10 Natural Science - The Chemistry of Life
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/65
Last updated 10:09 AM on 3/20/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
1
New cards
hypertonic
A higher concentration of solutes
2
New cards
hypotonic
A lower concentration of solutes
3
New cards
isotonic
An equal concentration of solutes
4
New cards
Inorganic compounds
Make up non-living things, make up many essential substances such as water, hydrogen and carbon
5
New cards
Organic compounds
make up living things, contain carbon bound to hydrogen, elements arranged into large, complex chemical compounds which consist of monomers bound together to form polymers
6
New cards
Carbohydrates
serve as fuel and building material, consist of C, H, and O (H to O ratio is 2:1)
7
New cards
Lipids
contain C, H, and O, but in different ratios, rich energy source but difficult to digest, insoluble, long chains of fatty acid molecules and glycerol units
8
New cards
Nucleic acids
The subunit is the nucleotide (consists of sugar, phosphate, and nitrogenous base), they provide genetic instructions that code for proteins
9
New cards
proteins
Contain C, H, O as well as N, P, S, and other elements, Each molecule is a long chain of amino acid units (20 or so various kinds), can be denatured by heat, strong acids, ad bases
10
New cards
Monosaccharide
Simple sugars, are soluble and used in respiration, e.g., glucose
11
New cards
Disaccharide
Complex sugars, consist of two saccharide units bonded together, e.g., lactose
12
New cards
Polysaccharide
Long chains of sugar units, are insoluble and used for energy storage (e.g. glycogen and starch) and structural purposes (e.g. cellulose and chitin)
13
New cards
Carbohydrate examples
Sugar, celery, pasta
14
New cards
Lipid examples
Waxes (e.g., plant cuticles), Steroids (e.g., sex hormones), Pigments (e.g., chlorophyll), Phospholipids (e.g., cell membranes)
15
New cards
Nucleic acid examples
deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA)
16
New cards
Protein examples
Enzymes, Hormones, Important blood proteins, Structural materials, Pigments
17
New cards
Monomers
Small molecules and building blocks for polymers
18
New cards
Polymers
Large molecules, made out of bonded monomers
19
New cards
Hydrolysis
The breaking down of polymers into monomers
20
New cards
Condensation
The bonding of monomers together to form polymers
21
New cards
Catalyst
A substance that speeds up a chemical reaction without being changed
22
New cards
Enzyme
A biological catalyst (usually a protein)
23
New cards
Substrate
The reactant molecules that an enzymes works on
24
New cards
Active site
The part of the enzyme where the substrate binds
25
New cards
Denature
Process of permanently modifying the structure of a protein (enzyme)
26
New cards
Factors affecting enzymes
there are many things that can affect the activity if enzymes, two of which are temperature and pH
27
New cards
Enzyme shape
the shape of enzymes is very important, the active site is extremely specific to the substrate that is acted on, this means that anything that causes the enzyme to change shape (denature) will stop it from working
28
New cards
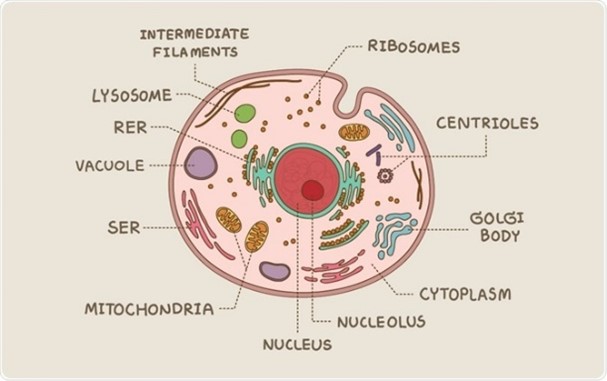
Eukaryote cell
Has membrane bound organelles, multicellular, big, has a nucleus
29
New cards
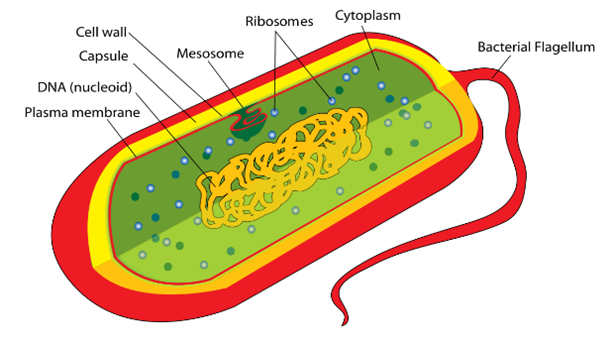
Prokaryote cell
Doesn’t have membrane bound organelles, unicellular, small, doesn’t have a nucleus
30
New cards
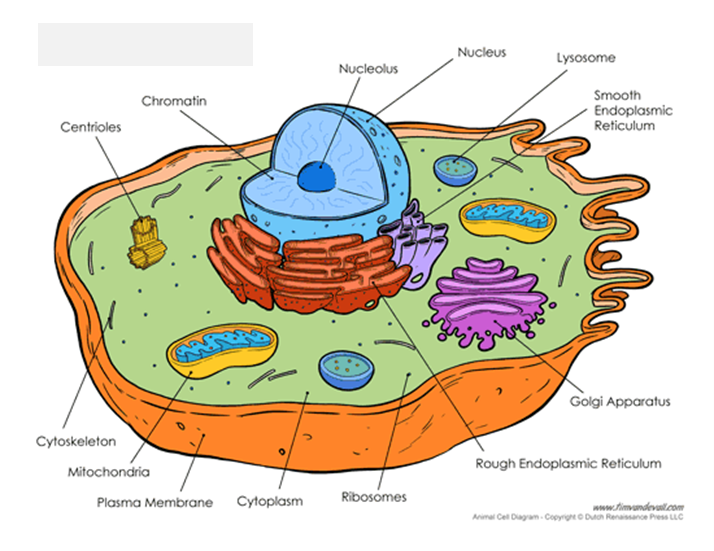
Animal cell
Have centrioles, lysosomes, flagella
31
New cards
Plant cell
Have cell wall, chloroplasts, chlorophyll, large vacuoles
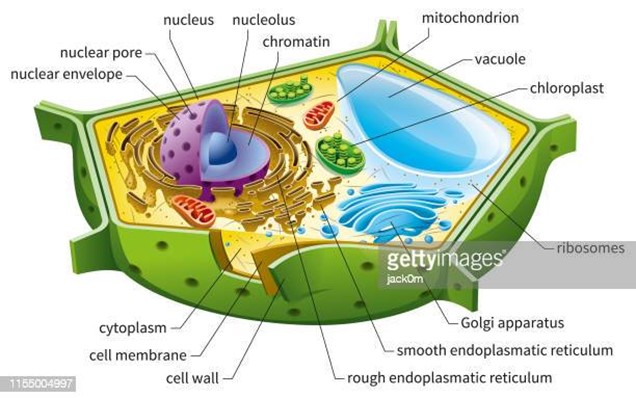
32
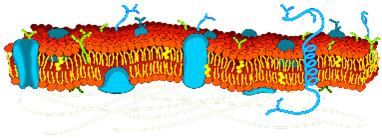
New cards
Cell/plasma membrane
helps to protect the cell, maintain their shape and keeps the cell from absorbing too much water, animal cells have an extracellular matrix that helps hold the cells together in tissues and protects and supports them
33
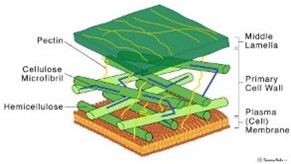
New cards
Cell wall
Only in plants, protects the insides and makes the cells rigid
34
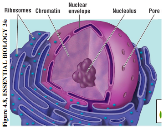
New cards
Nucleus
Contains the cell’s DNA, the largest of all organelles, genes in the nucleus carry information necessary to make proteins, the nucleus is bordered by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope
35
New cards
rough endoplasmic reticulum
Synthesises an enormous variety of molecules, Then packages the molecules into transport vesicles, Rough due to ribosomes on the outer membrane, Ribosomes synthesis proteins
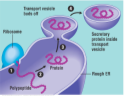
36
New cards
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
used for detoxification and makes some lipids, e.g., steroids
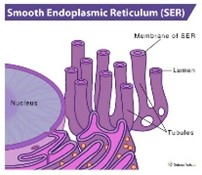
37
New cards
Golgi apparatus
Works in partnership with the endoplasmic reticulum, Refines, stores, and distributes the chemical products produced in the ER
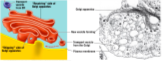
38
New cards
Lysosome
A membrane enclosed sac, Contains digestive enzymes, Has three main functions: Fuse with food vacuoles to digest the food, Break down damaged organelles, Help destroy harmful bacteria
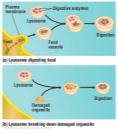
39
New cards
Vacuole
Membranous sacs used for storage (mostly in plants), Animals only have a few small vacuoles
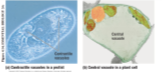
40
New cards
Chloroplast
Only found in plants and algae, Sites of photosynthesis, Convert light energy to chemical energy
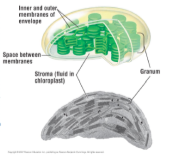
41
New cards
Mitochondria
The powerhouse of the cell, Sites of cellular respiration, Use glucose and oxygen to produce chemical energy (ATP), Found in all eukaryotic cells, CO2 + H2O -\> C6H12O6+O2+H2O
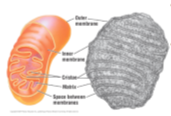
42
New cards
Cytoskeleton
Not a true organelle, Network of fibres that Provide mechanical support and allow cells to change shape and move, Assist on cell division
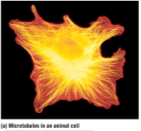
43
New cards
Cilia and flagella
Are motile appendages, flagella propel the cell in a whiplike motion, Cilia move in a coordinated back-and-forth motion
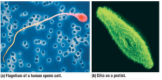
44
New cards
Selective permeability
a property of cell membranes, membranes are said to be semipermeable., i.e., they allow certain molecules or ions to pass through.
45
New cards
Osmosis
the overall (net) movement of water molecules from a dilute solution to a more concentrated solution through a semi-permeable membrane.
46
New cards
Concentration gradient
The difference in concentration of molecules across a space
47
New cards
Limitations to cell size
A cell needs to be able to take in nutrients and eliminate wastes effectively. Since this mainly occurs via diffusion, factors that affect the diffusion will also affect a cells ability to survive
48
New cards
Chromatid
One of two duplicated chromosomes connected at the centromere
49
New cards
Centromere
Region of chromosome where microtubules attach during mitosis and meiosis
50
New cards
Cell cycle
\
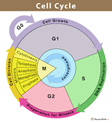
51
New cards
Mitosis
a part of the cell cycle process by which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus (diploid cells), a cell splits to create two identical copies of the original cell -\> asexual reproduction
52
New cards
Interphase
The cell at rest, Accounts for 90% of the cycle, During interphase, the cell grows and copies its chromosomes in preparation for cell division
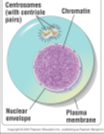
53
New cards
Prophase
Chromatin condenses into chromosomes, Nucleoli disappears, Each duplicated chromosome appears as two identical sister chromatids, joined at the centromere, Mitotic spindle begins to form, Centrosomes move to opposite ends of the cell, Nuclear envelope fragments, Microtubules extend from each centrosome and attach to the centromeres of the chromosomes
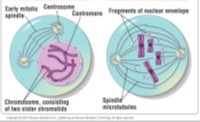
54
New cards
Metaphase
Longest state of mitosis, Centrosomes are at opposite ends of the cell, Chromosomes line up along the metaphase plate, an imaginary plane in the middle of the cell, Each sister chromatid is attached to a microtubule from the opposite side of the cell
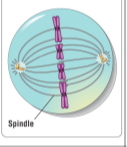
55
New cards
Anaphase
Shortest stage of mitosis, Sister chromatids separate, each becoming a full-fledged chromosome, The chromosomes are then pulled to opposite ends of the cell, The cell elongates
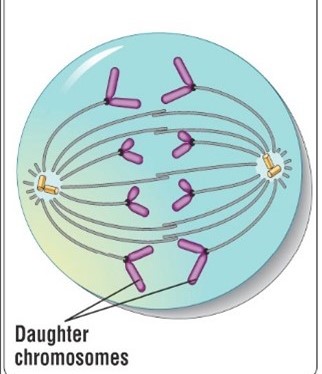
56
New cards
Telophase
Two daughter nuclei begin to form in the cell, Chromosomes are decondensing, Cytokinesis is underway
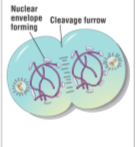
57
New cards
cancer
begins when genes controlling cell growth and multiplication become mutated by carcinogens, One example is the p53 gene, which normally acts to prevent cell division in damaged cells
58
New cards
Rate of diffusion
Temperature – higher temp -\> faster diffusion, Surface area – larger area -\> faster diffusion, Concentration gradient – higher gradient -\> faster diffusion, Size of particles – smaller particles -\> faster diffusion, Diffusion medium – solid \= slowest, liquid \= faster, gas \= fastest
59
New cards
Cell reproduction
Cell replication is a normal part of maintaining a healthy body, Growth, inheritance, and reproduction depend on cell division, Prokaryotic cells divide by binary fission, Eukaryotic cells divide by mitosis and meiosis
60
New cards
Chromosome replication
Before a cell can divide it must copy all of its chromosomes, Copied chromosomes remain joined and are called sister chromatids, Usually, chromosomes appear as chromatin but during cell division they become condensed packages so that they can be moved around easily, 46 chromosomes in each human cell
61
New cards
simple diffusion
Movement of solutes across the cell membrane with the concentration gradient between the phospholipid molecules.
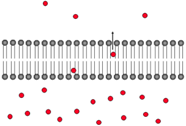
62
New cards
facilitated diffusion
Movement of solutes across the cell membrane with the concentration gradient through the carrier proteins
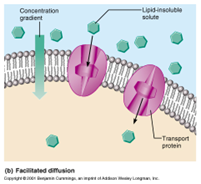
63
New cards
osmosis
Movement of solvent (water) across the cell membrane with the concentration gradient between the phospholipid molecules and via aquaporins (protein channels)
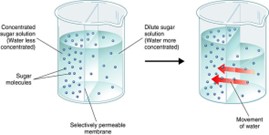
64
New cards
ion pumps
Movements of substances against the concentration gradient through the carrier proteins
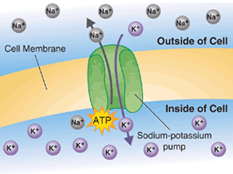
65
New cards
endocytosis
Bulk transport of liquids (pinocytosis) or solids (phagocytosis) into the cell
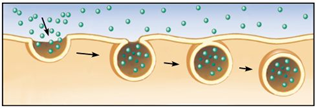
66
New cards
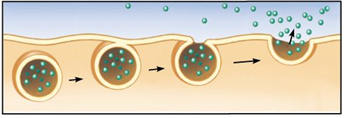
exocytosis
Bulk transport of substances out of the cell