HESI - Muscular
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
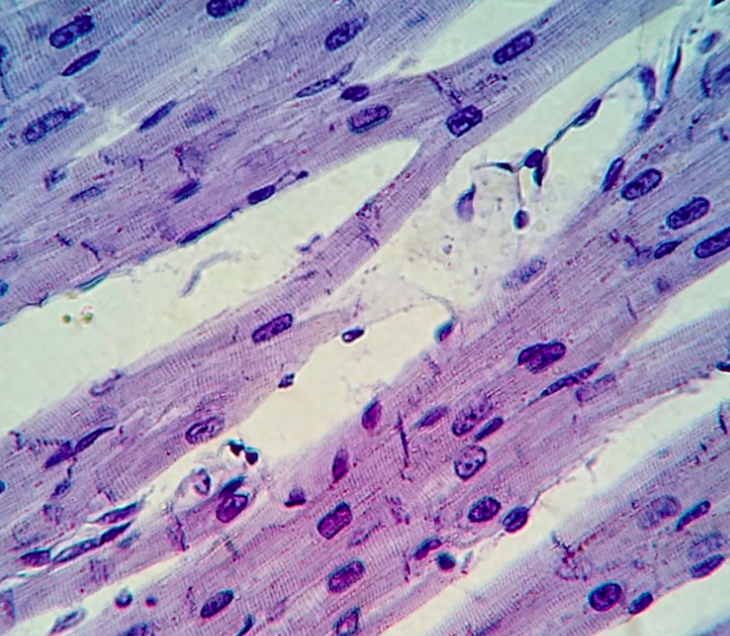
what type of muscle?
-cardiac muscle
-striated, branched
-cardiomyocytes with one nucleus
-cell junctions called intercalated discs
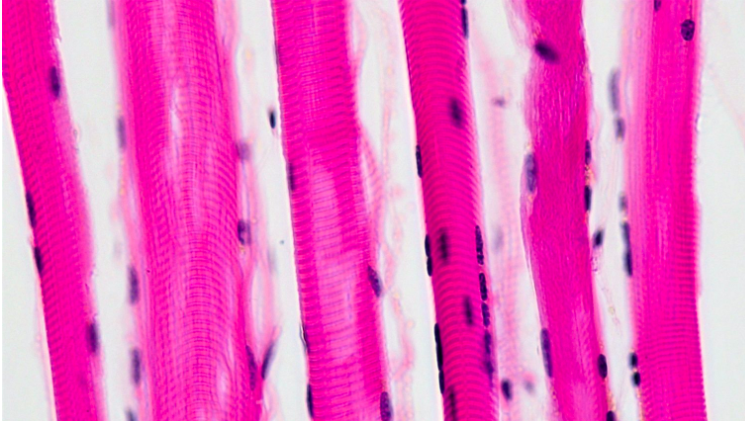
what type of muscle?
-skeletal muscle
-striated, long, cylindrical
-multiple nuclei
-myocytes with myoglobin make it reddish
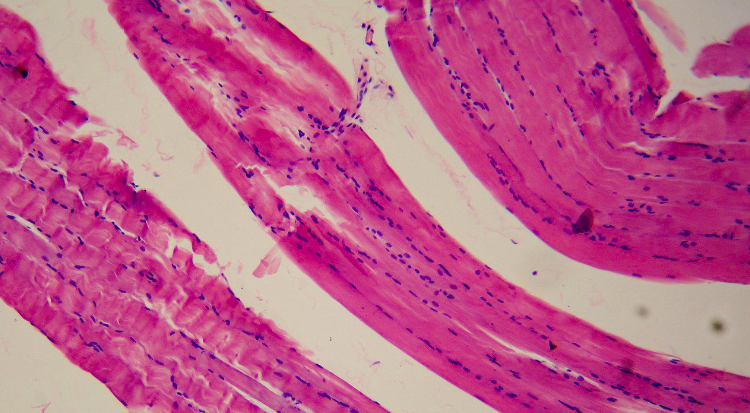
what type of muscle?
-smooth muscle
-not striated
-spindle shaped, one nucleus
-less organized
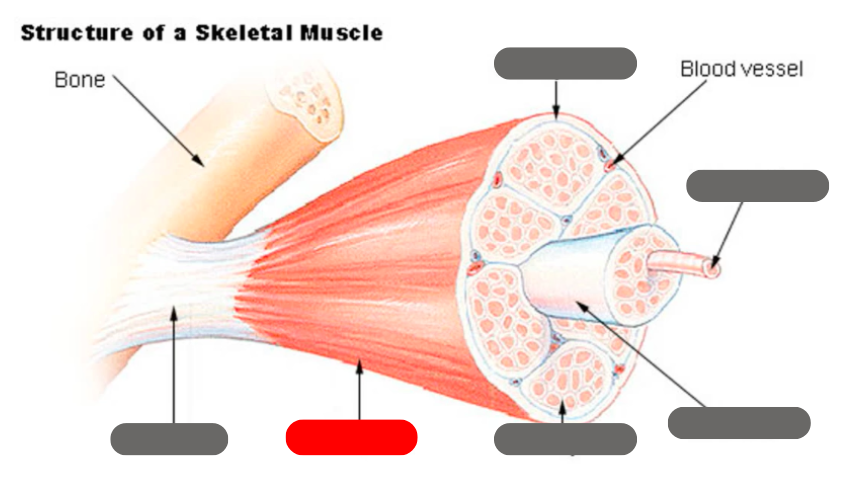
epimysium
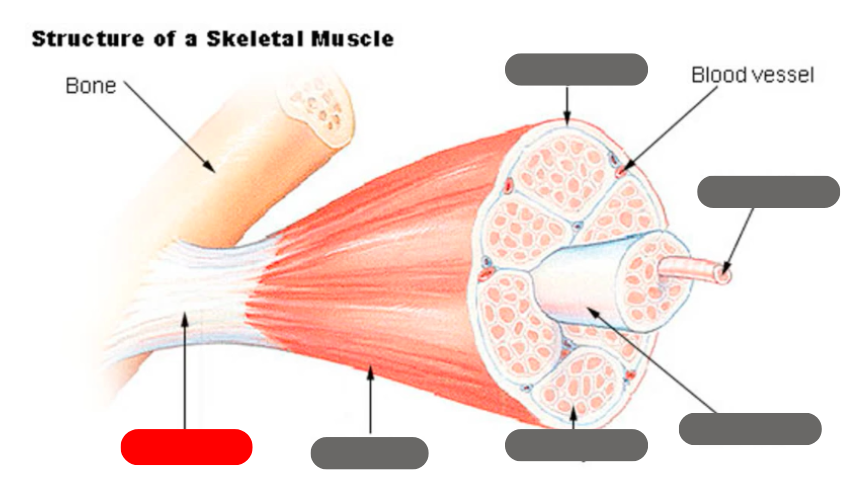
tendon
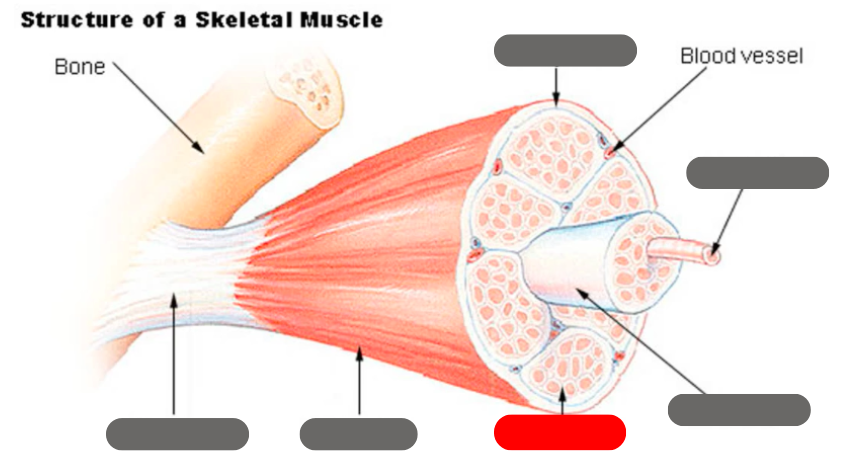
endomysium
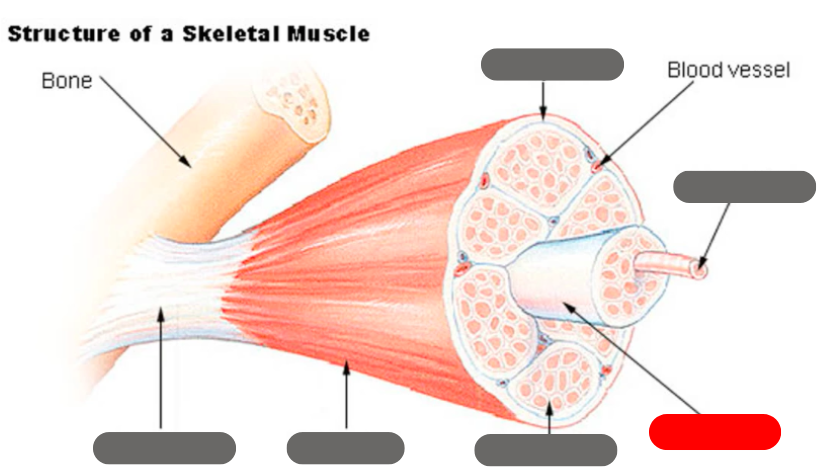
fasicle
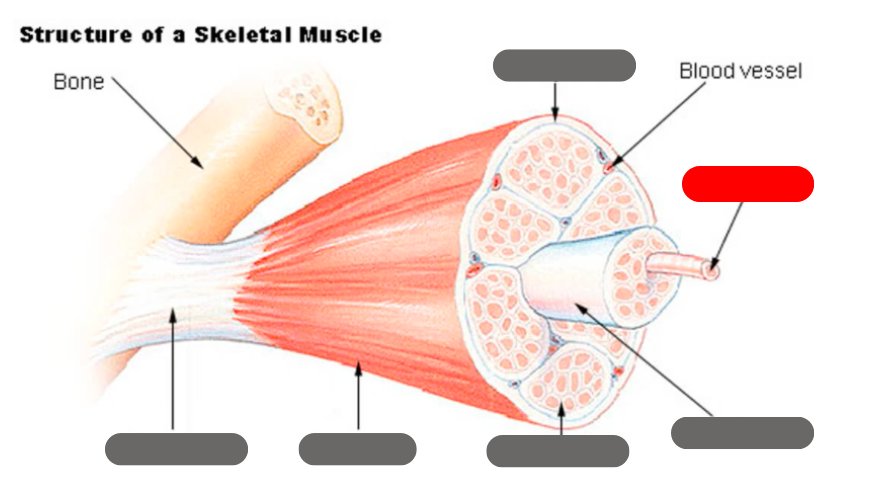
muscle fiber
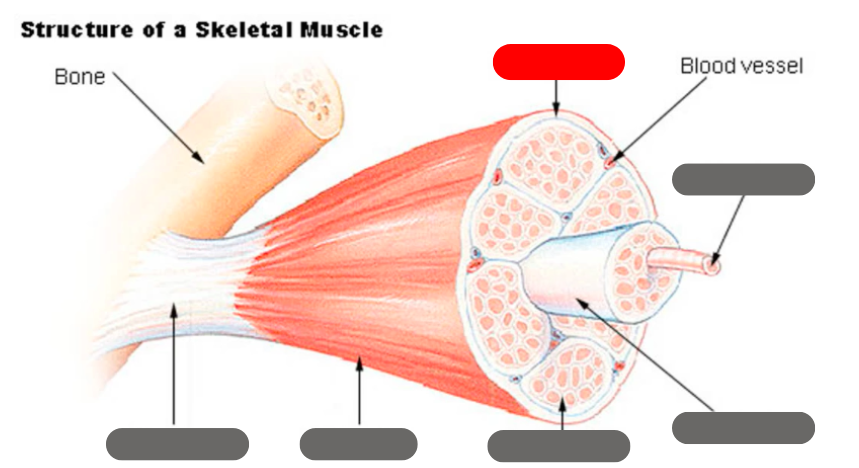
perimysium
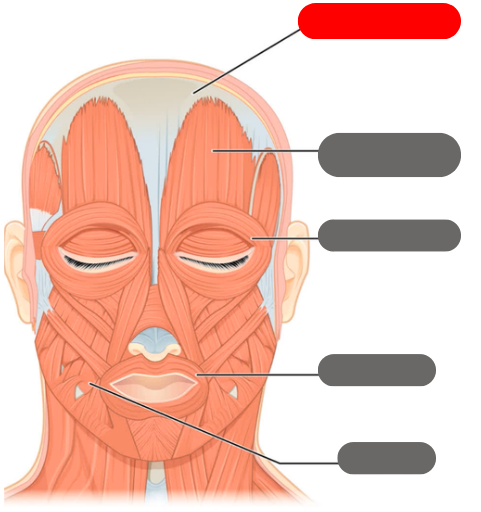
epicranial aponeurosis
-connective tissue band
-connects with the occipitofrontalis to wrinkle the forehead
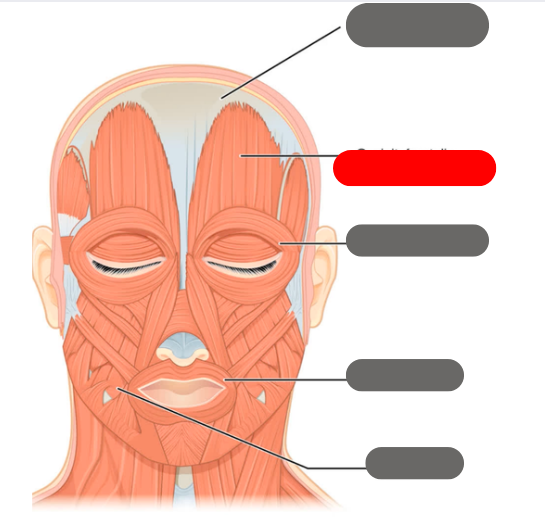
occipitofrontalis muscle
-wrinkles the forehead
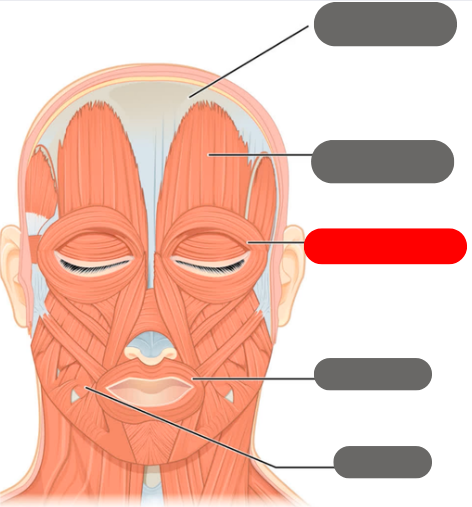
orbicularis oculi
-allows the eye to open and close
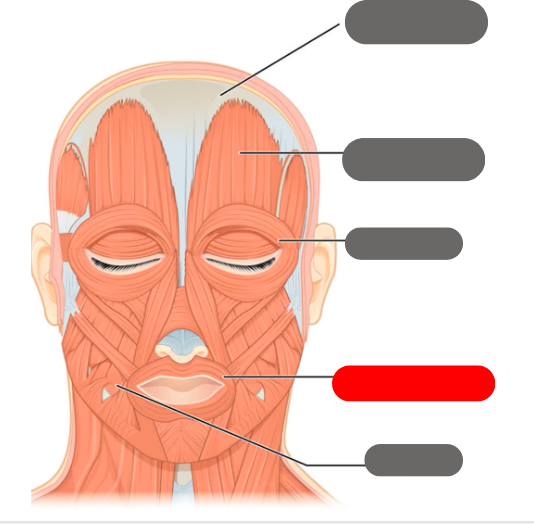
orbicularis oris muscle
-allows for puckering of the lips

buccinator
-chewing
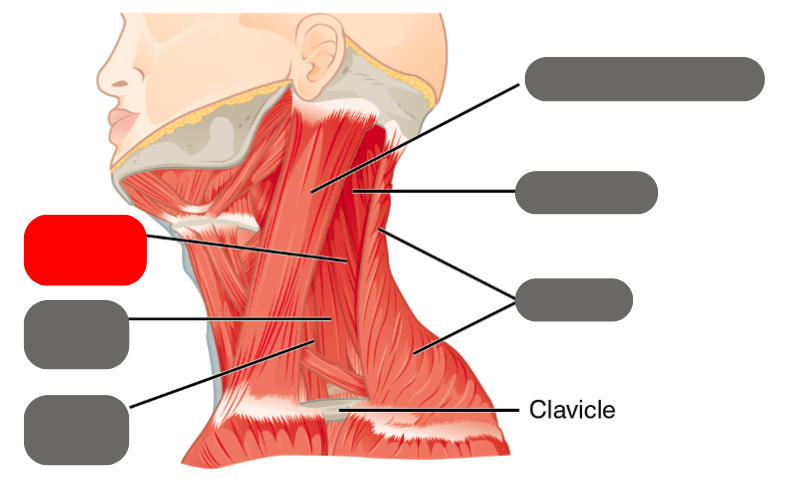
levator scapulae
-moves the scapula up
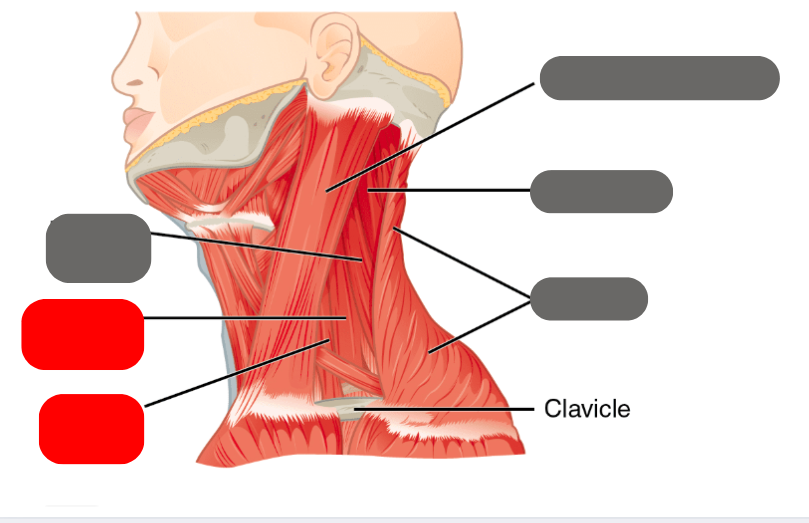
medial and anterior scalenes
-deep muscles that help with lateral flexion
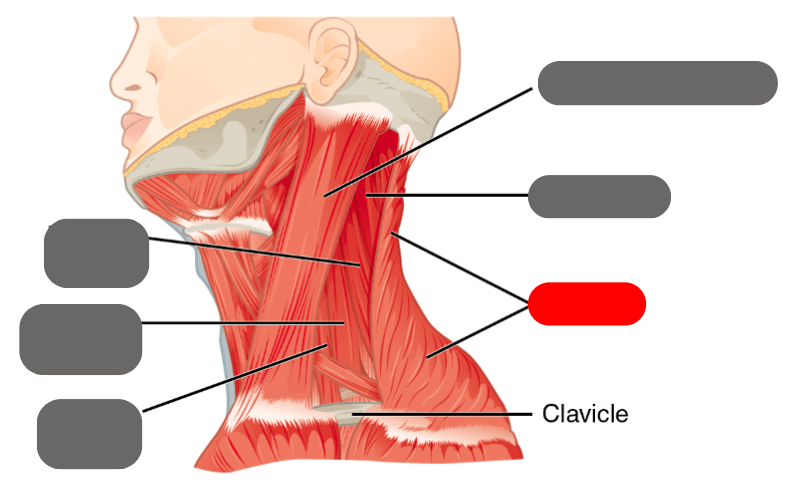
trapezius
-shrugs the shoulders
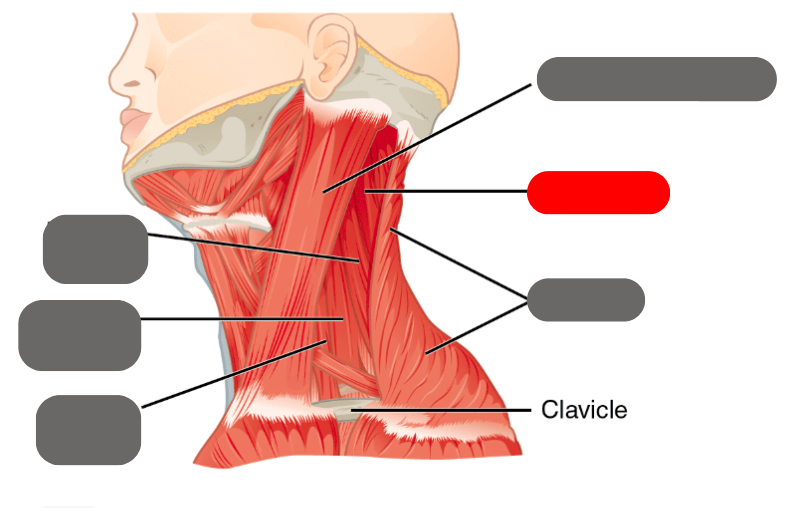
splenius
-neck and head movement
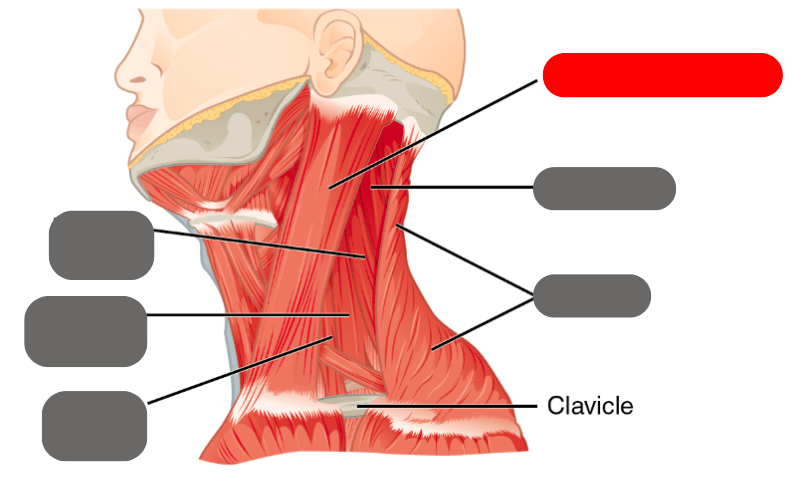
sternocleidomastoid
-important for turning the head

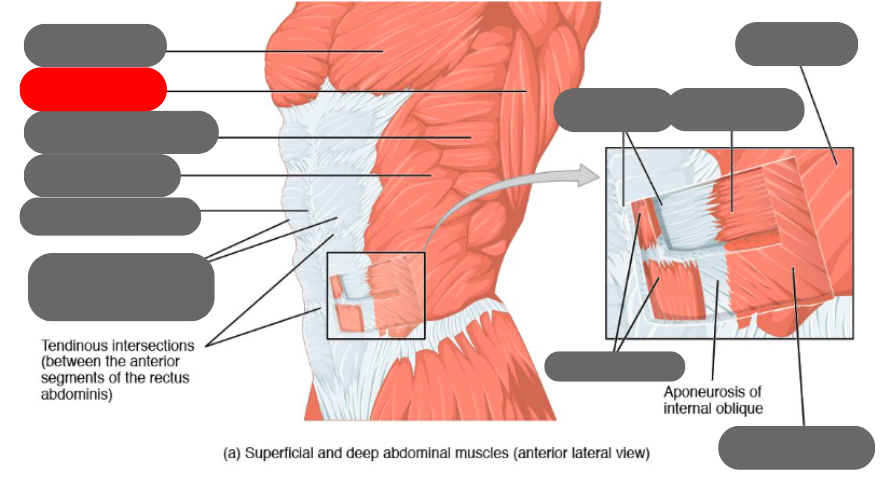
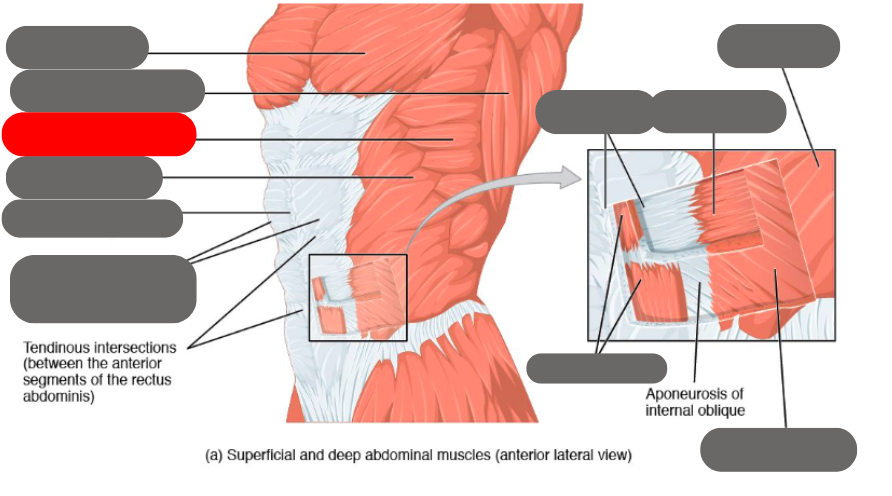
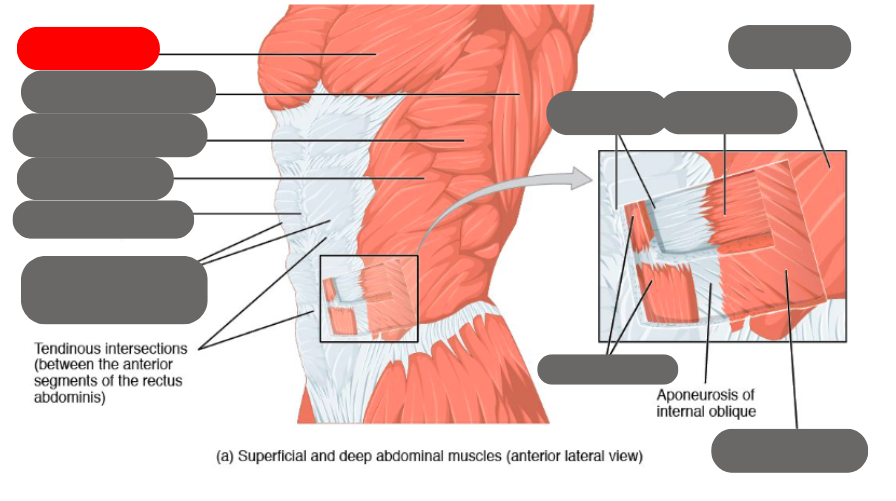
internal oblique
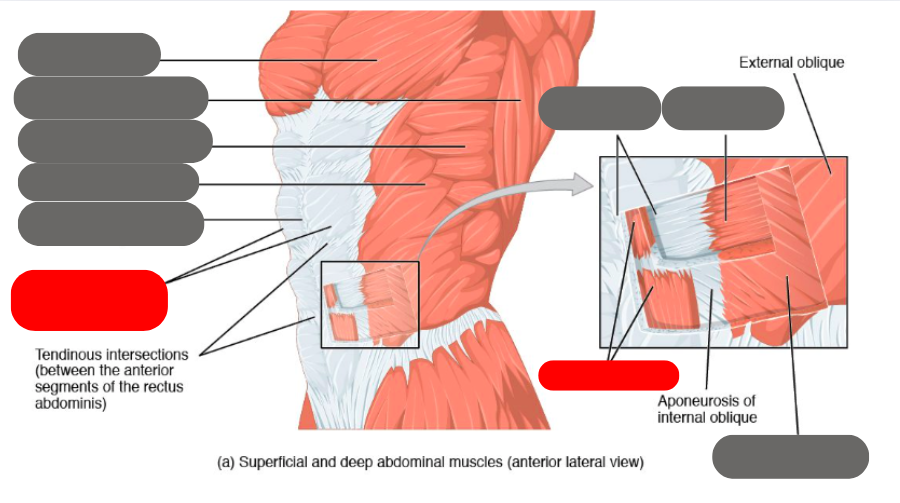
rectus abdominis (6 pack) within the rectus sheath
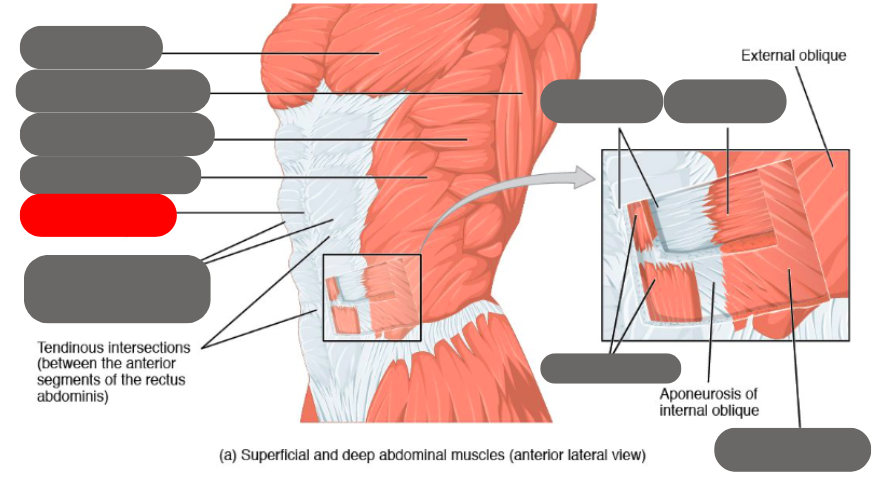
linea alba of the rectus sheath
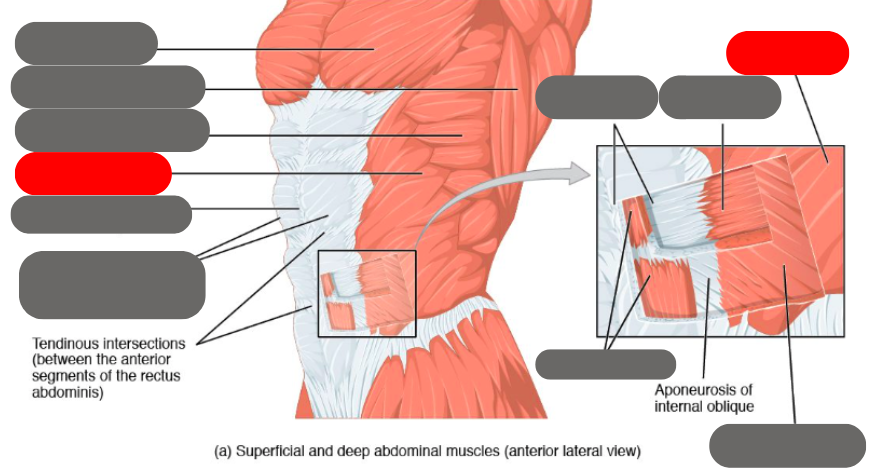
external oblique

transverse abdominis
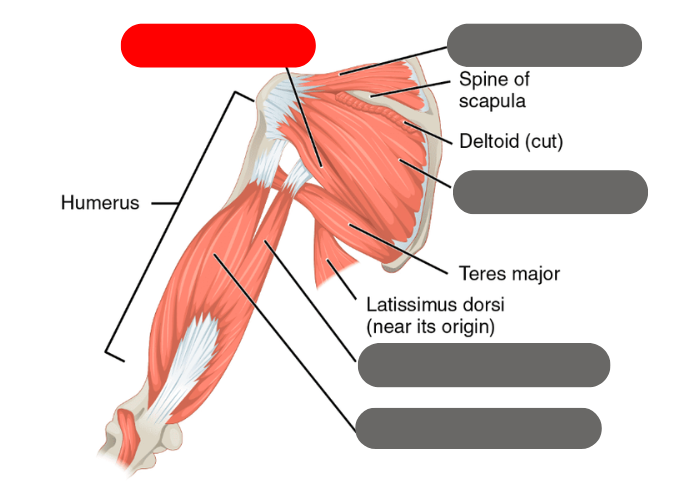
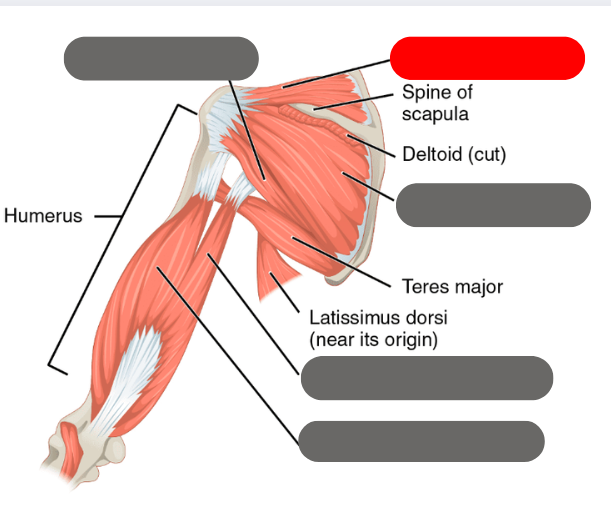
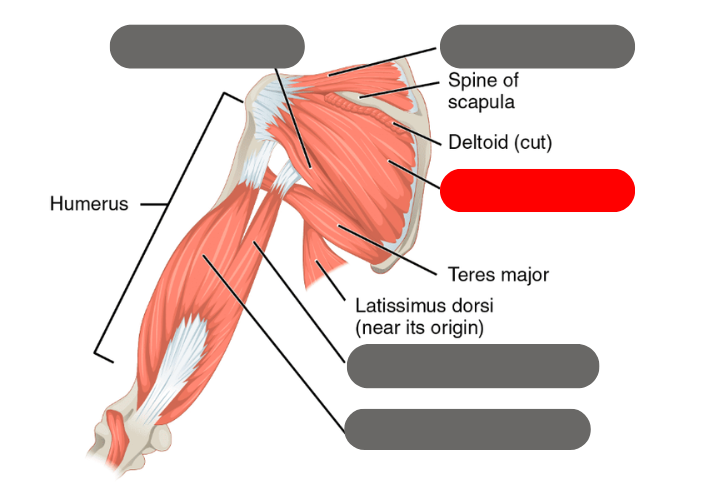
latissimus dorsi
-moves the humerous with the deltoid
anterior serratus muscle
pectoralis major
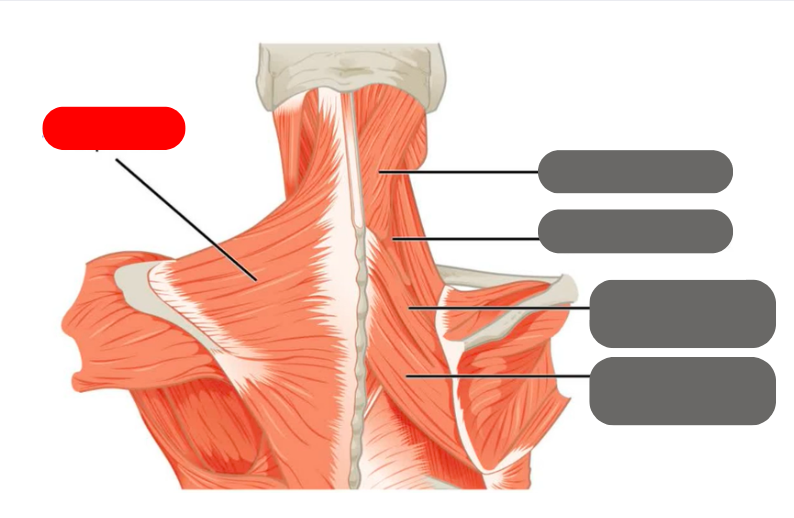
trapezius
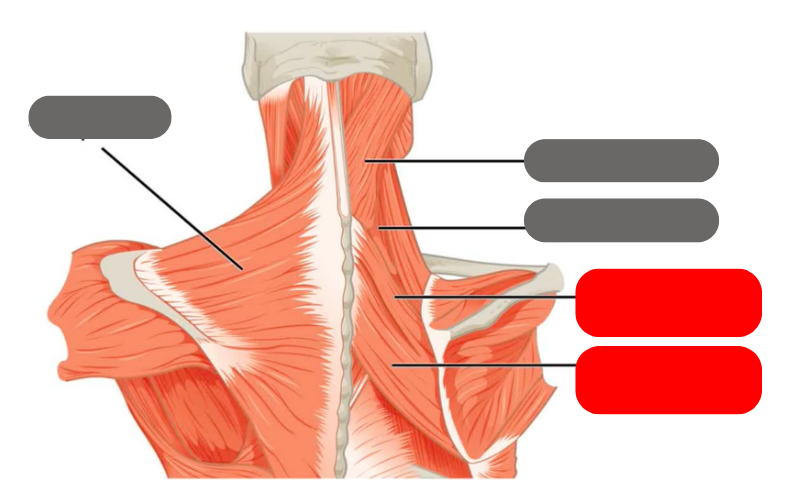
minor and major rhomboids
-squeeze the shoulder blades together
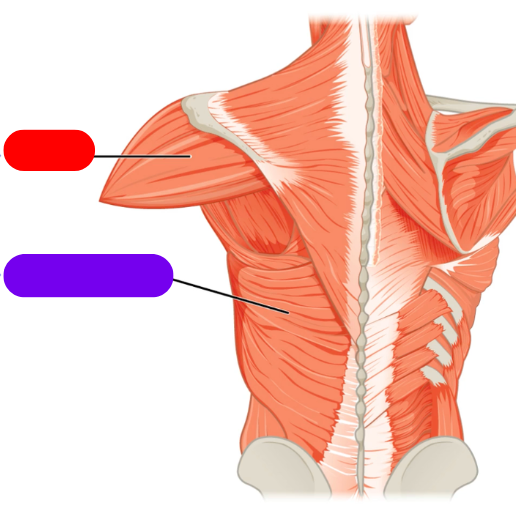
red is the deltoid
purple is the latissimus dorsi
-both move the humerous
cervices meaning
attaching to the neck
capitus meaning
attaching to the head
thoracis meaning
attaching to the middle back
longissimus meaning
long fibers
lumborum meaning
attaching to the low back
multifidis muscles
short muscles that attach directly to the spine
rotator muscles
very deep, very small muscles that attach directly to the spine and help roatate it
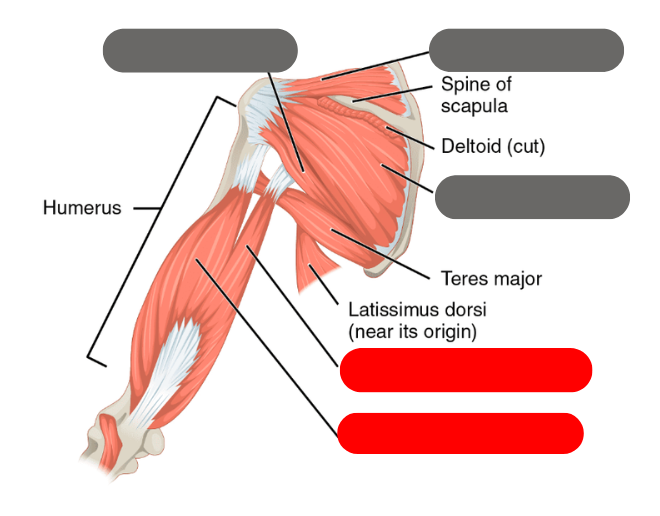
triceps brachii
teres minor
-one of the rotator cuff muscles
supraspinatus
-most commonly torn rotator cuff muscle
infraspinatus
-roatator cuff muscle
4 rotator cuff muscles
-supraspinatus
-teres minor
-infraspinatus
-subscapularis
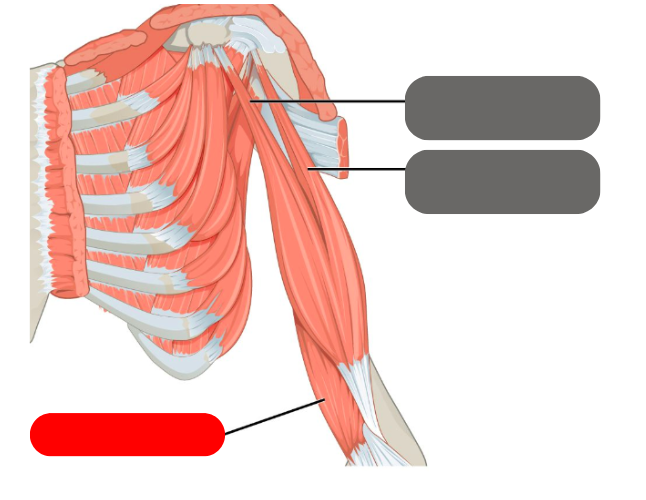
brachialis
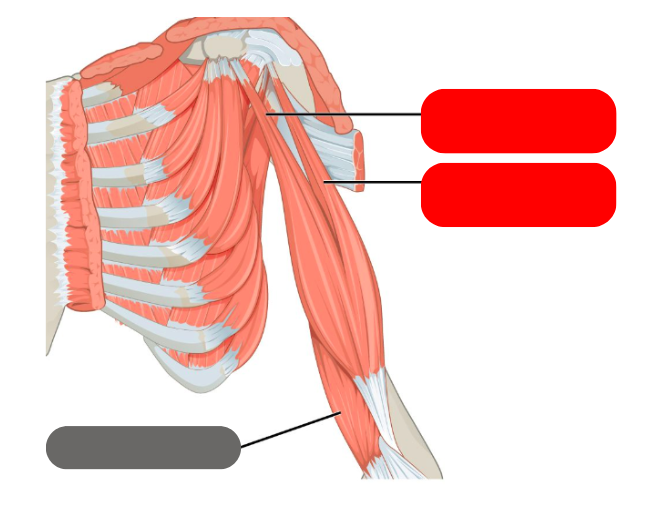
biceps brachii
muscles on the front of the forearm general name
flexors
muscles on the back of the forearm general name
extensors
2 wrist muscles that allow for rotation
-pronator teres
-anconeus
forearm muscle used for reflexes
brachioradialis
word for relating to the thumb
pollicis
muscle word for short
brevis
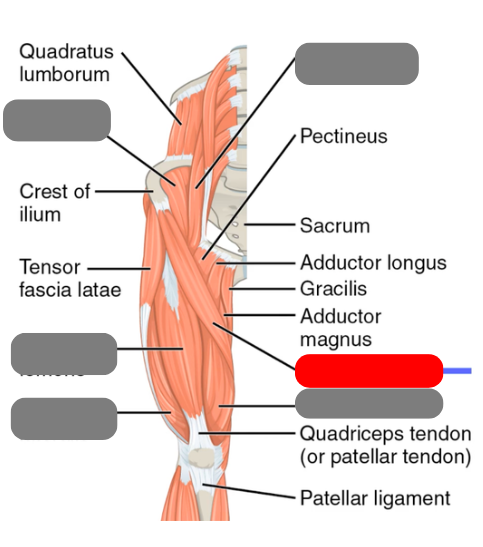
sartorius
-tailor’s muscle
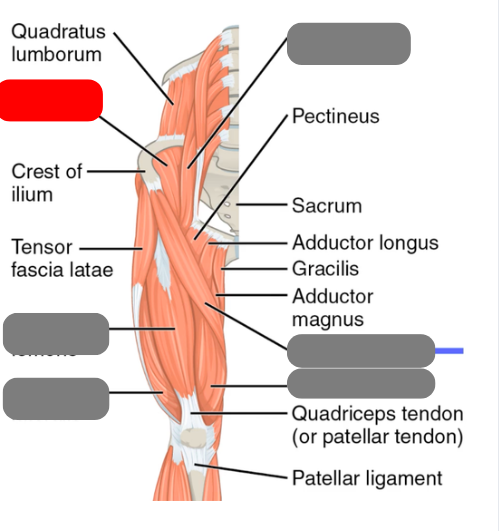
illiacus
-works with the psoas major for hip flexion form the iliopsoas
-runners can get tendonitis in it
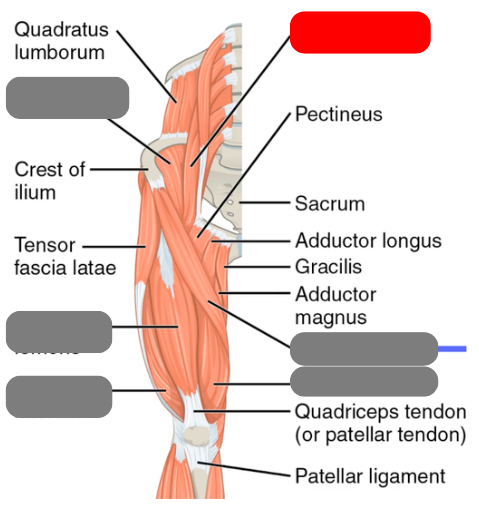
psoas major
-works with the illiacus to form the illiopsoas for hip flexion
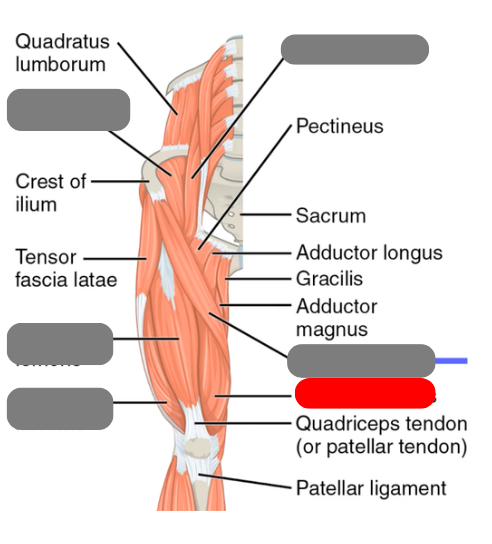
vastus medialis
-one of the quads

vastus lateralis
-one of the quads

rectum femoris
-one of the quads
4 quad muscles
-rectus femoris
-vastus medialis
-vastus lateralis
-vastus intermedias

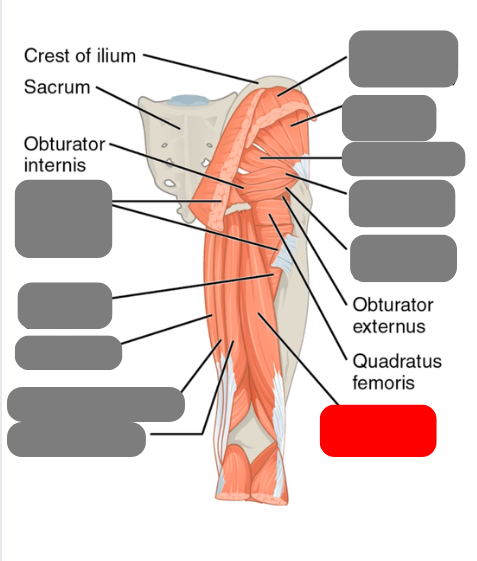
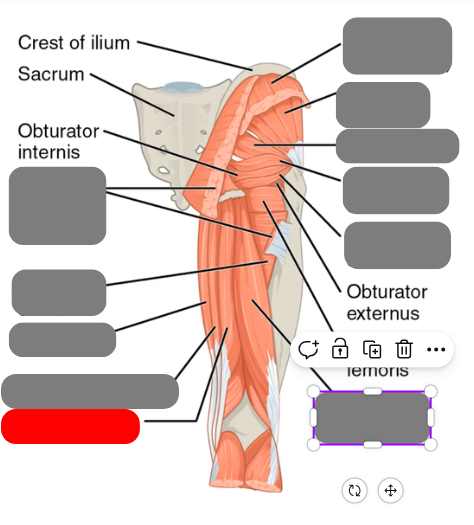
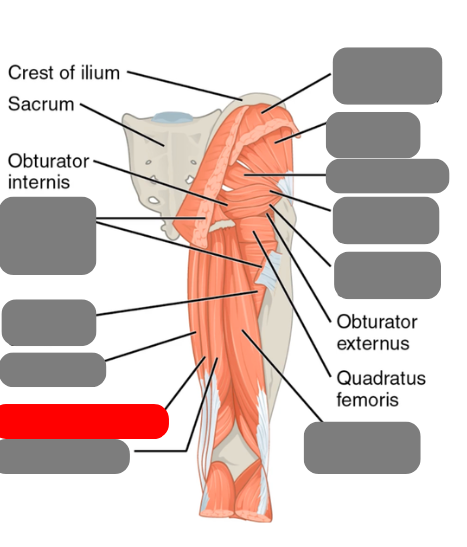
superior and inferior gamellus
-rotate the hip
biceps femoris
-one of the hamstrings
semitendinosus
-one of the hamstrings
semimembranosus
-one of the hamstrings
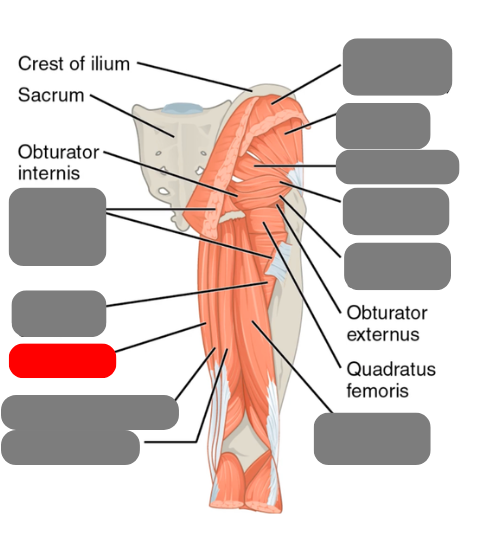
gracilis
-works with the adductor group for adduction
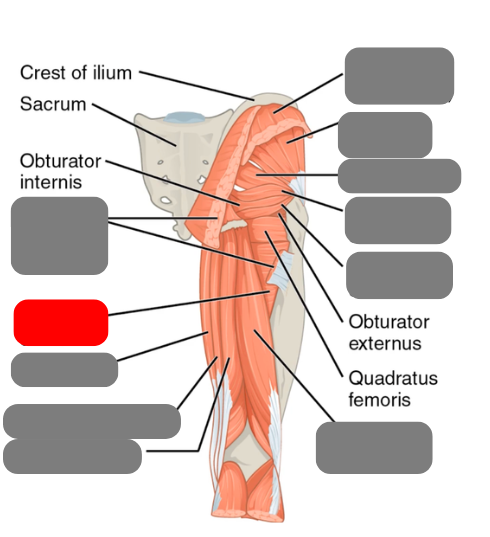
adductor group
-works with the gracilis for adduction
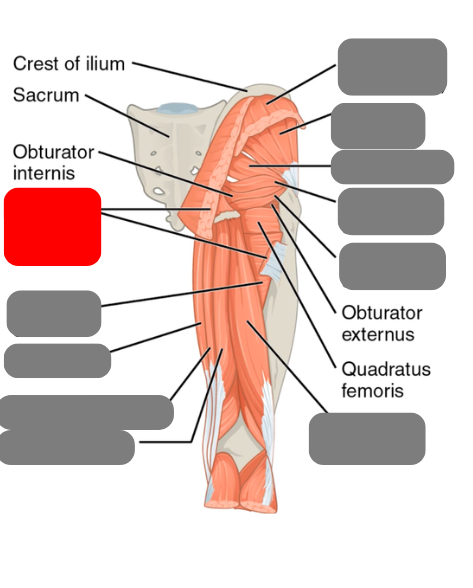
gluteus maximus
(cut)
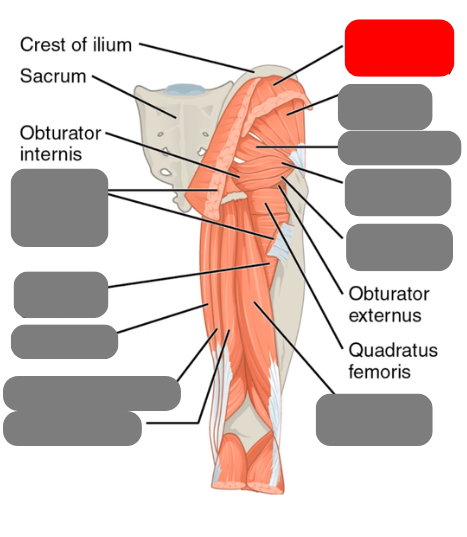
gluteus medius
-pelvic stability and injections
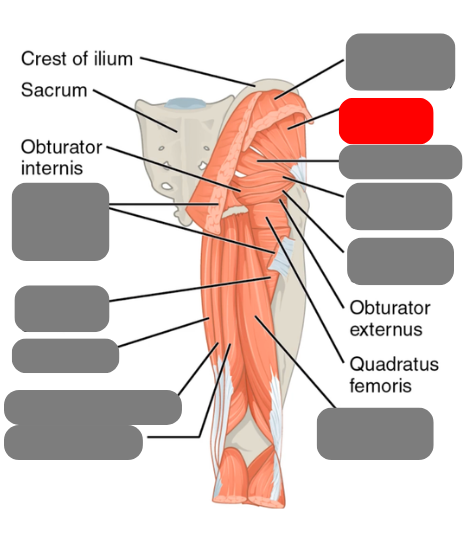
gluteus minimus
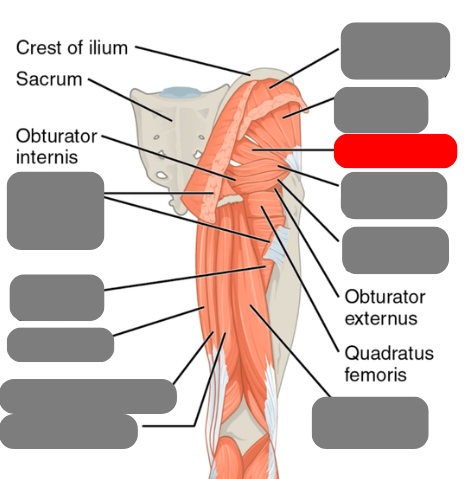
piriformis
-involved in sciatica
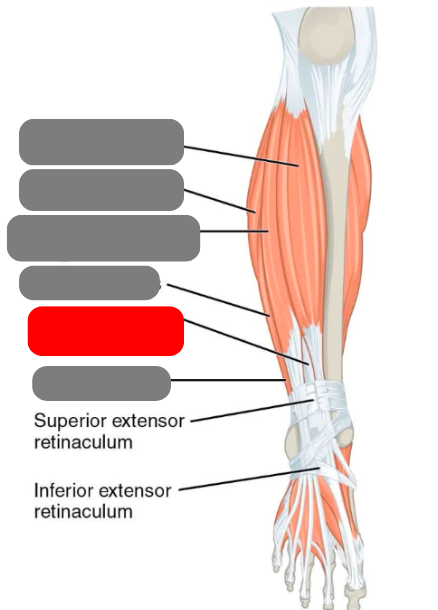
extensor hallicus longus
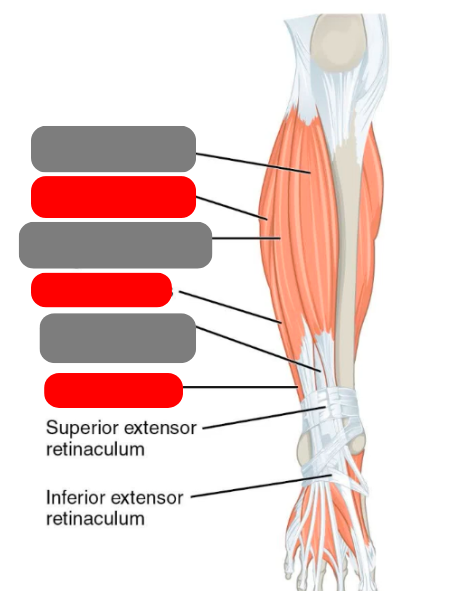
flibularis muscles
-longus
-brevis
-tertius
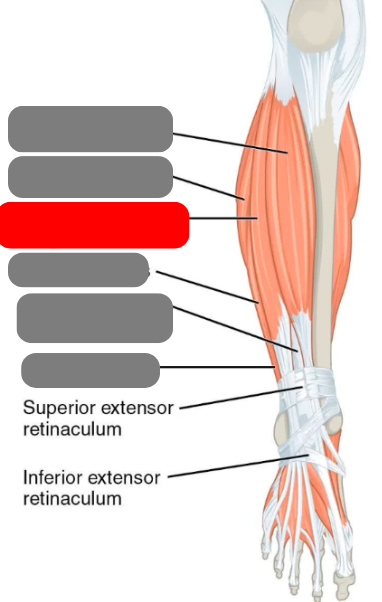
extensor digitorum longus

tibialis anterior
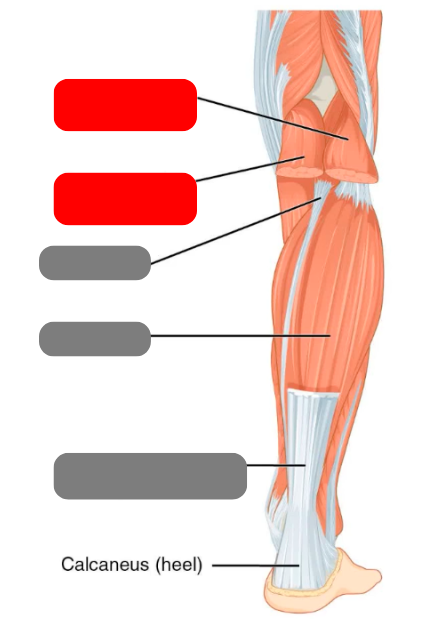
gastrocnemius
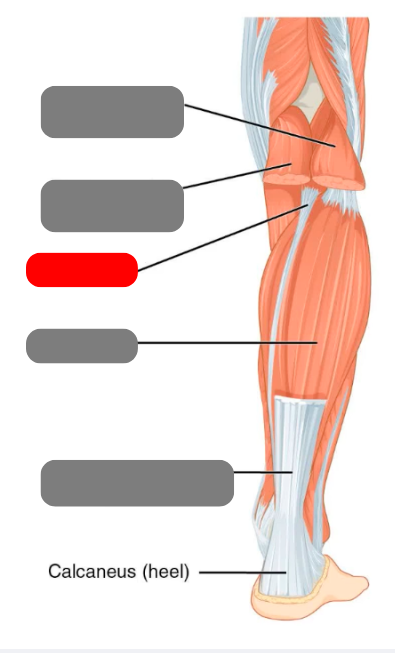
plantaris
-absent in 8-12% of population

soleus
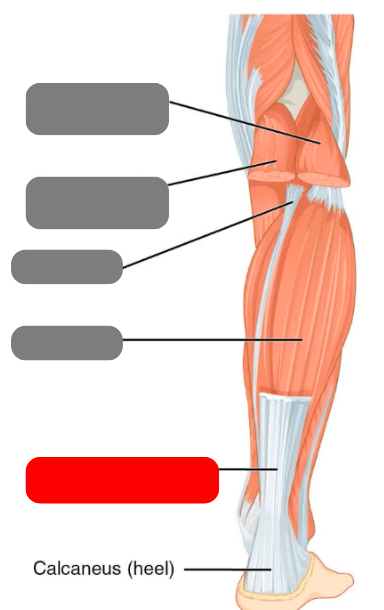
calcaneal/achilles tendon
digitorum
relating to the digits/toes
hallucis
relating to the big toe
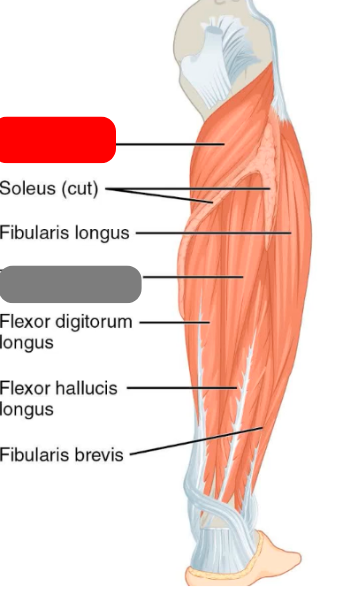
popliteus
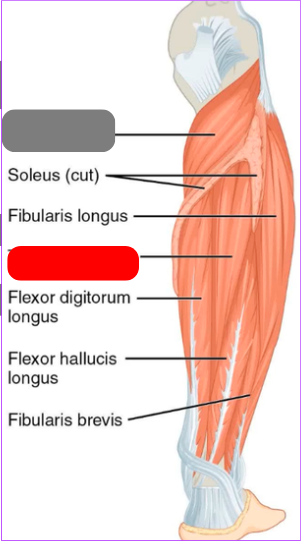
tibialis posterior
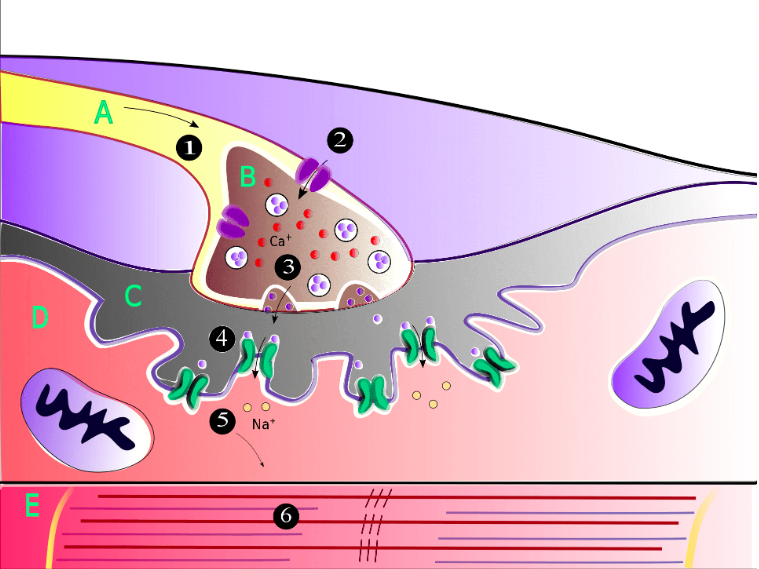
what happens at A?
action potential goes down the motor neuron causing an influx of Ca into the axon terminal (B)
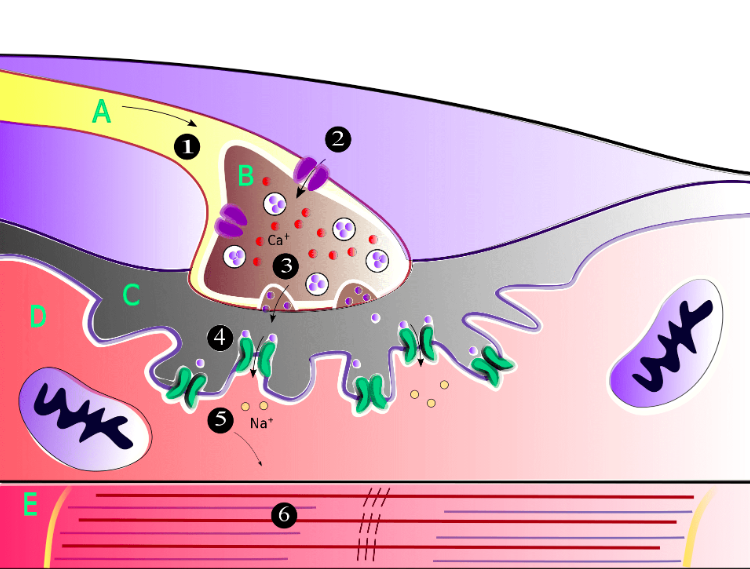
what happens at B/3?
Ca let into the axon terminal which causes the release of acetylcholine across the synaptic cleft to the motor end plate
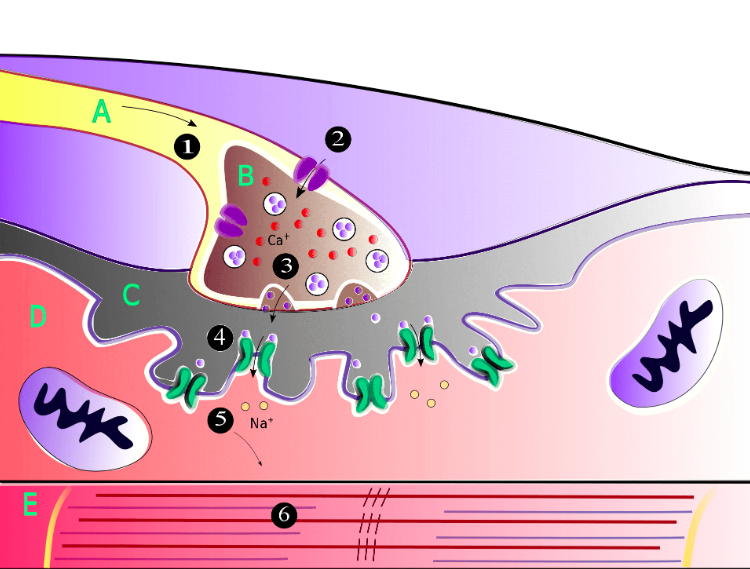
what happens at 4 and 5?
acetylcholine moves across the synaptic cleft to the motor end plate.
promotes the opening of sodium channels into the skeletal muscle cell.
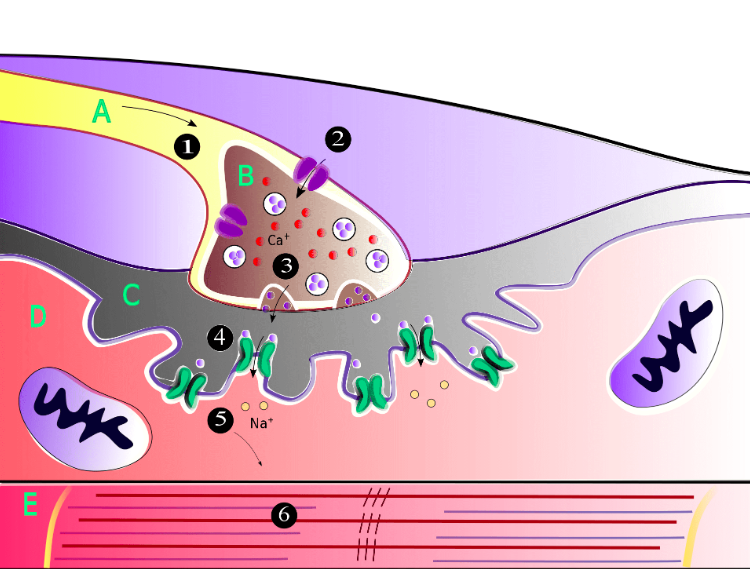
What happens at 6?
Na channels opening causes the sarcoplasmic reticulum to depolarize, queue actin myosin dance
what is the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
network of tubules that wraps around the muscle cell
-stores Ca from the blood until the muscle cell depolarizes, then releases Ca into the muscle cell
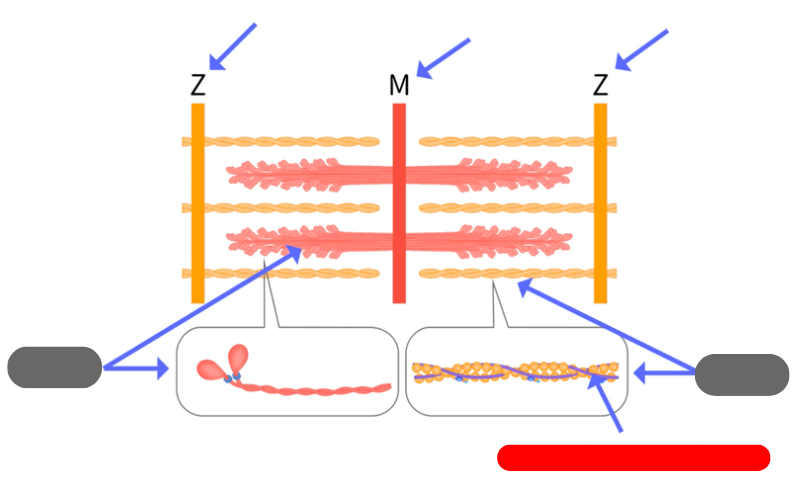
troponin-tropomyosin complex, double helix wrapped around actin
how big is a sarcomere
from 1 Z line to the next
-contractile unit
describe the T-tubules
-in the sarcolemma around the muscle cell
-tube like structures
-filled with extracellular fluid
-between them is the sarcoplasmic reticulum
cisternae
-network of membraneous channels in the sarcoplasmic reticulum
-cisternae near the T tubules are wider and called terminal cisterae
-tubule and 2 terminal cistern
steps of muscle contraction
myosin can’t attach to actin
Ca is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, binds to troponin and moves it exposing the binding site
myosin binds to actin powered by ATP
myosin pulls actin causing the sarcomere to shorten
extensor def
increases the angle at a joint
flexor def
decreases angle at a joint
supination def
rotate forarm so palm faces anteriorly
pronation
rotate forearm so the palm faces posteriorly