APHUG Final Semester1 Mr G (All Questions)
1/119
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AP Human Geography final for us who struggle with finding good studying methods!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
Globalization
A set of processes that are increasing interactions, interdependence without regard to country borders.
Pandemic
A worldwide outbreak of disease.
Epidemic
Regional outbreak of disease.
Cultural Landscape
The visible imprint of human activity on a landscape.
Cartography
The art and science of making maps.
Global Positioning System (GPS)
Satellite-based system for determining the absolute location of places or geographic features.
Remote Sensing
A method of collecting data or information through the use of instruments that are physically distant from the area or object of study.
Geographic Information System (GIS)
A collection of computer hardware and software that permits spatial data to be collected, recorded, stored, retrieved, manipulated, analyzed, and displayed to the user
Culture
The sum total of the knowledge, attitudes, and habitual behavior patterns shared and transmitted by the members of a society.
Expansion Diffusion
The spread of an innovation or an idea through a population in an area in such a way that the number of those influenced grows continuously larger.
Contagious Diffusion
The distance-controlled spreading of an idea, innovation, or some other item through a local population by contact from person to person.
Which of the following best defines Carl Sauer’s concept of cultural landscape?
The visible imprint of human activity on the cultural landscape.
Twenty four specific objects transmit complex radio codes, including time signals traveling at the speed of light. you can contact at least 4 of these 24 objects at any time of the day or night" (this is referring to technology for mapping)
Global Positioning
Toponyms in Southern California reflect?
Spanish Colonial Heritage / The cultural heritage of the settlers (listen to the recorded part)
The study of spatial patterns, distributions, and relationships.
Spatial Analysis Tradition in Geography
Examples of CULTURAL LANDSCAPE
Farms, roads, cities, buildings, and fields altered by humans
A straight line on a navigation map using the Mercator projection represents
A loxodrome/rhumb line (constant compass bearing) / The distance between two points
A ship's position is given as 0 degrees latitude and 27 degrees west longitude. We can conclude from this information that the ship is located
The Atlantic Ocean, on the equator west of Africa
The diffusion pattern of Walmart stores, which have spread from small towns to large cities throughout the United States, is an example of
Reverse hierarchical diffusion
The view that the natural environment has a controlling influence over various aspects of human life, including cultural development.
Environmental determinism
Arithmetic density
The total number of people divided by the total land area.
Crude Birth Rate (CBR)
The total number of live births in a year for every 1000 people alive in the society.
Crude Death Rate (CDR)
The total number of deaths in a year for every 1000 people alive in the society.
Demographic Transition Model
Historical population trends of two demographic characteristics – birth rate and death rate – to suggest that a country’s total population growth rate cycles through stages as that country develops economically.
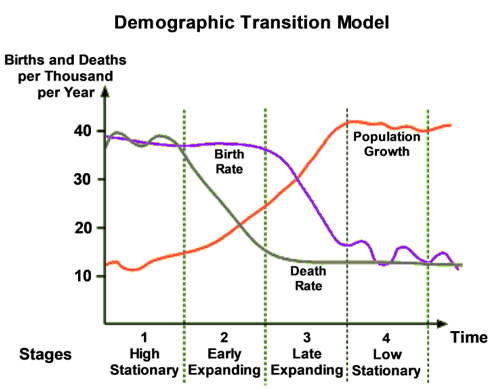
Stage 1
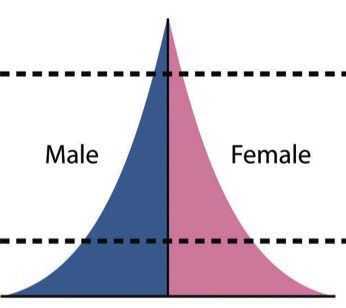
In Stage 1, which applied to most of the world before the Industrial Revolution, both birth rates and death rates are high. As a result, population size remains fairly constant but can have major swings with events such as wars or pandemics. (Thin Top, Wide Bottom!)
Stage 2
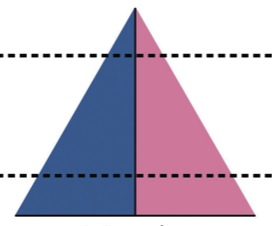
In Stage 2, the introduction of modern medicine lowers death rates, especially among children, while birth rates remain high; the result is rapid population growth. Many of the least developed countries today are in Stage 2. (Triangle)
Stage 3
In Stage 3, birth rates gradually decrease, usually as a result of improved economic conditions, an increase in women’s status, and access to contraception. Population growth continues, but at a lower rate. Most developing countries are in Stage 3. (Tombstone shape)
Stage 4
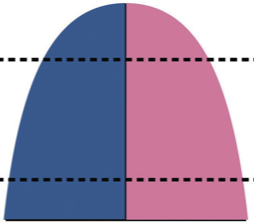
In Stage 4, birth and death rates are both low, stabilizing the population. These countries tend to have stronger economies, higher levels of education, better healthcare, a higher proportion of working women, and a fertility rate hovering around two children per woman. Most developed countries are in Stage 4. (Inverted Pyramid shape)
Stage 5
A possible Stage 5 would include countries in which fertility rates have fallen significantly below replacement level (2 children), and the elderly population is greater than the youthful population. (Kinda like a Rhombus)
In countries that would fall into Stage 2 of the model, the economy would be best characterized as (Use Diagram )
Agricultural
The process of change in a society's population from a condition of high crude birth and death rates and low rate of natural increase to a condition of low crude birth and death rates, low rate of natural increase, and a higher total population.
Demographic Transition
The highest dependency ratios are (population pyramids)
Stage 2 countries
The diagram that most resembles the population structure of the United States is (population pyramids)
A column-shaped pyramid with slight bulge—Stage 4
Which Population pyramid shown best represents a college town? (population pyramids)
Large ages 18–24 bulge
Which population pyramid shown best represents a town with a military base? (population pyramids)
Large numbers of young adult males
Doubling time
The number of years needed to double a population, assuming a constant rate of natural increase.
Epidemology
Branch of medical science concerned with the incidence, distribution, and control of diseases that affect large numbers of people.
Ecumene
The portion of Earth's surface occupied by permanent human settlement.
Infant Mortality Rate (IMR)
The total number of deaths in a year among infants under one year old for every 1000 live births in a society.
Medical Revolution
Medical technology invented in Europe and North America that is diffused to the poorer countries of Latin America, Asia, and Africa. Improved medical practices have eliminated many of the traditional causes of death in poorer countries and enabled more people to live longer and healthier lives.
Natural Increase Rate (NIR)
The percentage growth of a population in a year, computed as the crude birth rate minus the crude death rate.
Physiological density
The number of people per unit of area of arable land, which is land suitable for agriculture.
Zero Population Growth (ZPG)
A decline in the total fertility rate to the point where the natural increase rate equals zero.
Remittances
Money migrants send back to family and friends in their home countries, often in cash, forming an important part of the economy in many poorer countries.
Cyclic Movement
Movement - for example, nomadic migration - that has a closed route and is repeated annually or seasonally.
Periodic Movement
For example, college attendance or military service - that involves temporary, recurrent relocation.
Migration
A change in residence intended to be permanent.
Guest Workers
A common type of periodic movement involving millions of workers in the United States and tens of millions of workers worldwide who cross international borders in search of employment and become immigrants, in many instances.
Transhumance
A seasonal periodic movement of pastoralists and their livestock between highland and lowland pastures.
International migration
Human movement involves movement across international boundaries.
Immigration
The act of a person migrating into a particular country or era.
In the context of mass migration, the African Diaspora refers to
Forced migration of Africans during the slave trade
The gravity model states that as the distance increases between two equally-sized, equally populated cities, the level of economic and culture interaction
Decreases
Internal migration
Human movement within a nation-state, such as ongoing westward and southward movements in the United States.
Voluntary Migration
Movement in which people relocate in response to perceived opportunity, not because they are forced to move.
Developed by British demographer Ernst Ravenstein, five laws that predict the flow of migrants.
Ravenstein’s Laws about distance, migrants, etc.
Gravity Model
A mathematical prediction of the interaction of places, the interaction being a function of population size of the respective places and the distance between them.
Push Factors
Negative conditions and perceptions that induce people to leave their adobe and migrate to a new location
Pull Factors
Positive conditions and perceptions that effectively attract people to new locales from other areas.
Distance Decay
The effects of distance on interaction, generally the greater the distance the less interaction.
Step Migration
Migration to a distant destination that occurs in stages, for example, from farm to nearby village and later to a town and city
Forced Migration
The act of the government sending a migrant out of its country and back to the migrants home country.
Chain Migration / Kinship Links
Types of push factors or pull factors that influence a migrant's decision to go where family or friends have already found success
Chain Migration
A pattern of migration that develops when migrants move along and through kinship links (i.e. one migrant settles in a place and then writes, calls, or communicates through others to describe this place to family and friends who in turn then migrate there)
Chain Migration / Migration Stream
Phenomenon whereby different patterns of chain migration build upon one another to create a swell in migration from one origin to the same destination.
Wilbur Zelinsky's model of migration predicted
Migration patterns correspond to the DTM stages
International migration
Migration that takes place across international boundaries and between world regions.
Colonialism
A physical process whereby the colonizer takes over another place, putting its own government in charge and either moving its own people into the place or bringing in indentured outsiders to gain control of the people and the land.
Island Development
Place built up by a government or corporation to attract foreign investment and which has relatively high concentrations of paying jobs and infrastructure.
Russification
The Soviet policy to promote the diffusion of Russian culture throughout the republics of the former Soviet Union.
Guest Worker
Legal immigrant who has a work visa, usually short term.
Asylum Seekers
People who have fled their country because of political persecution and seek asylum in another country.
Asylum
Shelter and protection in one state for refugees from another state.
Repatriation
A refugee or group of refugees returning to their home country, usually with the assistance of government or a non-governmental organization.
Genocide
Acts committed with intent to destroy, in whole or in part, a national, ethical, racial, or religious group.
Immigration Laws
Laws and regulations of a state designed specifically to control immigration into that state.
Quotas
Established limits by governments on the number of immigrants who can enter a country each year.
Selective immigration
Process to control immigration in which individuals with certain backgrounds (i.e. criminal records, poor health, or subversive activities) are barred from immigrating.
Custom
The frequent repetition of an act, to the extent that it becomes characteristic of the group of people performing the act.
Many less developed countries fear the loss of folk culture because
Western perspectives may become more dominant
Which of the following statements reflects the environmental impact of culture?
Folk culture never causes environmental impacts, while popular culture does.
Terroir refers to
The sum of the effects of the local environment on a food item.
Typically popular culture
Diffuses rapidly to many locations
Folk culture refers to
Culture traditionally practiced by a small, homogeneous, rural group living in relative isolation from other groups.
Popular culture refers to
Culture found in a large, heterogeneous society that shares certain habits despite differences in other personal characteristics.
Dialect
A regional variety of a language distinguished by vocabulary, spelling, and pronunciation.
Extinct language
A language that was once used by people in daily activities but is no longer used.
Isogloss
A boundary that separates regions in which different language usages predominate.
Language Branch
A collection of languages related through a common ancestor that existed several thousands of years ago. Differences are not as extensive or old as with language families, and archaeological evidence can confirm that the branches derived from the same family.
Language Family
A collection of languages related to each other through a common ancestor long before recorded history.
Language Group
A collection of languages within a branch that share a common origin in the relatively recent past and display relatively few differences in grammar and vocabulary.
Trade Language
A language mutually understood and commonly used in trade by people who have different native languages.
Logogram
A symbol that represents a word rather than a sound.
Lingua Franca
A language understood by people who have different native languages.
Basque is a good example of a(n)
Isolated Language
Which of the following is not a Romance language?
Bulgurian
According to Colin Renfrew's research, Indo-European languages diffused across Europe
through the Diffusion of Agricultural
The language spoken by the greatest number of native speakers in the world is
Mandarin
Vulgar Latin
A form of Latin used in daily conversation by ancient Romans, as opposed to the standard dialect which was used for official documents.
Agnotisticism
Belief that nothing can be known about whether God exists.