Memory
4.7(3)
4.7(3)
Card Sorting
1/76
Last updated 10:21 PM on 8/31/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
1
New cards
Hippocampus
brain region that processes everyday new memories
ex. “what did I eat yesterday?”
* processes __spatial memory__
ex. “what did I eat yesterday?”
* processes __spatial memory__
2
New cards
Amygdala
brain region that’s responsible for threat detection
* tends to process negative emotions (anger, aggression, fear)
* PTSD patients show lots of activity in this region when having flashbacks
* __fear memory__
\
* tends to process negative emotions (anger, aggression, fear)
* PTSD patients show lots of activity in this region when having flashbacks
* __fear memory__
\
3
New cards
Cerebellum
Brain region responsible for balance, coordination, movement. (it’s the first part of the brain affected by alcohol)
* plays a role in 2 types of memory:
* memory in classical conditioning
* procedural memory (“__muscle memory__”)
* riding a bike, swimming, piano
\
* plays a role in 2 types of memory:
* memory in classical conditioning
* procedural memory (“__muscle memory__”)
* riding a bike, swimming, piano
\
4
New cards
Acetylcholine
a neurotransmitter involved in muscle control, learning and memory
5
New cards
Serotonin
a neurotransmitter involved with sleep, mood, and hunger
6
New cards
Neural Networks
a collection of neurons that fire together
7
New cards
Long-term Potentiation (LTP)
process by which synaptic connections between neurons become stronger w/frequent activation
* thought to be crucial mechanism involved in learning and memory formation
* thought to be crucial mechanism involved in learning and memory formation
8
New cards
Recognition vs. Recall
2 opposing type of long-term memory where:
* one is when one only needs to identify items previously learned (has a reference/memory cue)
* ex. multiple choice questions where the options are presented
and the other
* one is when one must retrieve information learned earlier (without a reference/memory cue)
* ex. fill in the blank questions
* one is when one only needs to identify items previously learned (has a reference/memory cue)
* ex. multiple choice questions where the options are presented
and the other
* one is when one must retrieve information learned earlier (without a reference/memory cue)
* ex. fill in the blank questions
9
New cards
@@Declarative@@ vs. ^^Procedural^^
2 opposing types of long-term memory where:
* one is with conscious recall
* AKA explicit memory
* processed in the hippocampus
* includes @@semantic and episodic memory@@
and the other
* one is without conscious recall
* AKA implicit memory
* processed by other brain regions like cerebellum
* includes motor/cognitive ^^skill^^ memory and ^^classical conditioning^^ memory
* one is with conscious recall
* AKA explicit memory
* processed in the hippocampus
* includes @@semantic and episodic memory@@
and the other
* one is without conscious recall
* AKA implicit memory
* processed by other brain regions like cerebellum
* includes motor/cognitive ^^skill^^ memory and ^^classical conditioning^^ memory
10
New cards
Semantic vs. Episodic
2 opposing types of explicit memory where:
* one is memory of facts and general knowledge
and the other
* one is the memory of personally experienced events
* one is memory of facts and general knowledge
and the other
* one is the memory of personally experienced events
11
New cards
Information Processing Model of Memory
“memory is like a computer; we remember information in 3 steps”
1) encoding = recording incoming info so it’s usable later
2) storage = holding that info until it is needed
3) retrieval = getting info from memory when you need it
1) encoding = recording incoming info so it’s usable later
2) storage = holding that info until it is needed
3) retrieval = getting info from memory when you need it
12
New cards
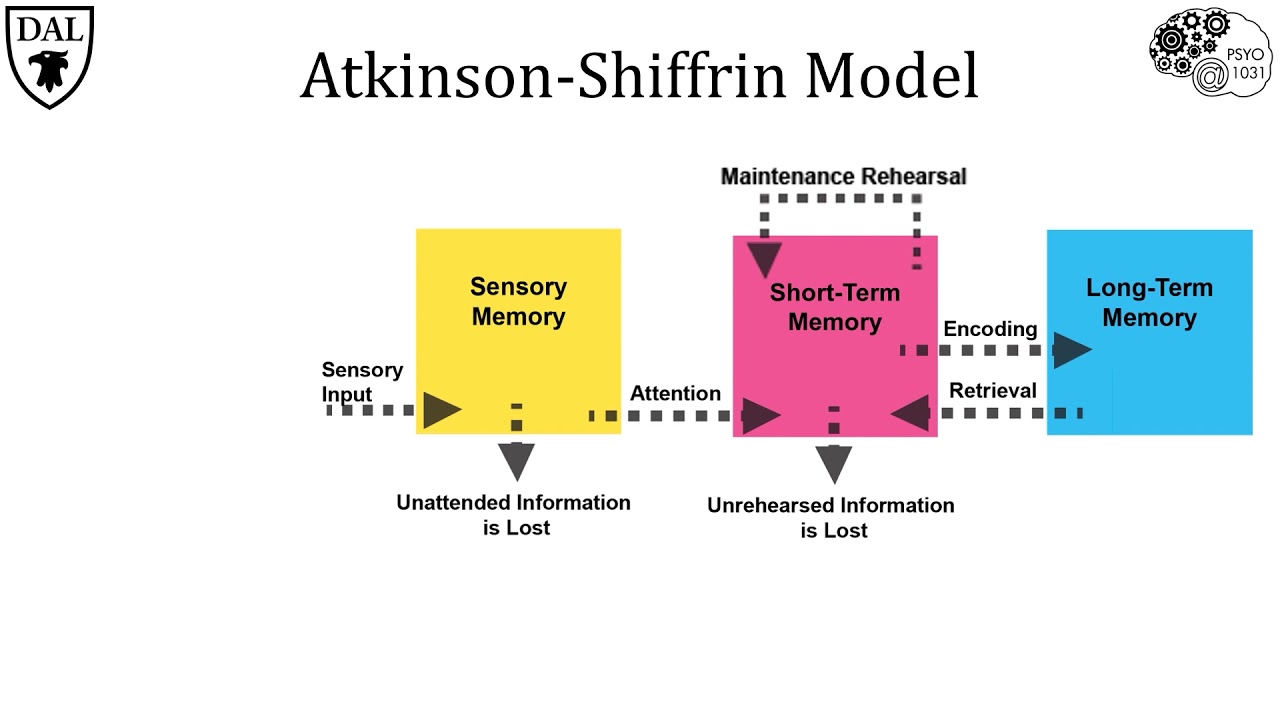
Atkinson-Shiffron Model of Memory
“stimuli move through 3 *levels* of memory”
1. sensory memory/register
* almost all stimuli are processed by sensory registers (iconic and echoic)
* most info decays in the sensory register (unless attention is directed to it and it moves on to the next level)
2. Working Memory
* processes conscious experiences and new learning
* working memory focuses attention on the important info and combines it w/info from long-term memory
3. Long-term memory
1. sensory memory/register
* almost all stimuli are processed by sensory registers (iconic and echoic)
* most info decays in the sensory register (unless attention is directed to it and it moves on to the next level)
2. Working Memory
* processes conscious experiences and new learning
* working memory focuses attention on the important info and combines it w/info from long-term memory
3. Long-term memory
13
New cards
Iconic Memory Registers
registers in the sensory memory level of A-S Model that processes __**visual**__ stimuli
14
New cards
Echoic Memory Registers
registers in the sensory memory level of A-S Model that processes __**auditory**__ stimuli
15
New cards
Miller’s Law
law that predicts that the average person can only keep 7 (±2) items in their working memory
16
New cards
Depths of Processing Model of Memory
“one either processes info shallowly or deeply”
\
Shallow Processing = doesn’t require much effort, BUT it doesn’t yield good results
vs.
Deep Processing = takes more effort, BUT more info stored
\
Shallow Processing = doesn’t require much effort, BUT it doesn’t yield good results
vs.
Deep Processing = takes more effort, BUT more info stored
17
New cards
Encoding Specificity
“the more specific your clues to help you remember items, the more you remember them”
18
New cards
Maintenance Rehearsal
a type of rehearsal using simple repetition
ex. “reps” for lifting weights
ex. repeating a # over and over until you don’t need ita
ex. “reps” for lifting weights
ex. repeating a # over and over until you don’t need ita
19
New cards
Elaborate Rehearsal
a type of rehearsal but adding a bit of info to make it easier to remember
20
New cards
Self-Reference Effect
an example of elaborate rehearsal where one uses some kind of personal info to help them remember
ex. setting password to anniversary date
ex. associating the date of Berline wall falling down (Nov 9) with your birthday on history test
ex. setting password to anniversary date
ex. associating the date of Berline wall falling down (Nov 9) with your birthday on history test
21
New cards
Chunking
an example of rehearsal where one groups info into ways that make sense
ex. breaking your SSN into groups
ex. breaking the numbers of pi into groups
ex. breaking your SSN into groups
ex. breaking the numbers of pi into groups
22
New cards
Categorization
an example of rehearsal where you rearrange info into categories that make sense
ex. grouping each section of the study guides by topics for better memorization
ex. grocery list: vegetables, dairy, etc. (and in case you lost it, you memorize better at grocery store)
ex. grouping each section of the study guides by topics for better memorization
ex. grocery list: vegetables, dairy, etc. (and in case you lost it, you memorize better at grocery store)
23
New cards
Acronym
a type of mnemonic
= a word composed of the first letters of a phrase
\
ex. **NASA** (**N**ational **A**eronautics and **S**pace **A**dministration)
ex. **SCUBA** (**S**elf **C**ontained **U**nderwater **B**reathing **A**pparatus)
= a word composed of the first letters of a phrase
\
ex. **NASA** (**N**ational **A**eronautics and **S**pace **A**dministration)
ex. **SCUBA** (**S**elf **C**ontained **U**nderwater **B**reathing **A**pparatus)
24
New cards
Mnemonic
a technique/strategy used to improve memory
25
New cards
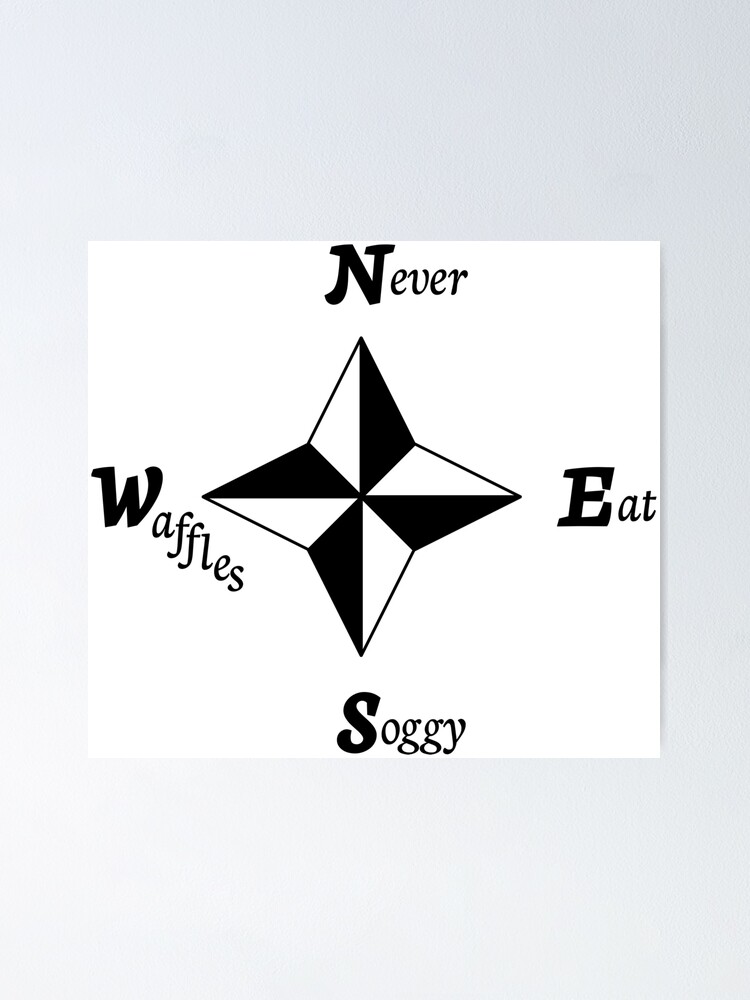
Acrostic
a type of mnemonic
= a sentence or phrase where each first letter represents something
ex. **N**ever **E**at **S**oggy **W**affles (phrase where first letters are cardinal directions)
ex. (phrase where first letters are taxonomy orders)
**K**ing
**P**hilip
**C**ame
**O**ver
**F**rom
**G**ermany
**S**miling
(think: up and down ACROSS the page)
= a sentence or phrase where each first letter represents something
ex. **N**ever **E**at **S**oggy **W**affles (phrase where first letters are cardinal directions)
ex. (phrase where first letters are taxonomy orders)
**K**ing
**P**hilip
**C**ame
**O**ver
**F**rom
**G**ermany
**S**miling
(think: up and down ACROSS the page)
26
New cards
Interactive Images
a type of mnemonic
= matching an image to a word
ex. Hippocampus = picturing a hippo wandering around thinking about its past in the brain region
= matching an image to a word
ex. Hippocampus = picturing a hippo wandering around thinking about its past in the brain region

27
New cards
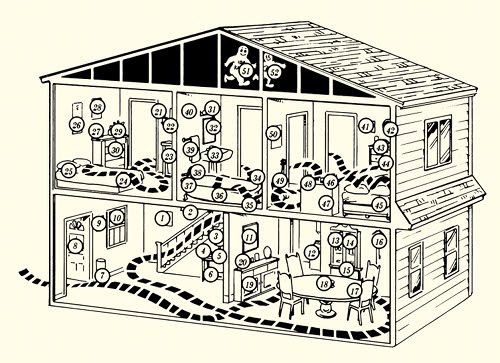
Method of Loci (Memory Palace)
a type of mnemonic
= uses visualizations of familiar spatial environments in order to enhance the recall of information
* helpful for memorizing lists of items in order
= uses visualizations of familiar spatial environments in order to enhance the recall of information
* helpful for memorizing lists of items in order
28
New cards
Peg words
previously memorized words (that you know because they rhyme with 1-10) that you connect with ten test words that you want to memorize
ex.
2 = shoe and you want to memorize lettuce as the second item in the list, so you picture lettuce stuffed in a shoe
10 = hen and you want to memorize getting peanut butter last, so you picture a hen doused in peanut butter
ex.
2 = shoe and you want to memorize lettuce as the second item in the list, so you picture lettuce stuffed in a shoe
10 = hen and you want to memorize getting peanut butter last, so you picture a hen doused in peanut butter

29
New cards
Distributive Learning vs. Massed Learning
ex. distributing your studying across a week instead of cramming the night before
30
New cards
Positive Transfer/Scaffolding
Building upon old knowledge
ex. learning math from 8th to 12th grade, first learn algebra, then precalc, trig, and finally calculus
ex. teaching limits, then derivatives
ex. learning math from 8th to 12th grade, first learn algebra, then precalc, trig, and finally calculus
ex. teaching limits, then derivatives
31
New cards
Negative Transfer
When current information/skills get in the way of learning something new
\
ex. false cognates in language learning
\
ex. false cognates in language learning
32
New cards
Memory Storage
facts/sensations/emotions are stored briefly in working memory then much longer in long term memory
33
New cards
Flashbulb memory
a vivid, enduring memory associated with a personally significant and emotional event, often including such details as where the individual was or what he or she was doing at the time of the event
ex. people remember vivid snapshot of what they were doing when they heard about
the 9/11 attacks
ex. people remember vivid snapshot of what they were doing when they heard about
the 9/11 attacks

34
New cards
Eidetic Memory
= photographic memory
* very rare
* those who have it struggle with prioritizing more important info
* remembering every word from textbook but also the coffee stain in the corner
* clutters the memory
* very rare
* those who have it struggle with prioritizing more important info
* remembering every word from textbook but also the coffee stain in the corner
* clutters the memory
35
New cards
Highly Superior Autobiographical Memory (HSAM)
= uncommon ability to recall vast amounts of __**personal**__ events/experiences and their associated dates
36
New cards
Context-Dependent Memory
= having better recall when you are in the same environment as when you encoded and retrieved the information
* uses ^^**external cues**^^ for recall
ex. chewing a certain type of gum while studying → better recall when chewing same gum
ex. losing car keys and “retracing steps” to determine all possible places
ex. scrolling back up to a TikTok to recall a thought you had at that time
* uses ^^**external cues**^^ for recall
ex. chewing a certain type of gum while studying → better recall when chewing same gum
ex. losing car keys and “retracing steps” to determine all possible places
ex. scrolling back up to a TikTok to recall a thought you had at that time
37
New cards
State-dependent memory
= memory that depends on state of consciousness due to drugs or alcohol
* using @@**internal cues**@@ for recall
\
ex.
learning while tipsy = better recall while tipsy
learning while sober = better recall while sober
(ofc sober group was overall better than the tipsy group, but within the test group performance differed)
* using @@**internal cues**@@ for recall
\
ex.
learning while tipsy = better recall while tipsy
learning while sober = better recall while sober
(ofc sober group was overall better than the tipsy group, but within the test group performance differed)
38
New cards
mood-congruent memory
= memory that depends on emotional state
* using @@**internal cues**@@ for recall
\
ex. people are more likely to recall happy memories when they are happy again
* using @@**internal cues**@@ for recall
\
ex. people are more likely to recall happy memories when they are happy again
39
New cards
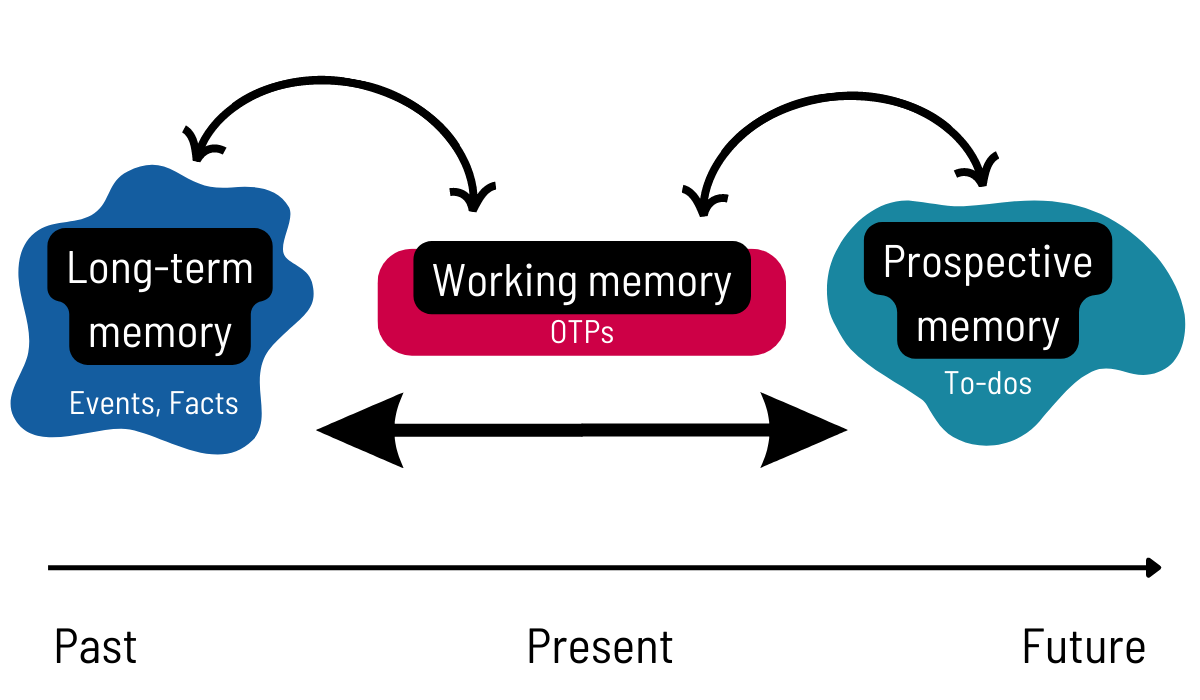
Prospective Memory
= remembering to do things __in the future__
* part of ^^executive functioning (prefrontal cortex in frontal lobe)^^
ex. planning ahead, keeping appointments, remembering birthdays, and meeting deadlines
* part of ^^executive functioning (prefrontal cortex in frontal lobe)^^
ex. planning ahead, keeping appointments, remembering birthdays, and meeting deadlines
40
New cards
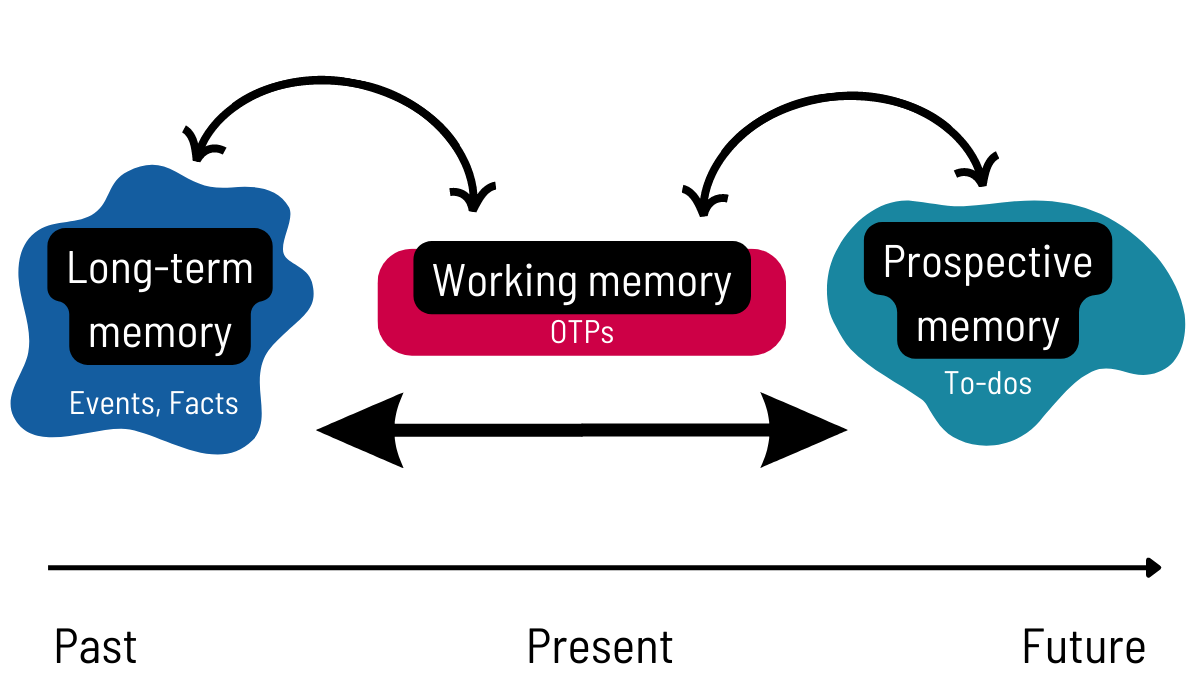
Retrospective Memory
= remembering events __from the past__ or previously learned info
* opposite of prospective memory
* opposite of prospective memory
41
New cards
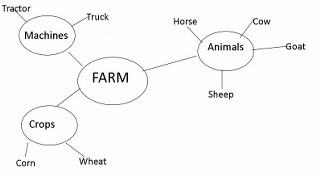
Semantic Networks
= closely related terms are stored together in memory and so when you recall one item, you probably will also recall other, similar items
42
New cards
Serial Processing
a type of memory retrieval where you recall one item at a time
43
New cards
Self-terminating serial processing
a type of serial processing where you stop looking once you’ve located the item
ex. it would be unnecessary to keep looking for car keys after you’ve found them
ex. it would be unnecessary to keep looking for car keys after you’ve found them
44
New cards
exhaustive serial processing
a type of serial processing where you search your entire memory list before making a choice
ex. looking at ALL the multiple choice answers before choosing one (because you don’t want to stop after an “almost best choice” when you could keep looking for a “BEST choice”
ex. looking at ALL the multiple choice answers before choosing one (because you don’t want to stop after an “almost best choice” when you could keep looking for a “BEST choice”
45
New cards
Parallel Processing
searching a group of items in memory **simultaneously**
ex. facial recognition (jumping around when looking at a yearbook page instead of going left to right and up and down like reading (which would be serial))
ex. facial recognition (jumping around when looking at a yearbook page instead of going left to right and up and down like reading (which would be serial))
46
New cards
Serial Position effect
tendency to better recall items at the __beginning or end__ of a list
47
New cards
Primacy Effect
tendency to better recall items at the __beginning__ of a list
48
New cards
Recency Effect
tendency to better recall items at the __end__ of a list
49
New cards
Tip of the Tongue Phenomenon
knowing you remember but you can’t seem to access the info in the moment
* is an example of blocking (the third sin of omission)
* is an example of blocking (the third sin of omission)
50
New cards
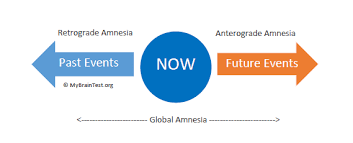
Retrograde Amnesia
a type of amnesia where you can't recall memories that were formed before the event that caused the amnesia. It usually affects recently stored past memories, not memories from years ago.
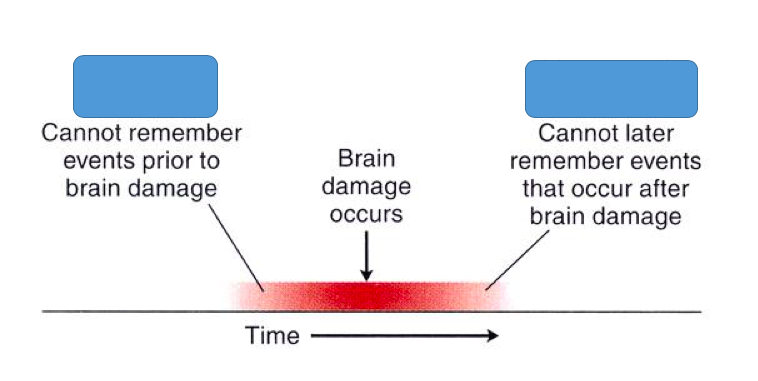
51
New cards
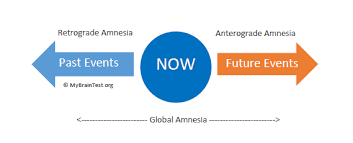
Anterograde Amnesia
a type of memory loss that occurs when you can't form new memories
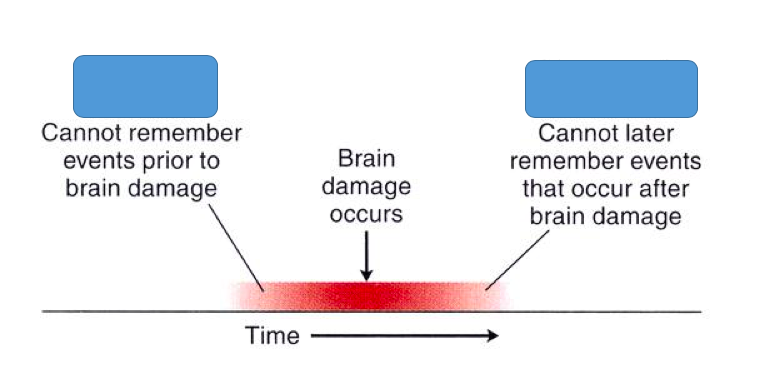
52
New cards
Alzheimer’s
A progressive disease where brain cell connections and the cells themselves degenerate and die,
* destroys memory and other mental functions
* destroys memory and other mental functions
53
New cards
Repression
__unconsciously__ blocking unwanted thoughts or impulses
54
New cards
Supression
__deliberately__ trying to forget or not think about painful or unwanted thoughts
55
New cards
Context
the conditions or circumstances in which a particular phenomenon occurs
56
New cards
Transience
Sin #1 (Omission)
= deterioration of memories over time
= deterioration of memories over time
57
New cards
Absent-mindedness
Sin #2 (Omission)
= breakdown at the interface of attention and memory
* person usually forgets to carry out specific action @ specific time in the absence of retrieval cues and when attention is not focused on task
* due to failure of attention (you remember, just can’t recall @ specific time, but will remember later)
= breakdown at the interface of attention and memory
* person usually forgets to carry out specific action @ specific time in the absence of retrieval cues and when attention is not focused on task
* due to failure of attention (you remember, just can’t recall @ specific time, but will remember later)
58
New cards
Blocking
Sin #3 (Omission)
= temporary inaccessibility of info stored in memory
* usually happens w/infrequently accessed memories
ex. tip of the tongue moments (you remember, but can’t seem to access it) (like forgetting an old acquaintance’s name)
= temporary inaccessibility of info stored in memory
* usually happens w/infrequently accessed memories
ex. tip of the tongue moments (you remember, but can’t seem to access it) (like forgetting an old acquaintance’s name)
59
New cards
Proactive Interference
a type of interference/blocking
= old memories disrupt the retrieval of %%new memories%%
ex. writing the old year for the first few weeks of the new year
= old memories disrupt the retrieval of %%new memories%%
ex. writing the old year for the first few weeks of the new year
60
New cards
Retroactive Interference
a type of interference/blocking
= new memories disrupt the retrieval and maintenance of old memories
ex. learning a new script but you forget the old one for an old play
= new memories disrupt the retrieval and maintenance of old memories
ex. learning a new script but you forget the old one for an old play
61
New cards
Misattribution
Sin #4 (Commission)
= a type of memory distortion where you attribute a memory/idea to the wrong source
= a type of memory distortion where you attribute a memory/idea to the wrong source
62
New cards
False Recognition
= a type of misattribution (#4) where you think you recognize a new stimulus but it’s just similar to an old stimulus you know
ex. “I feel like we’ve met before”
* but this new face is actually just similar to a face you already know
ex. “I feel like we’ve met before”
* but this new face is actually just similar to a face you already know
63
New cards
Déja Vu
= a type of misattribution (#4) where you feel like you’ve lived an experience before
* you’re __falsely recognizing__ the moment to be a new one when it’s just a moment that familiar to an old one
* you’re __falsely recognizing__ the moment to be a new one when it’s just a moment that familiar to an old one
64
New cards
Cryptomnesia (Source Amnesia)
a type of misattribution (#4)
= thinking that you have an original idea but it’s actually just a memory of someone else’s
* could lead to accidental plagiarism!!
ex. a musician comes up with an “original” melody but they don’t realize that they’ve actually heard it in another song
= thinking that you have an original idea but it’s actually just a memory of someone else’s
* could lead to accidental plagiarism!!
ex. a musician comes up with an “original” melody but they don’t realize that they’ve actually heard it in another song
65
New cards
Source Monitoring
a type of misattribution (#4)
= an unconscious mental test that humans perform in order to determine if a memory is "real" and accurate as opposed to being from a source like a dream or a movie
= an unconscious mental test that humans perform in order to determine if a memory is "real" and accurate as opposed to being from a source like a dream or a movie
66
New cards
Conflation
a type of misattribution (#4)
= the merging of two or more sets of information, texts, ideas, opinions, etc., into one, often in error
* treating two similar but disparate concepts as the same
= the merging of two or more sets of information, texts, ideas, opinions, etc., into one, often in error
* treating two similar but disparate concepts as the same
67
New cards
Constructive Memory
a type of misattribution (#4)
involving the use of general knowledge stored in one’s memory to construct a more complete and detailed account of an experience
* changing or filling in various features of the memory.
involving the use of general knowledge stored in one’s memory to construct a more complete and detailed account of an experience
* changing or filling in various features of the memory.
68
New cards
Suggestibility
Sin #5 (Commission)
= implanted memories that result from suggestion or misinformation
\
key takeaway → our memory are malleable: external information that’s not part of a memory can influence it
= implanted memories that result from suggestion or misinformation
\
key takeaway → our memory are malleable: external information that’s not part of a memory can influence it
69
New cards
Framing
a type of suggestibility (#5)
= a cognitive bias in which the brain makes decisions about information depending upon how the information is presented
* effect → people decide on options based on whether the options are presented with positive or negative connotations
= a cognitive bias in which the brain makes decisions about information depending upon how the information is presented
* effect → people decide on options based on whether the options are presented with positive or negative connotations
70
New cards
Eyewitness Testimony
an account given by people of an event they have witnessed
\
* can be affected by leading questions:
“the suspect had an earring, remember?”
“oh yeah, they did!” (they did not)
\
* can be affected by leading questions:
“the suspect had an earring, remember?”
“oh yeah, they did!” (they did not)
71
New cards
“Lost in the Mall” (Loftus)
* Participants were told some stories about their childhood (gathered from their family)
* 1 of them was false with a lot of details (lost in a mall and got rescued)
* was asked to recall after and then a week after
* 20% believed the false story to be true
\
Takeaway → suggestive procedures (social influence and mere visualizations) can create false memories
* 1 of them was false with a lot of details (lost in a mall and got rescued)
* was asked to recall after and then a week after
* 20% believed the false story to be true
\
Takeaway → suggestive procedures (social influence and mere visualizations) can create false memories
72
New cards
Repressed Memories
inability to recall autobiographical info (usually traumatic)
73
New cards
Recovered Memories
memory of traumatic event recalled years later
ex. childhood sexual abuse victims remembering later
* BUT sometimes is invalid/false memory due to outside influence (suggestibility)
ex. childhood sexual abuse victims remembering later
* BUT sometimes is invalid/false memory due to outside influence (suggestibility)
74
New cards
Bias
Sin #6 (Commission)
= retrospective distortions produced by current knowledge, beliefs, and feelings
= retrospective distortions produced by current knowledge, beliefs, and feelings
75
New cards
Consistency Bias
a type of bias (#6)
= rewriting the past to make it consistent w/current info
= tendency to think our current beliefs/perspectives have been consistent all along
ex. “I’ve always had this opinion”
= rewriting the past to make it consistent w/current info
= tendency to think our current beliefs/perspectives have been consistent all along
ex. “I’ve always had this opinion”
76
New cards
Hindsight Bias
a type of bias (#6)
= tendency to perceive past events as having been more predictable than they actually were
* AKA “knew it all along” bias
ex. insisting that you knew the winning team was going to win all along
= tendency to perceive past events as having been more predictable than they actually were
* AKA “knew it all along” bias
ex. insisting that you knew the winning team was going to win all along
77
New cards
Persistance
Sin #7 (Commission, a type of memory distortion)
= intrusive remembering of events
* usually negative, traumatic memories
ex. PTSD patients having flashbacks
ex. embarrassing/distressing moments that you just can’t seem to forget
= intrusive remembering of events
* usually negative, traumatic memories
ex. PTSD patients having flashbacks
ex. embarrassing/distressing moments that you just can’t seem to forget