Biology - Nervous System and Musculoskeletal system
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Function of Nervous System
Controls actions of the body by communicating via neurons transmitting signals, and coordinates movement
responds to stimuli by electrochemical messages relayed to and from brain OR by hormones, chemical reactions carried by blood
2 division of Nervous System
Central Nervous System
brain+spinal cord
intergates and processes info sent by nerves
Peripheral Nervous System
Sensory neurons carry signals from sensory receptors to CNS
Motor neurons carry signals from CNS to effectors (muscles + glands)
Neurons
Basic structural and functional unit of nervous system
Individual cell that quickle carries electrical impulses from one point of body to another
respond to stimuli (chemical and physical)
conduct electrochemical symbols
release chemicals that regulate body processes
Glial Cells
Cells that support neurons and provide supporting framework to nervous system tissue
nourish, remove waste, protect against infection
Nerves
Individual neurons organized into tissues
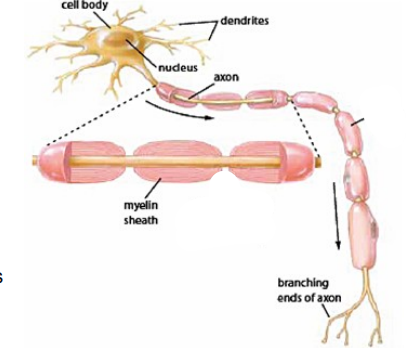
Neuron Structure
Dendrites = convert chemical info into electrical signals (from other neurons/receptors)
Axon = Transmit electrical signals to terminal regions for communication (w/ other neurons/effectors)
Soma = Cell body, contains nucleus and organelles where essential metabolic processes occur for cell survival
Myelin sheath
Stimulus Response
Basic Pathway for a nerve impulse
1) Receptor detects change in internal/external environment, a stimulus
2) Receptor transforms stimuli into electrical nerve impulse
3) Neurons transmit impulses to CNS where decision making occurs
4) CNS selects a conscious/unconscious response, and neurons transmit signals to effectors
5) Effectors (organs, muscles/glands) produce response and there is a change in the organism from detection of this stimulus
Musculoskeletal System Function
Allows for movement, gives support and protection, through collaboration of the nervous, muscular and skeletal system
3 systems involved w/ musculoskeletal system
Nervous - Motor neurons send signals to muscles from CNS, which cause them to contract and create movement. Also control timing of contractions.
Muscular - Muscles deliver required force to move one bon in relation to another
Skeletal - Consist of bones that act as levers and provide structure for muscles to pull
Neuron Diagram
(6)