Exam Topics
Label upward and downward force on an object
- Lift/Upthrust reaction/normal - upward force
- Drag/friction - backward force
- thrust - forward force
- weight - gravitational force
Name the type of energy stored in the spring
- elastic potential energy
Convert mass to weight
- Weight = mass x gravity
- Weight = N
Calculate the value of an upward force based on a spring scale
- Force = spring constant x extension
- Force = N
- Force = spring constant x extension
Stare whether mass and weight are vectors or scalar quantities
- Mass - Scalar
- Weight - Vector
Use and rearrange the formula for force extension and spring constant (f=ke) (Hooke's law)
- Force = spring constant x extension
- Force = N
- Extension = Force / Spring Constant
- Extension = m
- Spring Constant = Force / Extension
- Spring Constant = N/m
- Force = spring constant x extension
Label the electromagnetic spectrum (just know where they are on the spectrum- don't need to know numbers)
- Radiowaves
- Microwaves
- Infrared
- Visible Light
- Ultra Violet
- Xrays
- Gamma Rays
Properties of each wave in the electromagnetic spectrum
- Radiowaves - Long wavelength - Low Frequency
- communication, radio, tv
- Microwaves
- cooking, mobile phone
- Infrared
- cooking, remote controls, night vision
- Visible Light
- seeing, communication
- Ultra Violet
- UV tanning lamps, security
- Xrays
- X-rays for health, security at airports
- Gamma Rays - Short wavelength - High Frequency
- sterilising food and medical equipment, radio therapy
- Radiowaves - Long wavelength - Low Frequency
How x-rays show broken bones
- X-rays pass easily through flesh but not through bone
- Identify 2 waves used for communication
- Radiowaves
- Microwaves
- State the difference between transverse and longitudinal waves
- Longitudinal Waves - transmit energy in the same direction as the wave. Longitudinal waves, therefore, move backward and forwards. Sound is a longitudinal wave
- Transverse Waves - transmit energy by motion at right angles to or across the direction in which the energy is moving. transverse. waves move side to side or up and down
- Calculate frequency
- Frequency = cycles or waves / per second
- Frequency = Hz
- Calculate the distance of an echo
- Two times the distance
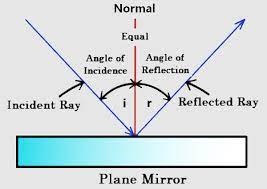
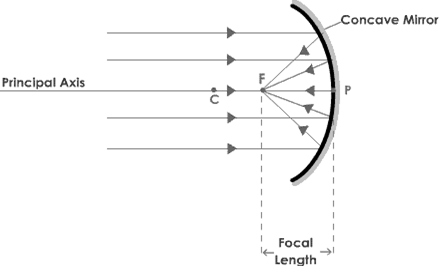
- Calculate the angle of reflection, critical angle, and angle in incidence, and label the focal point of rays bouncing off a concave mirror, draw ray diagrams on graph paper
The Normal - the perpendicular to the mirror at the point where the incident ray strikes it
Incident Ray - light ray which hits the mirror
Reflected Ray - light ray which bounces off the mirror
Angle of incidence (i) - the angle between the incident ray and the normal
Angle of reflection (r) - the angle between the reflected ray and the normal
- The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection i = r
- What the closeness of lines of a graph paper represent
- concentration
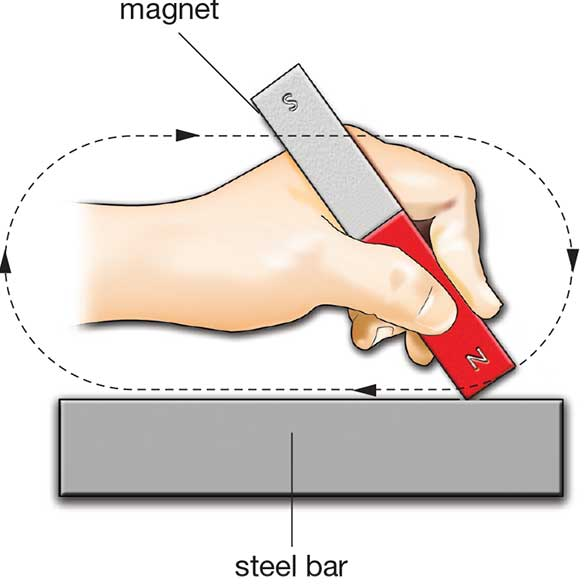
- Ways that steel can be magnetized
By stroking - stroking an un-magnetized material in one direction only, with a magnet, lines up each domain, so that they are all ‘pointing’ in the same direction
\
- Magnetic Induction - a magnetic pole induces an unlike pole near it and a like pole away from it
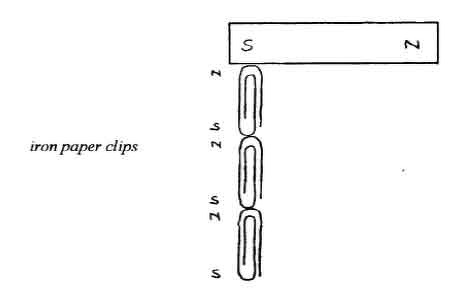
Increasing the speed of the magnet
\
- Electrical method - forms a temporary magnet, wrap the steel bar with a solenoid
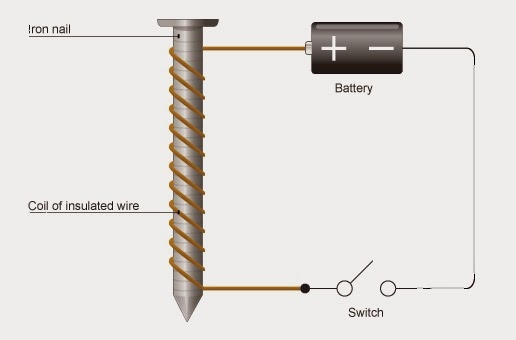
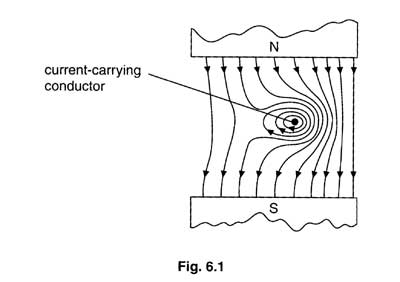
Be able to draw a diagram representing copper wire in a magnetic field
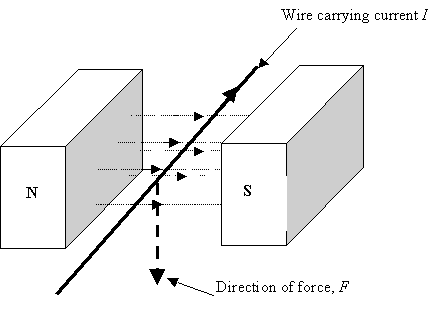
Current, resistance, and voltage in series and parallel circuits
Parallel Circuits
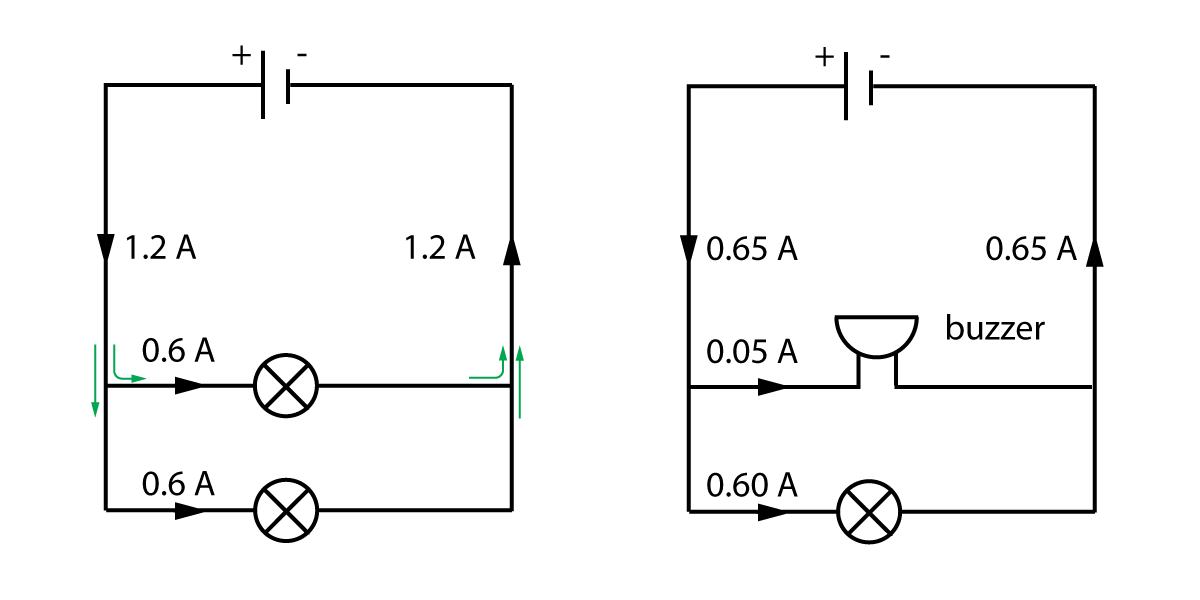
- Current = A1 = A2 + A3 = A4
- Current = Amperes
- 1 / Resistance Total = 1 / R1 + 1 / R2 + 1 / R3
- Resistance = Ohms
- Voltage Supply = V1 = V2 = V3
- Voltage also potential difference = Volts
Series circuits
- Current = Voltage / Resistance
- Current = Amperes
- Resistance = Voltage / Current
- Resistance = Ohms
- Voltage = Resistance x current
- Voltage also potential difference = Volts
Explain how a galvanometer measures electric current
- it deflects a pointer in response to an electric current flowing through a coil in a magnetic field
- A needle is held in place by a coil or spring in the presence of a permanent magnet. When current flows through the coil it causes the coil to stretch until the restoring force of the coil balances with the motor force of the coil. The position of the needle indicates the size of the motor force and thus the size of the current.
- it deflects a pointer in response to an electric current flowing through a coil in a magnetic field
How an electromotor force is induced in a wire and how it can be increased
- Add more coils
- Increase the current
- use a stronger magnet
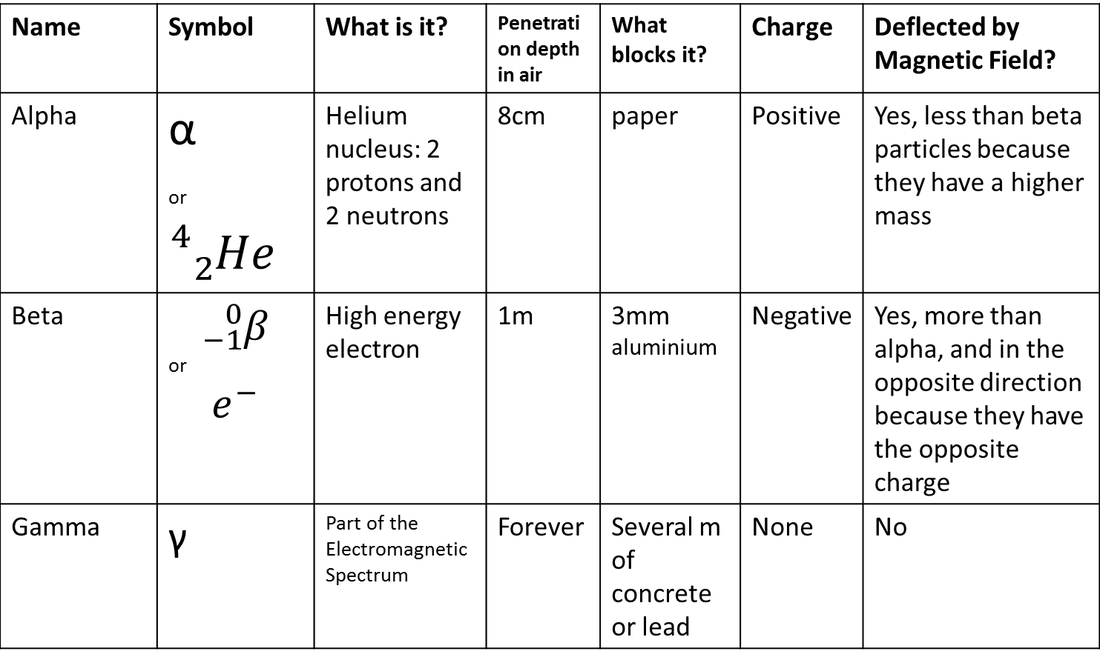
Radioactivity
- The process by which the nuclei of unstable atoms decay
- Alpha, Beta, and Gamma
- unit is Bexquerel (Bq)
Calculate half-life
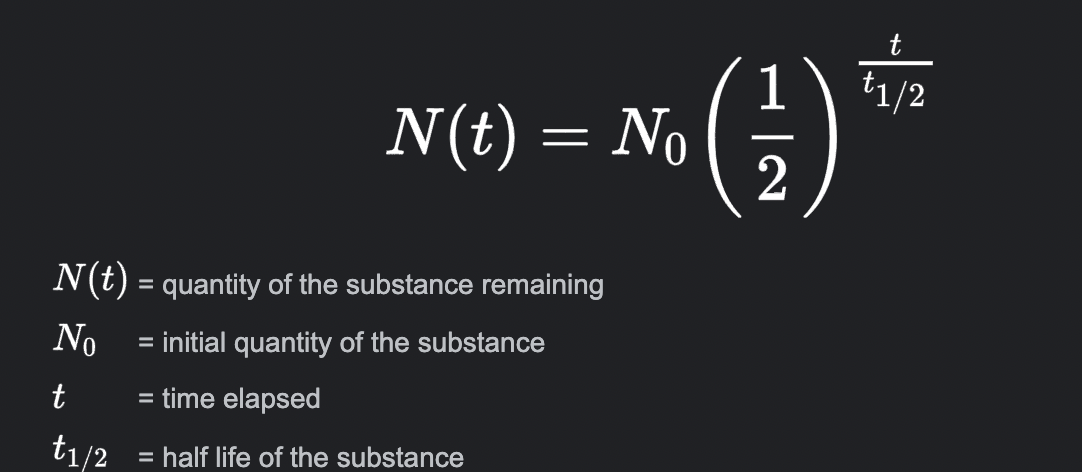
Ionizing properties of beta, gamma, and alpha
Determine mass and atomic number
- Basic chem knowledge
Principle of quantum momentum
- when two or more bodies act on one another, as in a collision, the total momentum of the bodies remains constant, provided that no external forces act (friction)
- Calculate momentum and acceleration and velocity
- Momentum = mass x velocity
- kgm/s = kg x m/s
- Mass = Momentum / Velocity
- kg = kgm/s / m/s
- Velocity = Momentum / Mass
- m/s = kgm/s / kg
- Acceleration = Force / Mass
- Momentum = mass x velocity
- Momentum before collision = momentum after collision
Newton’s laws of motion
- A body stays at rest stays at rest or a body in motion stays in motion until an external force acts upon it
- Force is equal to mass times acceleratoin
- Every action has an equal and opposite reaction
State properties of gases
- No definite shape
- indefinite volume
- can be easily compressed
- low density
- is fluid
- weak intermolecular forces
- particles are far appart
- more kinetic energy than in liquid or solid
- random and rapid motion
Determine where pressure is greatest and least
- pressure = force / area
- pressure = pascals (Pa)
- pressure = force / area
Changes of state
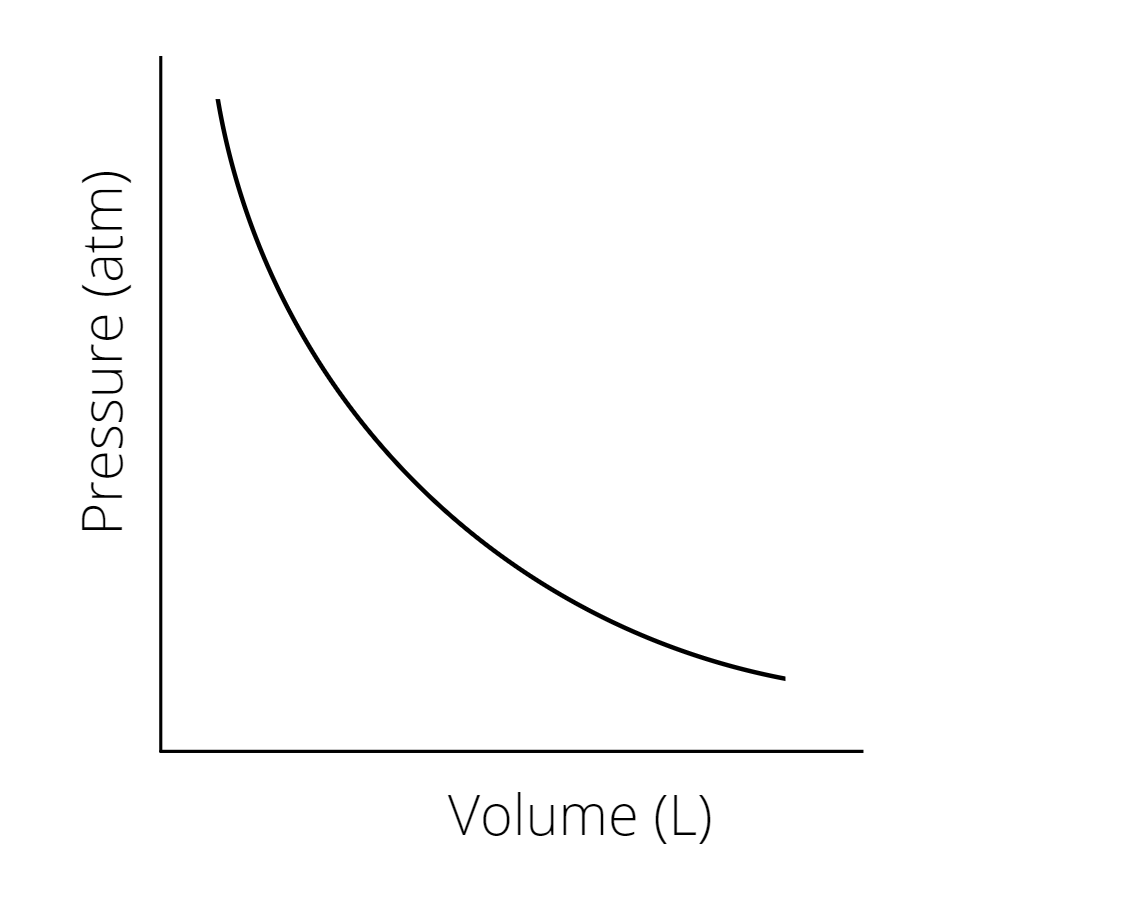
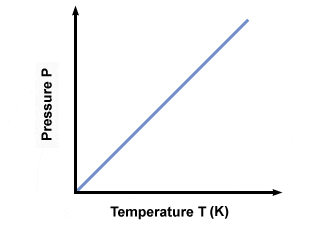
Recognize gas laws on graphs
- Boyles law
- Charles law
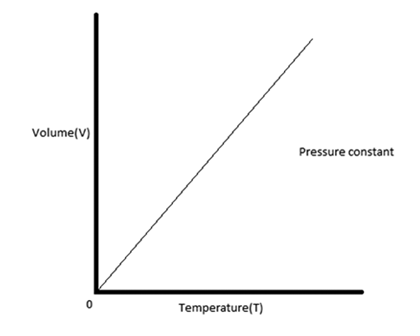
- The pressure law
Calculate density
- ==Density = Mass / Volume==
- ==Density = ρ==
- ==Density = Mass / Volume==
Calculate mechanical advantage
- Mechanical Advantage = Load / Effort
- no unit
- Mechanical Advantage = Load / Effort
Define infrasound and ultrasound
- Infrasound - sound waves with a frequency below human audibility (20Hz)
- Ultrasound - sound waves with a frequency higher than human audibility (20,000Hz)
Energy transfer
- energy can be transferred from one form to another. If a ball is thrown into the air, it starts with Kinetic energy. Since it goes up it gains gpe and loses ke. when it stops moving up it only has pe. when it falls to the ground it loses gpe. this gets transferred to increasing ke. Kinetic energy which strikes the ground, is lost as heat and sound.
Calculate weight and moments
- ==Weight = mass / distance==
- ==moments = force x distance==
Non-renewable versus renewable energy examples
- Non-renewable
- coal
- fossil fuels
- natural glass
- nuclear
- Renewable
- tidal
- wind
- dams
- wave
- solar
- geothermal
- Non-renewable
Methods of heat transfer(know what they are)
- Conduction
- flows through matter
- Convection
- flows through fluid from a higher temperature to a lower temperature
- Radiation
- transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves
- Conduction
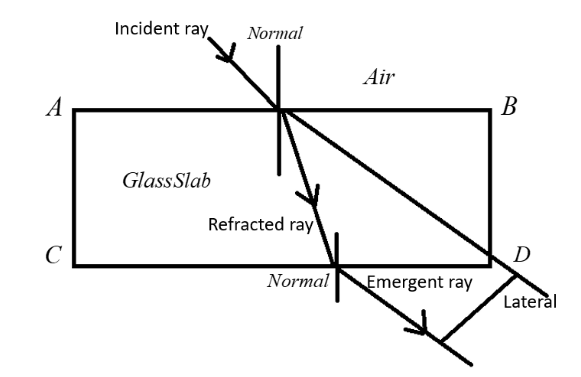
Draw refraction
State how heating affects density, volume, and mass
- density
- makes things lighter
- volume
- spreads out particles
- mass
- doesn’t change
- density
Identify reflection in a plain mirror
Properties of an image formed through a convex lens
- diminished, virtual, upright images behind the mirror
Calculate gpe (gravitation potential energy)
- work done = energy transferred = weight x distance
- potential energy = weight x change in height
- work done = energy transferred = weight x distance
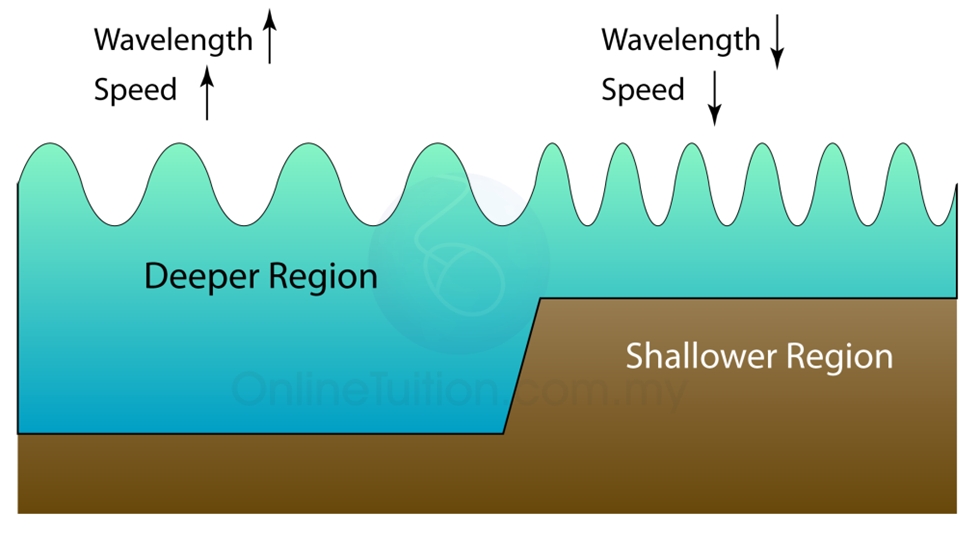
The frequency and wavelength of shallow water versus deep water
Calculate the specific heat capacity
- Specific heat capacity = (energy) / mass x temperature
- Specific heat capacity = J / kgK
- Specific heat capacity = (energy) / mass x temperature
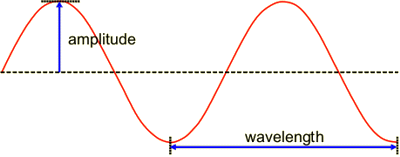
Label the amplitude and wavelength on a soundwave
Transformers step up step down
a device used for changing the voltage of an alternating current
without changing the frequency of the supply.
has two coils which are magnetically linked by being both on the same core of the transformer.
An alternating voltage is applied to primary coils, causing alternative currents to flow in this coil.
This current produces a charging magnetic field in the laminated iron core(which cuts across the secondary coils)
Electromagnetic induction then occurs in the coil producing the alternative voltage
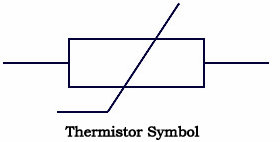
Symbol for thermistors
The function of a fuse
- breaks the circuit if a fault in the circuit causes too much current to flow
Calculate the power energy in a circuit
- Power = Voltage x Current
- Power = V x C
- Power = Joules
- Power = Voltage x Current