Geri E1 Study Guide
1/110
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
What are the 5 Ms in the framework of friendly care?
Multicomplexity (whole person)
Mind (mentation, dementia, delirium, depression)
Mobility (function, impaired gait & balance, fall prevention)
Meds (polypharmacy, optimal/deprescribing, ADRS/burden)
what Matters most (individual goals & preferences)
In normal aging, which lobes of the brain have the most prominent volume loss?
Frontal & temporal
In normal aging, which sections of the brain have the greatest neuronal loss?
Cerebellum & cerebral cortex (d/t apoptosis)
How much does the blood flow to the brain decrease?
5-20%
Which cognitive and behavioral changes are most affected by aging?
Episodic & working memory and executive function /high level cognitive skills
*critical role in ability to care for themselves; declines after 70 yo
Which two primary cardiovascular diseases increase with age?
HTN & CAD
What cardiovascular structural changes are associated with aging?
Inc RA & LA volume, dec SVC/IVC flow, LVH, AV & mitral annulus thicken/calcify (conduction problems), large arteries stiffen, apoptosis & necrosis of myocytes, hypertrophy, poorer diastolic function
What cardiovascular rhythm changes are associated with the aging population?
SA node function declines → arrhythmias, inc CCB sensitivity
Inc isolated PACs & PVCs, Afib (dec electrical properties &conduction)
S4 normal > 75 y/o if in NSR secondary to rigid ventricle
What changes to the resting and maximum heart rate are seen in the aging population?
Resting unchanged; marked decrease in maximum (target HR = 220-age)
What changes are seen in the aorta with aging?
Inc diameter & stiffness → inc cardiac load
*chronic exercise can reduce this
What respiratory changes are seen in the elderly (most evident > 70)?
Dec chest wall compliance, resp muscle strength & forced expiratory volume
Describe the changes seen in cough power, mucociliary clearance and air and gas exchange in the elderly.
Dec muscle strength + inc closing capacity → cough power diminished
Slower & less efficient mucociliary clearance → delayed recovery, inc infx
Less air & gas exchange d/t general decline in elasticity & muscles
What changes to the chest wall are seen in the aging population?
Inc stiffness, dec compliance, & abd muscles play a greater role than intercostal muscles in chest expansion (less effective supine/seated, full expansion standing)
What changes are seen in the diaphragm in the aging population?
Flattens and less efficient → contributes to inc work of breathing which contributes to difficulty weaning from ventilator
What changes seen in the aging population put them at an increased risk for aspiration?
Impaired strength & coordination of tongue, less effective mastication, impaired food clearance, reduced or absent gag reflex
What esophageal changes are observed in the elderly?
Upper 1/3 of skeletal muscle hypertrophies, muscles lose compliance (resistance to food passage), dec coordination & amplitude of peristalsis, dec LES tone & strength of contractions (gastric acid exposure), dec sensation (distention, tissue damage, esophagitis)
Why can reflux esophagitis become so severe in elderly despite minimal symptoms?
Decreased sensation
What changes are seen in the large intestine and what conditions / disease processes increase with these changes?
Muscular atrophy, cellular/structural mucosal gland abnormalities, reduced colonic motility, dec anal sphincter tone & thin external sphincter →
Chronic constipation, colon cancer, diverticula, fecal incontinence
What change is seen with hepatic blood flow & perfusion?
Decrease up to 50%
What happens to the renal mass, functional glomeruli, renal plasma blood flow and creatinine clearance in the aging population?
Decreased
What clinical changes are seen in the aging renal system?
Progression of new CKD, worse function & survival after transplant, lower functional renal reserve, susceptibility to AKI
What functional changes are seen in the aging renal system?
Dec: GFR (in most), NA resorption, K excretion, urinary concentration, plasma flow
Inc: renal vascular resistance
What changes are associated with the aging bladder?
Dec: detrusor contractility, maximum capacity, maximum flow rate, ability to withhold voiding
Inc: PVR
What GU symptoms do the elderly experience?
Inc occurrence of urinary incontinence, UTIs, ED, & dyspareunia
What is sarcopenia?
Loss of muscle mass, strength, & performance
What happens to aging bone?
Proinflammatory environment promotes bone loss, loss of mineral in cortical & trabecular, trabecular dec and the distance inc, osteoblast dec & osteoclast unchanged → inc fx risk & slow repair rate
What is the normal rate of decline of bone starting at 40 y/o? What other factors play a role in developing osteoporosis?
0.5% per year
Further contributors: menopausal changes, vit D def, reduced weightbearing exercises
What changes occur in the skin and what injuries are common secondary to these changes?
Epidermis thins & dermoepidermal junction flattens -> inc fragility → stress wounds, bleeding into the tissue, dermis tears easily (adhesive dressing removal), delayed wound healing
What changes are seen in the aging eye?
Atrophy, yellowing, entropion/ectropion, dec lacrimal gland function & tear production, watery eyes, dec cornea sensitivity, arcus seniles, sluggish pupillary response, presbyopia, slow adaptation to low light & sensitivity to glare
What changes in hearing are seen with the elderly?
Internal: sensorineural hearing loss, dec high frequency acuity (presbycusis), difficulty w/ speech recognition in noisy environments, speech discrimination & localizing source of sound
External: auditory canal thins & cerumen becomes drier
What is the primary cause of conductive hearing loss? How would you evaluate for this & what handheld instrument is used to evaluate hearing?
Cerumen impaction; otoscope exam + handheld audioscope
What percentage of the elderly population with a severe infection will present with a blunted or absent fever?
20-30% d/t dec ability to mount cytokine responses
What nonspecific signs might an older person with a severe infection present with?
Falls, delirium, anorexia, generalized weakness
What are the 5 MC chronic conditions in individuals > 75?
Hearing loss, cataracts, HTN, arthritis, heart disease
What are the 10 topics used on the Barthel self care index to assess functional independence?
Bowels, bladder, grooming, toilet use, feeding, transfer, mobility, dressing, stairs, bathing
What is the MC type of elder abuse?
Self neglect
What is delirium?
Acute disturbance in attention, awareness, and baseline cognition that is not better explained by and underlying neurocognitive disorder
What screening tools for delirium have the highest sensitivity and specificity?
Confusion Assessment Method and 4AT Rapid Clinical Test
*digital span memory test can be done for quick assessment of attention
What are the 4 features associated with the confusion assessment method?
Acute onset & fluctuating course, inattention, disorganized thinking, altered level of consciousness
What are the subtypes of delirium regarding psychomotor activity?
Hyperactive: restless, agitated, refusing care, emotional lability; mistaken for psychosis or mania
Mixed: normal or fluctuating
Hypoactive (MC): sluggish or lethargic, poor prognosis; mistaken for depression,
What is the cholinergic deficiency associated with delirium?
Hypocholinergic-hyperdopaminergic: vascular dz → hypoxia → dec ACh, the primary NT of RAS which is responsible for alertness & attention → deficiency in all domains of cognition
What are the predisposing factors associated with delirium?
Dementia (strongest RF), cognitive impairment, prior episode, comorbidities, functionally dependent, sensory impairment, malnutrition or dehydration, advanced age, male
What are the precipitating factors associated with delirium?
acute cardiac/pulm events, bed rest, drug withdrawal (sedatives, alcohol), fecal impaction, fluid/elyte disturbance, indwelling devices, infx, anemia, restraints, uncontrolled pain, urinary retention
Meds (MC): sedatives, opiates, H2 blockers, anticholinergics, polypharmacy
What are the categories associated with reversible causes of delirium?
Drugs (MC)- opioids, benzos
Electrolytes- hyper/hyponatremia, hyper/hypoglycemia, etc
Lack of drugs, water, food- pain, withdrawal, dehydration, malnutrition
Infection- sepsis, UTI, asp PNA
Reduced sensory input- impaired vision/hearing, neuropathy
Intracranial causes- SDH, meningitis, seizure
Urinary infx/fecal impaction- drugs, constipation
Myocardial- MI, CHF, arrhythmia
What is the peak post-operative timeframe an individual develops delirium?
POD 2-7 (peak inflammatory mediators)
*ensure adequate pain control- consider PCA or topicals, standing orders for bowel regimen, & avoid sedatives- BZDs, opioids, meperidine
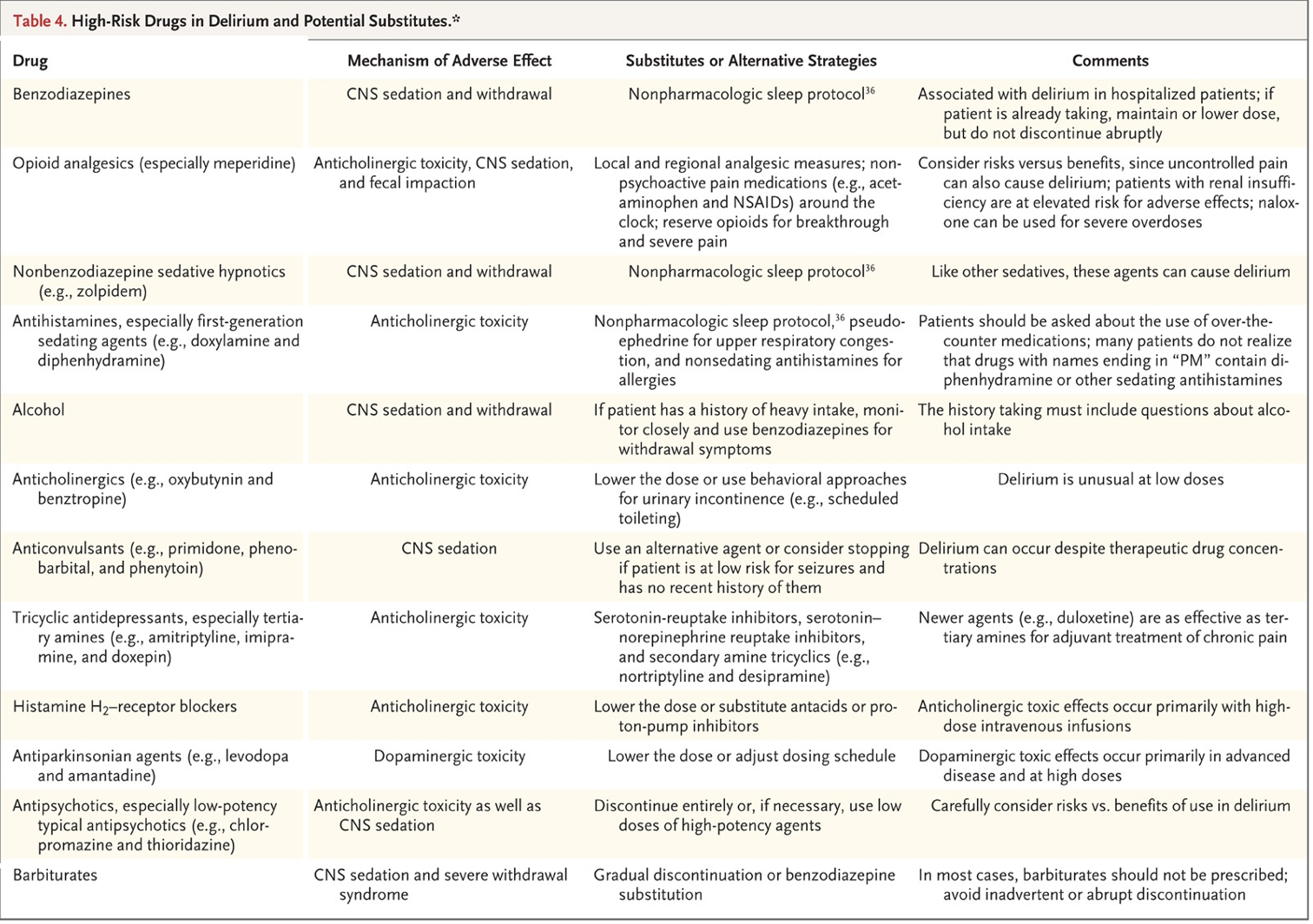
What are the high risk drug categories associated with delirium?
*table 4 on slide 26
BZDs, Opioids, Non-BZD sedative hypnotics, Antihistamines, Alcohol, Anticholinergics, Anticonvulsants, TCAs, H2RAs, Antiparkinsonian agents, Antipsychotics, Barbiturates
Which 2 antipsychotic meds are appropriate and commonly used to treat delirium?
Haloperidol & quetiapine
*avoid w/ Parkinsonism & alcohol
What is dementia and what are the 6 cognitive domains?
Decline in intellectual functioning significant enough to affect daily life and independence
Decline in ≥1: learning & memory, language, executive function, complex attention, perceptual motor, social cognition
What is the MC form of dementia?
Alzheimers
The following DSM-5 criteria is for what condition?
A: evidence of significant cognitive decline from a previous level of performance in one or more cognitive domains
Learning and memory, language, executive function, complex attention, perceptual motor, social cognition
B: cognitive deficits interfere w/ independence in everyday activities.
At a minimum, assistance required w/ complex ADLs, such as paying bills or managing meds
C: cognitive deficits do not occur exclusively in the context of delirium
D: cognitive deficits are not better explained by another mental disorder
Major neurocognitive disorders (dementia)
What is vascular dementia?
Any dementia that is caused by cerebrovascular dz or impaired cerebral blood flow
*stepwise progression w/ further ischemia; can be slowed, halted or reversed if treated
What is mixed dementia?
Dementia that is secondary to the coexistence of ≥ 1 dementia producing condition
Ex: Alzheimers plus- vascular (MC), normal hydrocephalus, alcohol related, chronic SDH, HIV infx
The following DSM-5 criteria is for what condition?
A: criteria are met for major or mild neurocognitive disorder
B: clinical features are consistent w/ a vascular etiology:
Onset of cognitive deficits is temporally related to ≥ 1 cerebrovascular events
Evidence for decline is prominent in complex attention and frontal-executive function
C: evidence of cerebrovascular disease from hx, PE, & neuroimaging sufficient to account for the neurocognitive deficits
D: sx are not better explained by another brain disease or systemic disorder
Vascular dementia
What is mild cognitive impairment (MCI)?
Cognitive impairments w/o overall decline in function; can be a precursor to dementia but can also be secondary to a reversible condition (ex- tolerodine)
*6-15% conversion rate to dementia
What is the one year rule in differentiating between Dementia w/ Lewy Bodies & Parkinson’s Disease Dementia?
*have similar features- fluctuating memory, visual hallucinations
Dementia onset within 12 mos of motor sx onset → Lewy Body
Dementia onset > 12 mos after motor sx → Parkinson’s disease dementia
The following features are seen with what condition?
age category: < 60
gradual onset of behavior changes, disinhibition, apathy
gradual progression but faster than AD
atrophy in temporal & frontal lobes
Frontotemporal dementia (Pick’s disease)
What is the Hakims-Adams triad of normal pressure hydrocephalus, which is caused by a build up of CSF?
Progressive dementia, urinary incontinence, gait instability
Which genetic disorder has a strong correlation with an early onset of alzheimers disease?
Down syndrome / Trisomy 21
What are possible DDX for dementia?
Normal cognition, MCI, MDD, delirium, learning disability, NPH, B12 deficiency, hypothyroidism, PD
What is the MMSE / Folstein test?
30 point test used to measure thinking ability
*score < 24 recommends further testing, does NOT provide diagnosis
What acetylcholinesterase inhibitors have been shown to provide some benefit of modest delay in in cognitive decline for mild-moderate dementia?
Donepezil (Aricept), rivastimine (Exelon), galantamine (Razadyne)
*MC SE → GI disturbance, N/V/D
What is the N-methyl-D- aspartate inhibitor that is approved for moderate-severe dementia?
*dec glutamate excitotoxicity; benefits cognition, ADLs, behavior
Memantine (Namenda)
*MC SE → constipation, dizziness, HA
What are the 4 types of incontinence?
Stress, urge, mixed, overflow
What is stress incontinence?
Leakage w/ inc intra-abdominal pressure, small volume
What is urge incontince?
Urge to void immediately preceding leakage, larger volume
What is mixed incontinence?
Stress & urgency
What is overflow incontinence?
Continuous leaks or dribbling w/ incomplete bladder emptying
What is the percentage of elderly that are incontinent?
11-34% males, 17-85% females
What are the 4 main drug classes associated with elderly hospitalization d/t adverse drug effects?
Warfarin, insulins, oral antiplatelet agents, oral hypoglycemic agents
What are the RF associated with osteoporosis?
F>M, asian/caucasian > AA/hispanic, older age, small, thin boned, FHx, post-menopausal, hypogonadism, smoking, excessive EtOH, low physical activity, glucocorticoid use > 3 months
What are common PE findings associated with osteoporosis?
BMI < 19, loss of height, localized vertebral pain, kyphosis
What are the 3 MC osteoporotic fracture sites?
Wrist > hip > vertebrae
What is the daily recommended dosage of Ca and vit D supplementation?
Ca: 1000-1500 mg QD
Vit D: 400-800 IU QD
What is the first line medication for osteoporosis?
PO BSS → alendronate (Fosamax), risedronate (Actonel)
What are the 4 MC indicators associated with failure to thrive (FTT)?'
*state of decline that is multifactorial and may be caused by chronic concurrent diseases and functional impairments
Weight loss > 5%, dec appetite, poor nutrition, inactivity
or its depression, malnutrition, cognitive impairment, functional impairment/dec mobility idek
What exams can quickly be performed in office to evaluate cognition, affect & mobility?
Cognitive: mini cog (3 item recall) + clock drawing test or MMSE
Affect: GDS; > 5 warrants FU, ≥10 indicates depression
Mobility: timed up & go (tug) test; >12s inc risk falling, >20s warrants evaluation
What are the 7 domains involved in a geriatric rapid assessment?
Functional status: d/t health or physical problem, needs help with ADLs
Mobility: Timed up & go test → > 12 s = inc risk of falls
Nutrition: lost > 10 lbs in 6 mos w/o trying or BMI < 20
Vision: can’t read newspaper headline w/ glasses, test w/ Snellen, >20/40
Hearing: hand held audioscope → cant hear 40 dB at 1000-2000 hz
Cognitive function: 3 item recall after 1 minute
Depression: feels sad or depressed
What kind of gait abnormality?
pain induced limp w shortened phase of gait on painful side
Antalgic gait
What kind of gait abnormality?
outward swing of leg in semicircle from hip
d/t lack of movement at the knee (limited knee flexion) or a leg length discrepancy
Muscles affected are the knee
Circumduction
What kind of gait abnormality?
excessive plantar flexion and inversion of ankle
Equinovarus
What kind of gait abnormality?
acceleration of gait
Festination
What kind of gait abnormality?
loss of ankle dorsiflexion secondary to weakness of ankle dorsiflexors
Foot drop
What kind of gait abnormality?
early frequent audible foot-floor contact with steppage gait compensation
Foot slap
What kind of gait abnormality?
hyperextension of knee
d/t inherent laxity of knee ligaments / ACL tear, etc
Genu recurvatum
What kind of gait abnormality?
tendency to fall forward
Stooped, stiff posture w head and neck bent forward
May be caused by toxins, CO poisoning, certain meds (haloperidol) or parkinsons dz
Propulsion
What kind of gait abnormality?
tendency to fall backward
Occurs d/t worsening of postural stability & an associated loss of postural reflexes
Cerebellar dysfunction/ataxia
Retropulsion
What kind of gait abnormality?
hip adduction such that knee crosses in front of each other w each step
Knees and thighs pressed together or crossing each other while walking
Caused by high muscle tone (spasticity) in hip adductors
Seen in cerebral palsy, post stroke, TBI, brain or spinal cord tumors
Scissoring
What kind of gait abnormality?
exaggerated hip flexion, knee extension, and foot lifting, usually accompanied by foot drop
Steppage gait
What kind of gait abnormality?
shift of the trunk over the affected hip, which drops bc of hip abductor weakness
Defective hip abductor mechanism
Primary musculature - gluteus medius, gluteus minimus -> weakness causes drooping of pelvis to CL side while walking
Trendelenburg gait
What kind of gait abnormality?
moving whole body while turning
Turn en bloc
What are causes of UL foot drop & stoppage gait?
Peroneal nerve palsy & L5 radiculopathy
What are causes of BL stoppage gait?
ALS, CMT dz, other severe peripheral neuropathy, some forms of muscular dystrophy
What are examples of the low classification gait disorders?
Pathology of muscles, skeleton, peripheral nerves, peripheral vestibular system and anterior visual pathway
Ex: antalgic, trendelenburg, waddling, steppage, sensory ataxia
What are examples of the middle classification gait disorders?
Lesions in ascending or descending sensorimotor tract, cerebellar dysfunction, bradykinesia, and hyperkinetic movement disorder
Ex: hemiplegia/paresis, paraplegia/paresis, Parkinsonism, cerebellar ataxia
What are examples of the high classification of gait disorders?
Psychogenic; Impairment of cortico-basal ganglia-thalamocortical pathways
Ex: Dementia (cautious gait, fear of falling), advanced Parkinson (freezing gait), frontal related (cerebrovascular, NPH)
What is an example of a condition that involves overlap with multiple levels of gait?
Parkinsons → High (cortical) & middle (subcortical) structures
What are the main PE components when evaluating an individual for falls?
BP & pulse both supine and standing; Vision screening; CV exam; MSK exam; Neuro exam
What are the American geriatric society falls prevention guidelines?
Asses all older adults & anyone w/ hx of falls → minimize meds, initiate tailored exercise program, tx vision impairment, tx postural hypotension & rhythm abnormalities, supplement vit D, manage foot & footwear problems, modify the house environment
What are the 10 most widely used herbal supplements by older adults?
Ginkgo biloba, St. John’s Wort, echinacea, ginseng, black cohosh, garlic, saw palmetto, hawthorn, valerian root, goldenseal
What herbal supplement increases the risk of bleeding when taken with warfarin?
Ginkgo biloba