7.3 Translation
- Conversion of sequence of bases on mRNA into sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide.
- Polypeptides are synthesized by ribosomes and tRNA.
tRNA
- Delivers the amino acid to the ribosome as the polypeptide chain elongates.
- 70-90 nucleotides long.
- Folds into a cloverleaf shape.
- One arm of tRNA contains the anticodon, which is complementary to codon in mRNA.
- The amino acids is attached to the opposite end of the tRNA molecule.
The Wobble Hypothesis
- The anticodon only needs to match the first TWO bases in the codon, The third can be incorrect but still retrieve the correct amino acid.
- Remember that multiple codons may encode for the same amino acid.
Aminoacylation
- Amino acids are linked to tRNA in a process called aminoacylation.
- This process is performed by the enzyme aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase.
- There are 20 enzymes, one for each amino acid. The product is called an aminoacyl-tRNA
Ribosomes
Composed of 2 subunits: large ribosomal subunit and small ribosomal subunit, both composed of rRNA (ribosomal RNA)
mRNA moves through groove between subunits
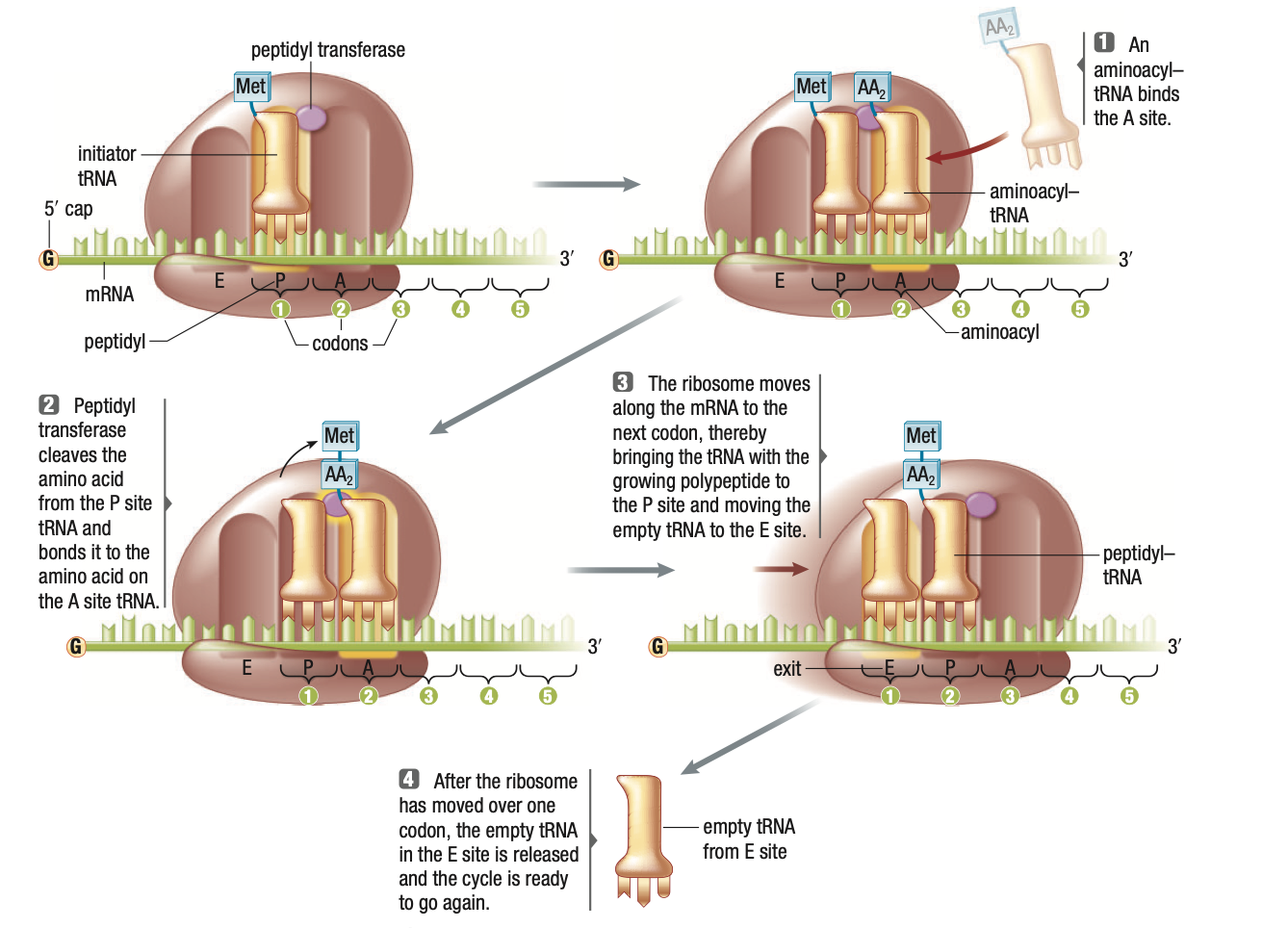
Contains 3 binding sites
- A (aminoacyl) site – aminoacyl tRNA containing next amino acid binds to MRNA
- P (peptidyl) site – TRNA binds to ribosome
- E (exit) site – tRNA leaves ribosome

3 stages of translation:
Initiation
- Translation begins at the start codon (AUG) on mRNA
- AUG is the codon for the amino acid methionine
- The aminoacyl-TRNA for methionine (the initiator tRNA) binds the small ribosomal subunit and scans the mRNA for the start codon
- When met-tRNA recognizes the start codon, the large ribosomal subunit binds
- A reading frame is established such that the bases are read 3 at a time from start codon.
Elongation
- Begins with initiator tRNA bound to P site and empty A site
- Aminoacyl-tRNA with next amino acid binds to A site
- Amino acid in P site is removed from its tRNA and a peptide bond is formed with the amino acid in the A site
- Ribosome moves to next codon, all tRNA’s shift (P --> E, A --> P)
- A site is now ready to accept next aminoacyl-tRNA. E site ejects its tRNA.
Termination
Occurs when stop codons enter the A site (UAA, UAG, UGA)
Protein release factor binds instead of aminoacyl-tRNA (there are no corresponding amino acids for stop codons)
Polypeptide is released, ribosomal subunits detach.