Sports Science IB Exam
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
154 Terms
Inferior
Closer to the feet (below)
Superior
Closer to the head (above)
Proximal
Closer to the trunk
Distal
further from the trunk
Posterior
Closer to the back (behind)
Anterior
closer to the front (in front)
Internal
on the inside
External
On the outside
Lateral
away from the midline of the body
Medial
Closer to the midline
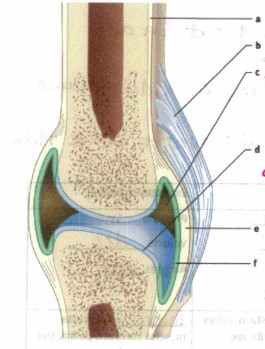
What is “a”
bone
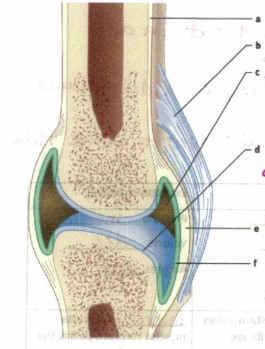
What is “b”?
Ligament, connects bone to bone
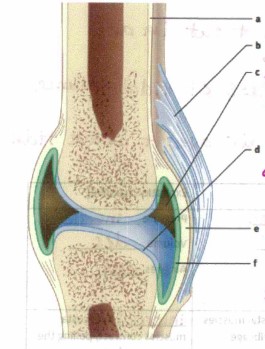
What is “c”?
Synovial cavity, holds synovial fluid (lubrication)
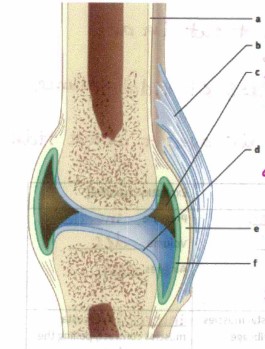
What is “d”?
Articular cartilage, absorbs shock and cushions joint
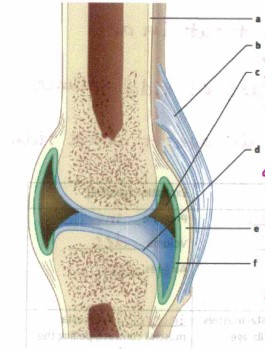
What is “e”?
Joint capsule

What is “f”?
synovial membrane, Secretes synovial fluid
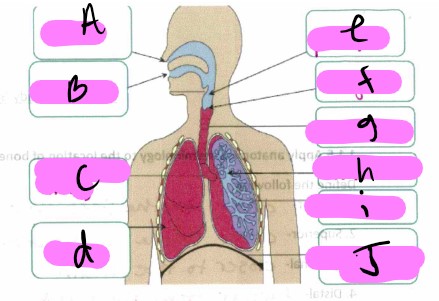
What’s a?
nose
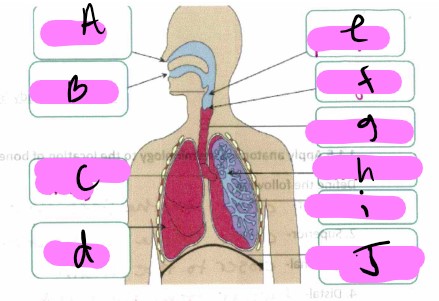
What’s b"?
mouth
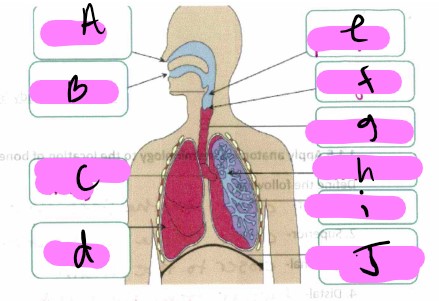
What’s “c"?
bronchus
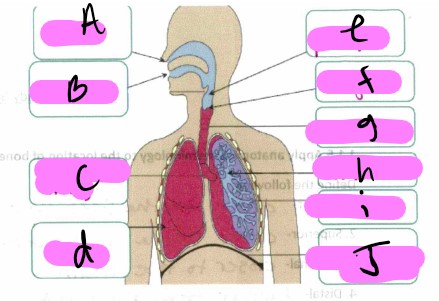
What’s “d"?
lung
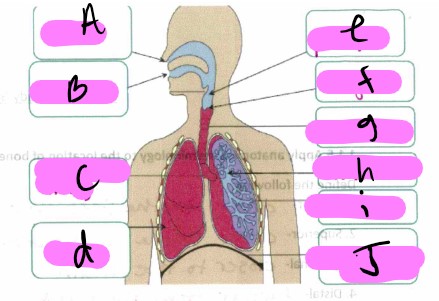
what’s “e”
pharynx

What’s “f"?
larynx
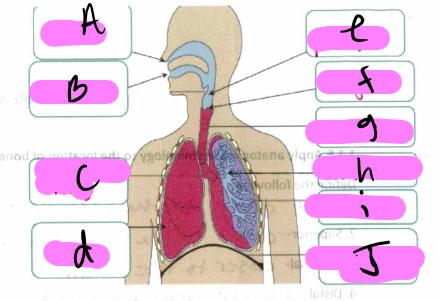
What’s “g"?
trachea
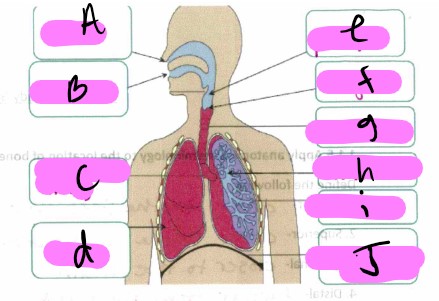
What’s “h"?
Bronchioles

What’s “i"?
alveoli
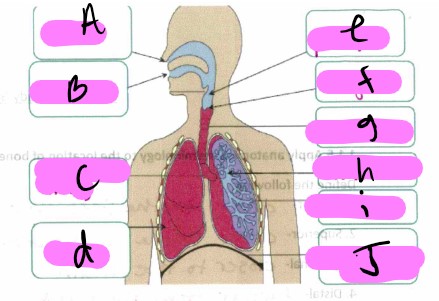
What’s “J "?
diaphragm
Pulmonary Ventilation (PV)
Inflow and outflow of air between the atmosphere and the lungs (breathing)
Total Lung Capacity (TLC)
Volume of air in the lungs after maximun inhalation
What is the equation to find total lung capacity (TLC)?
VC+RV
Vital Capacity (VC)
Maximum volume that can be exhaled after a maximum inhalation
Residual Volume (RV)
Volume still contained in the lungs after a maximum exhalation
Tidal Volume (TV)
Volume of air breathed in and out in any one breath during normal breathing.
Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV)
Volume of air in excess of tidal volume that can be exhaled forcibly
Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV)
Additional inspired air above and over tidal volume
What’s the Vital Capacity (VC) equation?
TV+IRV+ERV
What is the pressure, volume, and where does the air go in inspiration (active)?
The pressure decreases, the volume goes down, and the air goes in
What is the pressure, volume, and where does the air go in expiration (passive)?
Pressure decreases, the volume decreases, and the air goes out
In inspiration, what intercostal muscles and what direction is the ribcage pulled?
The external intercostal muscles contract which pulls the ribcage up and out.
In expiration, what intercostal muscles and what direction is the ribcage pulled?
The internal intercostal muscles contract which pulls the ribcage in and down.
In inspiration the diaphragm does what and moves where?
diaphragm contracts and moves down
In expiration the diaphragm does what and moves where?
diaphragm relaxes and moves up
Heart rate is
beats per minute
Cardiac output
Stroke volume x heart rate (total volume of blood pumped)
Stroke Volume
Expands + heart rate increases during exercise (amount of blood pumped by each ventricle)
Compare the distribution of blood at rest and the redistribution of blood during exercise.
During exercise the muscles being used become the main demand on blood flow. At rest blood is distributed to major organs such as kidneys and liver.
Vo2 Max
represents the functional capacity of the oxygen transport system/ measures how much O2 your body uses during exercise
Carbohydrates
energy source
Fats
protection, buoyancy, synthesis + transport hormones, energy store
Proteins
Structure, transport/ communication, enzymes
Water
transports nutrients, waste products, hormones, gases
Vitamins +minerals
regulates metabolism, heartbeat, cellular pH, bone density
Essential amino acids
Cannot be synthesized by the human body and must be obtained through your diet
Non-essential amino acids
Can be synthesized by the human body
Glycogenolysis
Breaking down of glycogen into glucose
Lipolysis
Breaking down of lipids into fatty acids
Outline the function of glucagon and adrenaline during fasting and exercise
During fasting and exercise the blood glucose levels drop which makes adrenaline and glucagon to be released. This results in an increase in blood glucose through glycogenolysis and lipolysis for energy supply.
Describe the production of ATP by the lactic acid system.
Breakdown of glucose to pyruvate without the use of O2. Pyruvate is the converted to lactic acid which limits the amount of ATP produced (2ATP).
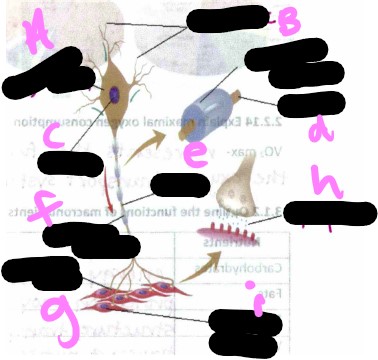
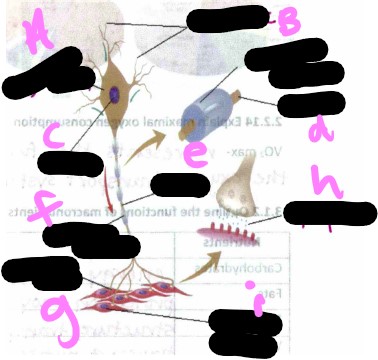
Motor unit- what is a?
cell body
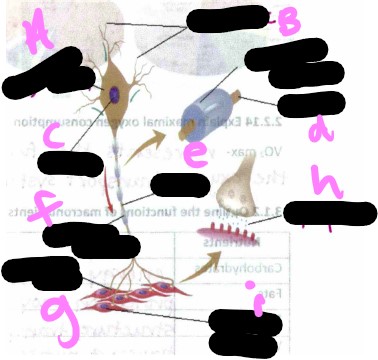
Motor unit- what is b?
dendrite
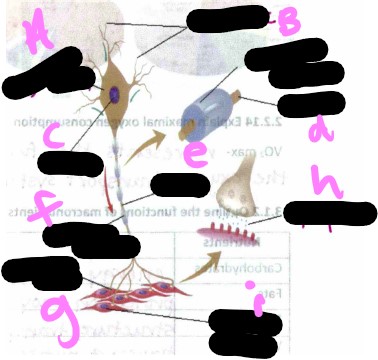
Motor unit- what is c?
nucleus

Motor unit- what is d?
axon

Motor unit- what is the missing one?
myelin sheath

Motor unit- what is e?
axon
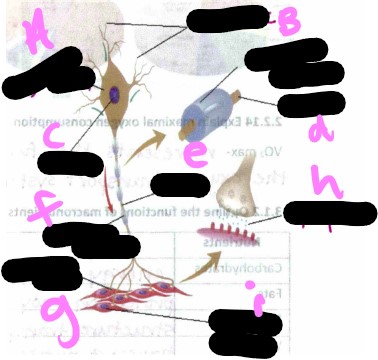
Motor unit- what is f?
myelin sheath
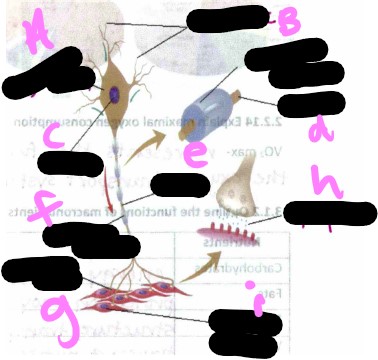
Motor unit- what is g?
motor unit
Motor unit- what is h?
synapse
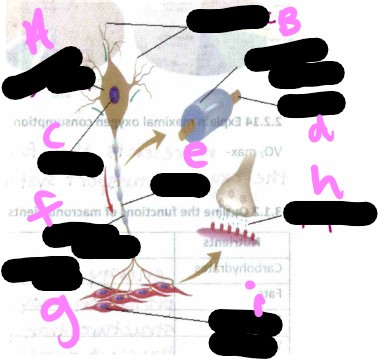
Motor unit- what is i?
muscle cells
Concentric Contraction
muscle is shortened during contraction
Eccentric contraction
muscle is contracting while lengthening
Isometric contraction
Muscle generates force without joint change
Isotonic Contraction
increase load on muscles
Isokinetic motion
Speed is fixed and resistance varies
Flexion Plane
Sagital
Flexion Def
Decreasing angle between joints
Extension Plane
sagital
Extension Def
Increasing angle between joints
Dorsiflexion Plane
sagital
Dorsiflexion def
elevating the sole
Plantar Flexion Plane
Sagital
Plantar Flexion Def
Elevating the heel (pointing toes)
Abduction Plane
Frontal
Abduction Def
movement away from the center
Adduction Plane
frontal
Adduction def
movement towards the center
Inversion Plane
frontal
Inversion Def
Ankle rolls out
Eversion Plane
Frontal
Eversion def
ankle rolls in
Medial rotation plane
transverse
medial rotation def
rotation towards midline
Lateral rotation plane
transverse
lateral rotation def
rotation away from midline
Supination plane
transverse
supination def
rotating palm up
Pronation plane
transverse
pronation def
rotating palm down
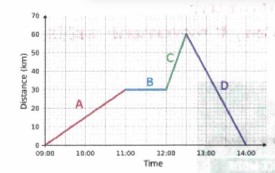
Analyze the distance time graph
A- moving away from start (positive velocity), B- standing still, C- moving forward at a faster speed, D- returning to home. Slope=velocity (m/s)
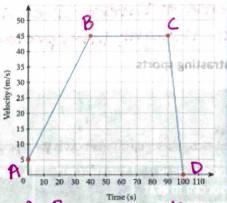
Analyze the velocity time graph
A-B= accelerating slope, B-C= moving at a steady speed, C-D= decelerating rapidly

Analyze Force-Time graph
larger area under the curve means there’s a larger force
Center of mass
point in which the mass of the body is evenly distributed