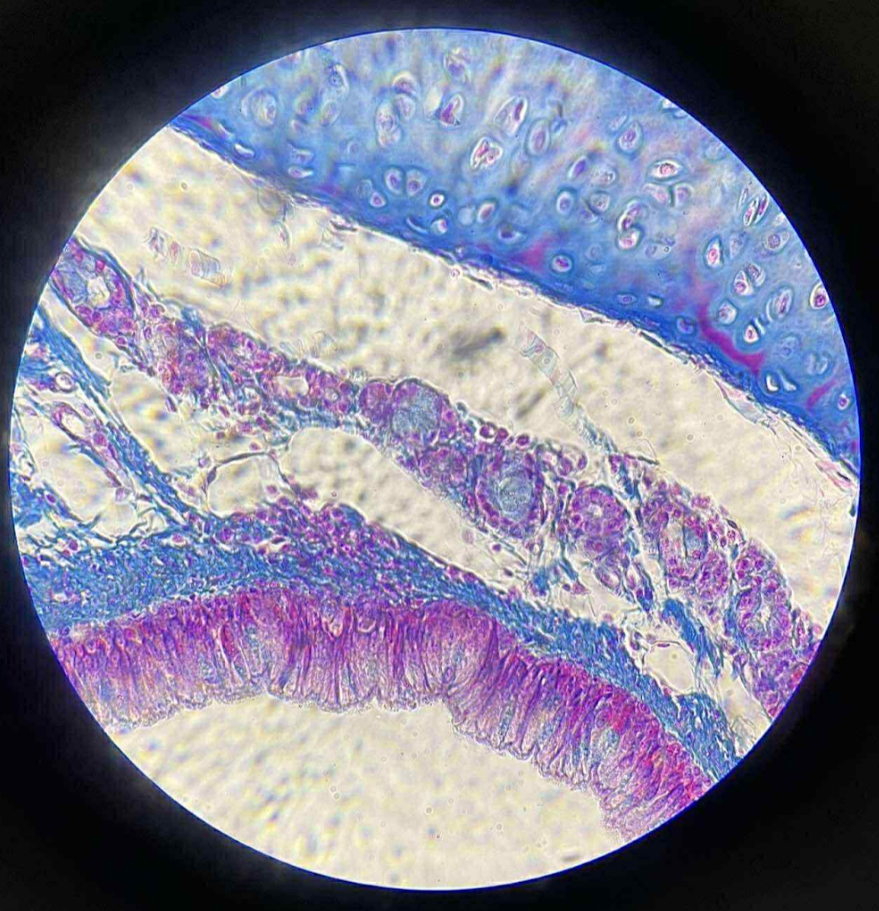
what organ is this?
trachea
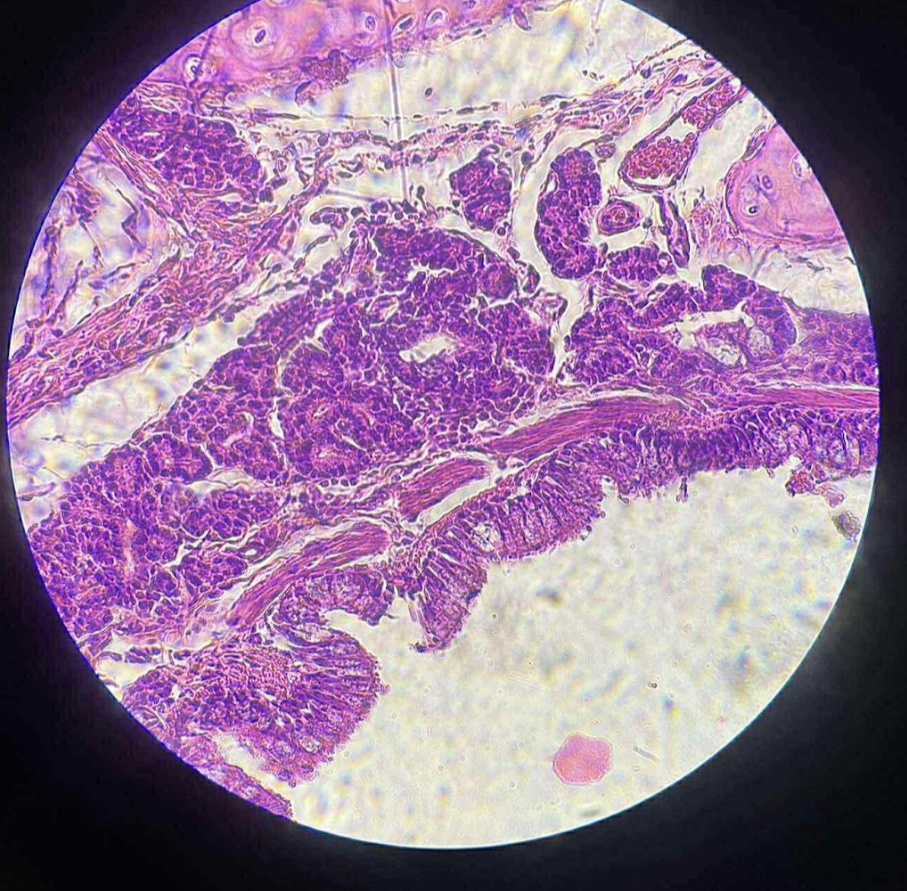
what organ is this?
mammal lung
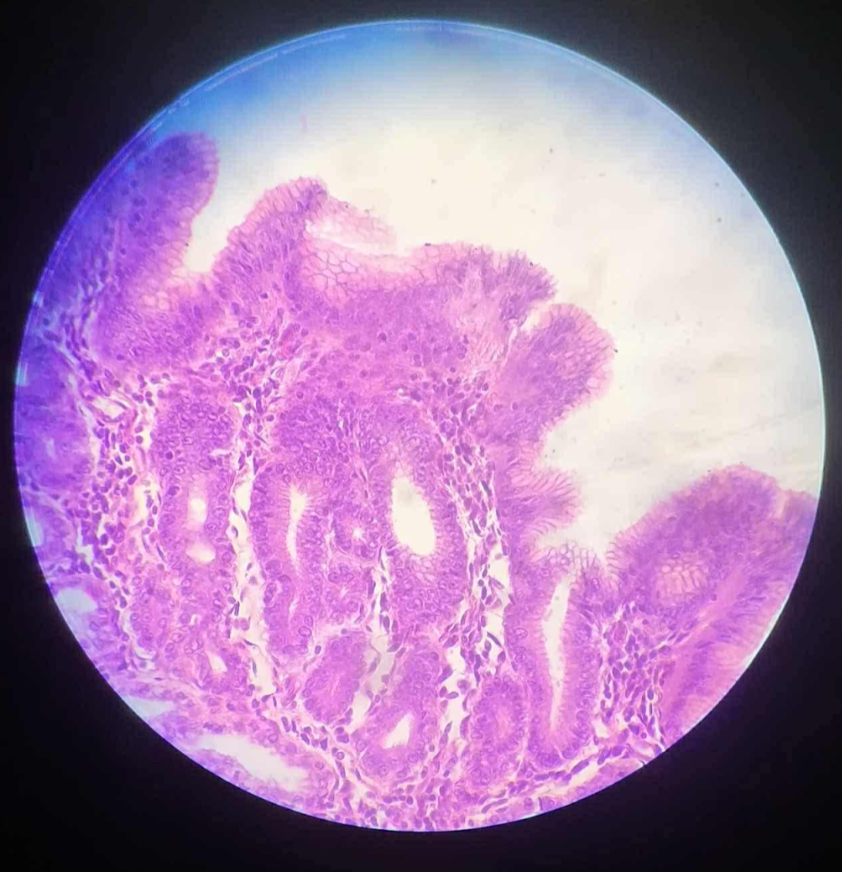
what organ is this?
human pyloric stomach
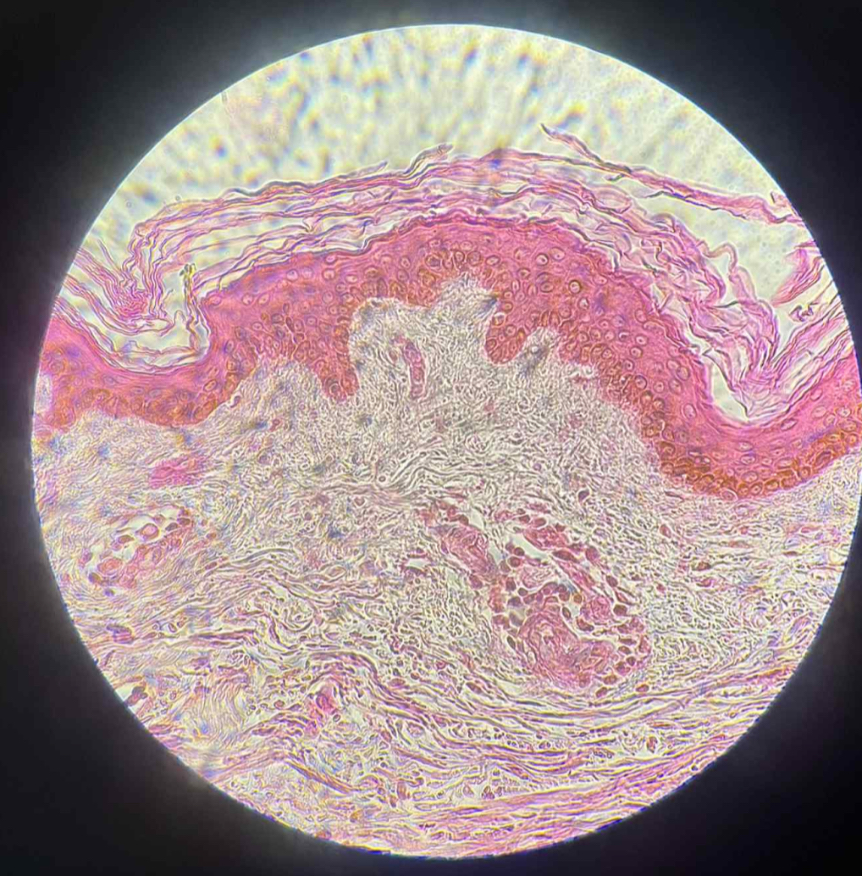
what tissue is this?
keratinized stratified squamous
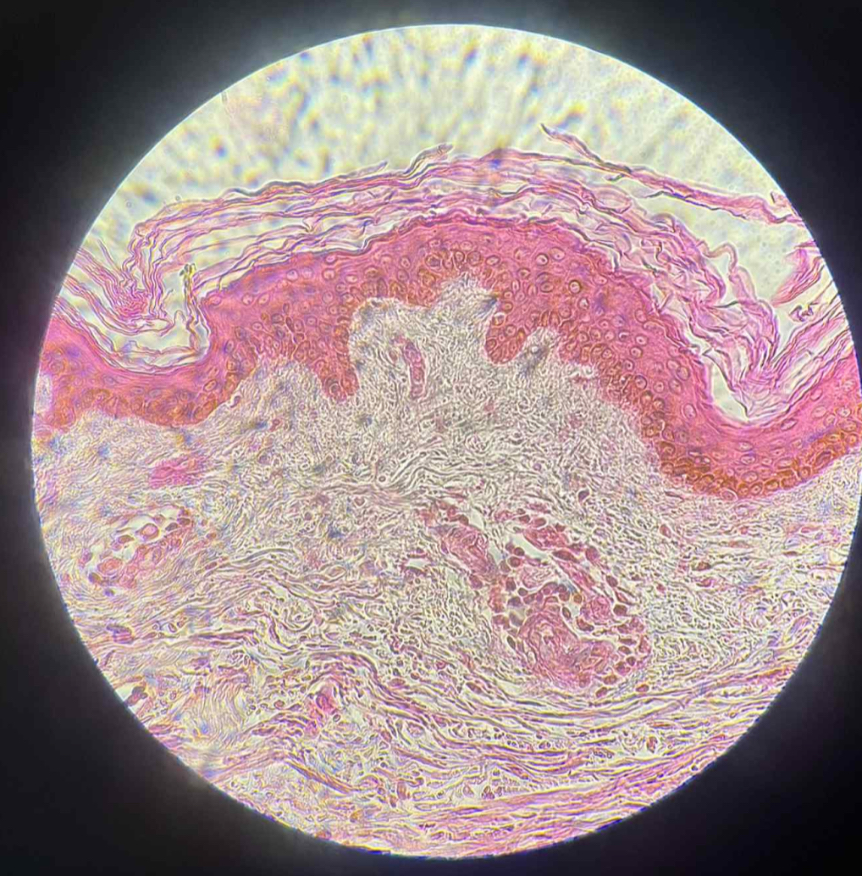
what are the functions of this?
Protection of underlying tissues that are subject to abrasion.
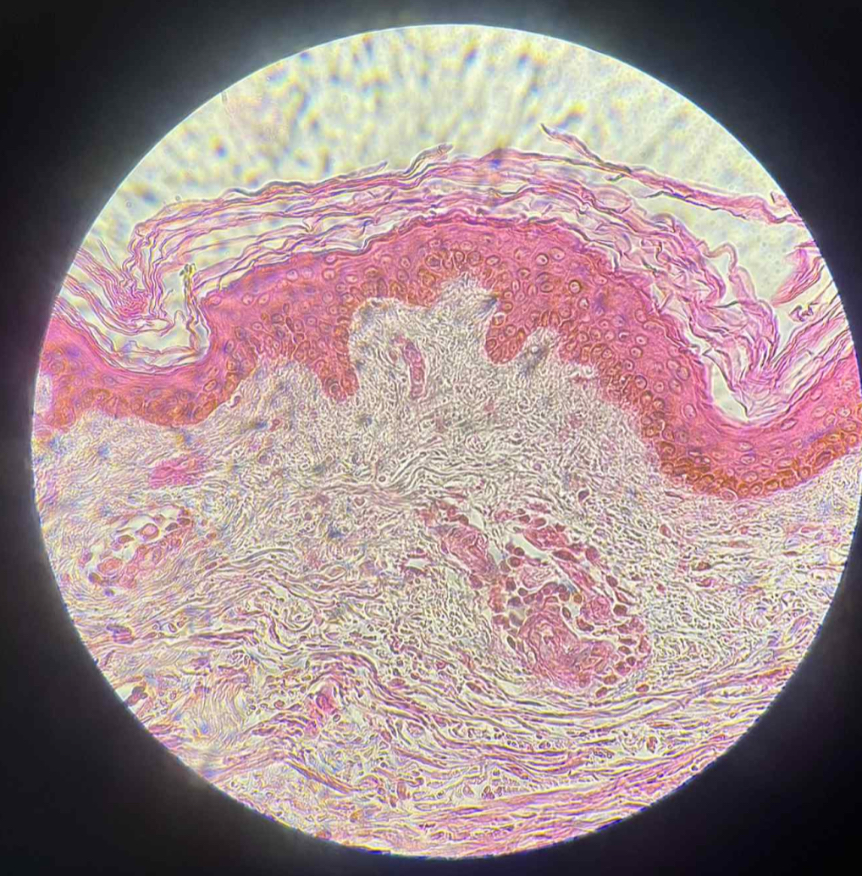
what organ is this?
human brown skin
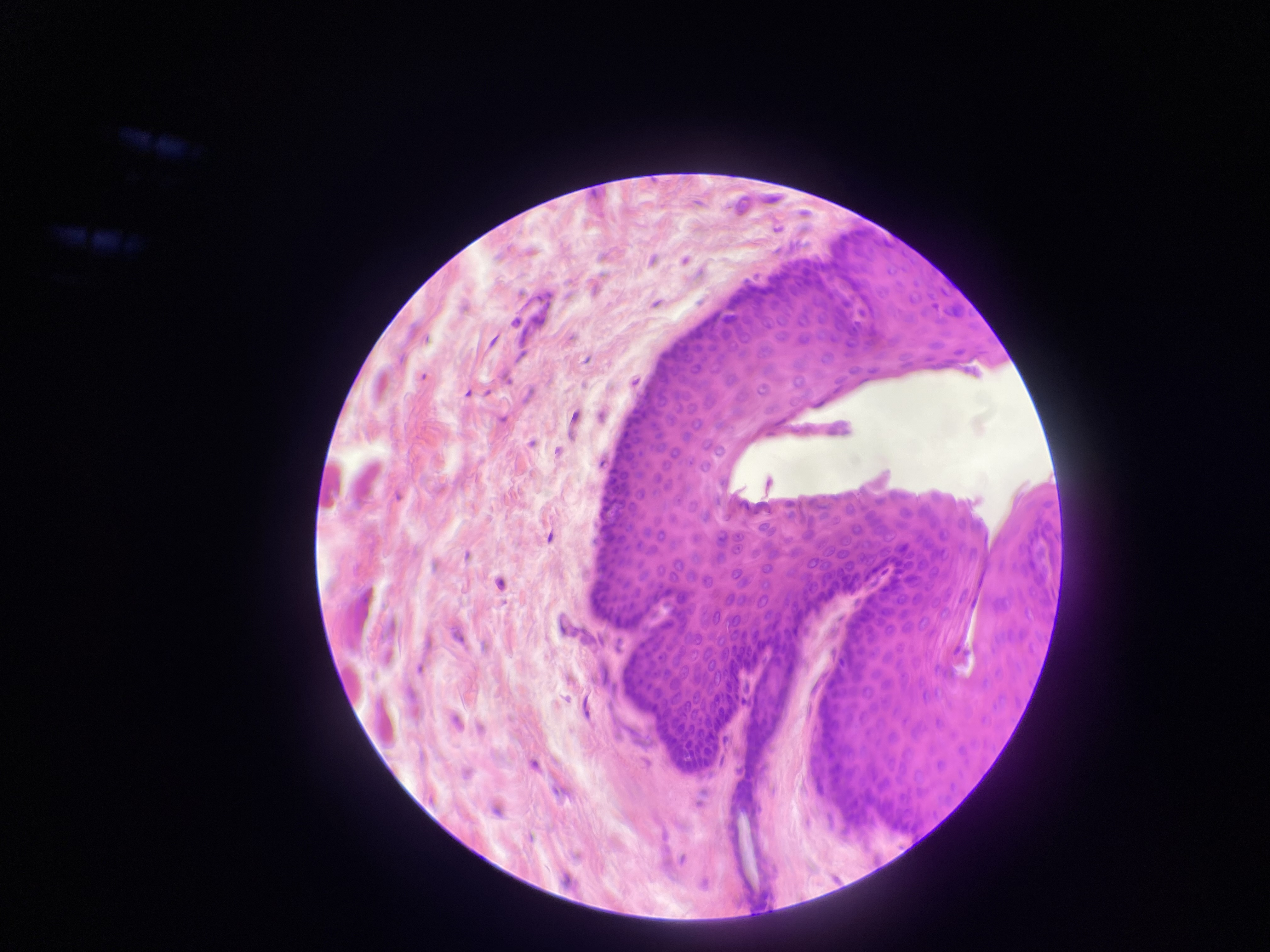
what tissue is this?
non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
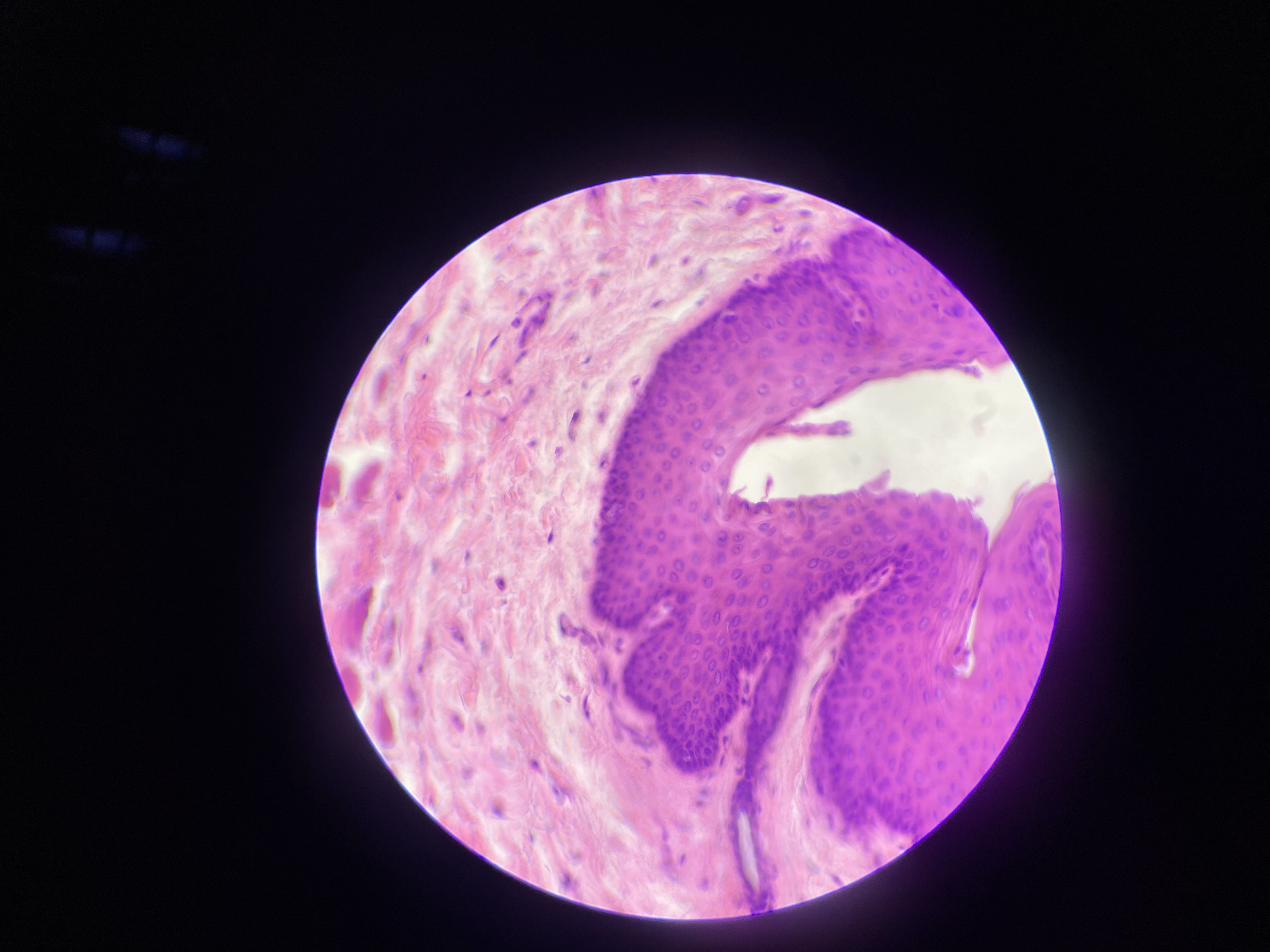
what is the function of this?
Protection of underlying tissues that are subject to abrasion.
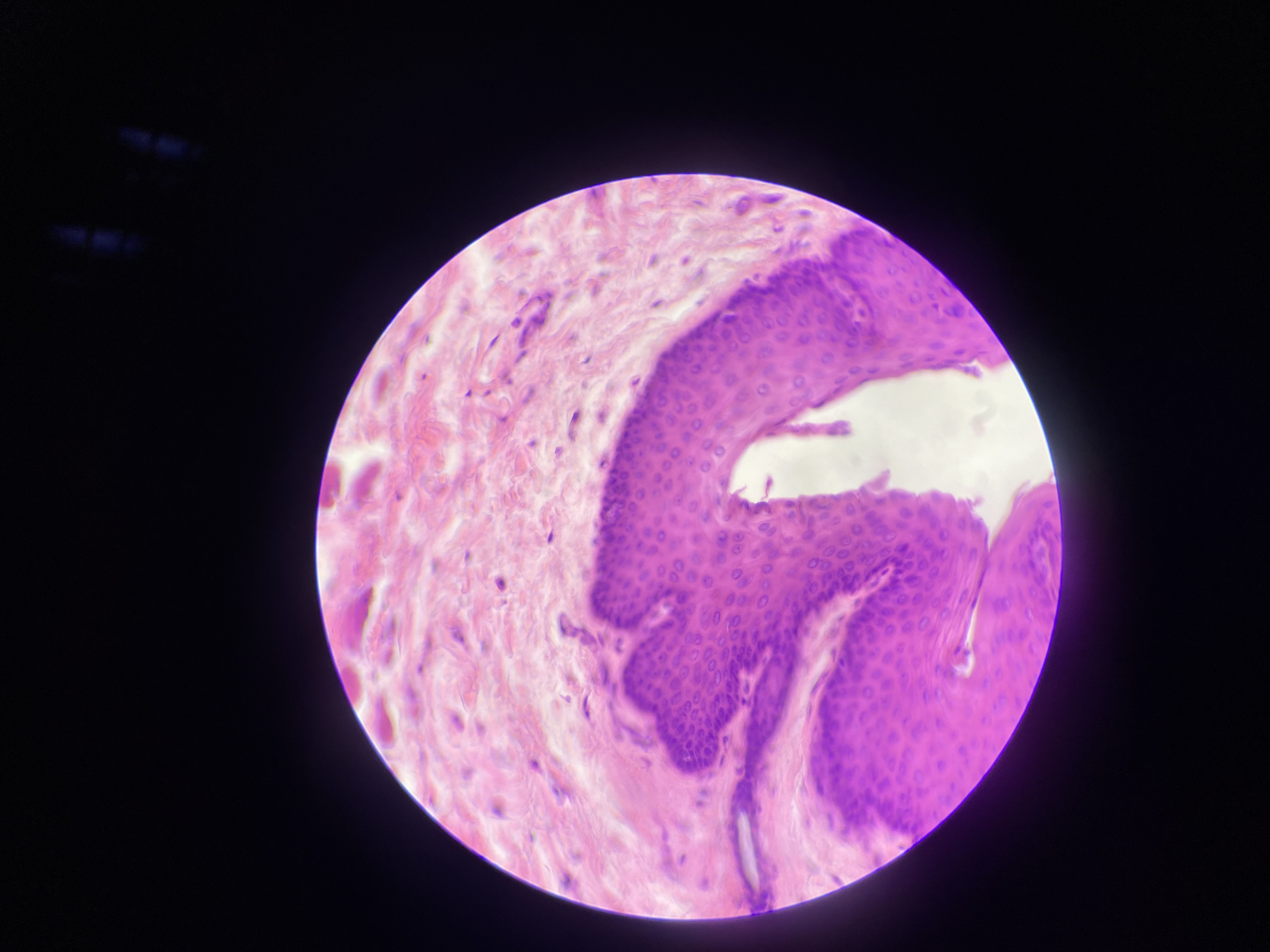
what organ is this?
esophagus
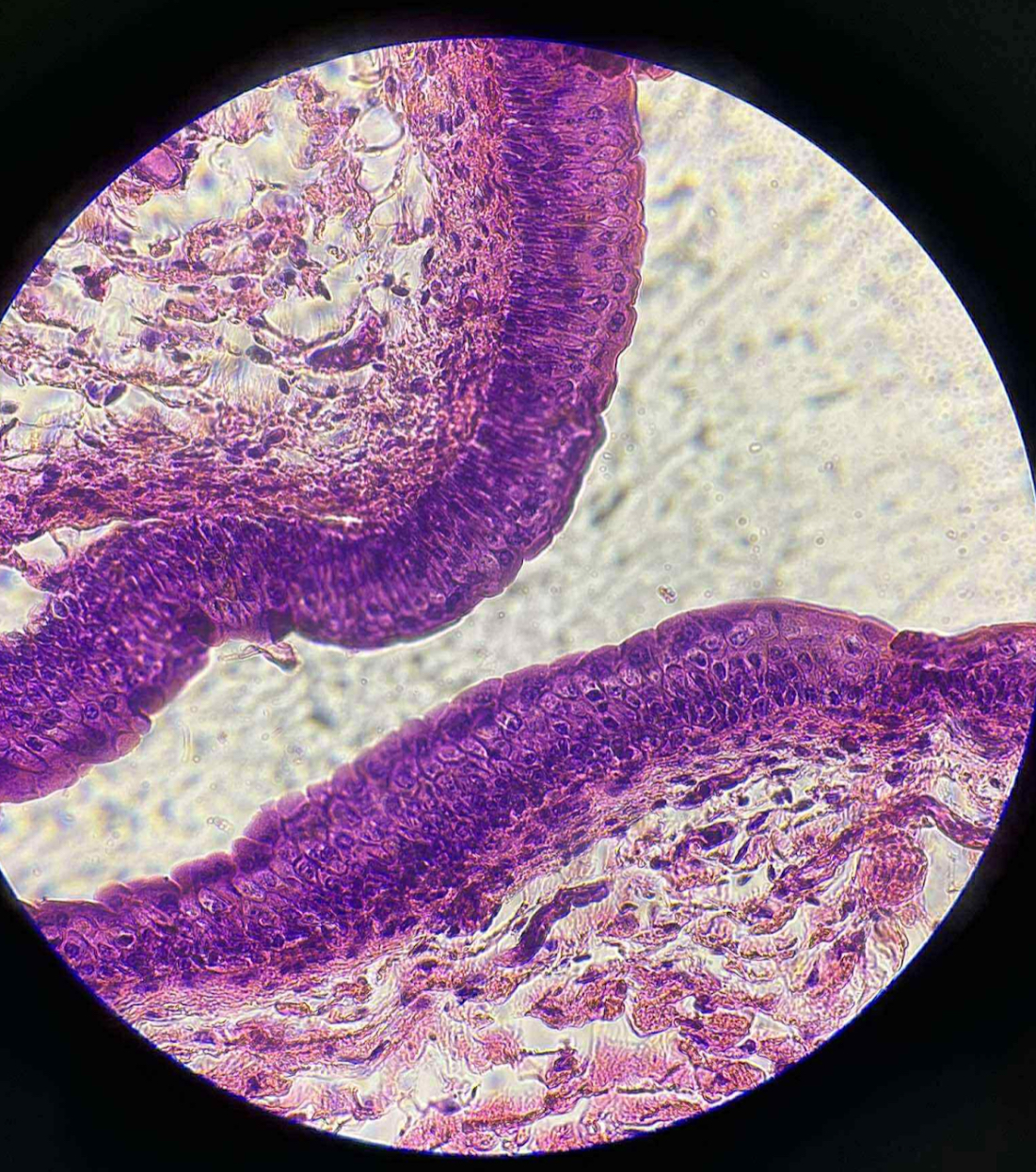
what is this tissue?
transitional epithelium
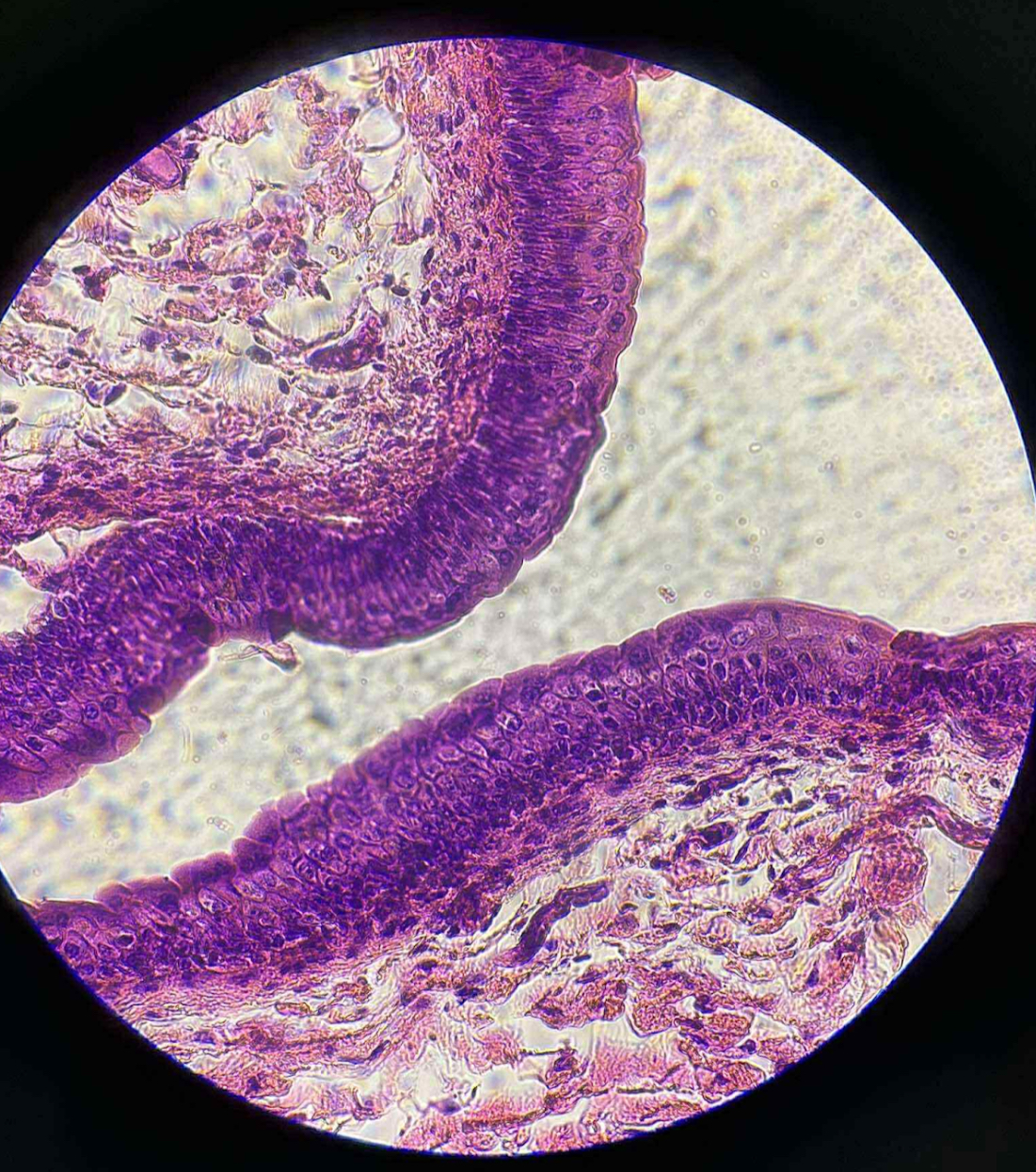
what are the functions of this?
Forms the lining, usually those that have the capacity to stretch.
Stretches readily and allow the tissue to contract or expand.
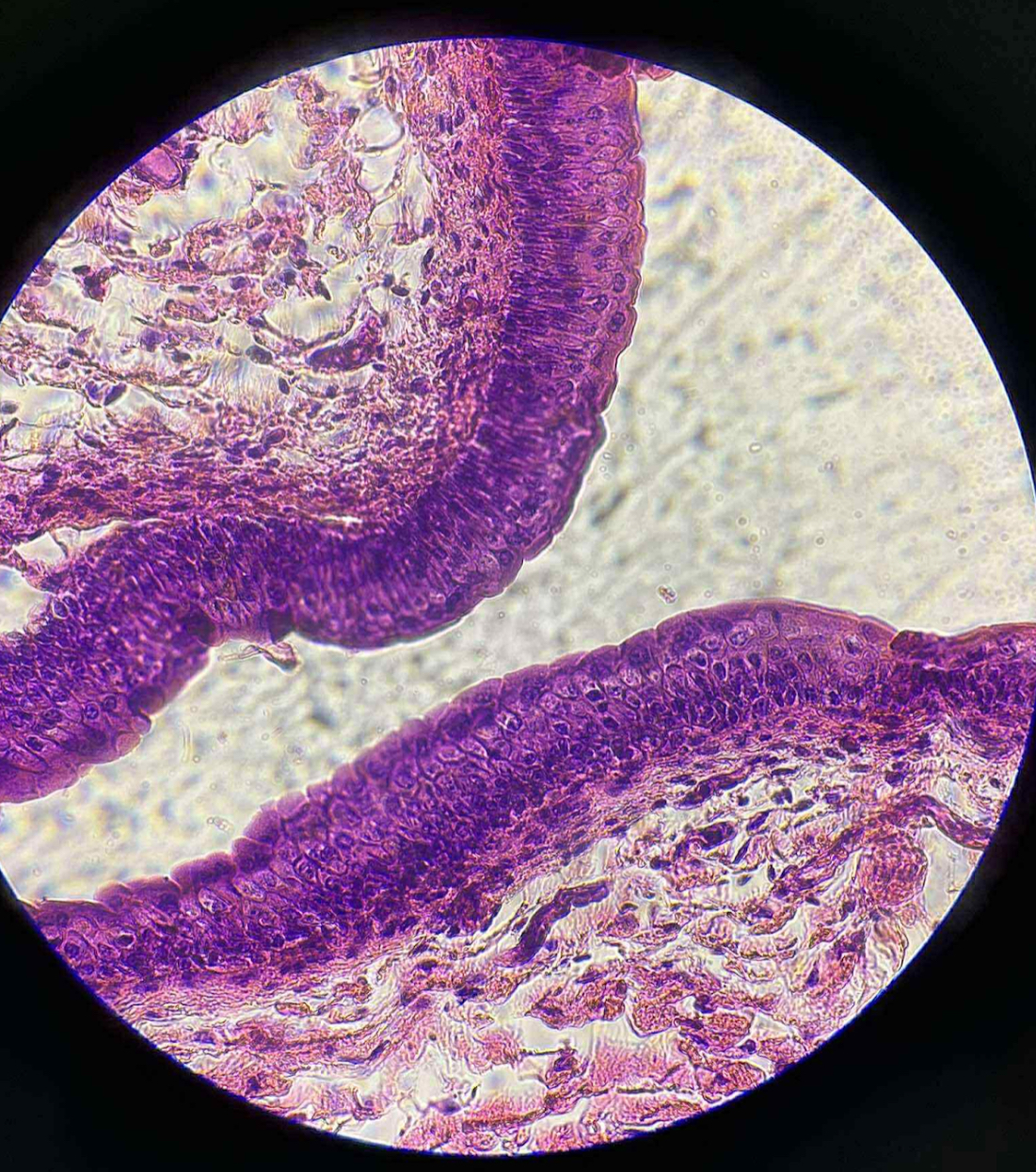
where is this mostly located?
Found in areas subject to a great deal of elastic stress.
Lining of urinary bladder
Ureter
Parts of urethra
Uterus
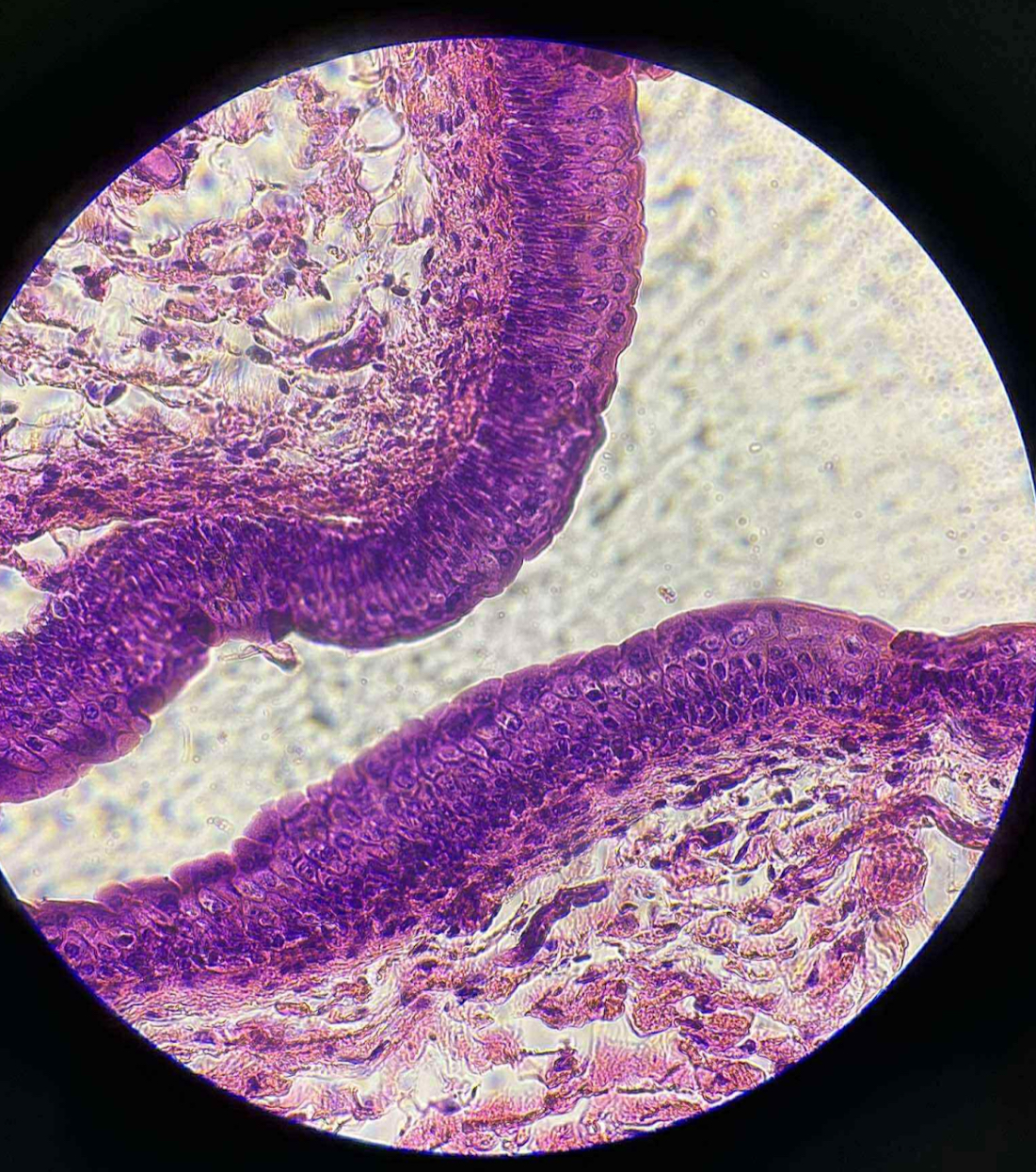
what organ is this?
human urinary bladder

what tissue is this?
loose fibrous tissue/areolar tissue

give the functions of this
Supports epithelium and internal organs.
Forms a protective covering enclosing muscles, blood vessels, and nerves.
Provides a reservoir of water and salts for surrounding due to its loose and fluid consistency.

where is this mostly located?
Beneath epidermis of skin.
Found in superficial and deep fascia.
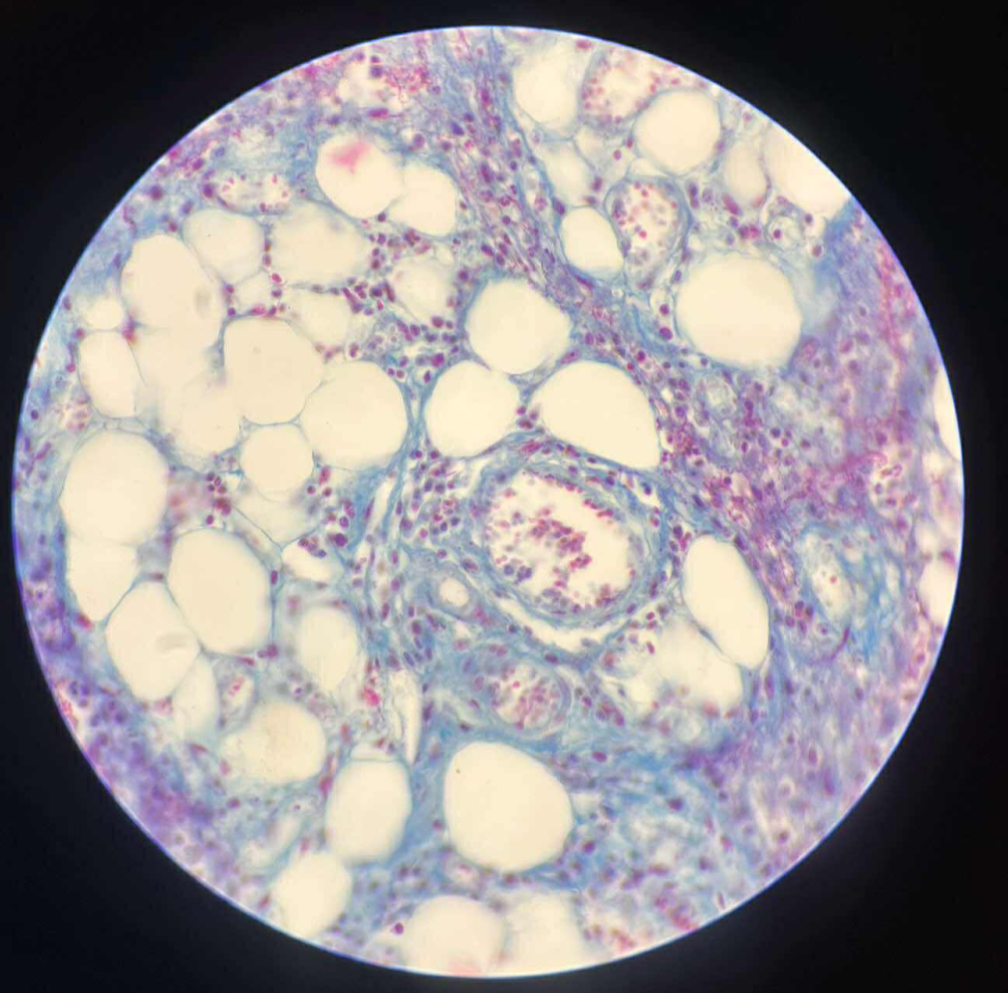
what tissue is this?
loose adipose connective tissue
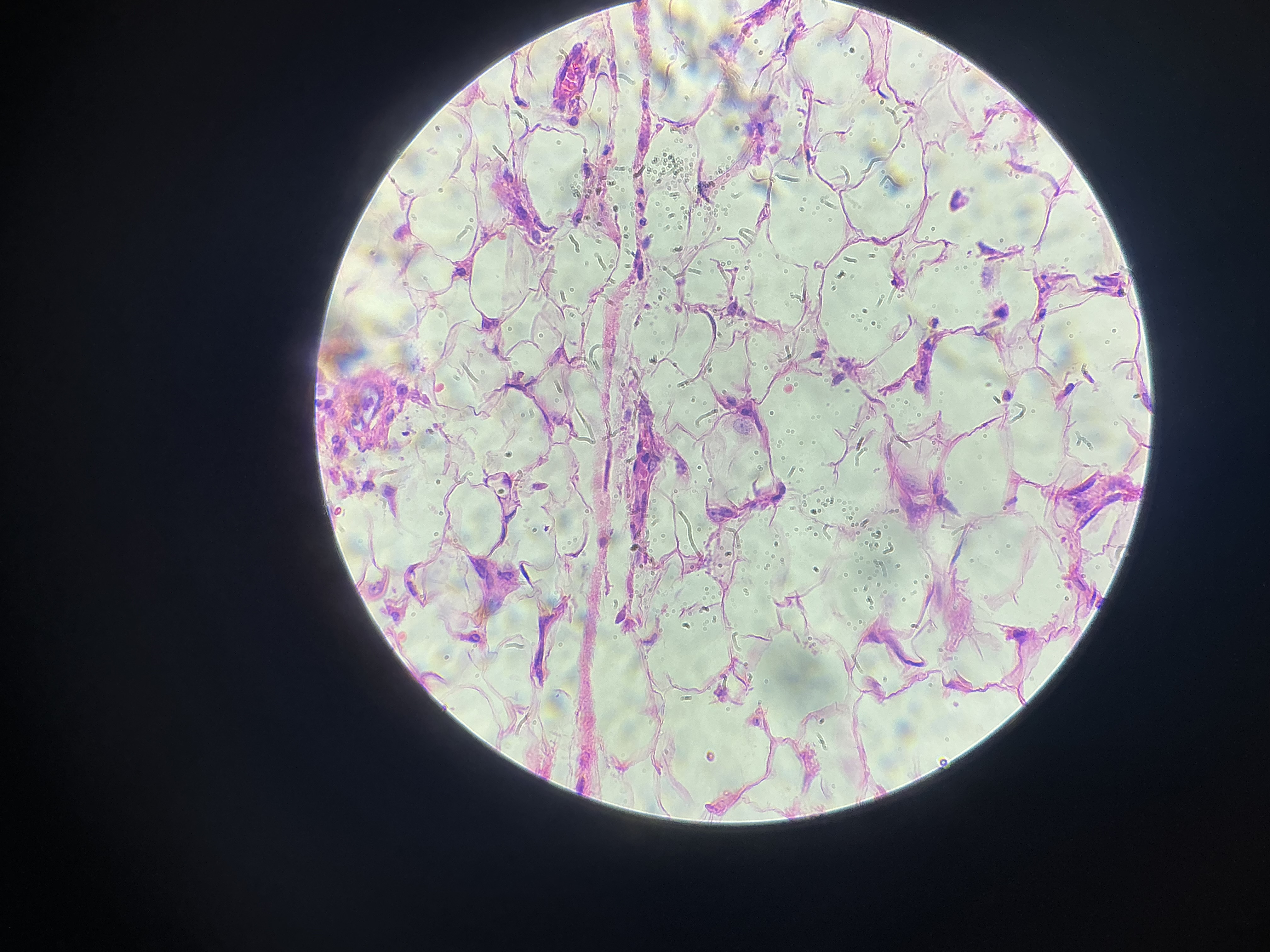
give the functions of this
Specialized to store lipids in large vesicles.
Protects some organs
Insulates the body
Reserve food
Fat storage
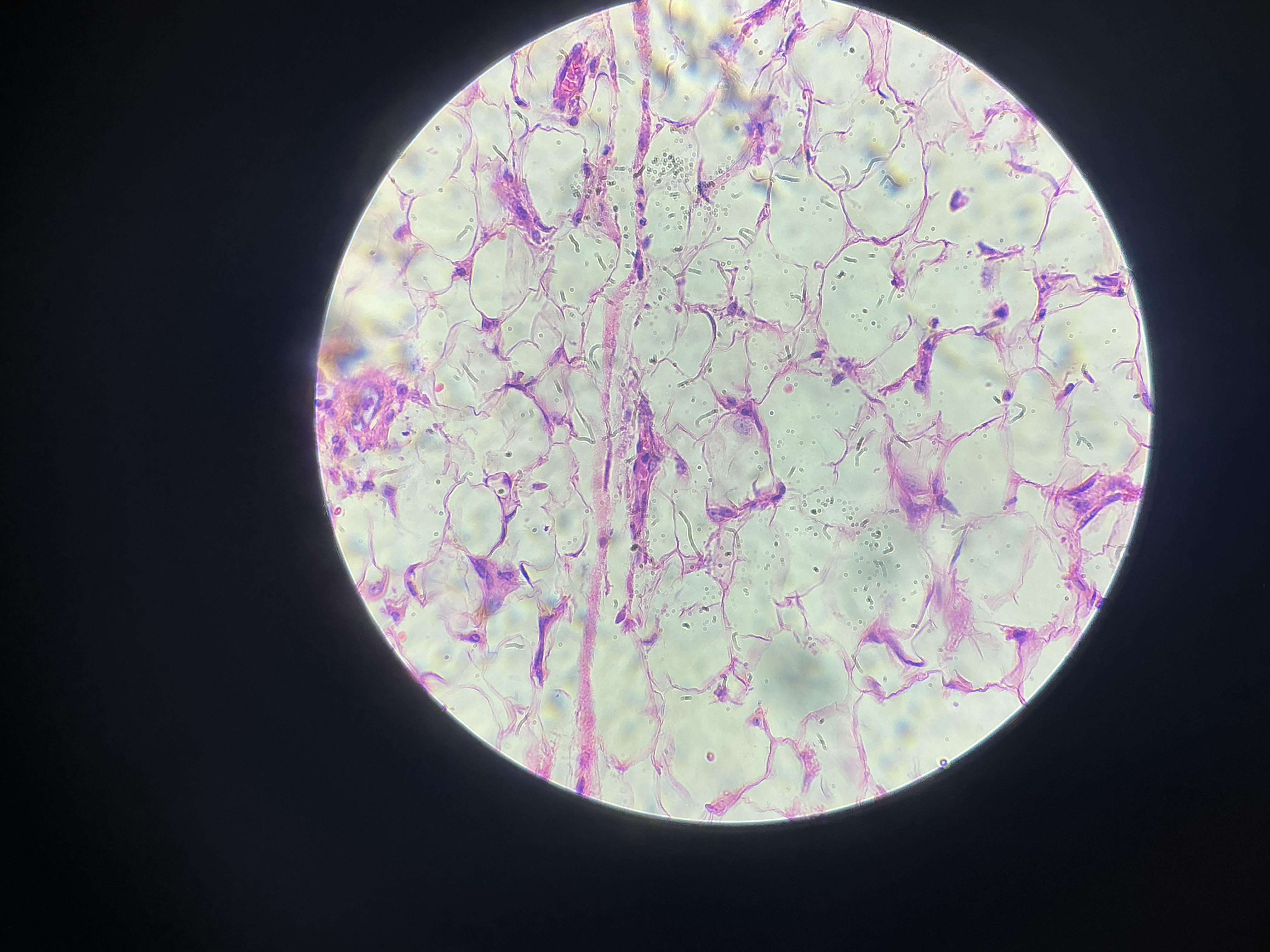
where is this mostly located?
Found wherever areolar tissue is found, but it is most often seen around the heart, kidney, and under the skin.
Subcutaneous tissue beneath the skin
Protects organs, such as the kidneys
Fat depots include hips, breasts, and belly
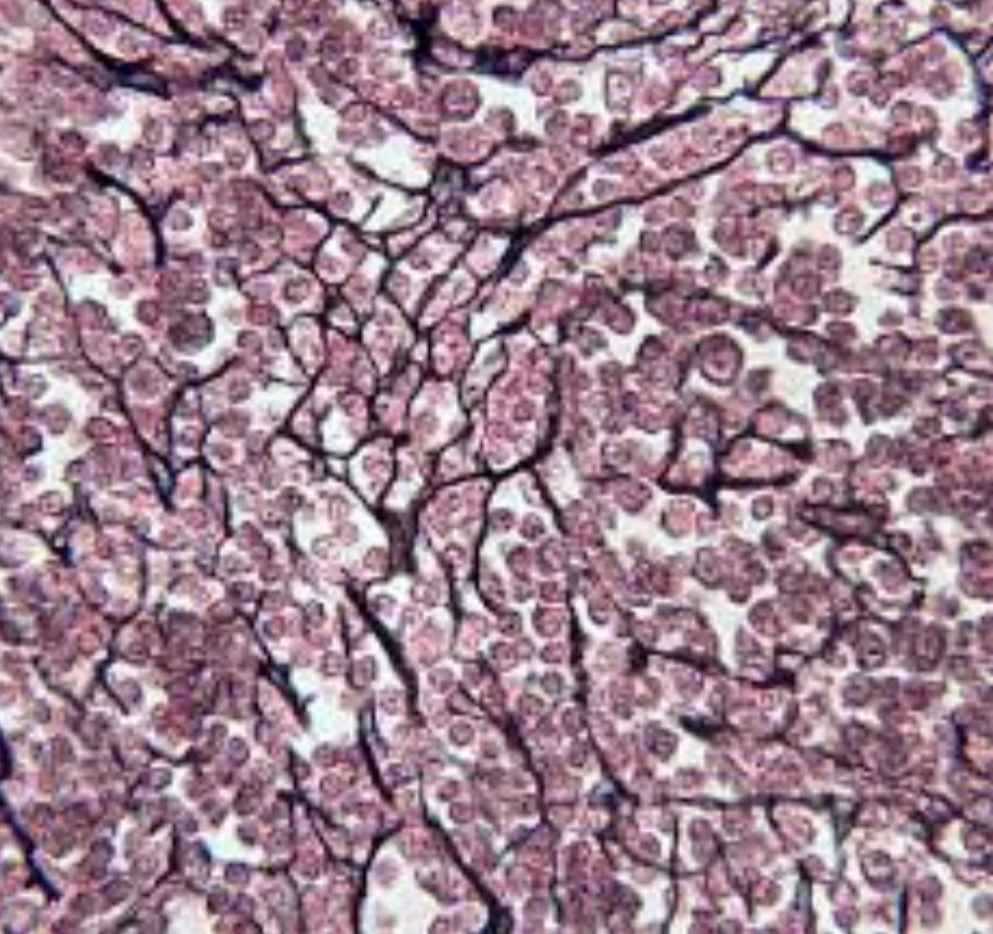
what tissue is this?
loose reticular connective tissue
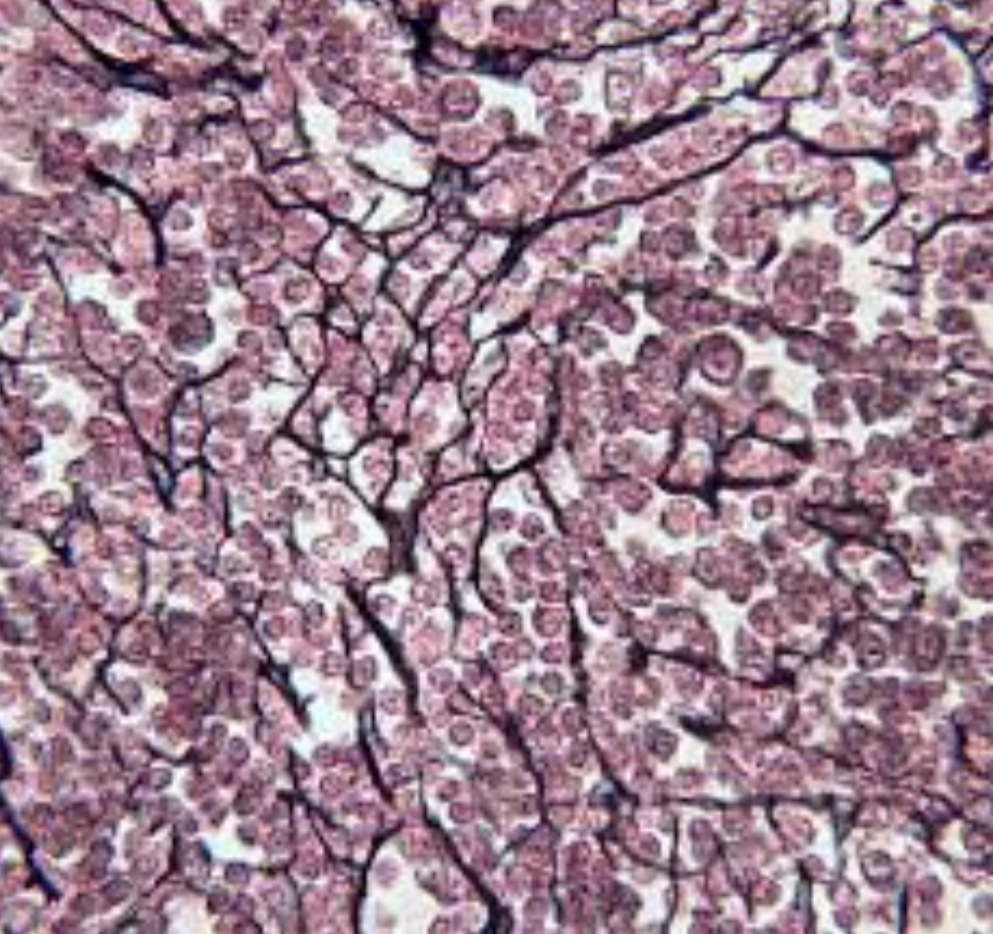
give the functions of this
Structural support by creating and maintaining the fine networks of fibers that serve as the framework.
Support
Filtration
Functions as part of the body’s defensive system.
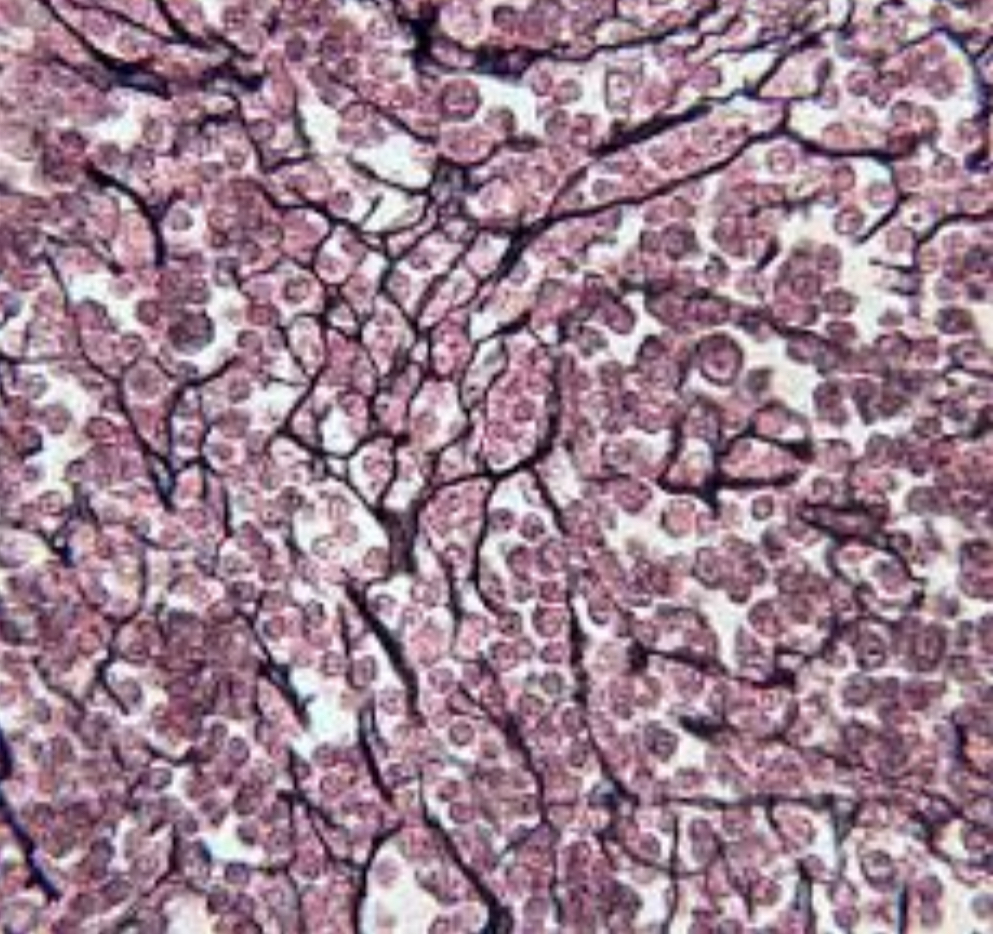
give the location
Forms the framework of:
Spleen
Lymph nodes
Bone marrow cavities
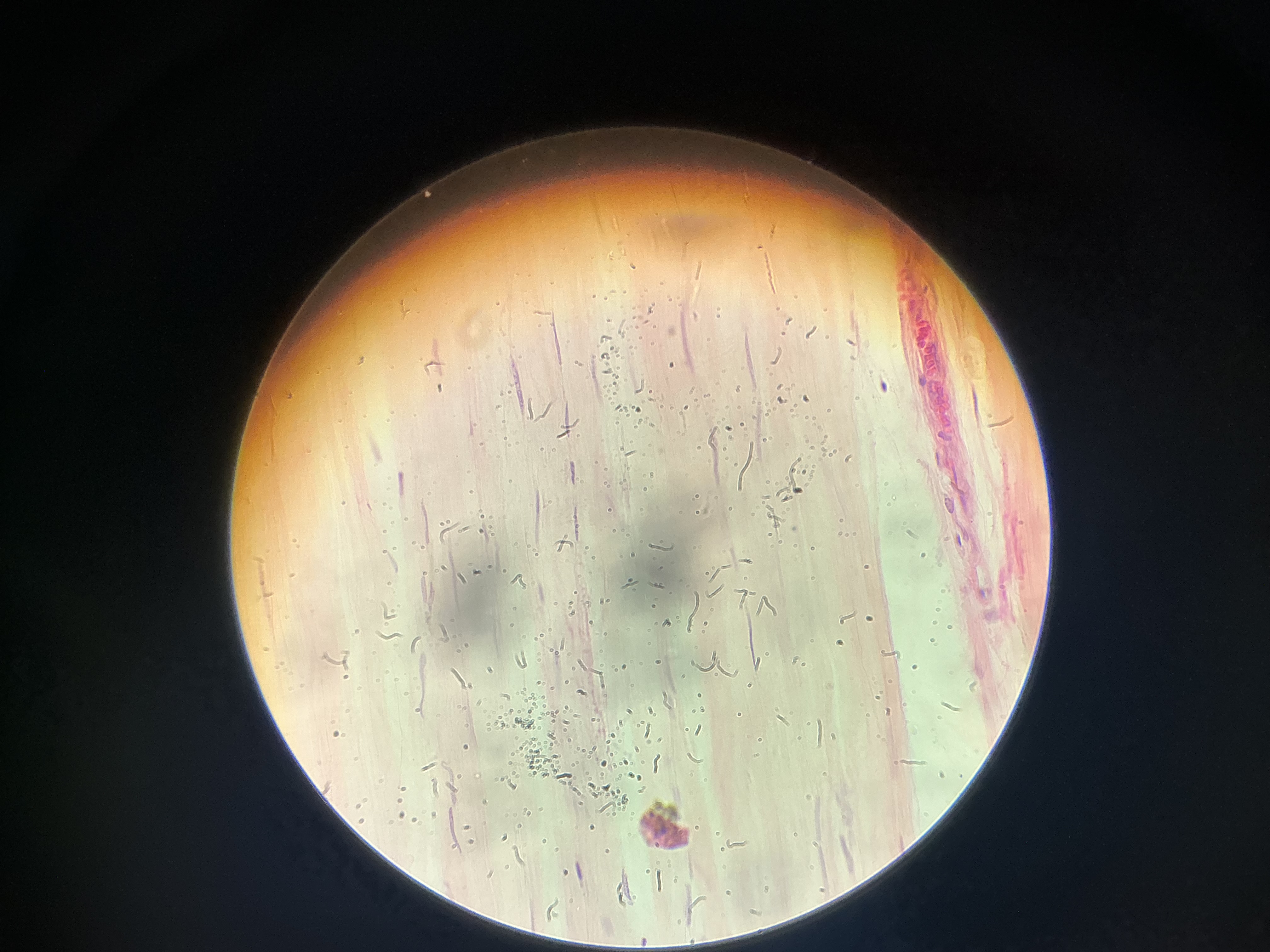
what tissue is this?
dense regular fibrous tissue
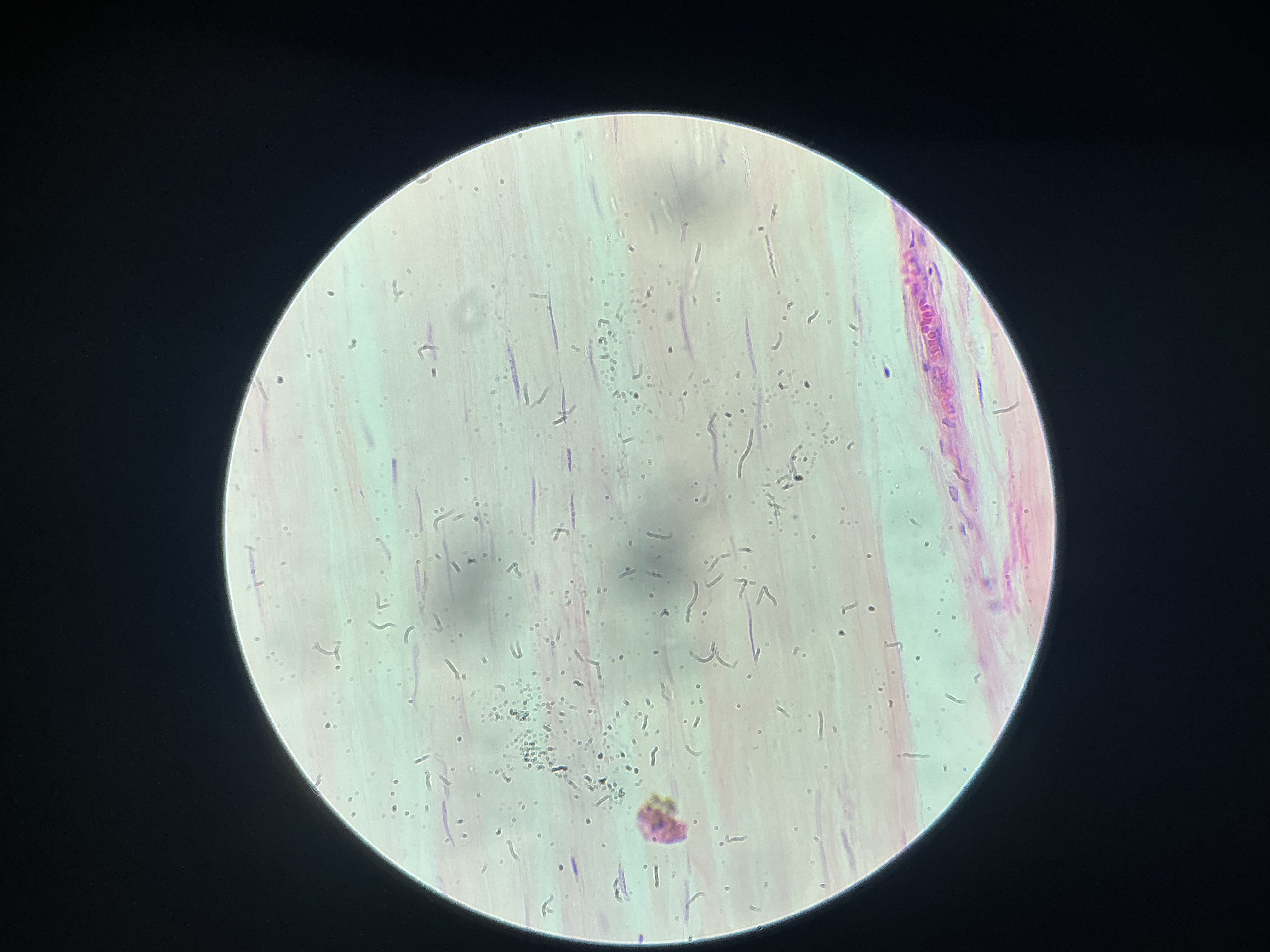
give the functions of this
Used for structures that require a better-engineered connection between parts that are pulled with great force.
Tendon → attach skeletal muscle to bone.
Ligament → attach bone to bone at joints; more elastic than tendons.
Flexible but strong connection
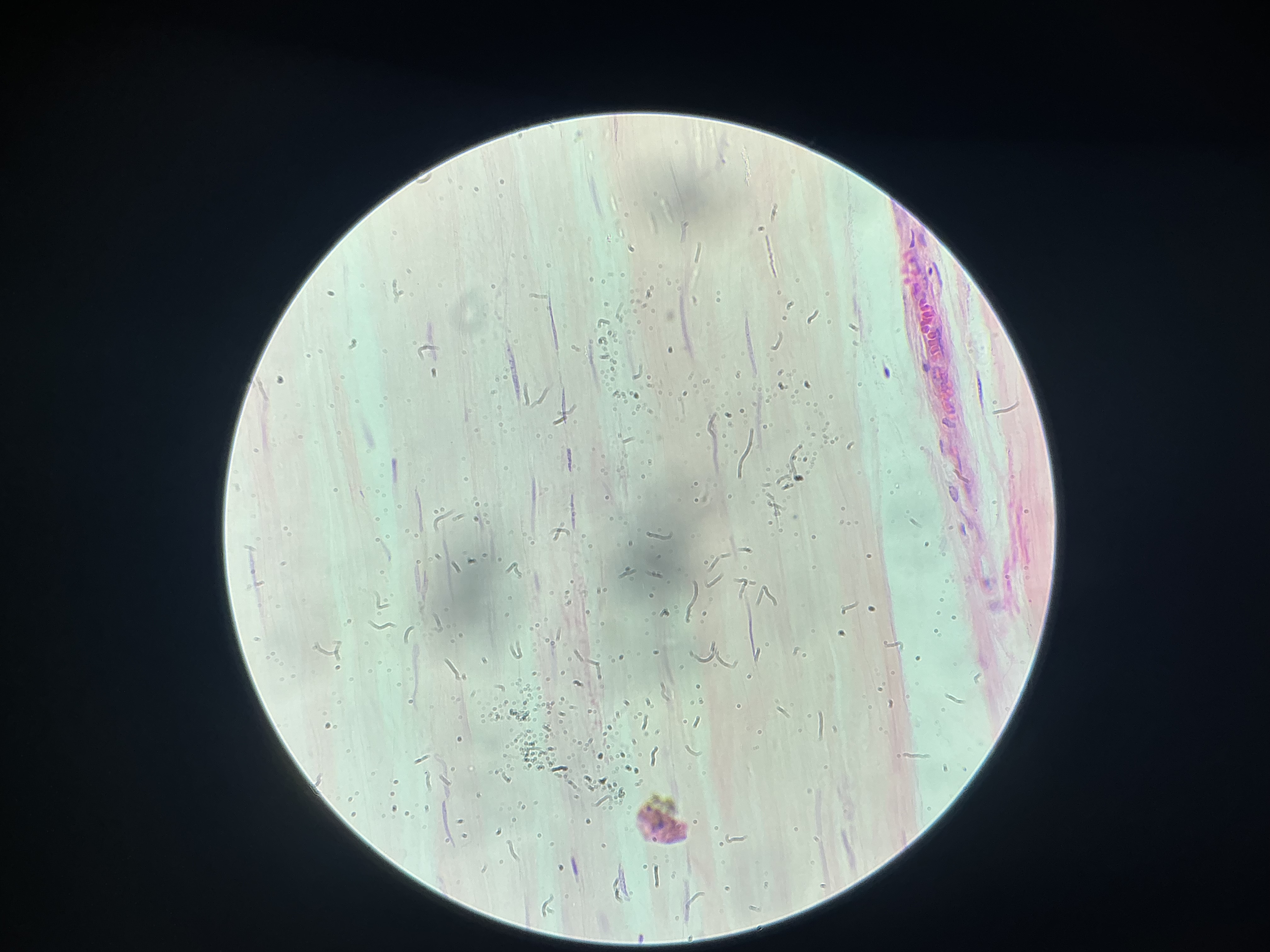
give the locations of this
Tendons
Ligaments
Aponeuroses
Large arteries
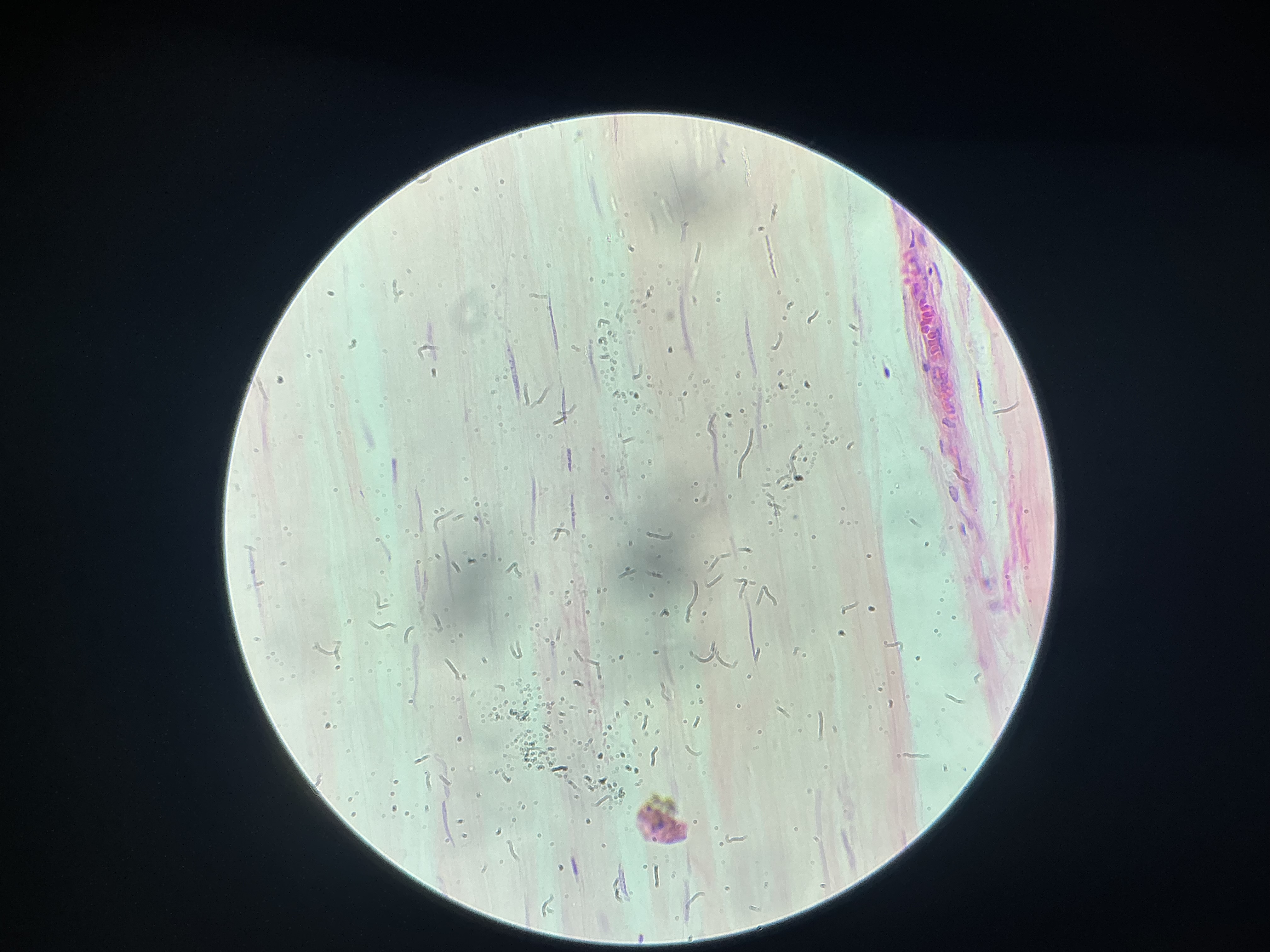
what organ is this?
tendon
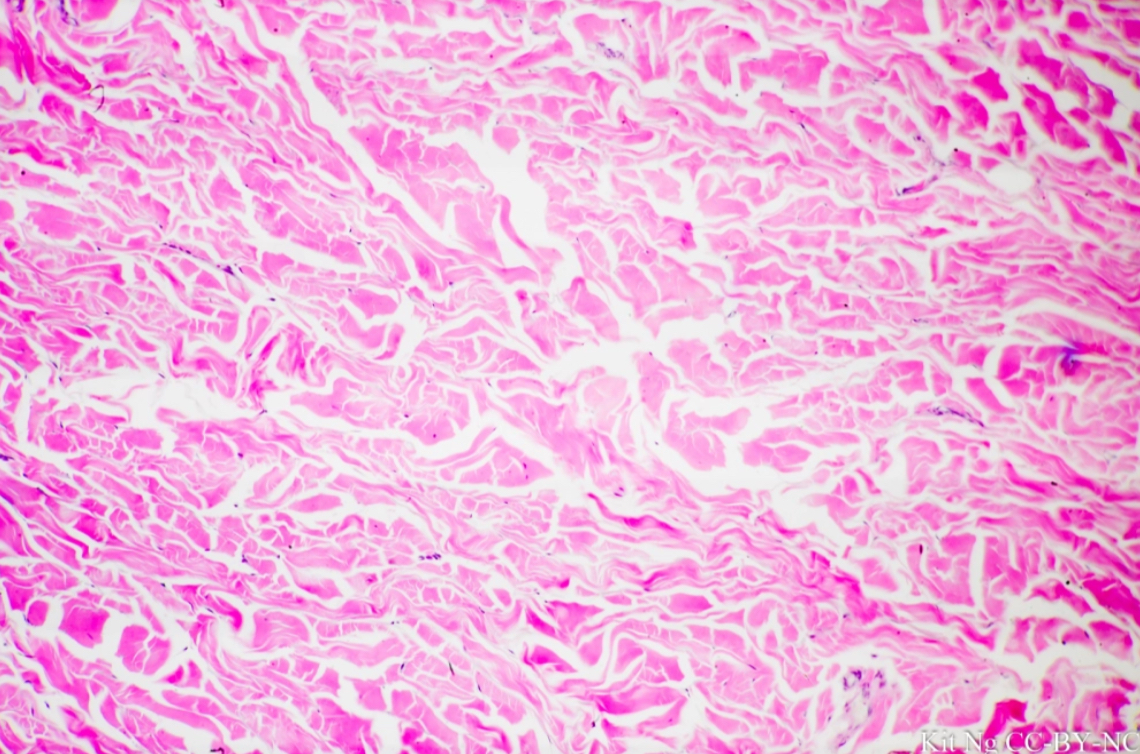
what tissue is this?
dense irregular fibrous tissue
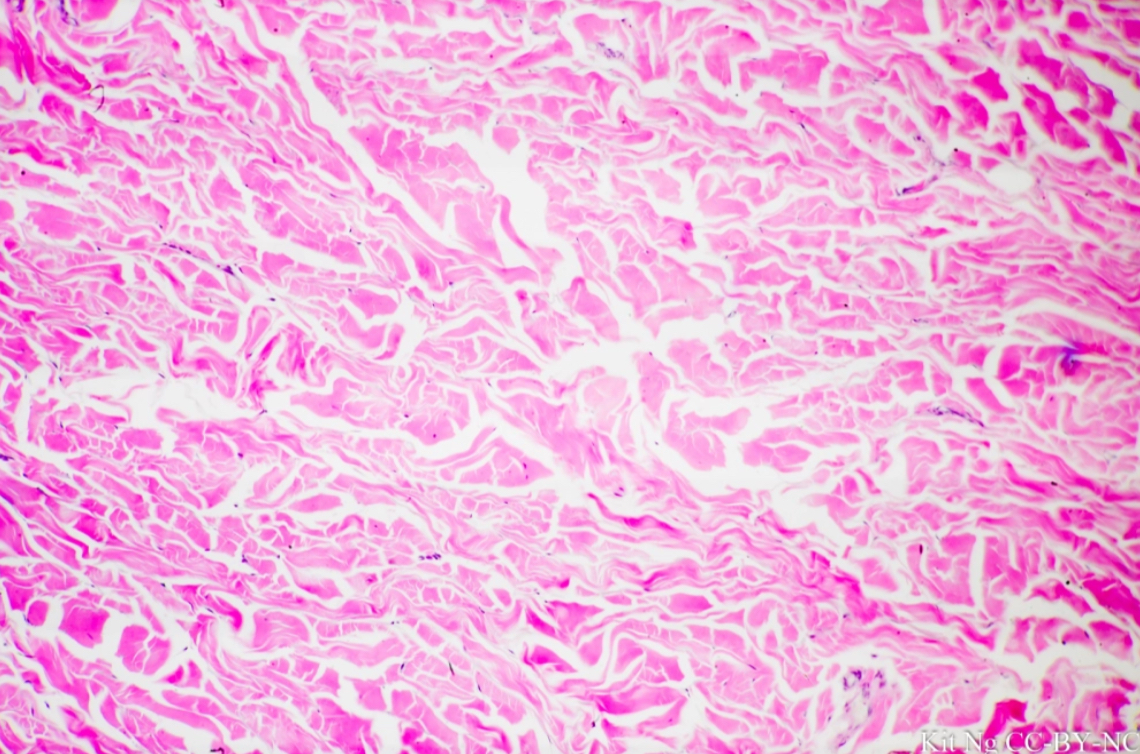
give the functions of this
Connection
Support
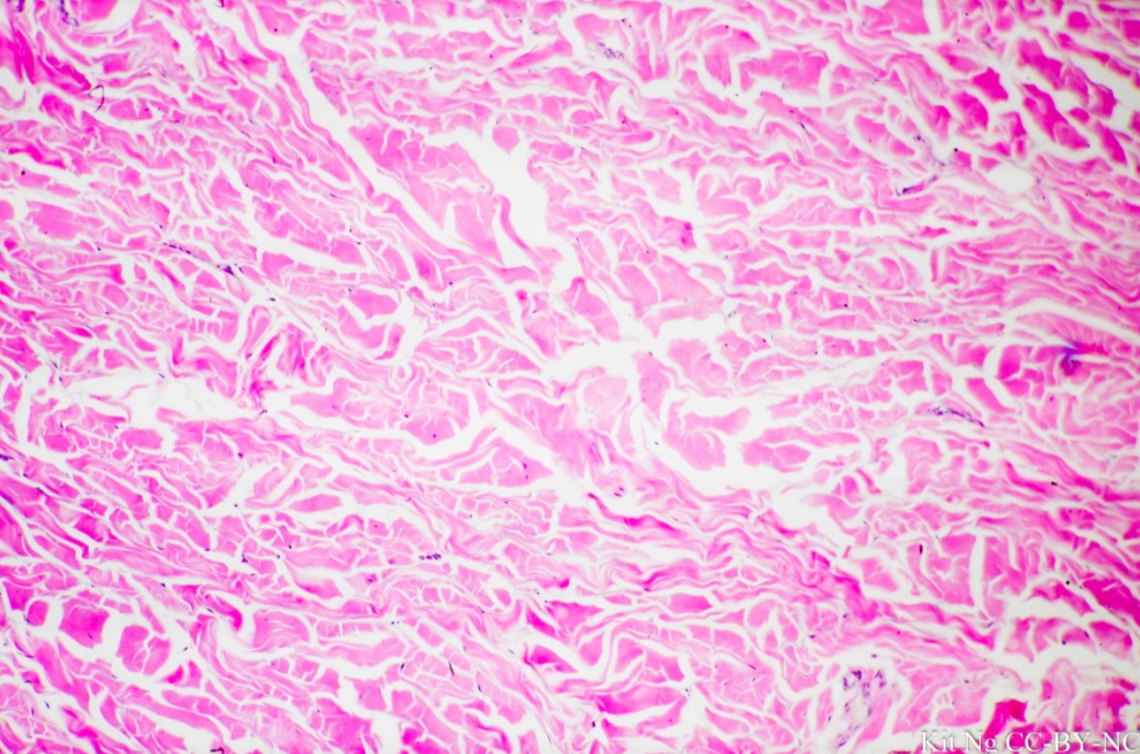
give the locations of this
Deep fascia
Dermis
Scars
Capsule of kidney, etc.
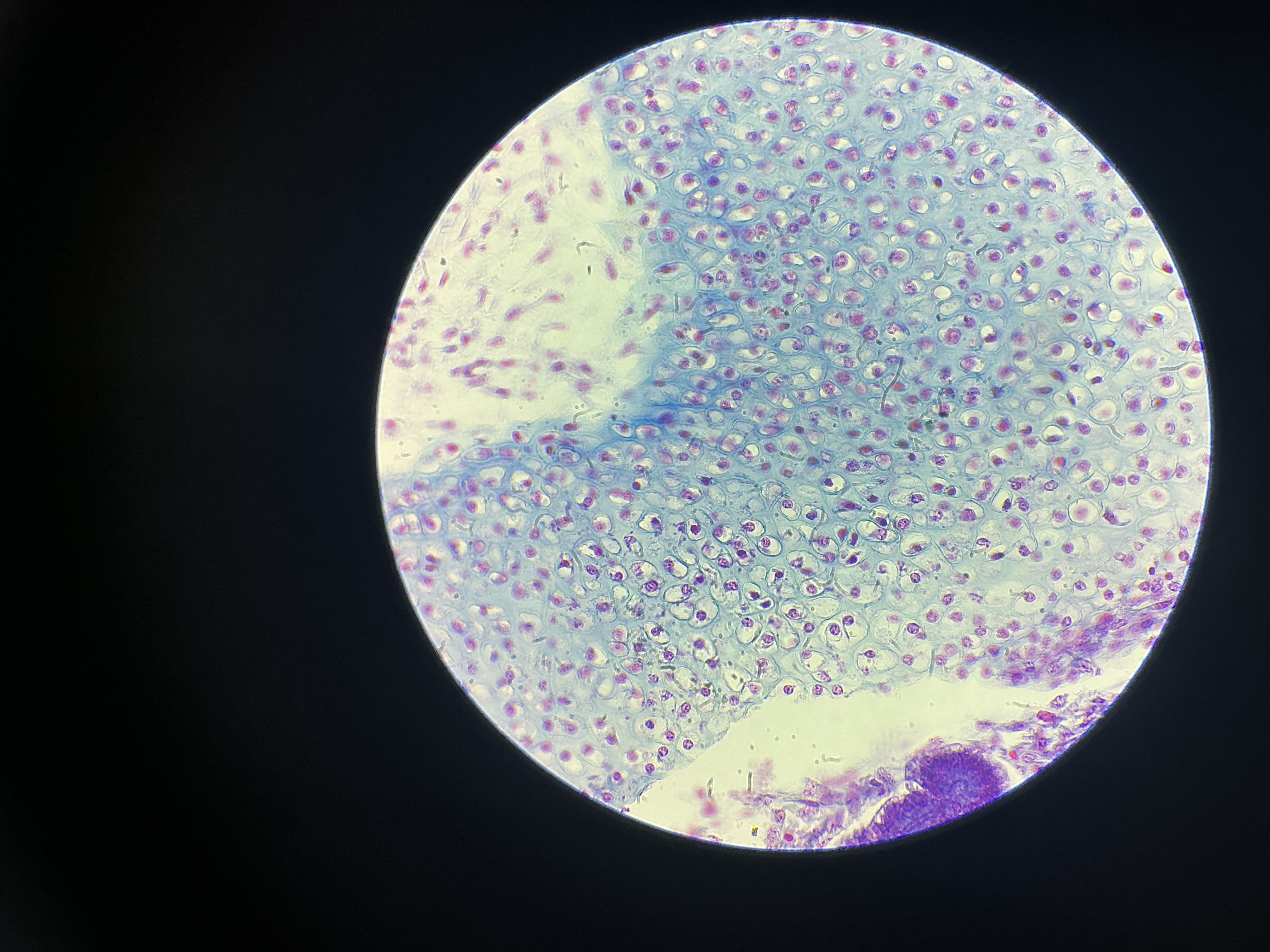
what tissue is this?
hyaline cartilage
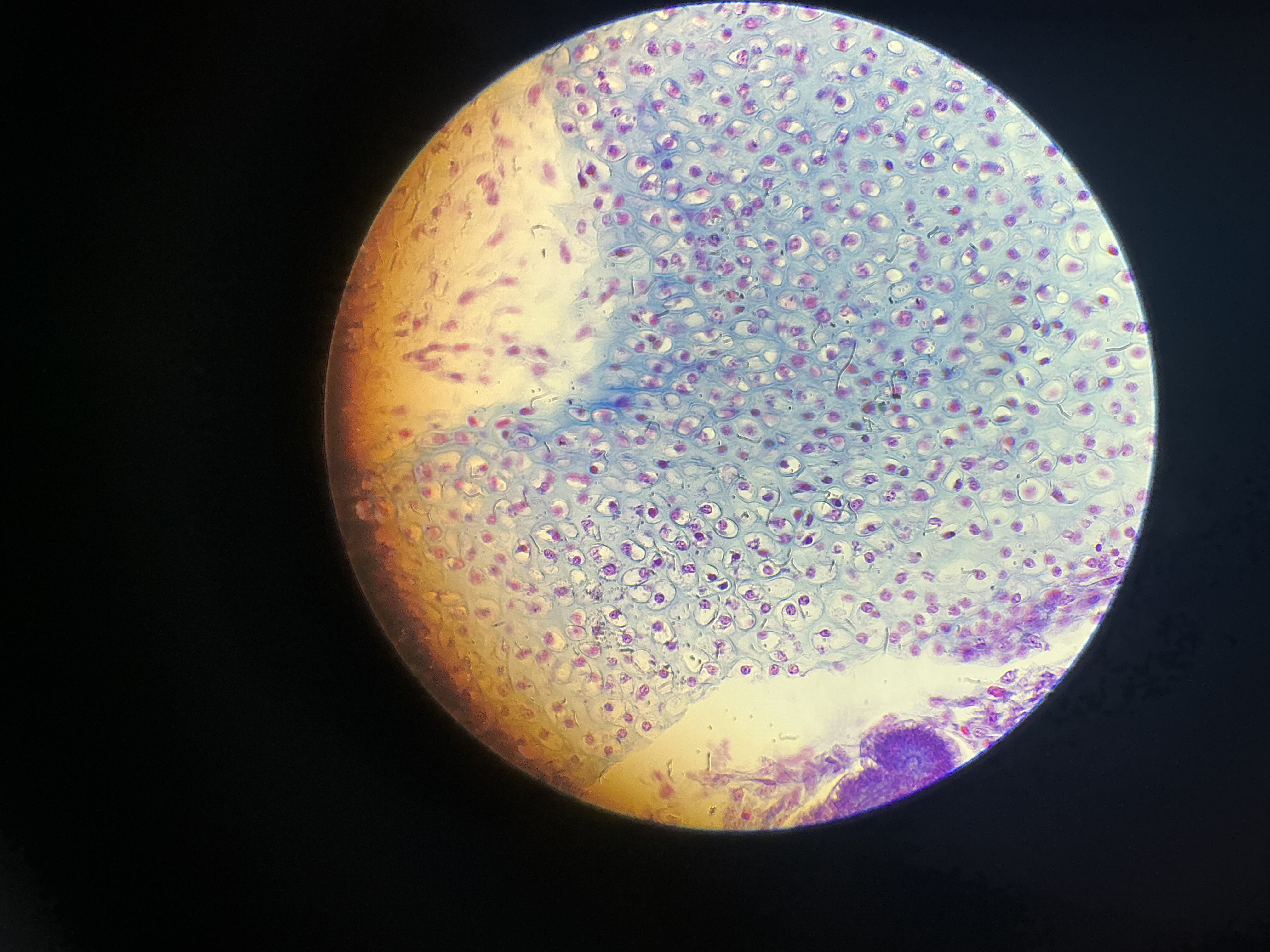
give the functions of this
Firm but flexible support.
Lines your joints and caps the ends of your bones.
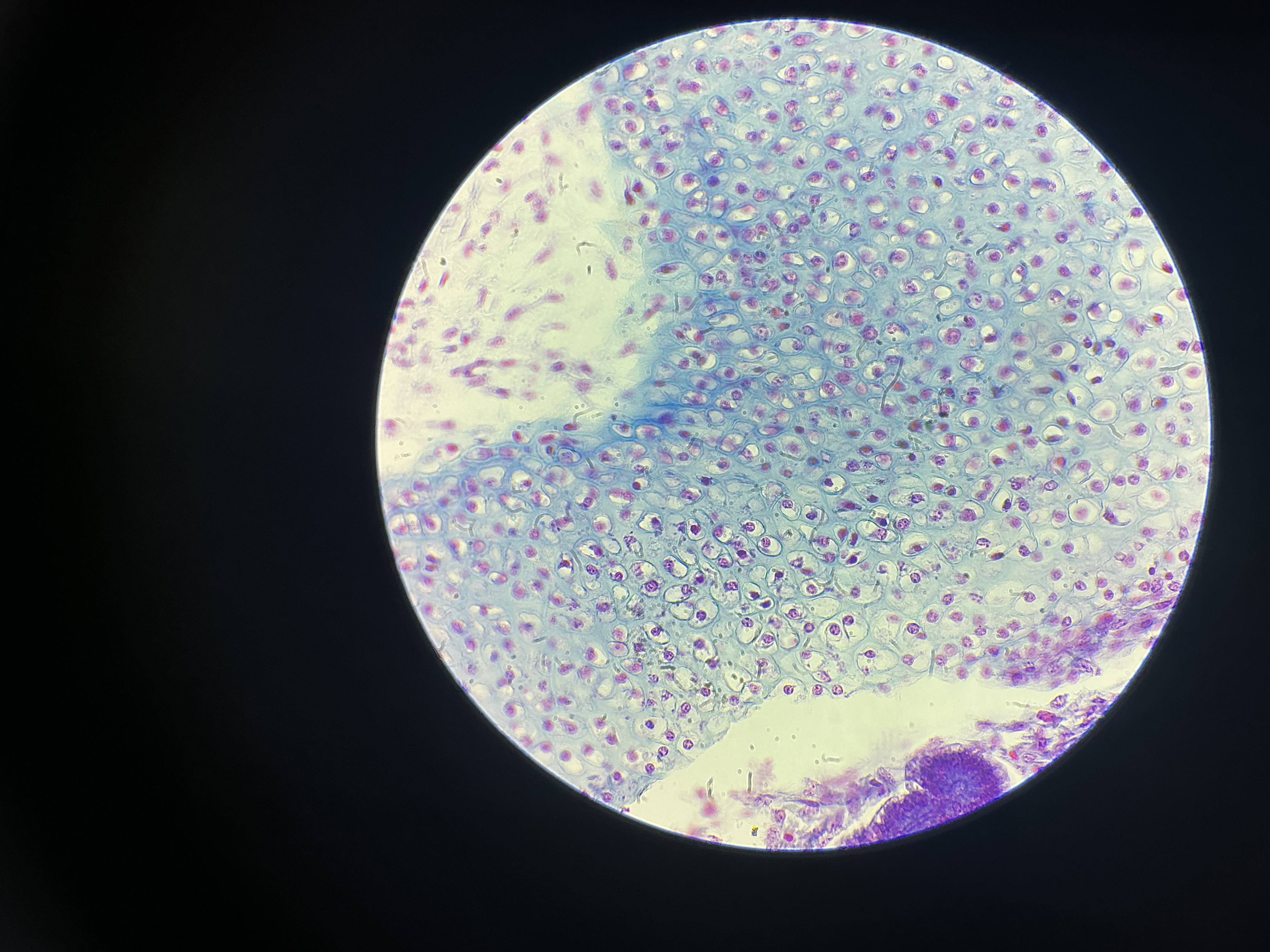
give the locations
Nose
At the ends of long bones and ribs
Larynx
Rings in trachea and bronchi
Entire fetal skeleton before birth
Epiphyseal (growth) plates in long bones
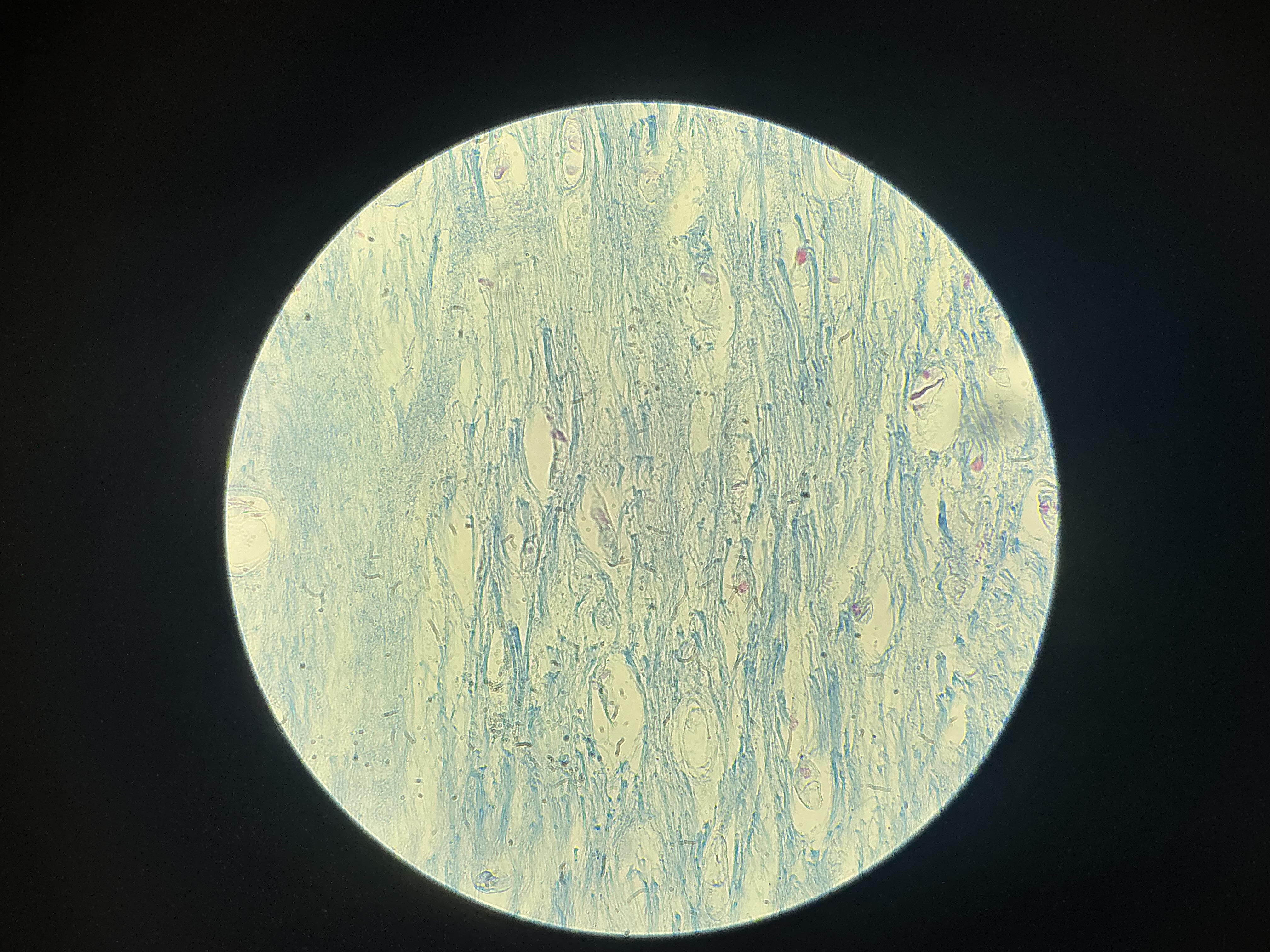
what tissue is this?
fibrocartilage
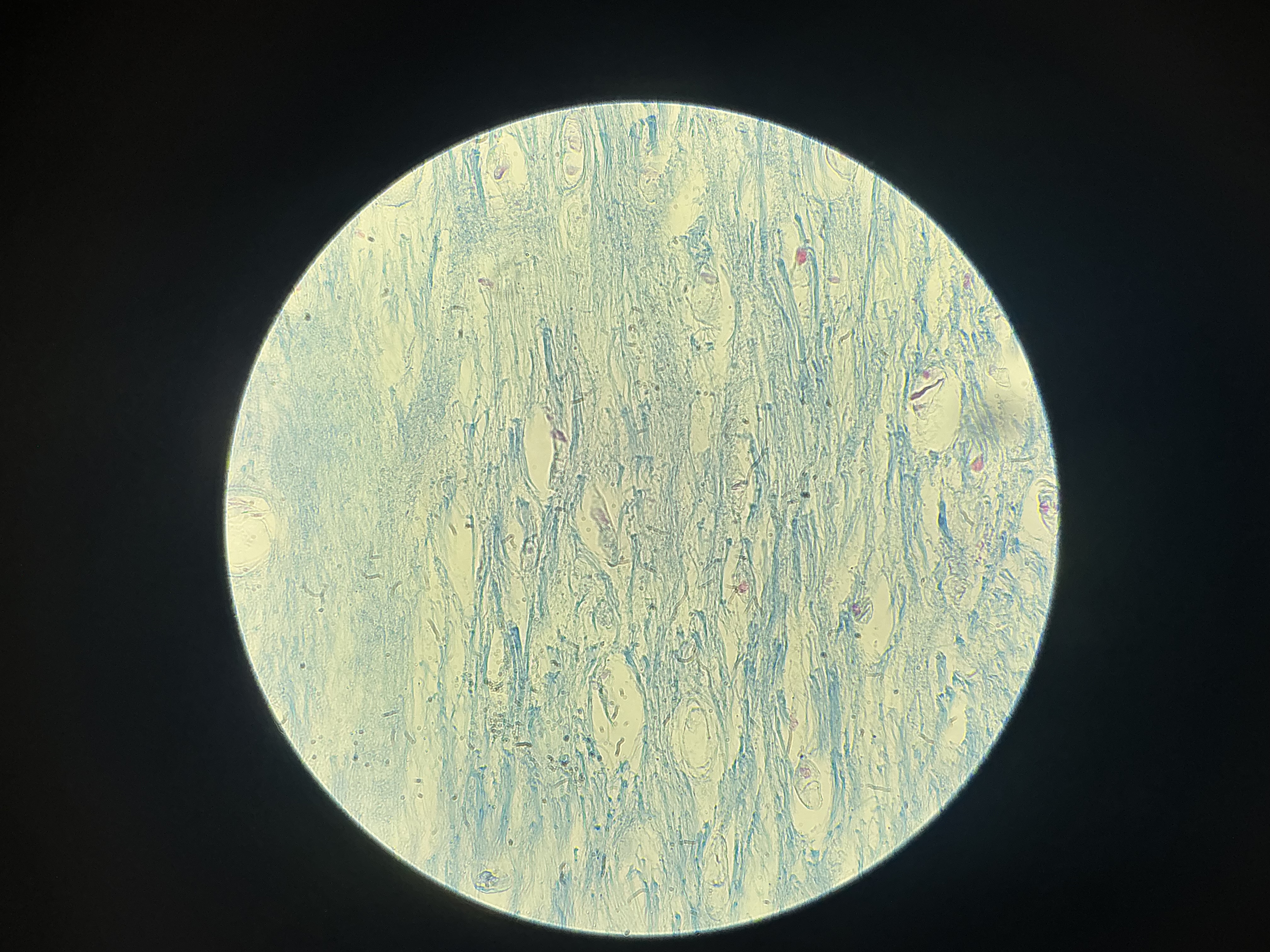
give the functions of this
Shock absorption
Acts as a cushion within joints, where it helps manage compression forces and reduces stress placed on joints.
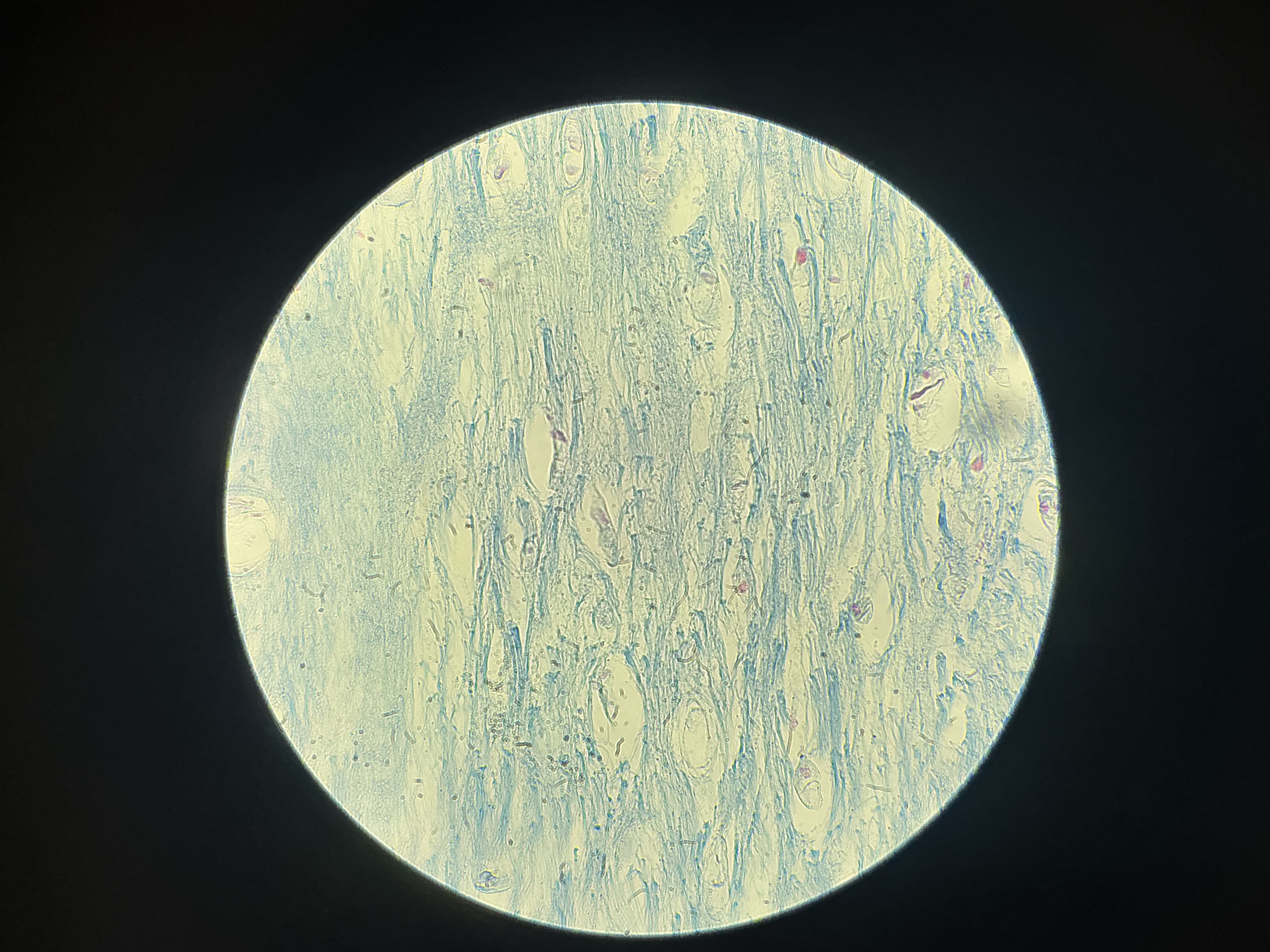
give the locations
Found in structures than can withstand tension and pressure:
Joints
Vertebrae
Wedges found in the knee joint
Symphysis pubis
Forms cushion-like discs between vertebrae of the spinal column.
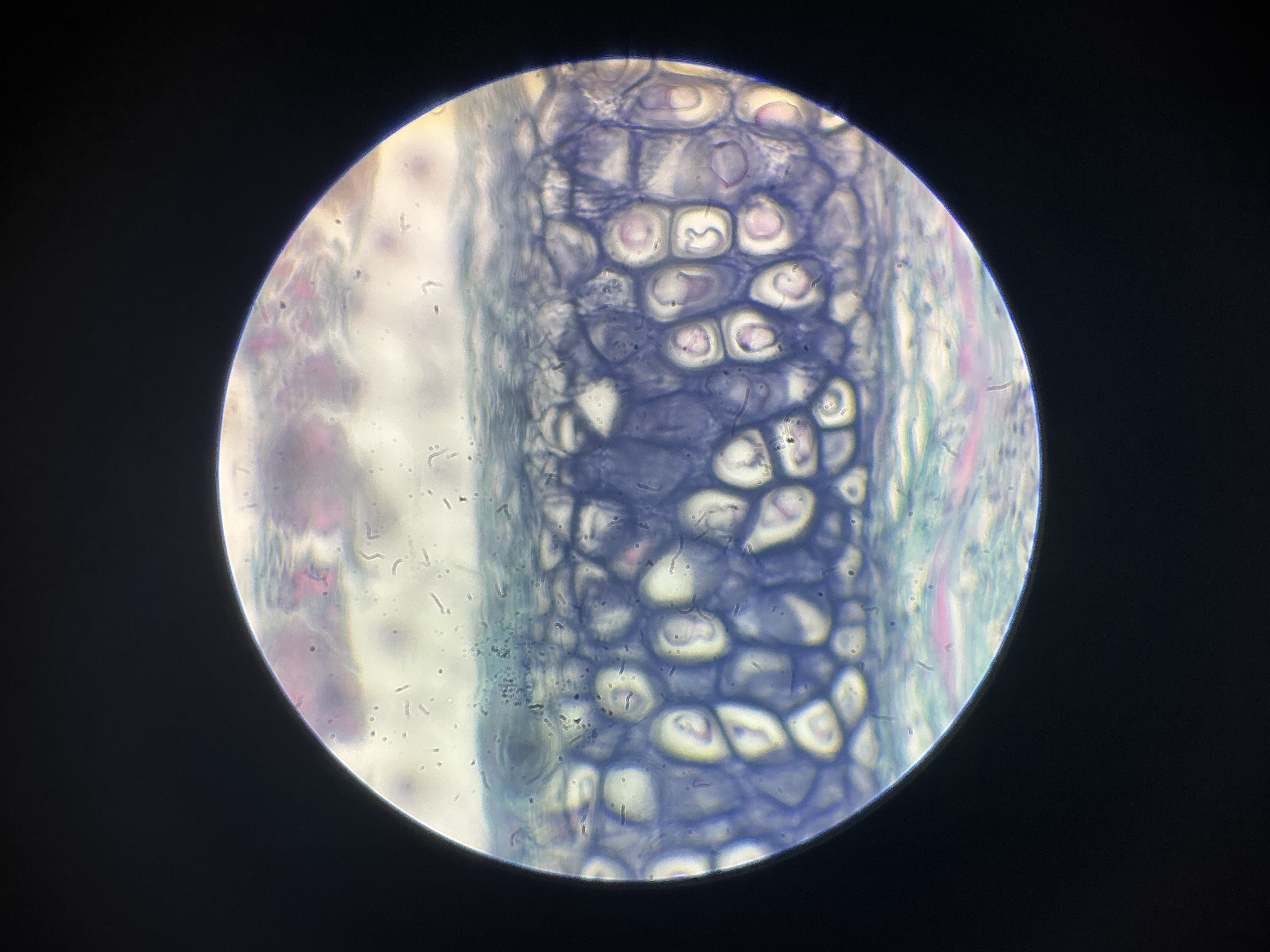
what tissue is this?
elastic cartilage
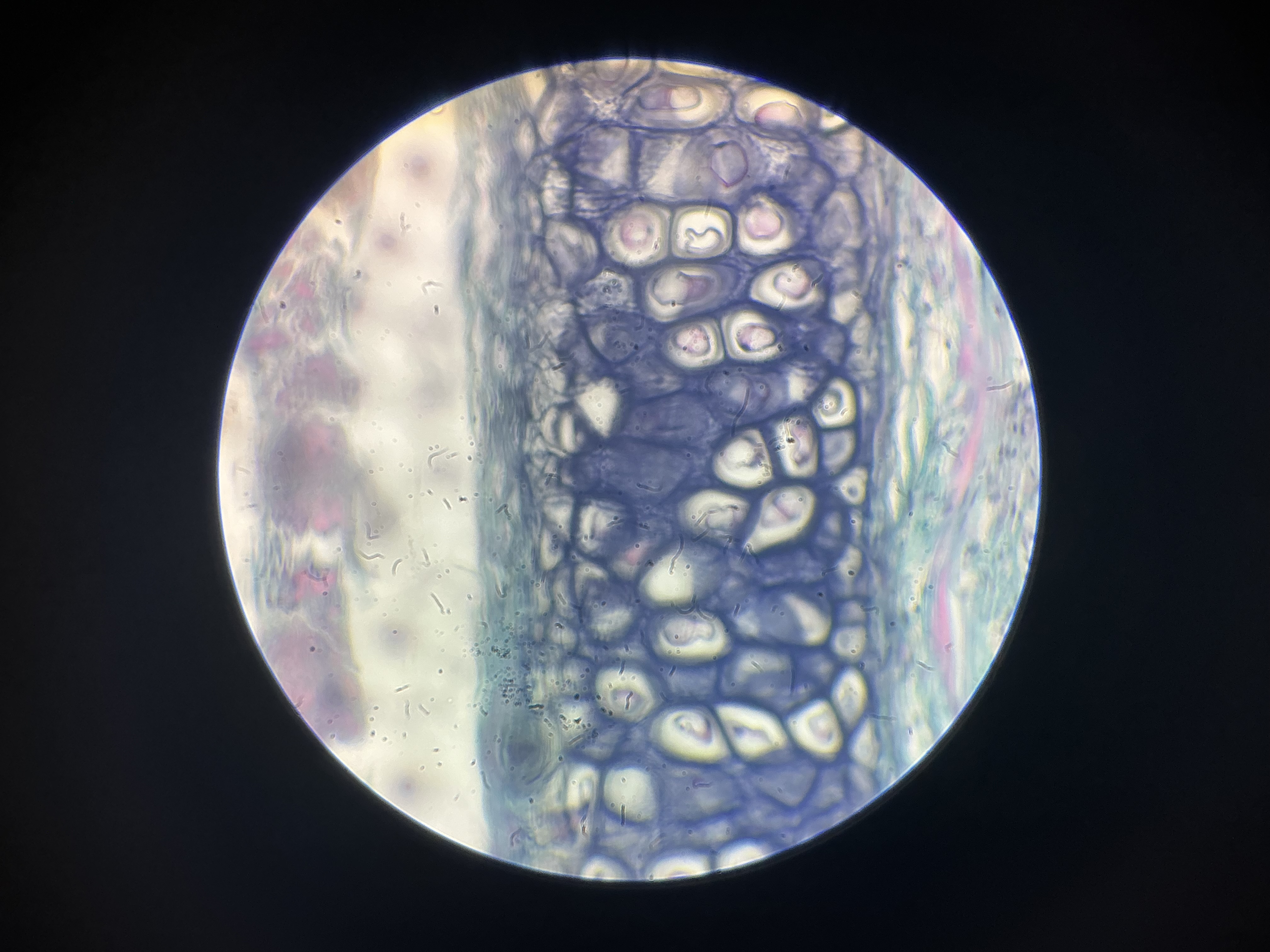
give the function of this
Supports parts of your body that need to bend and move to function.
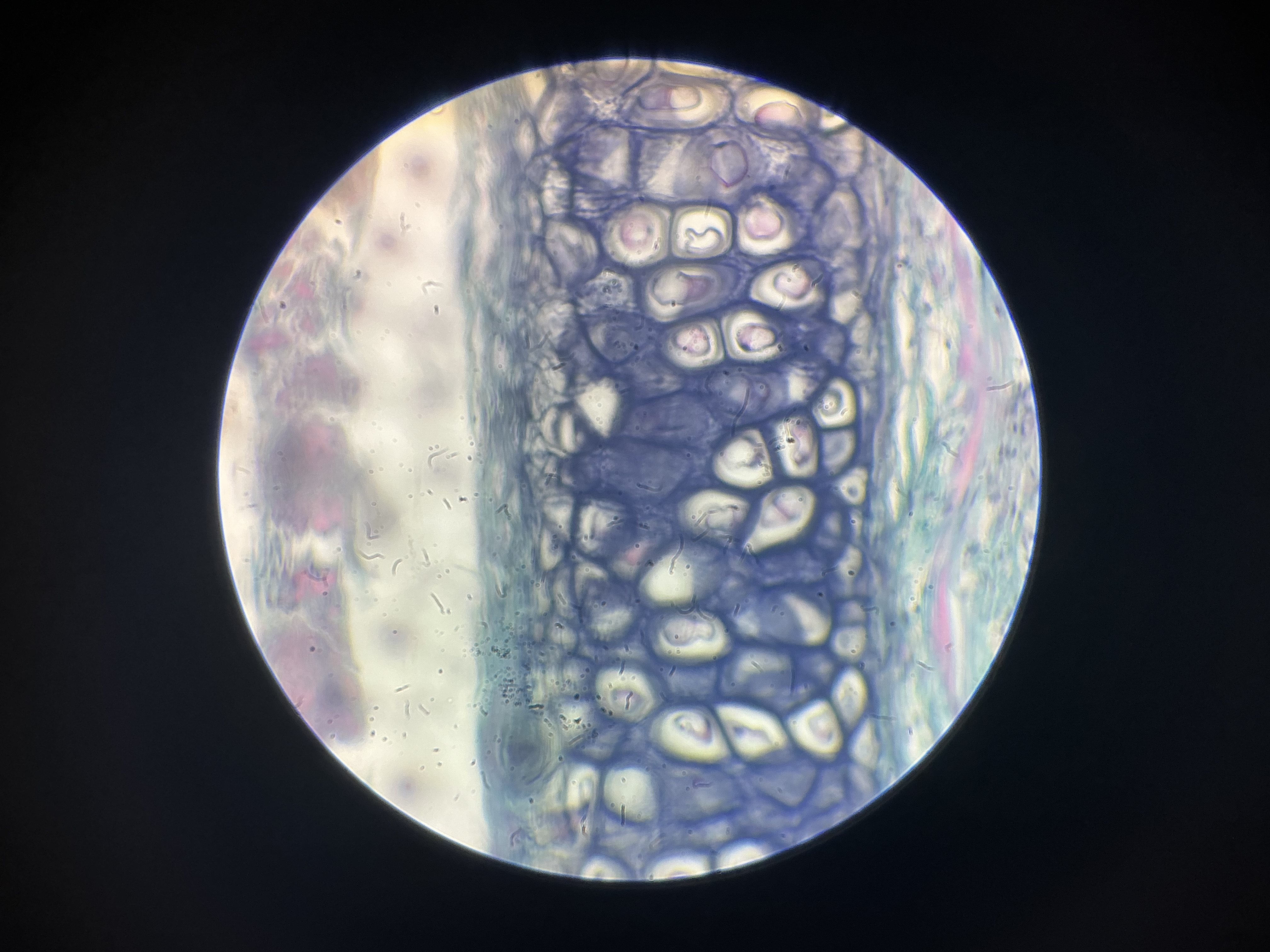
give the locations
Found in structures in which springiness is desirable in the support material.
Outer ear
Auditory tube
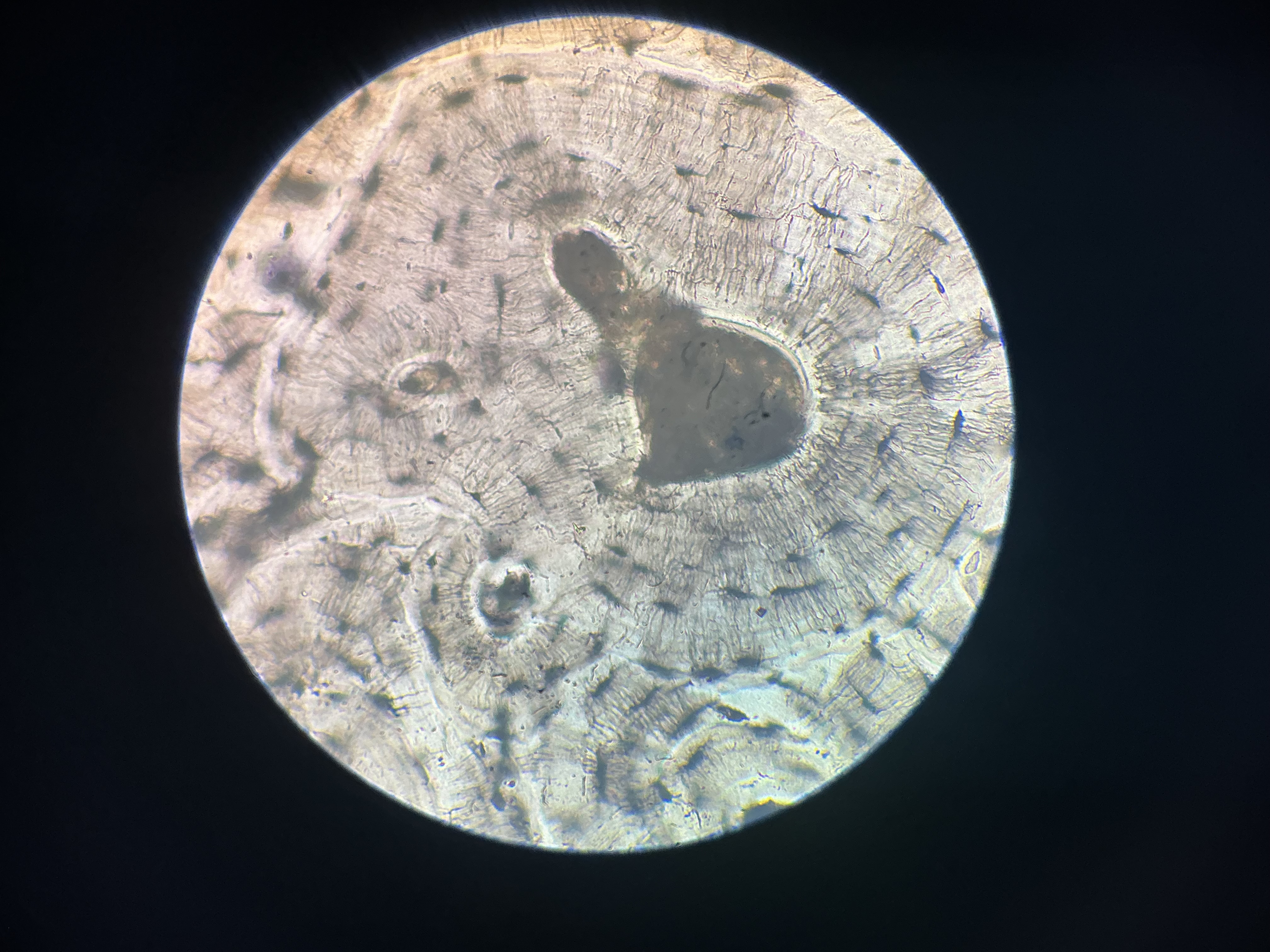
what tissue is this?
compact bone
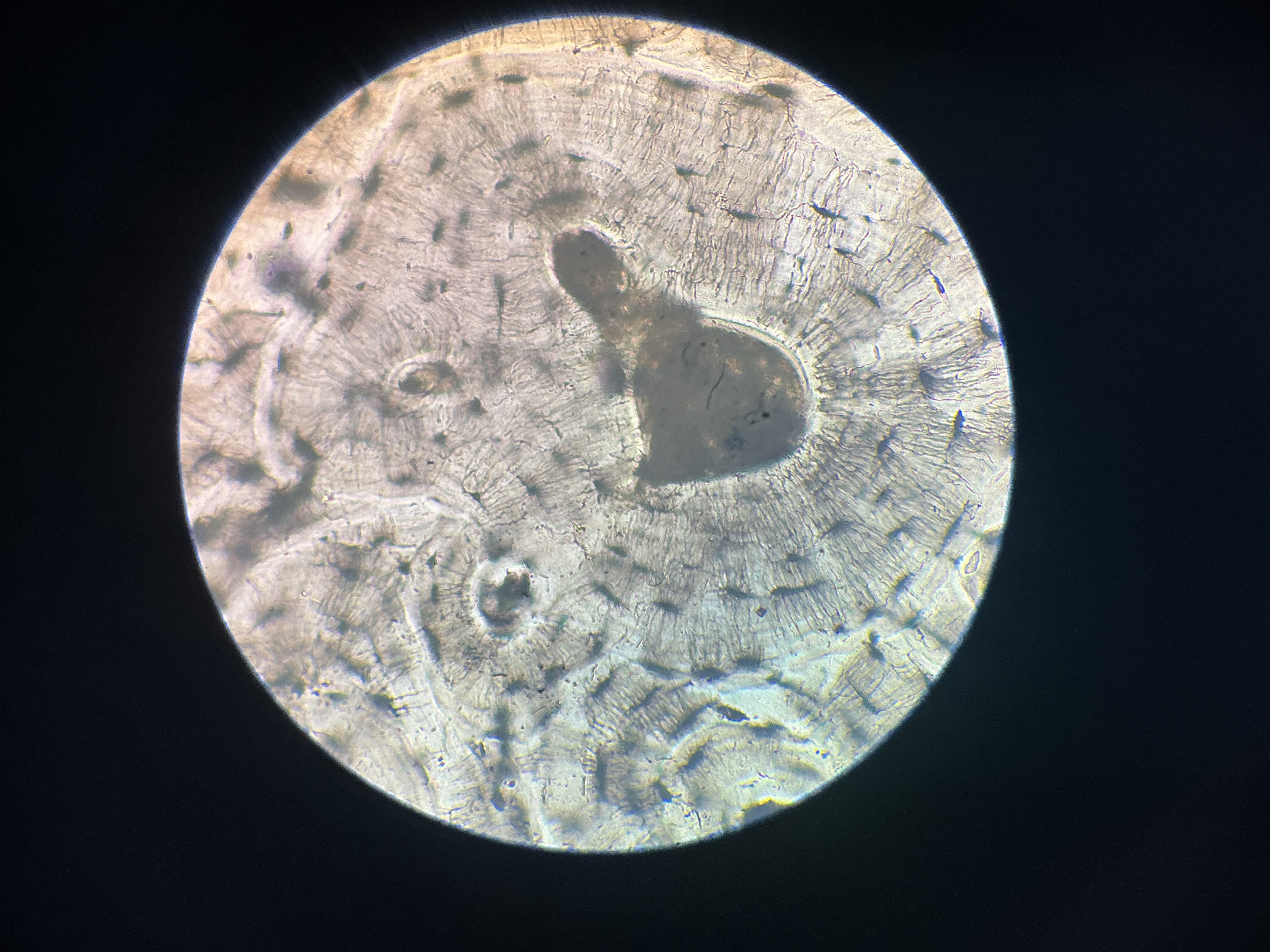
give the functions of this
Support
Protection
Calcium reservoir
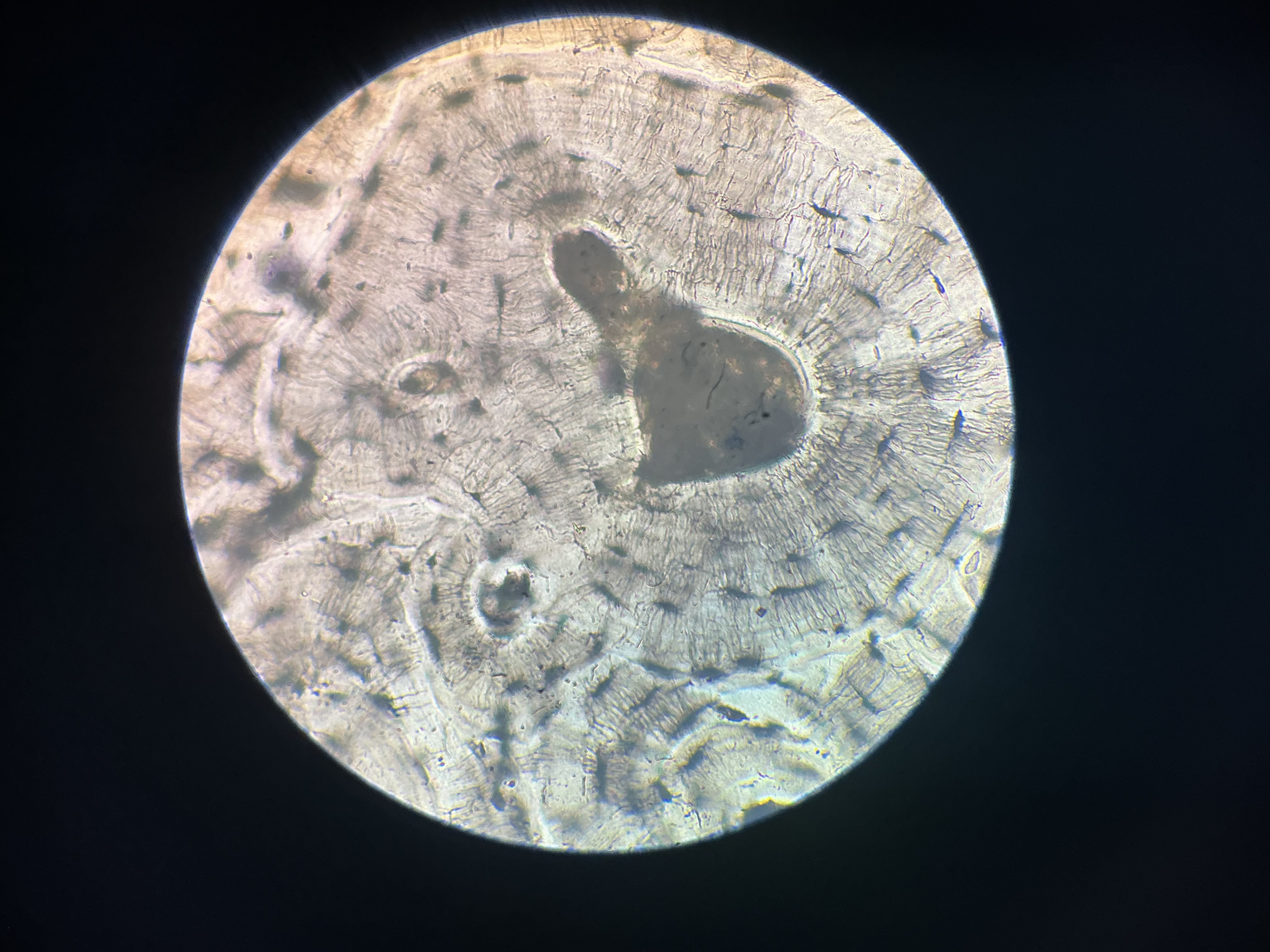
give the location
skeleton
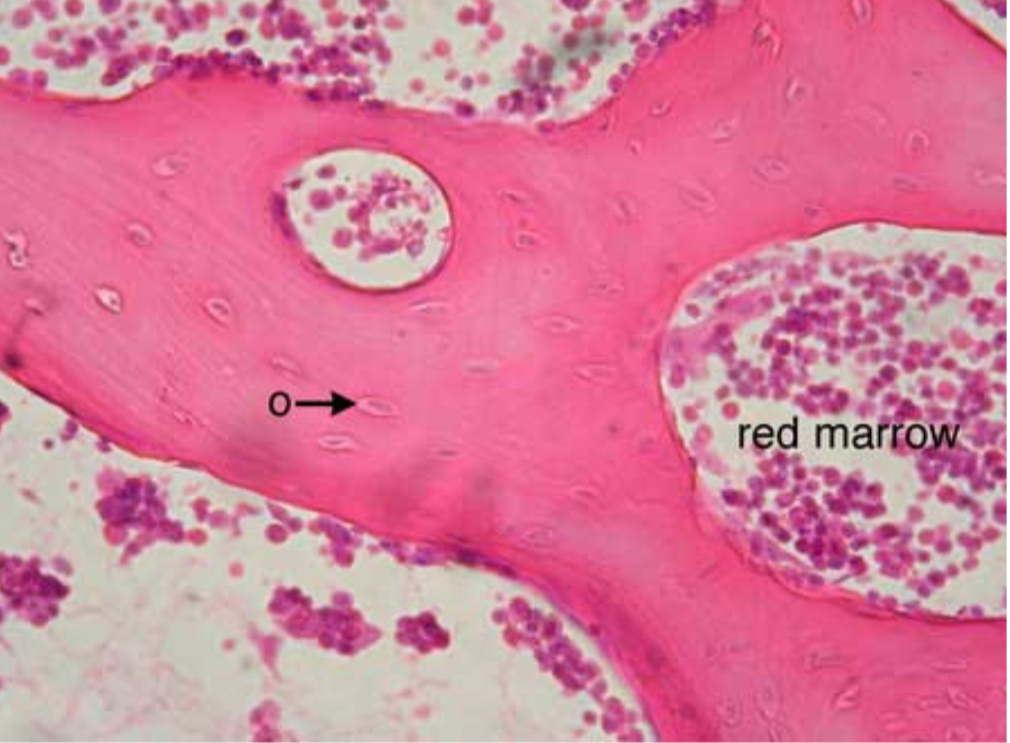
what tissue is this?
cancellous bone
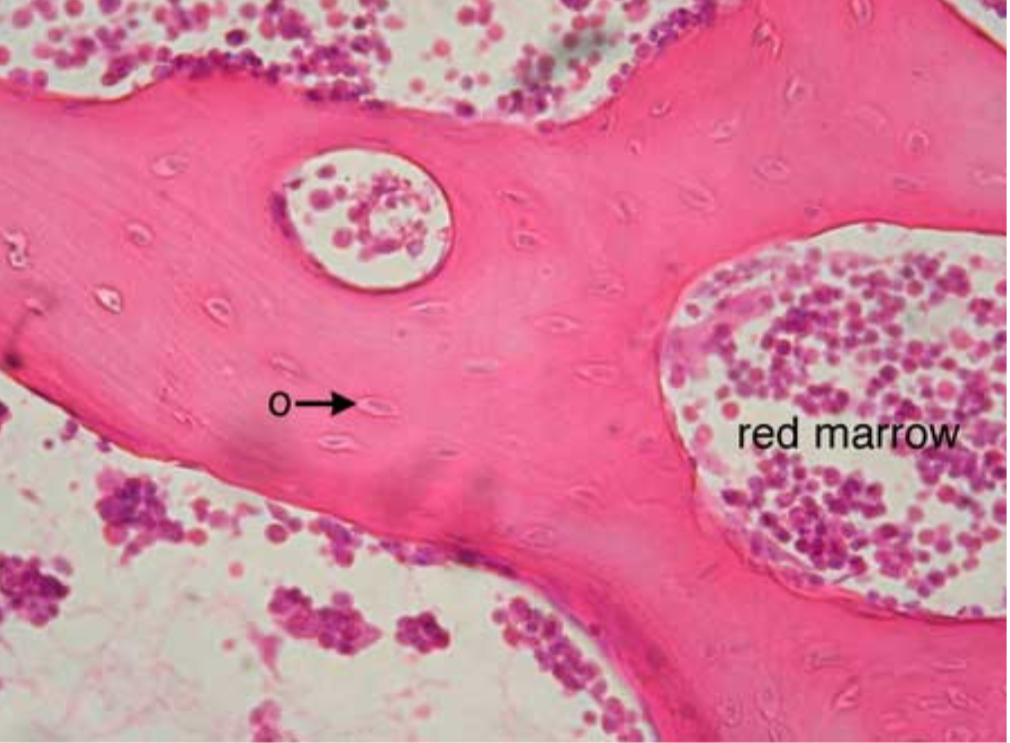
give the function of this
Support of bone marrow
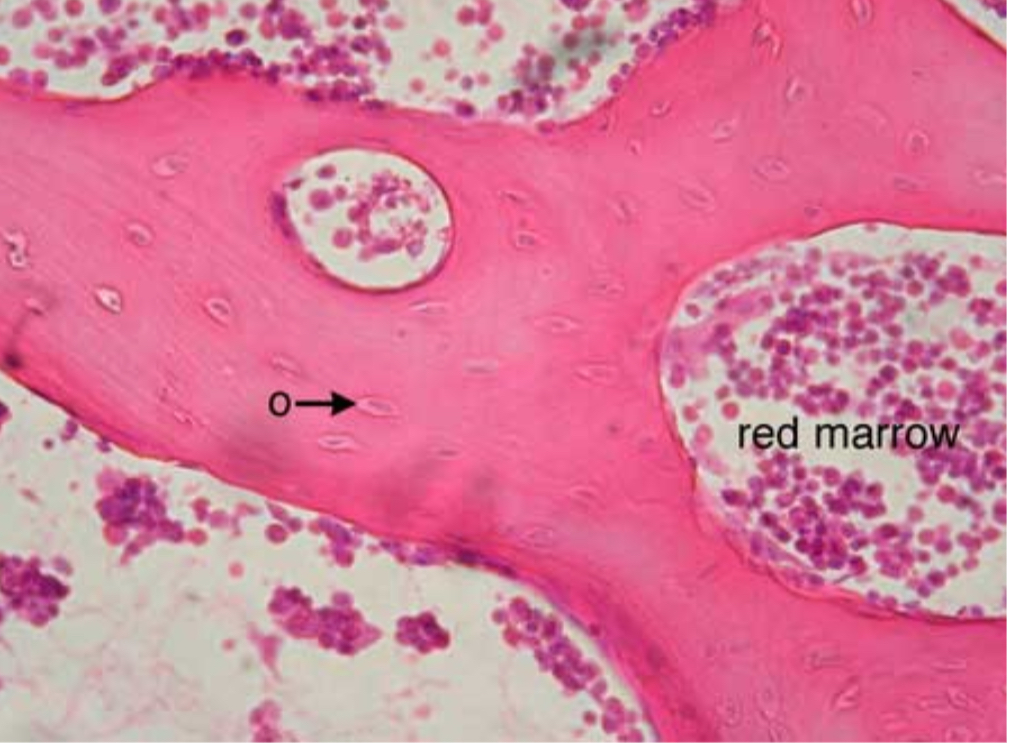
give the location
skeleton
what tissue is this?
osseous tissue/blood tissue
give the functions of this
Transport nutrients and oxygen.
Removes carbon dioxide and other wastes.
Protects the body (immunity and clot to present fluid loss).
Helps to regulate body temperature.
give the location
blood vessels in the body
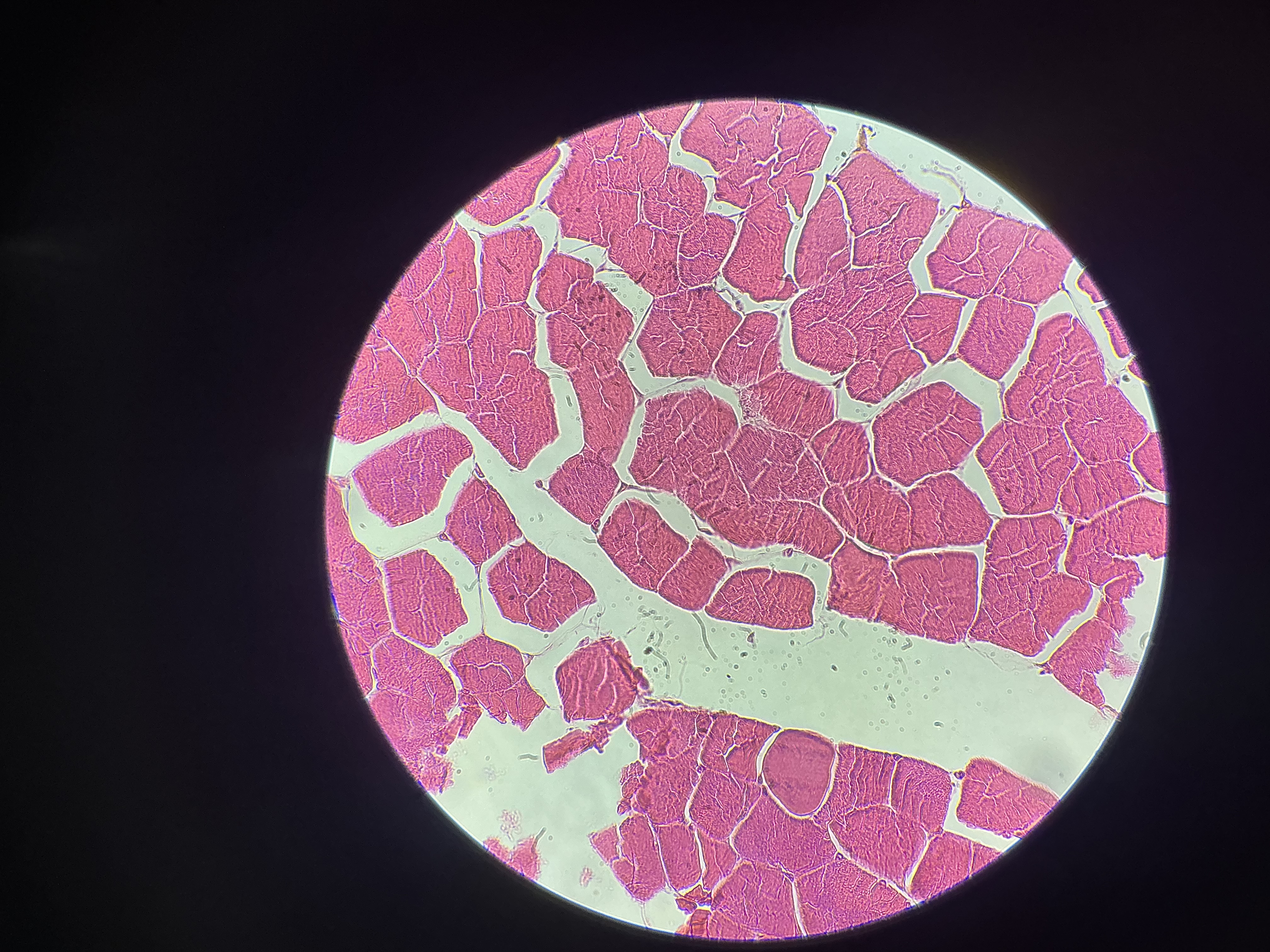
what tissue is this?
skeletal muscle
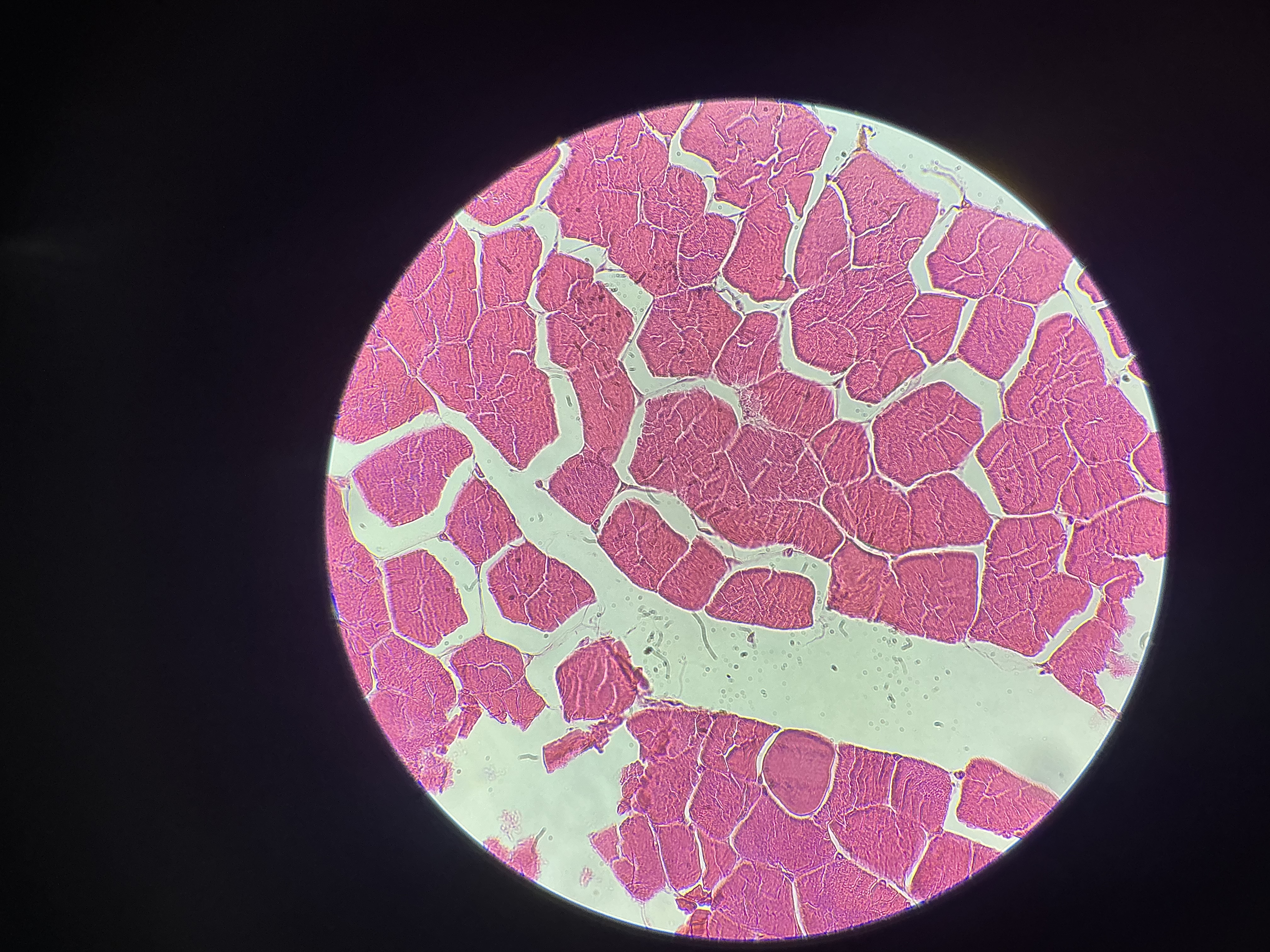
give the functions
Forms muscular organs that attach to the skeleton and move its parts.
Guards entrance or exit to the digestive tract.
Generates heat.
Protects internal organs.
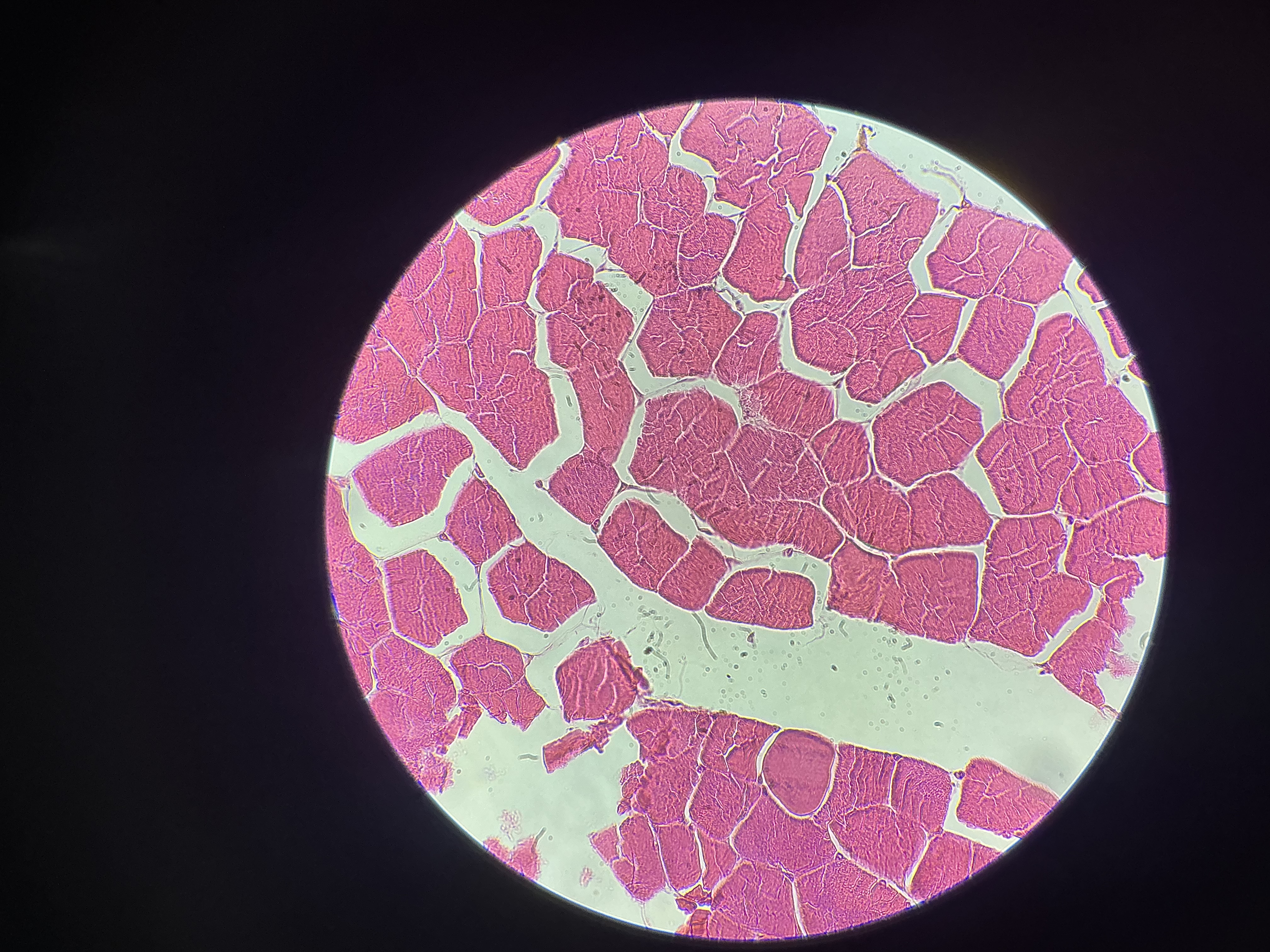
give the locations
Muscles that attach to bones
Extrinsic eyeball muscles
Upper third of esophagus
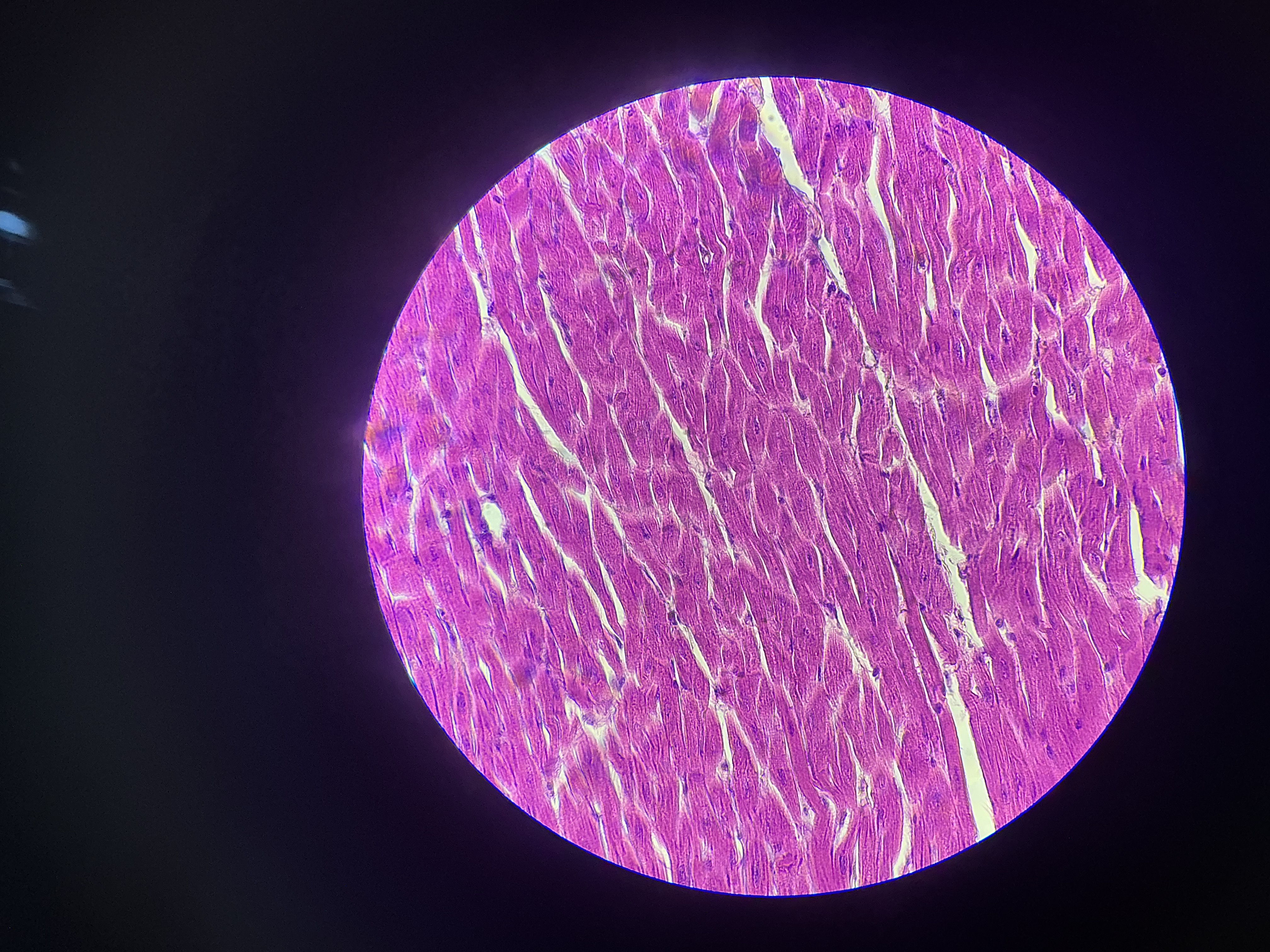
what tissue is this?
cardiac muscle
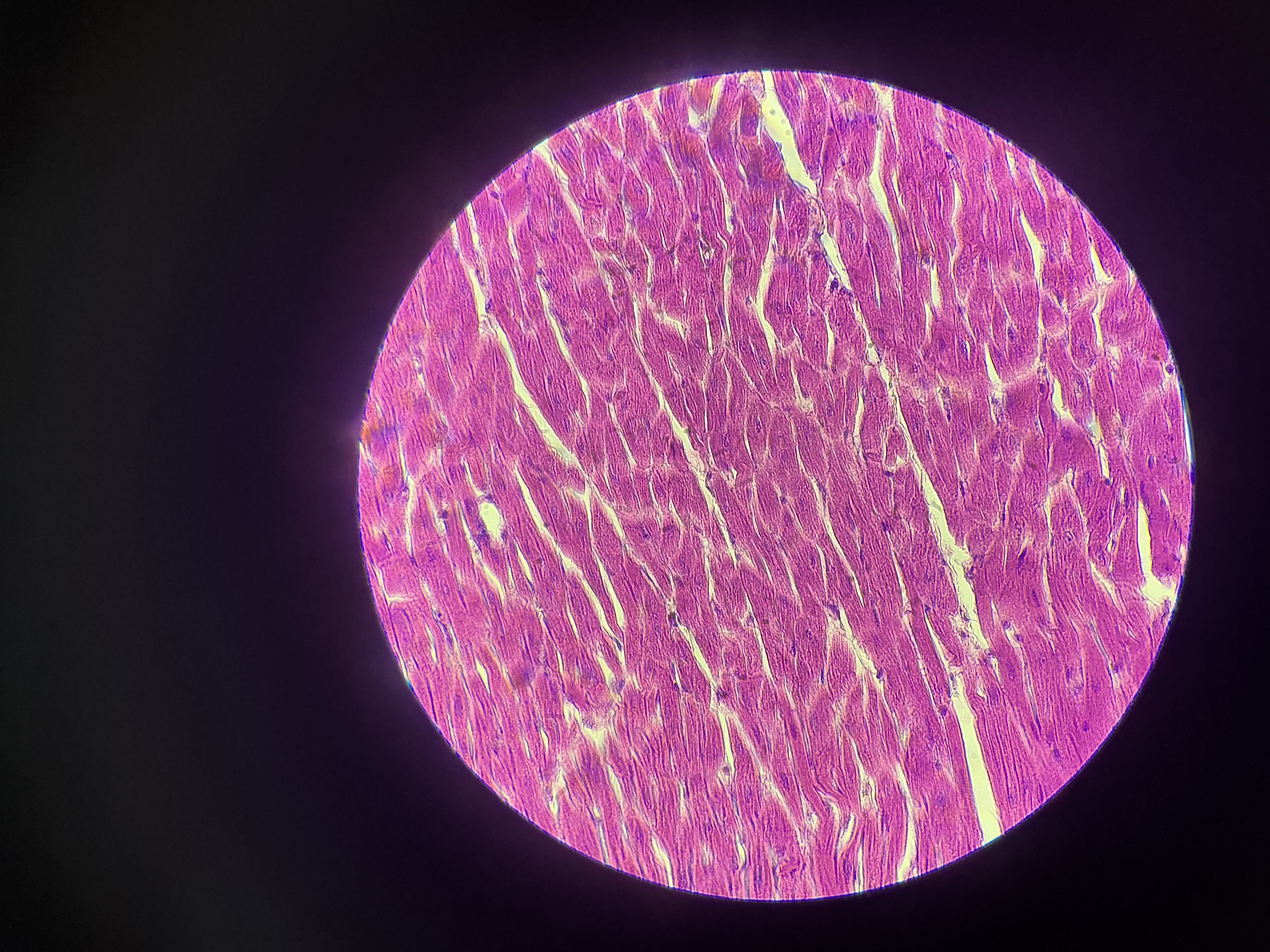
give the functions
Circulation of blood
Maintenance of blood pressure
Contraction of heart
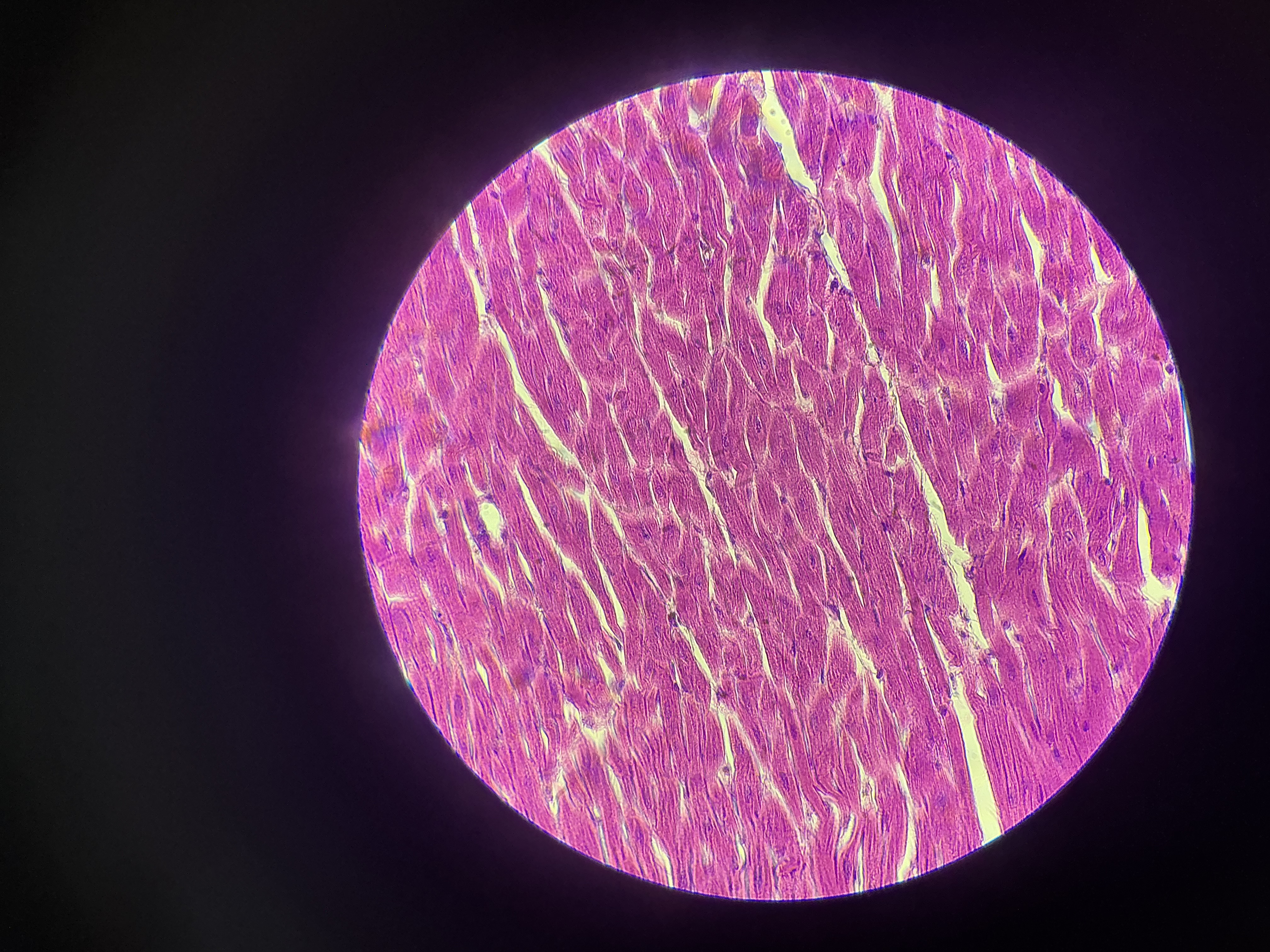
give the location
found only in the walls of the heart
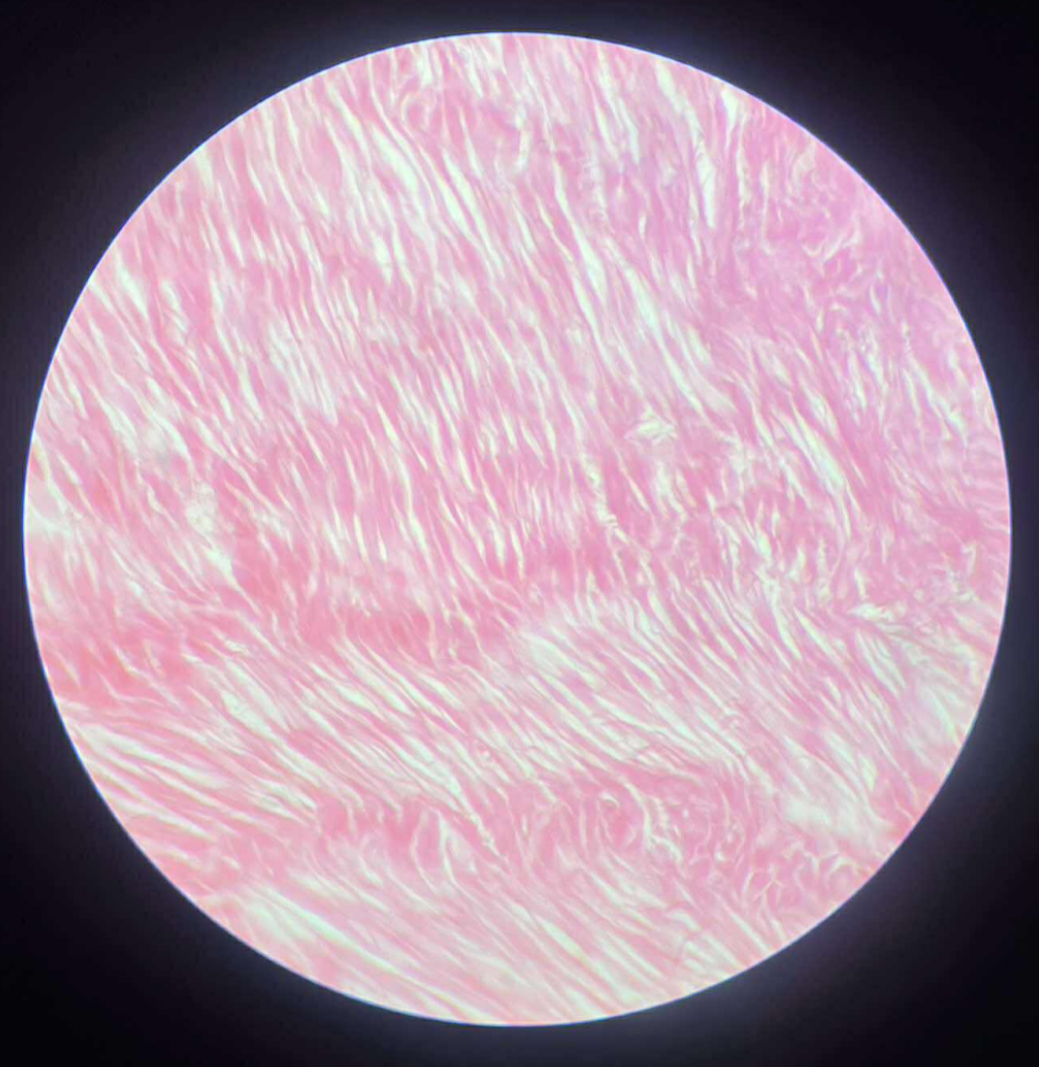
what tissue is this?
smooth muscle
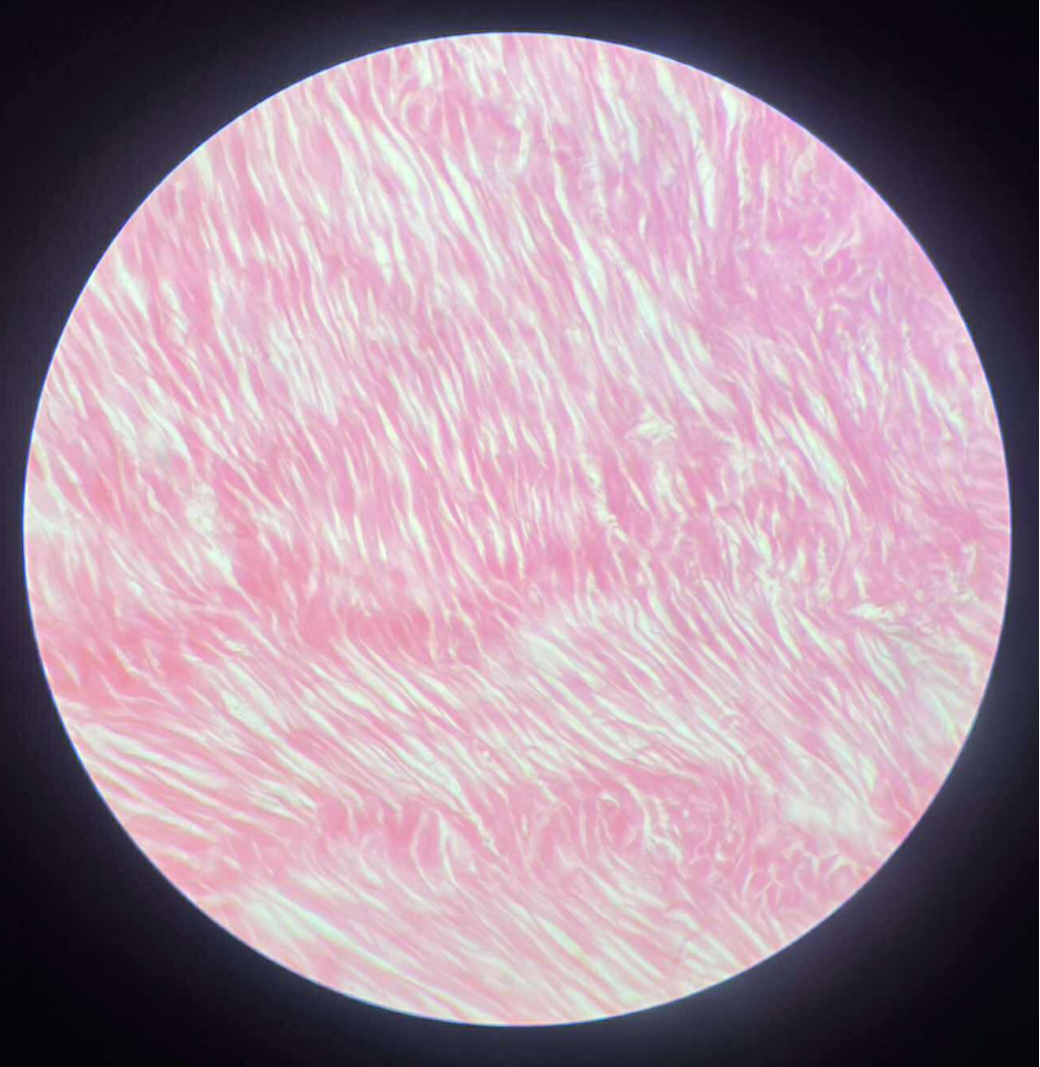
give the functions
Movement of substances along respective tracts.
Change diameter of blood vessels, thereby aiding in regulation of blood pressure.
Movement of substances along ducts.
Change diameter of pupils and shape of lens.
Erection of hairs
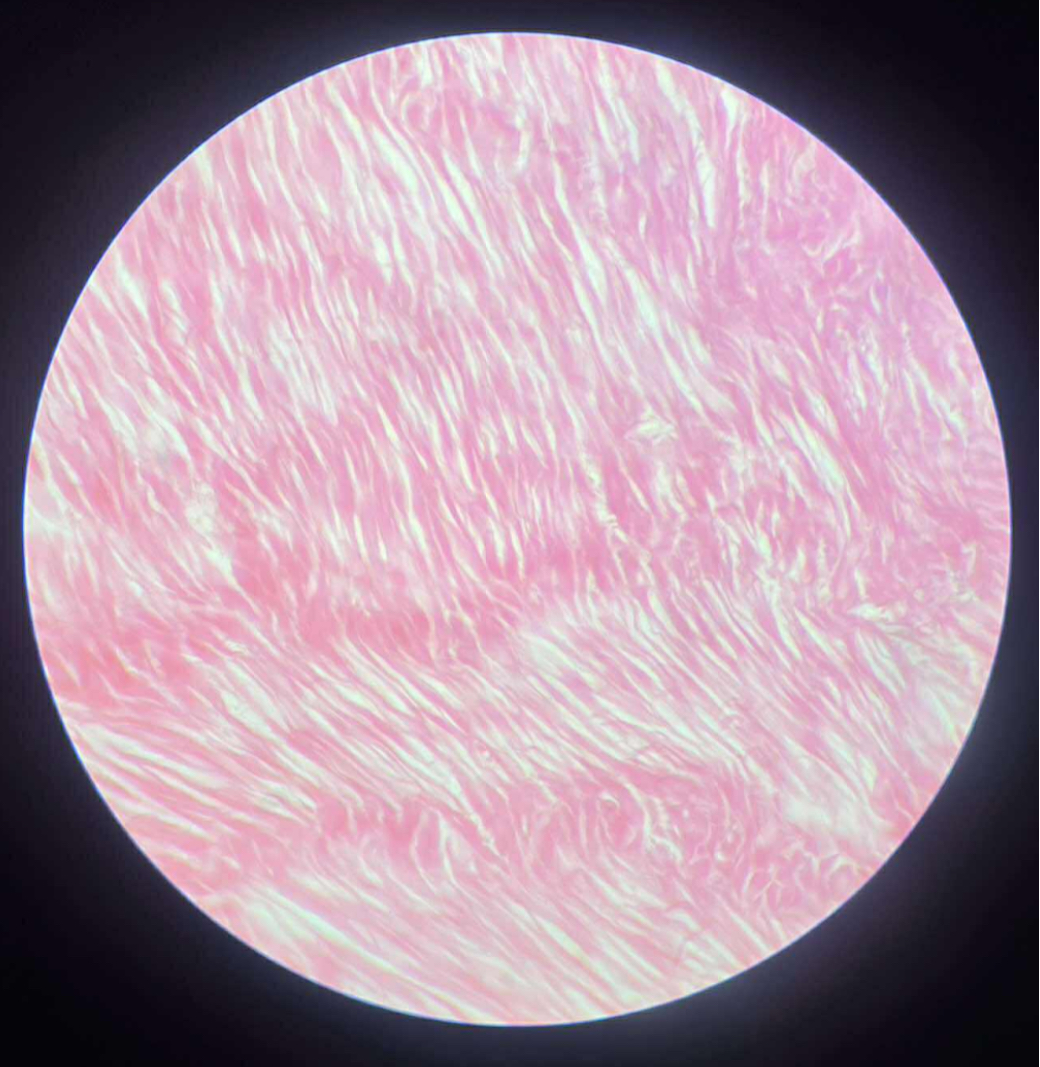
give the locations
Walls of hollow organs, such as digestive organs and blood vessels.
Hollow organs: stomach, uterus, blood vessels.
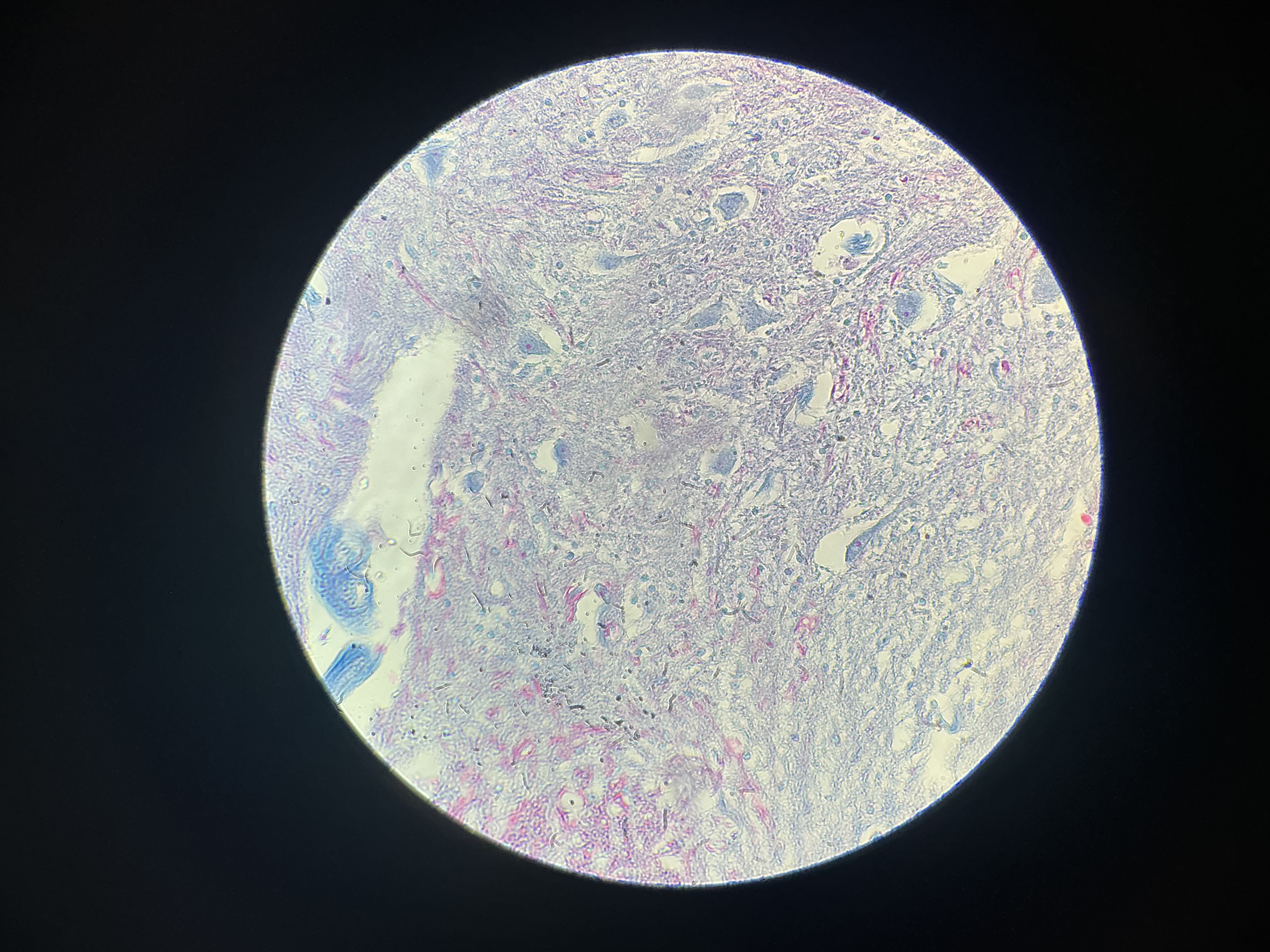
what tissue is this?
nervous tissue
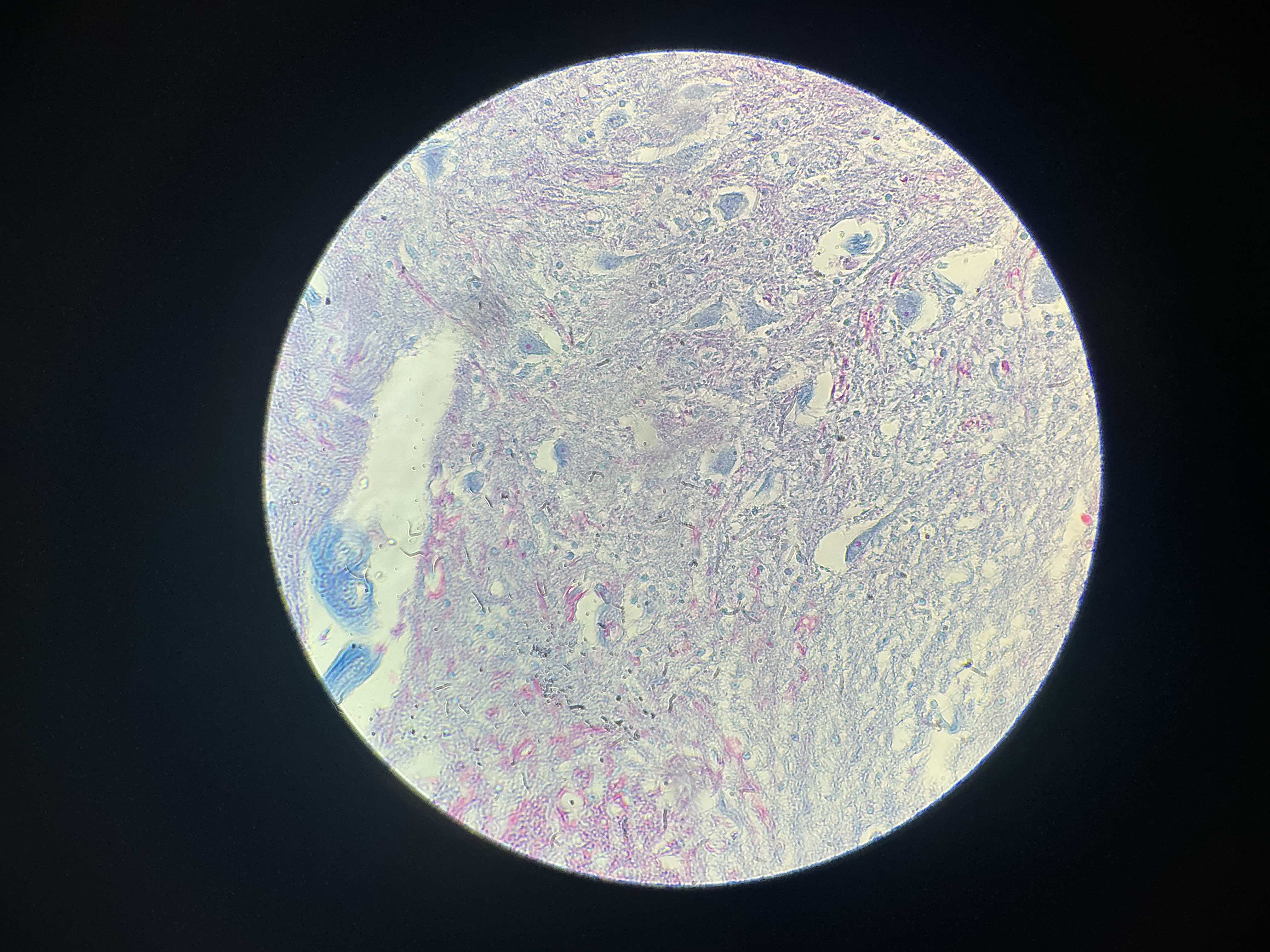
give the functions
Receive and conduct electrochemical impulse to and from body parts through:
Irritability
Conductivity
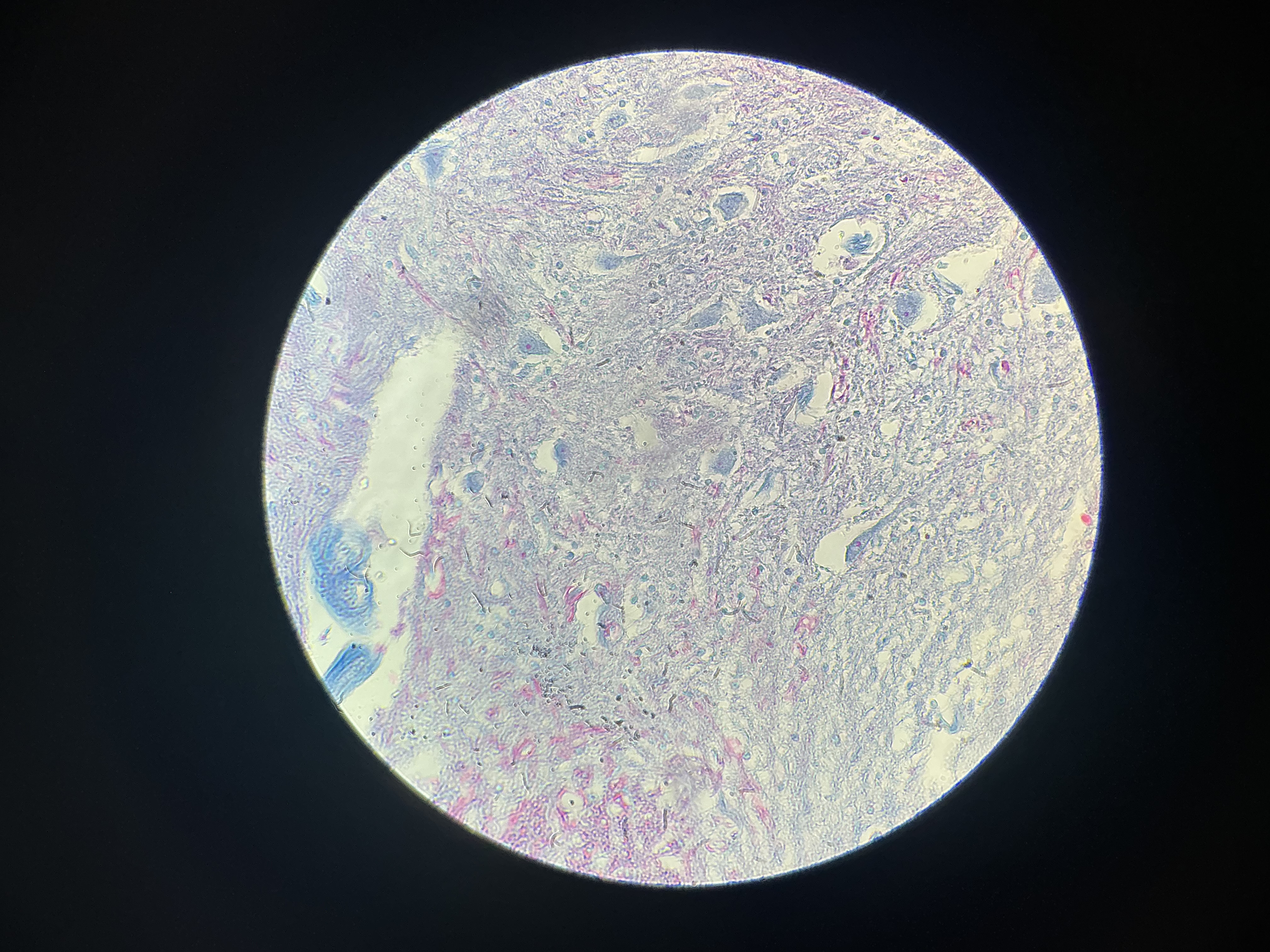
give the locations
Brain
Spinal cord
Nerves
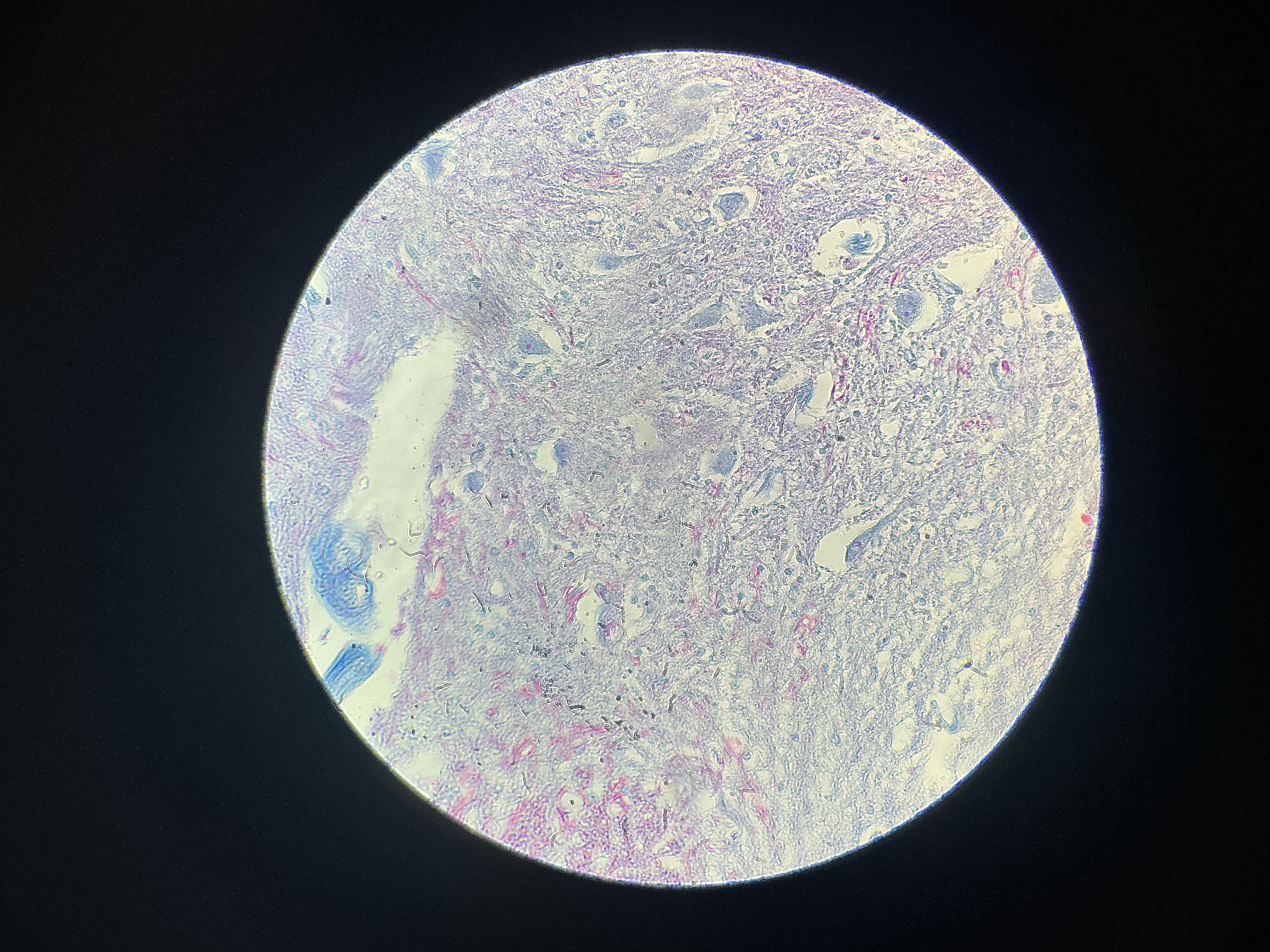
what organ is this?
mammal spinal cord
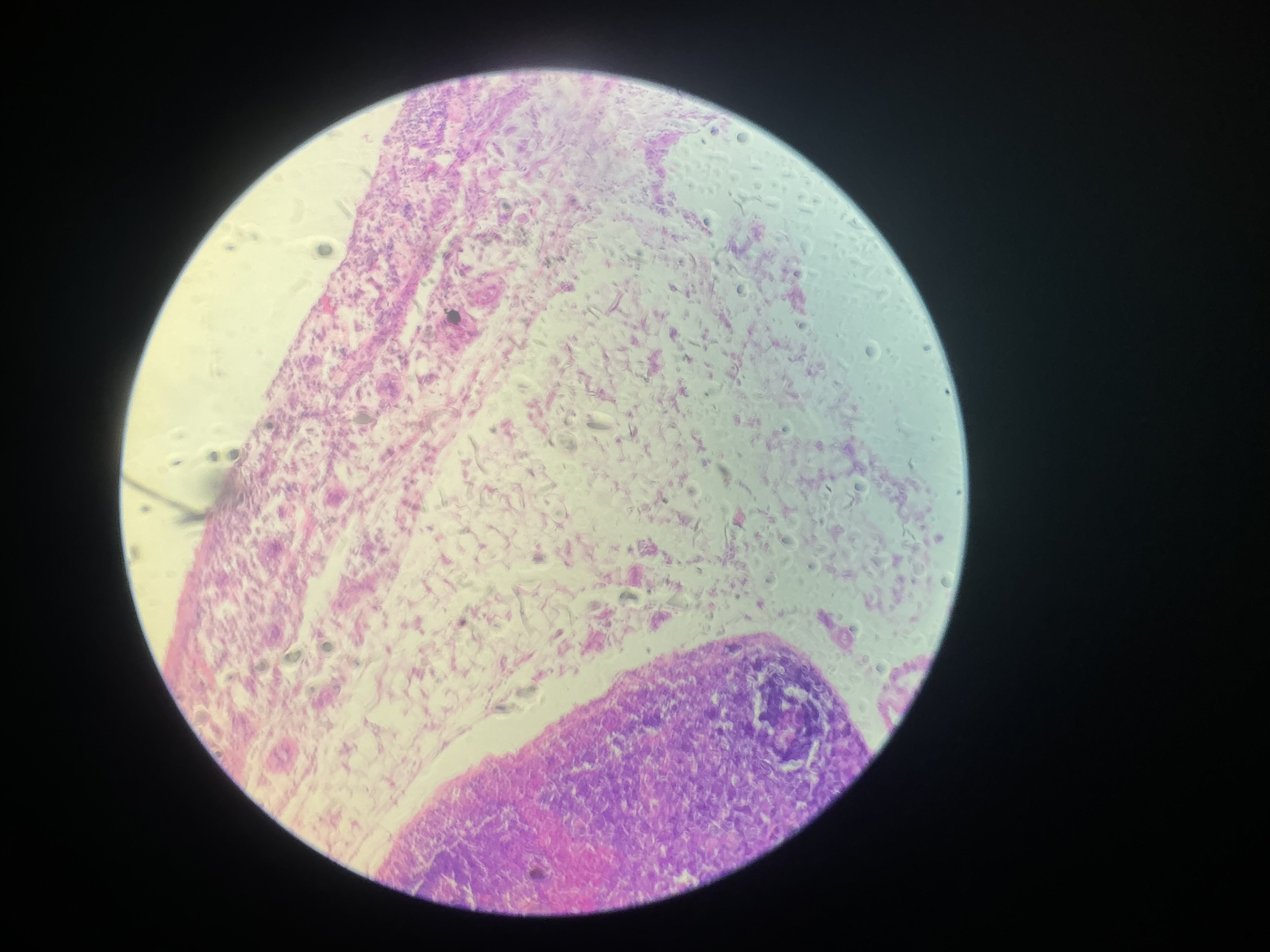
what tissue is this?
adipose
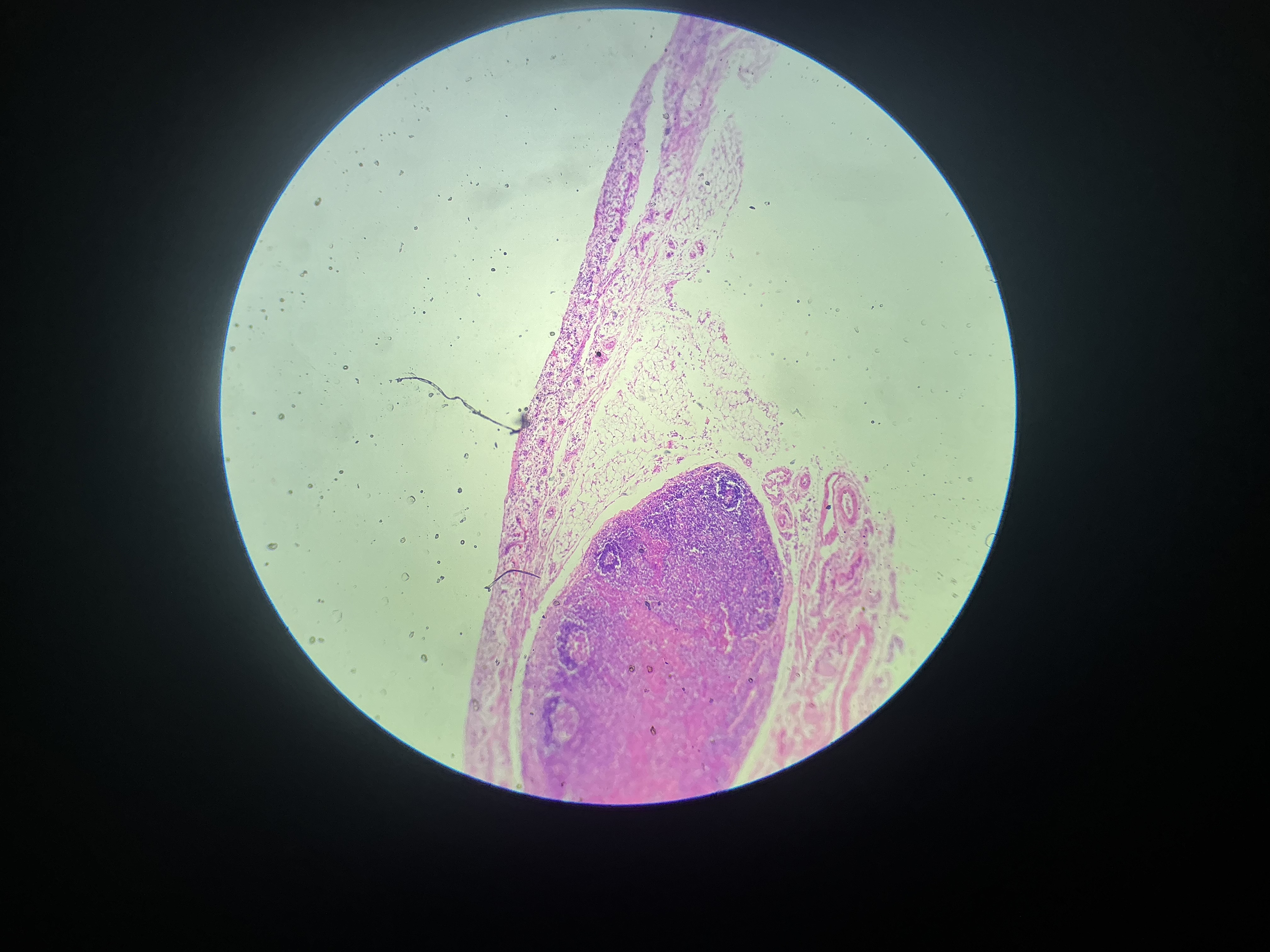
what tissue is this?
adipose
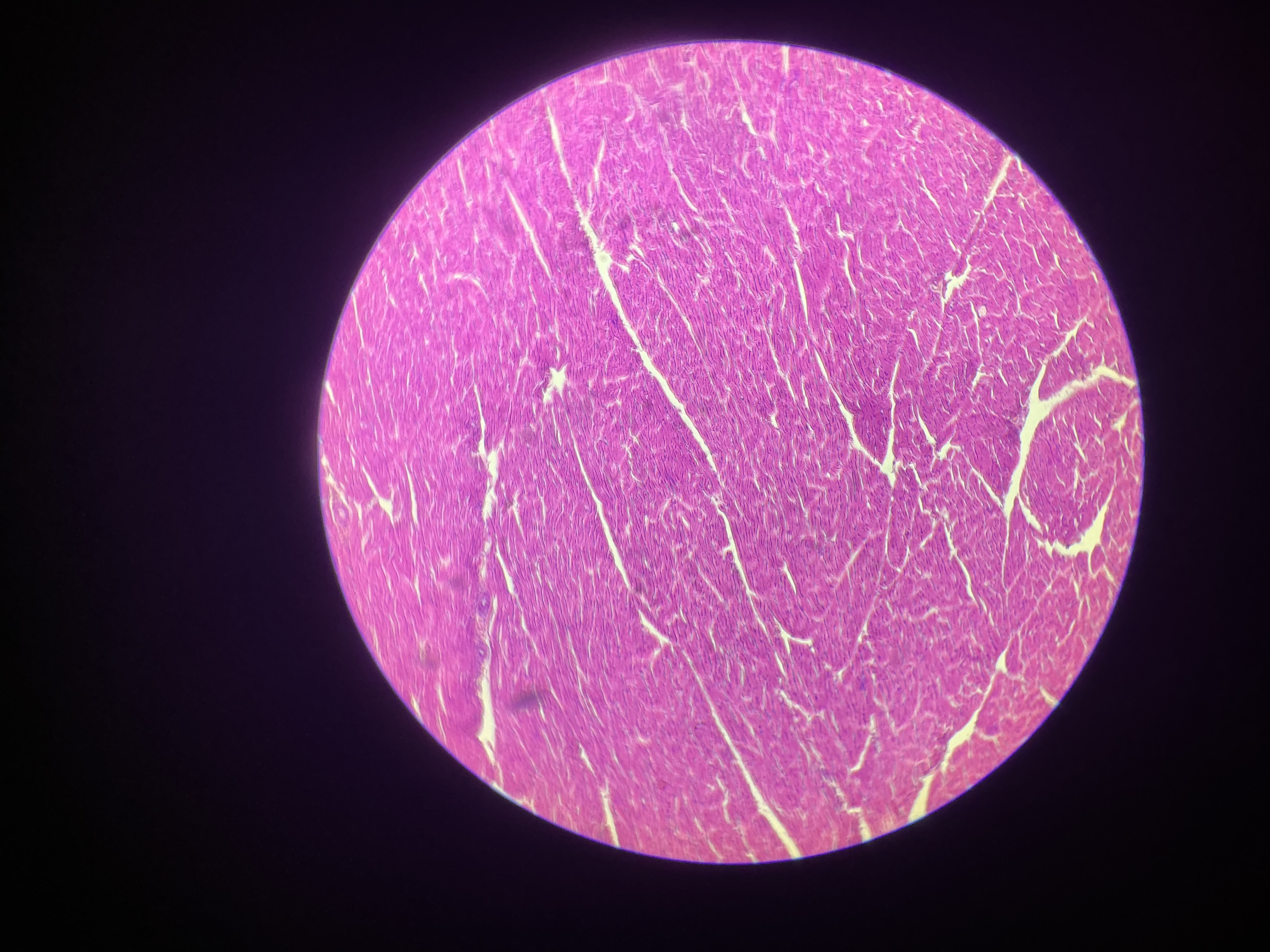
what tissue is this?
cardiac muscle
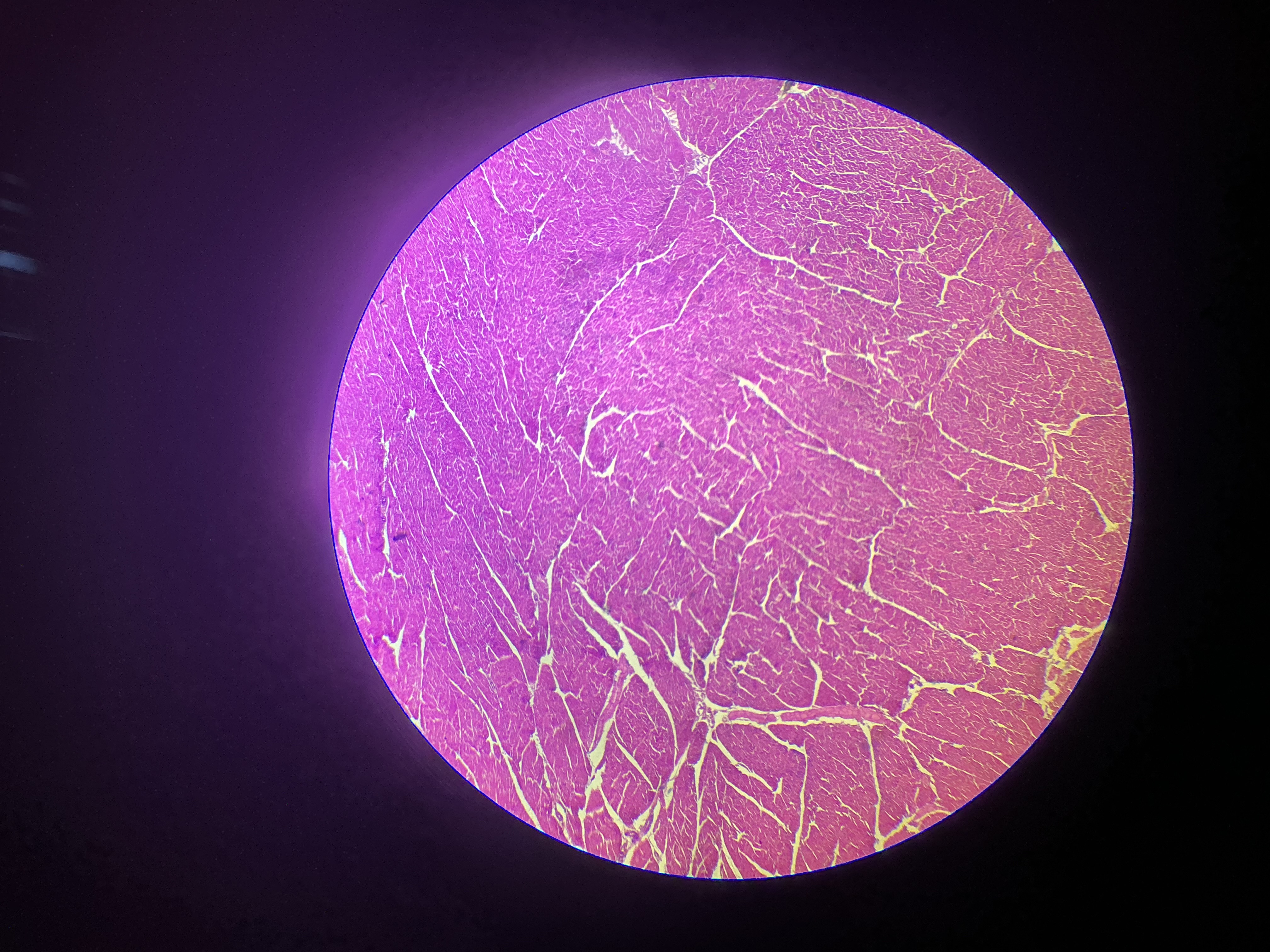
what tissue is this?
cardiac muscle
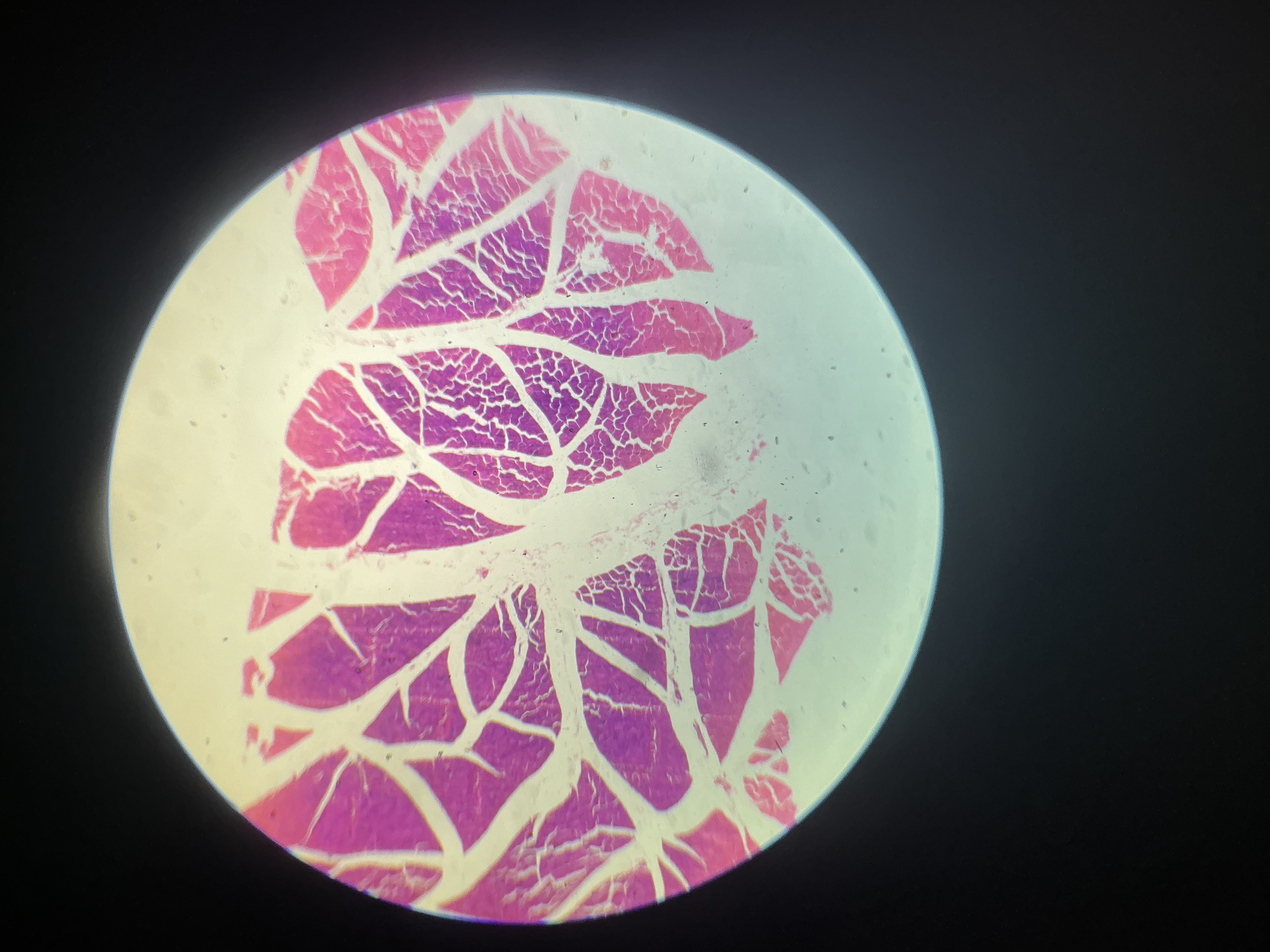
what tissue is this?
skeletal muscle
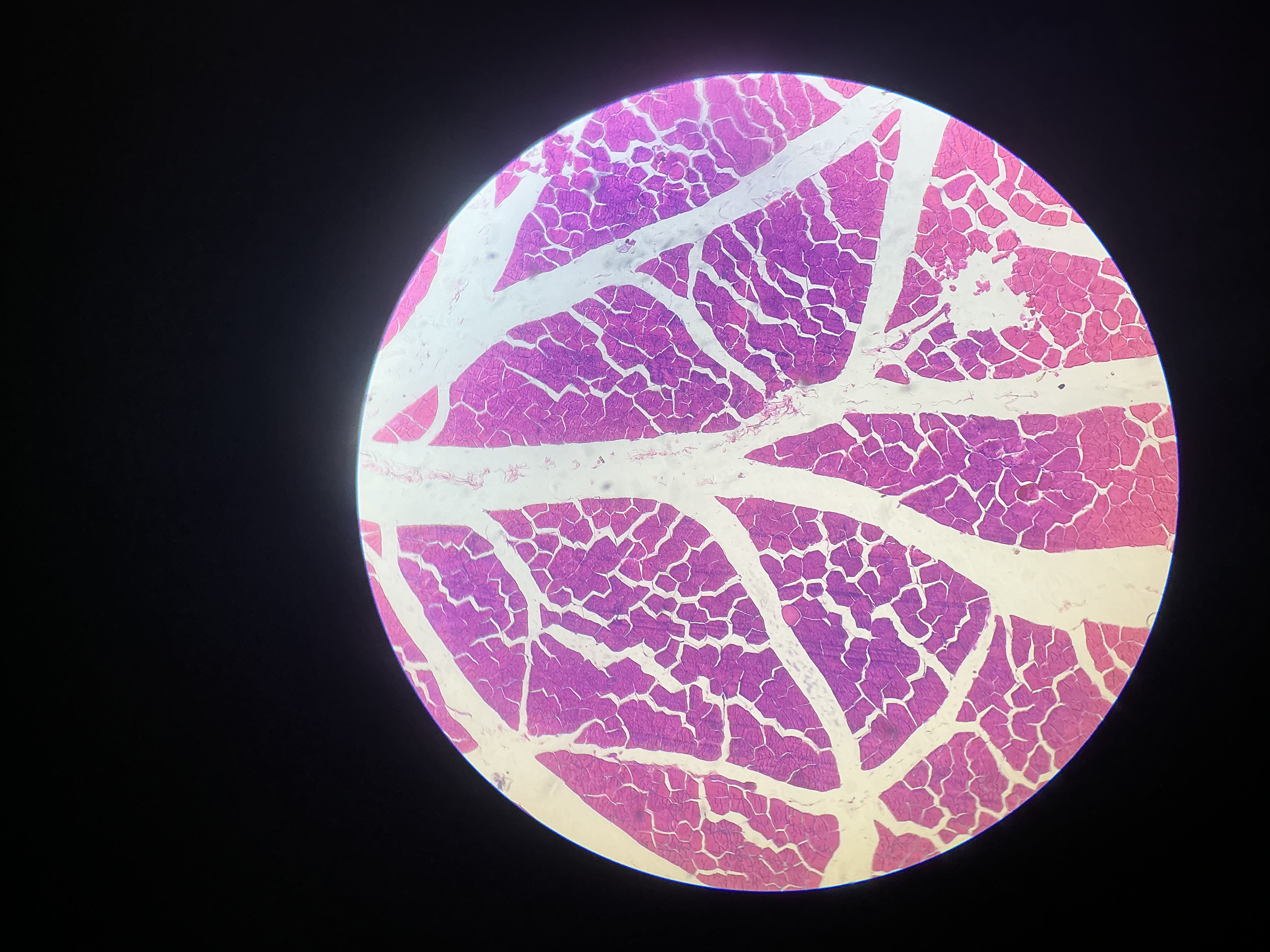
what tissue is this?
skeletal muscle
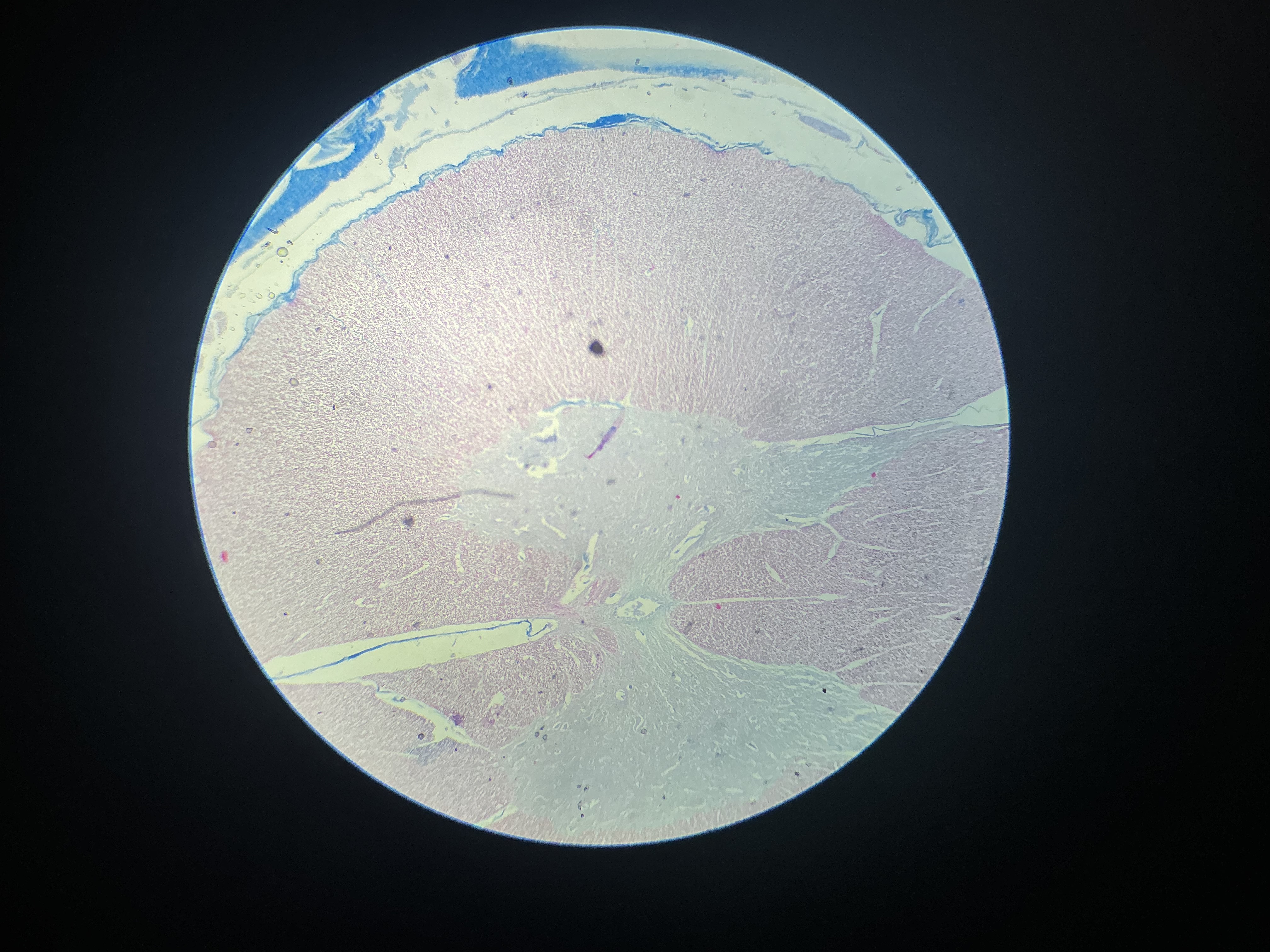
what tissue is this?
nervous tissue
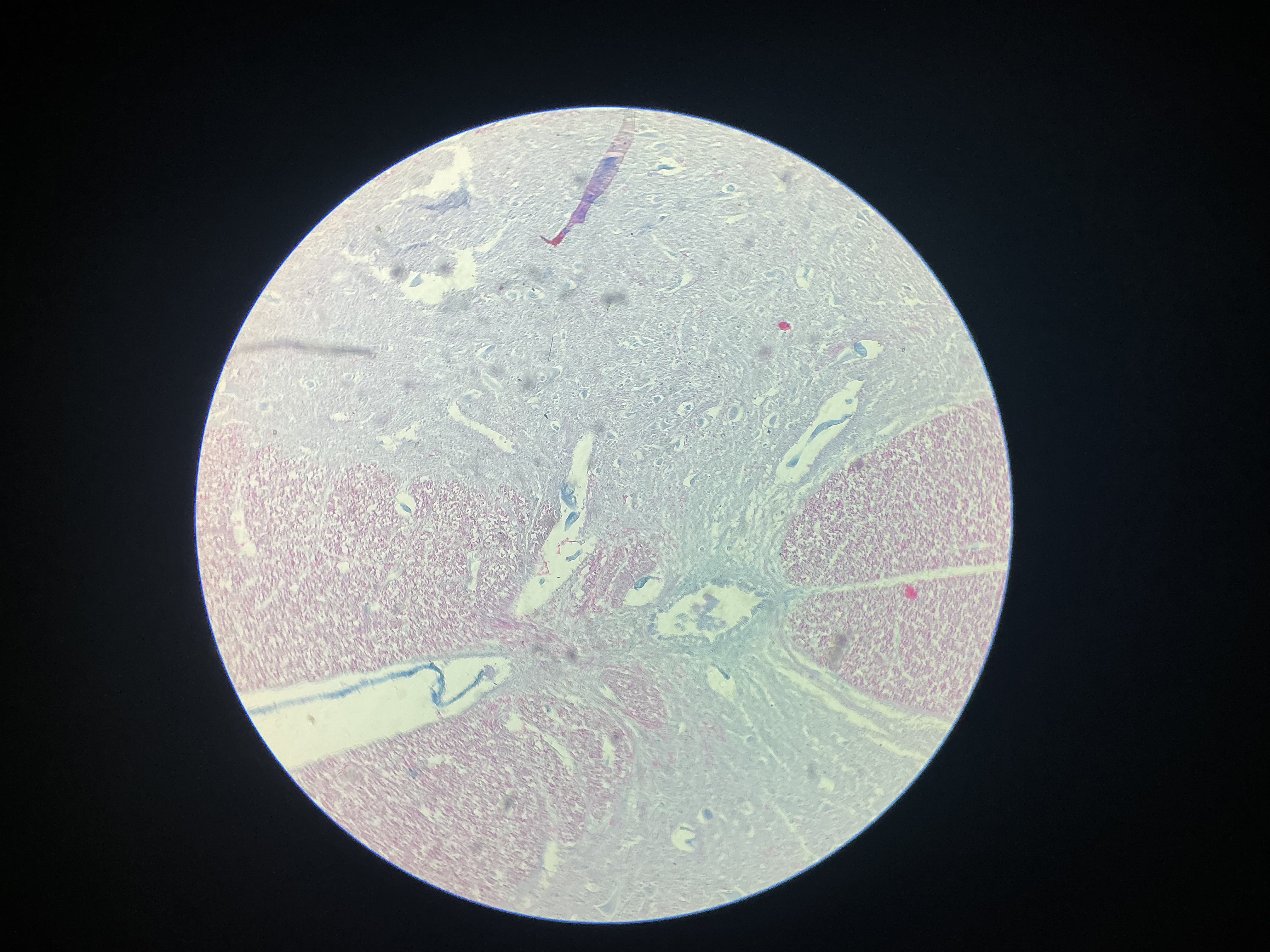
what tissue is this?
nervous tissue
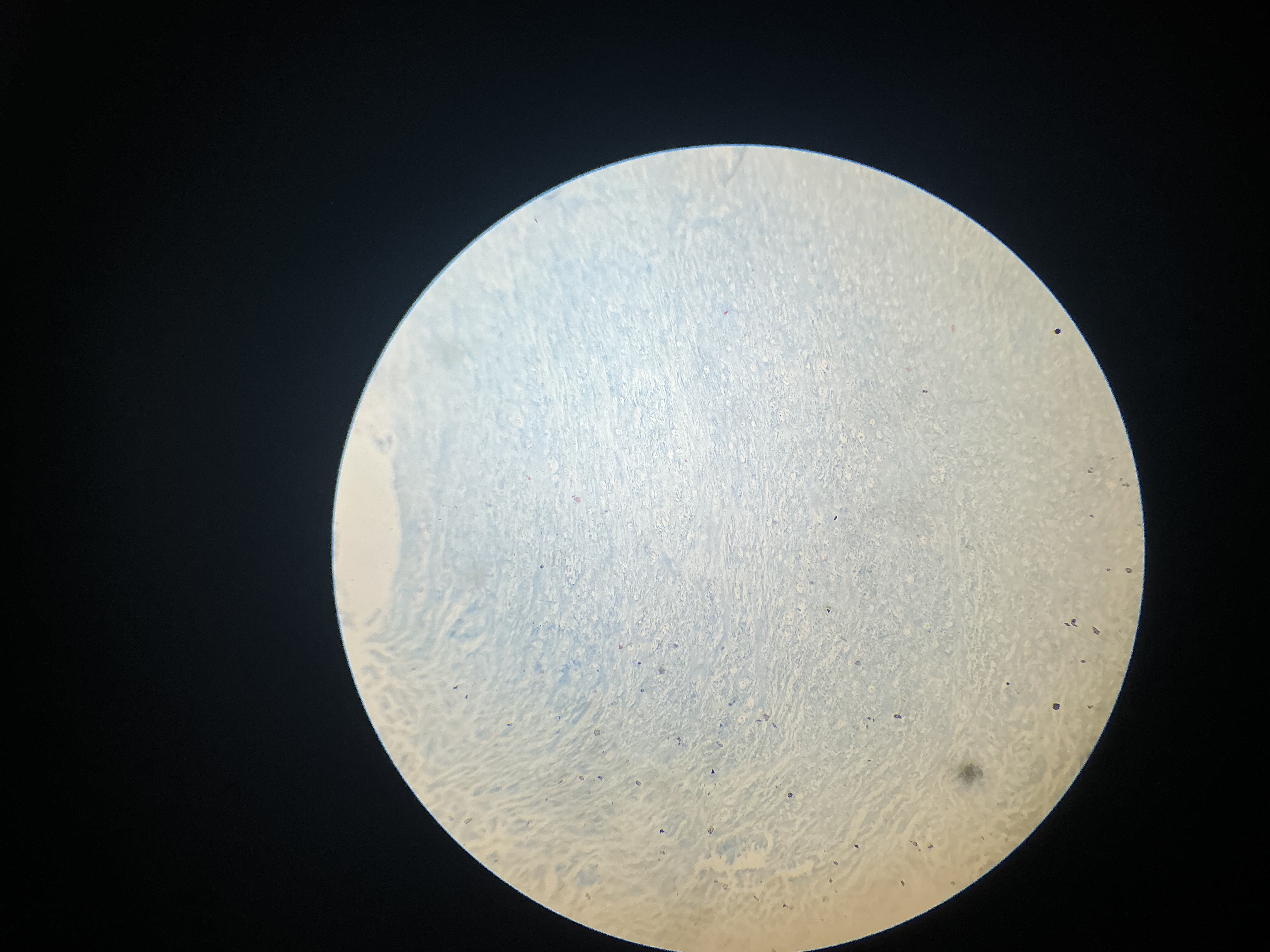
what tissue is this?
fibrocartilage
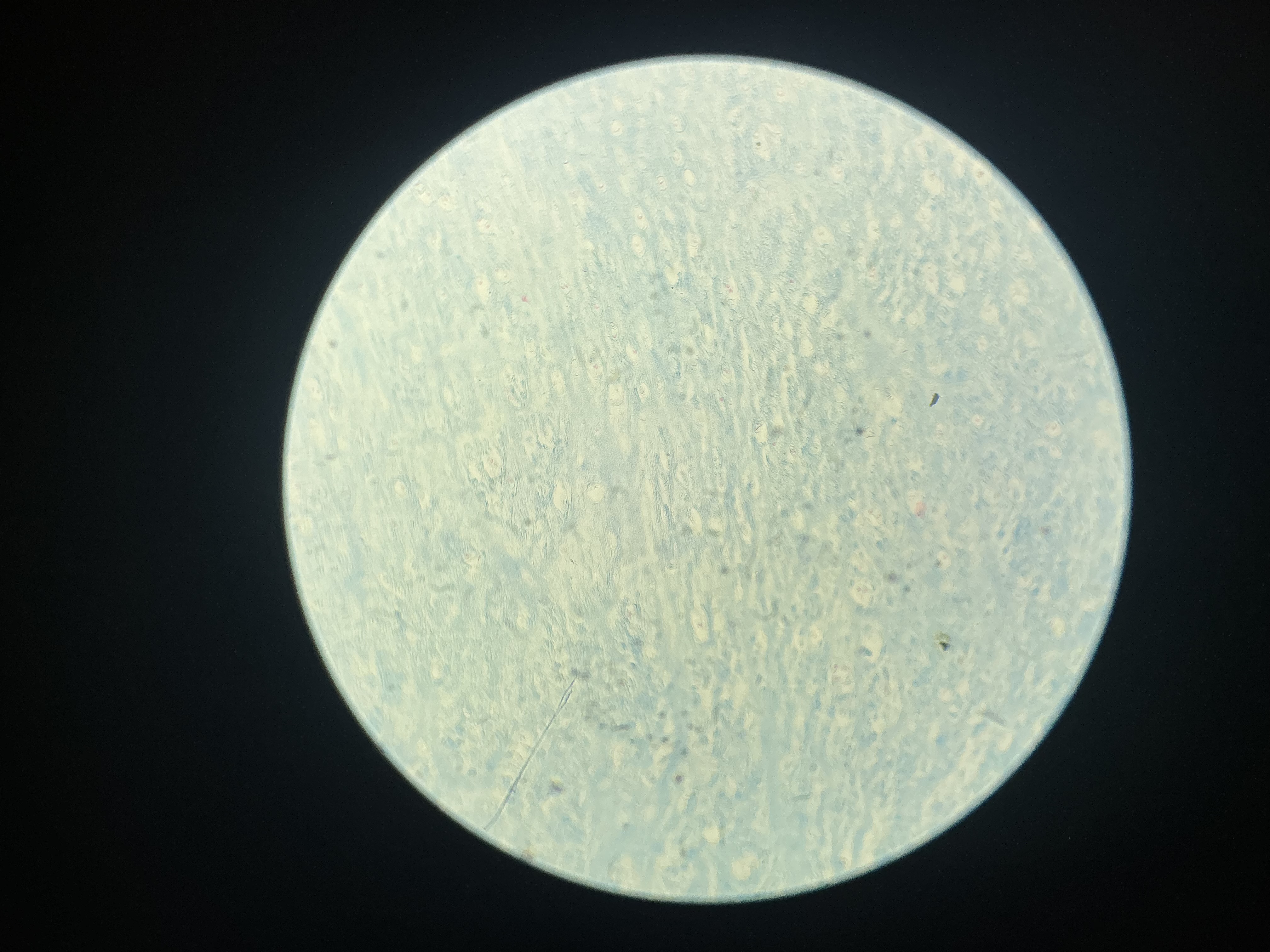
what tissue is this?
fibrocartilage
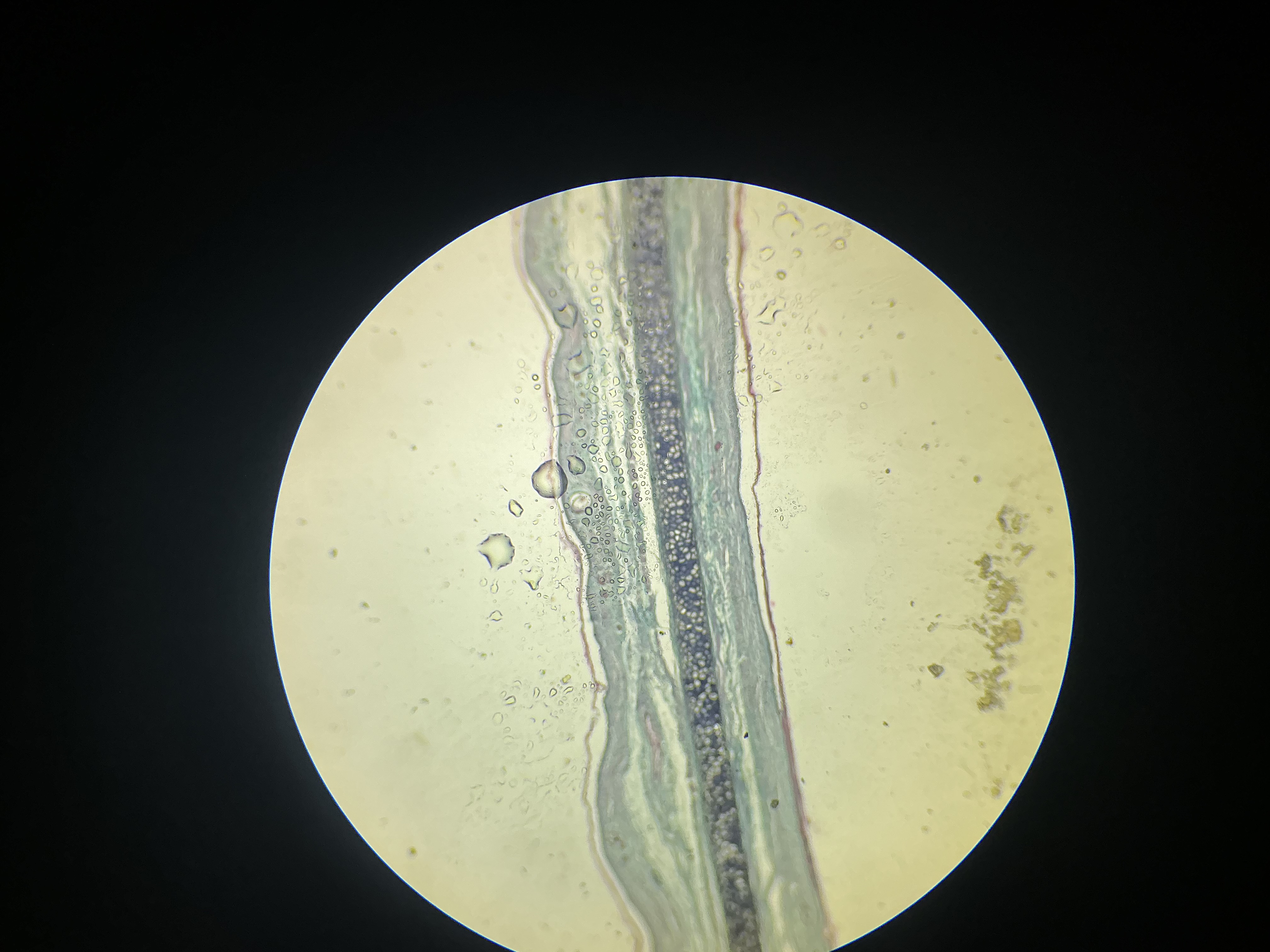
what tissue is this?
elastic cartilage
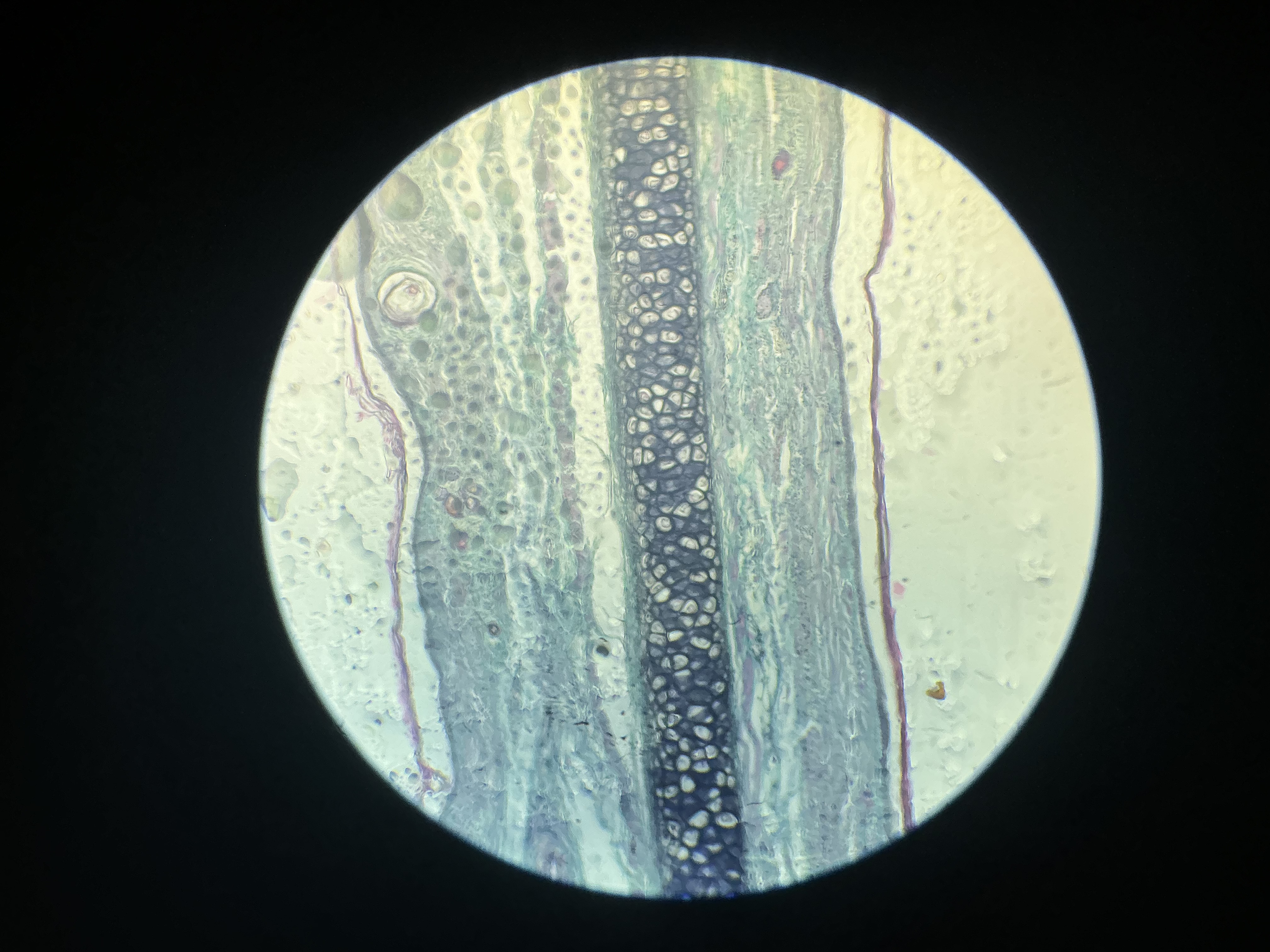
what tissue is this?
elastic cartilage
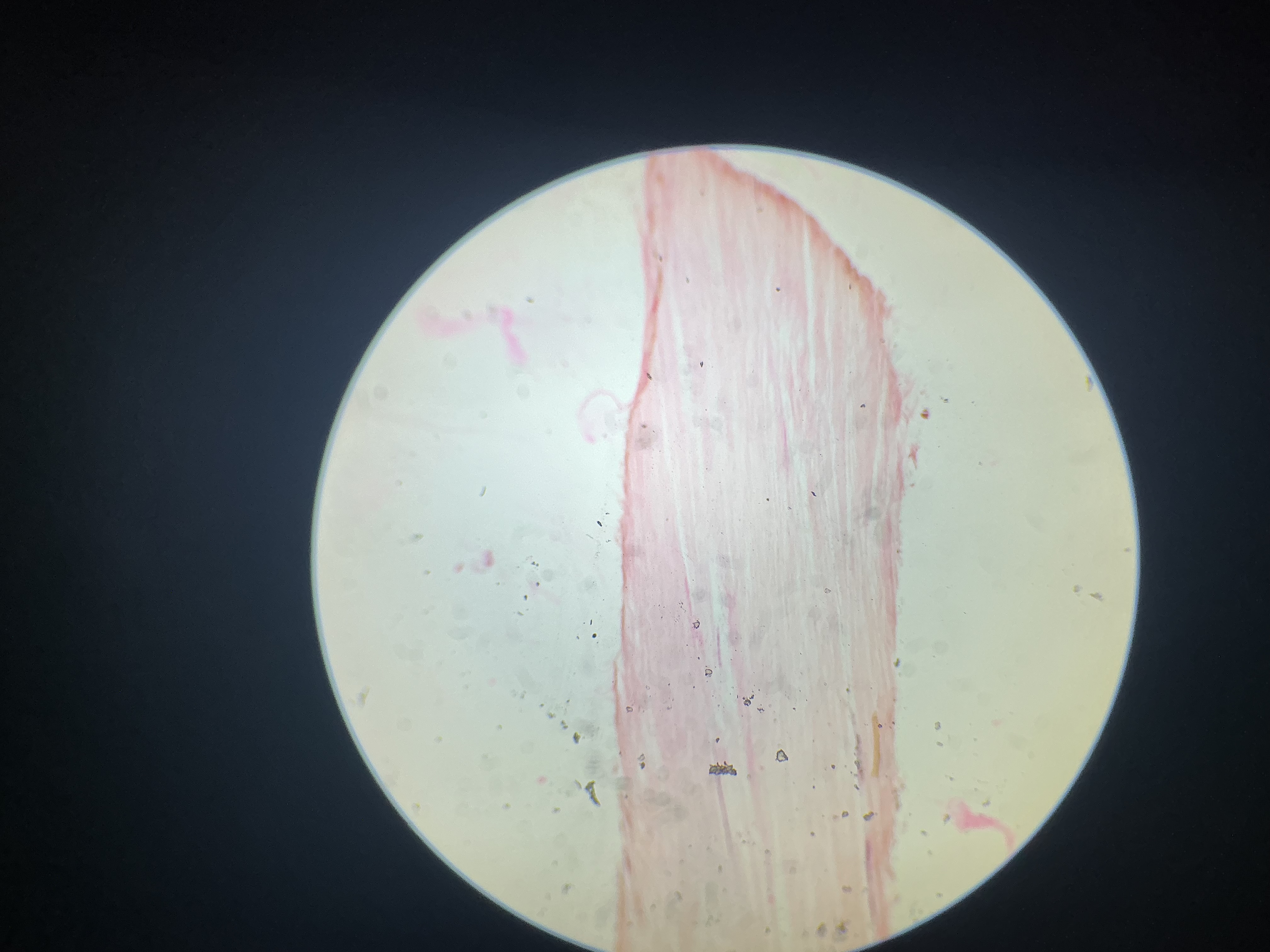
what tissue is this?
dense regular fibrous tissue
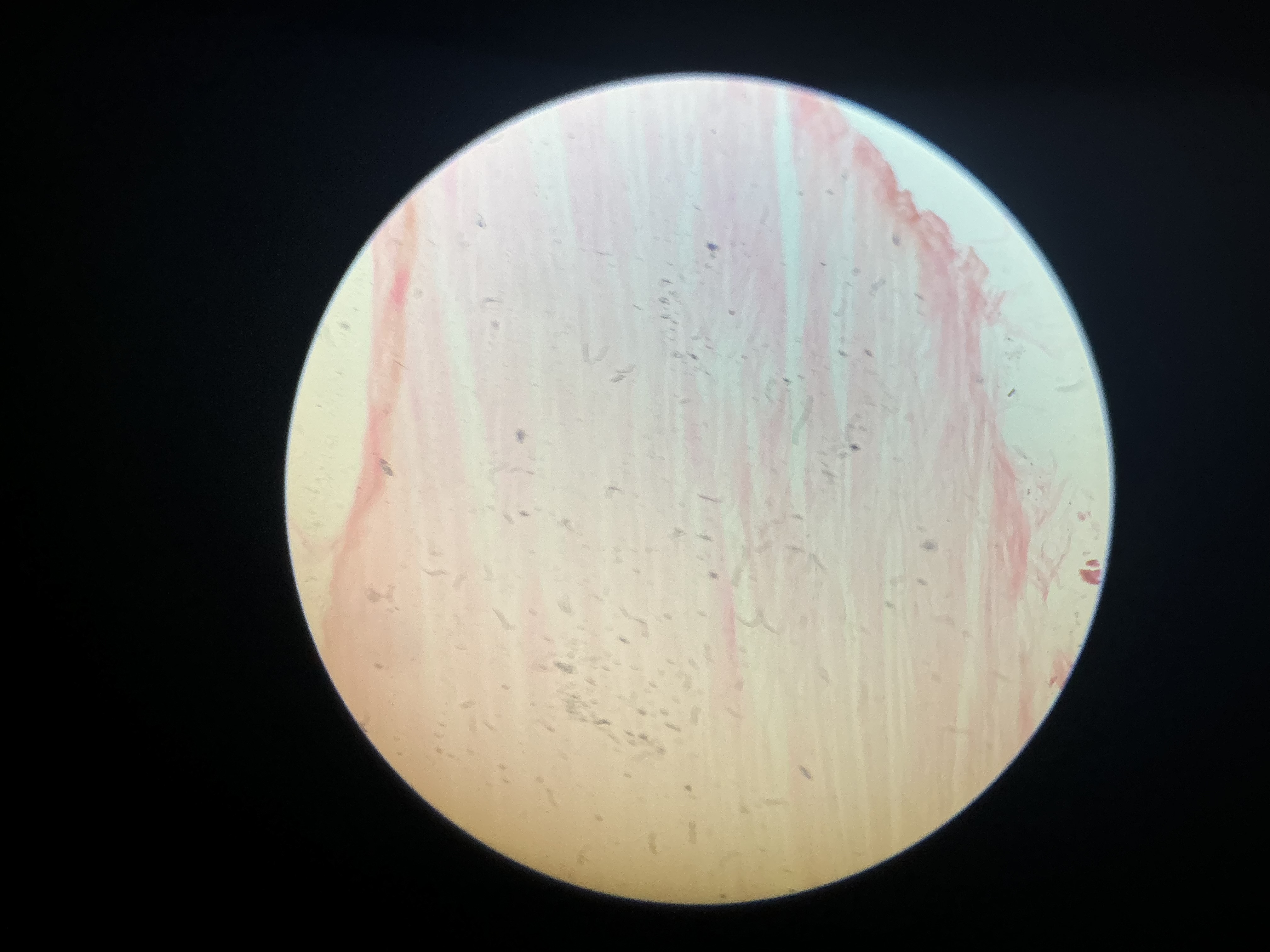
what tissue is this?
dense regular fibrous tissue