Chem 102 Exam 1
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Boiling point , Higher IMF
Higher BP
Viscosity, Higher IMF
Higher viscosity
Surface Tension, Higher IMF
Higher surface tension
Vapor Pressure, Higher IMF
Lower vapor pressure
delta H
change in enthalpy or heat
delta S
change in entropy or disorder
Solid to liquid to gas
positive Delta H and S
gas to liquid to solid
negative delta H and S
Dela H Fusion
melting (solid to liquid)
Delta Hvap
heat of vaporization (liquid to gas)
delta H freezing
negative delta H fusion
delta H condensation
negative delta Hvap
delta G =
Delta H (enthalpy) - T(time) Delta S (entropy)
*g(l)=
C(specific heat) (mass) (change in temp)
g(l)=
C(molar heat capacity) (mols) (change in temp)
q=
Delta H x Moles
Clausius Clapeyron
Ln(p1/p2)=Delta Hvap/R (1/T2 - 1/T1), Temp in K, R=3.14
Crystalline solid
Lattice structure, rigid and long range order
Amorphous Solid
lack a regular three dimensional arrangement of atoms
Ionic Crystals
Metal + nonmetal, hard, high melting points, brittle
Covalent crystals
held together by covalent bonds, hard, high melting point, brittle
Molecular crystals
molecules held in a repeating pattern by IMF, low melting point, soft
Metallic crystals
metal atoms sharing a valence electron
Unit cell
basic repeating structural unit of a crystalline solid
Simple cubic
atom in each corner, coordination number 6,
Body centered face cubic
the spheres in each layer rest in the depression between the spheres in the previous layer, coordination # 8
Body centered cubic
atoms per cell: 2
Primitive cubic
atoms per cell: 1
Hexagonal closest packing
A, B pattern, coordination # 12
Cubic closest packing
A, B, C pattern, coordination # 12
face centered cubic
Atoms per unit cell: 4
Solvent + solvent
IMF forces present
Solute + solvent
New IMF forces being made
Solute + solute
Some IMFs are broken
Delta H solution =
delta H solvent-solvent + delta H solute-solute + delta H solute-solvent
Molarity (M)
mol solute/l of solution
Mole fraction (X)
mol of component/ total mols
Mass %
(mass solute/mass solution) x 100
parts per million (ppm)
(mass solute/mass solution) x 10^6
parts per billion (ppb)
(mass solute/mass solution) x 10^9
Molality (m)
mol solute/kg solvent
Solubility and temperature of solids in liquid
temp increases, solubility increases
Solubility of temperature of gas in liquids
temp increases, solubility decreases
Pressure of gas above liquid
directly proportional to solubility of gas in a liquid
Vapor pressure lowering equation
Psolution= Psolvent(pure)x Xsolvent(mole fraction)
Nonvolatile
has no vapor pressure
Volatile
has vapor pressure
Colligative properties depend on?
the number of dissolved particles
Boiling point elevation equation
delta Tb = Kb(boiling point constant) x m (molality), add value to boiling point of pure solute
Freezing point depression equation
delta Tf = -Kf(freezing point constant) x m (molality), subtract value from freezing point of pure solute
Osmotic pressure equation
=M(molarity)R(constant 0.08206)T(temp in K)
Equilibrium constant given partial pressure
C(equilibrium constant)= K(constant) P(pressure atm)
miscible
when two liquids form a homogenous mixture
Experimental equation for determining rate law
(ration of concentrations)^x = (ratio of initial rates), where x is the order with respect to that component
Rate equation
= K[A]^x[B]^x, where K is rate constant
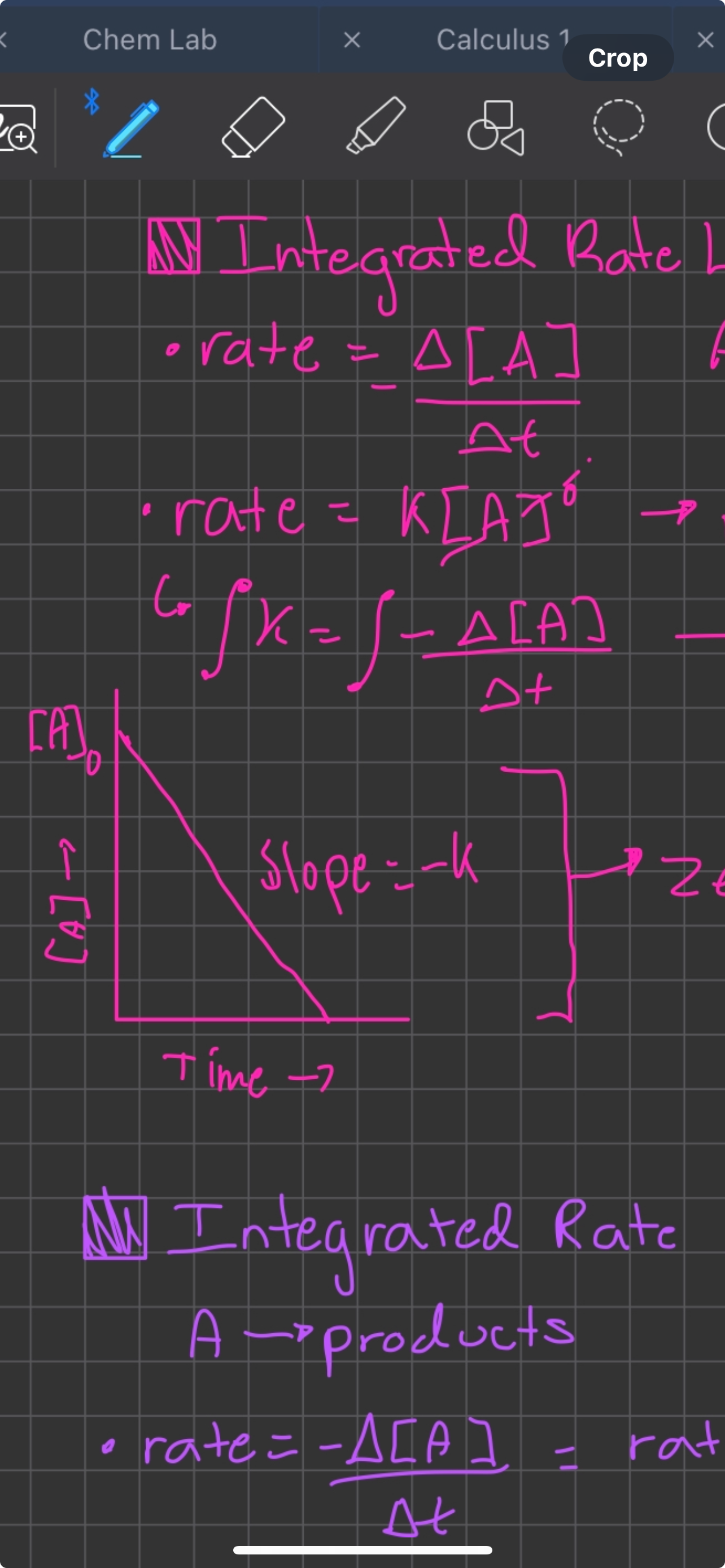
Integrated rate law zero order
[A]t = -kt + [A]0, slope of [A]0/time
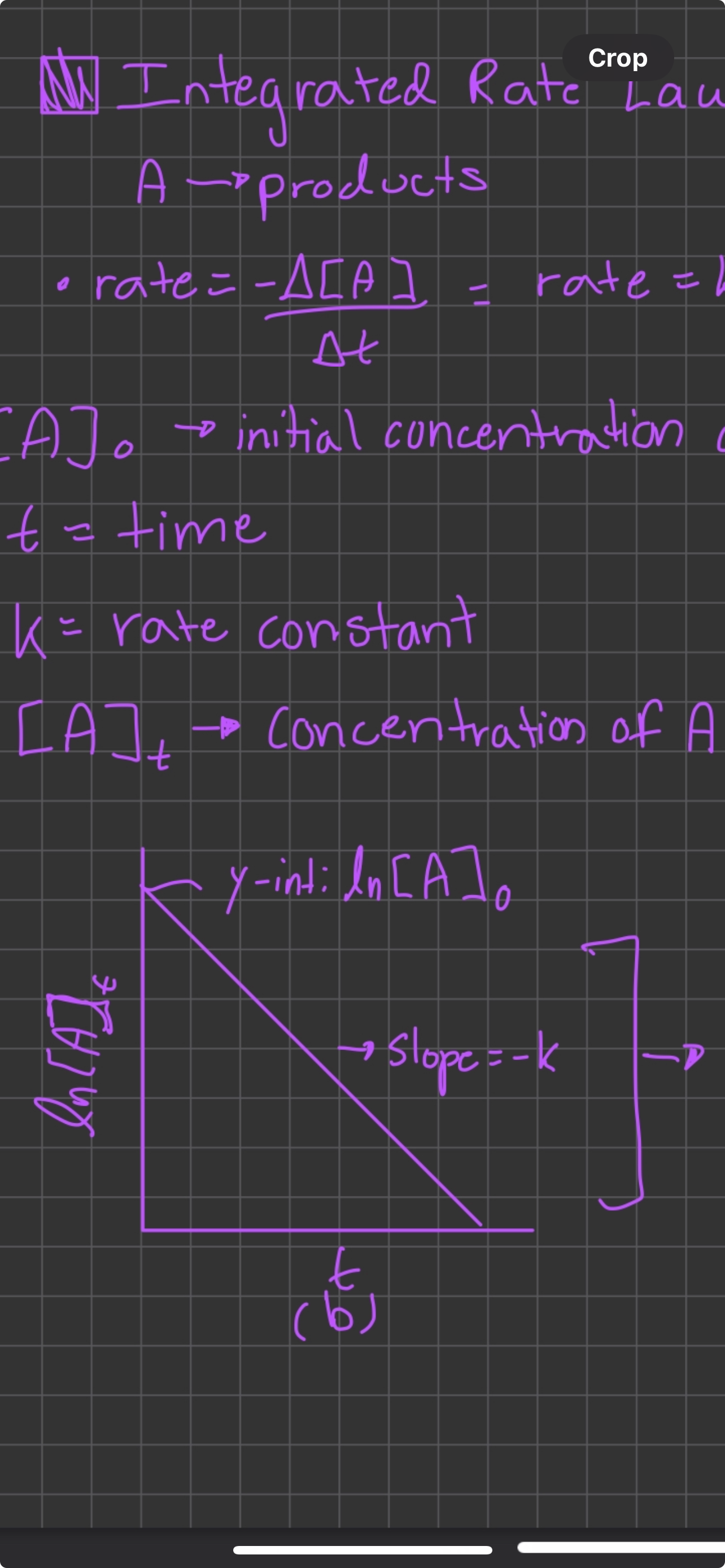
Integrated rate law first order
Ln[A]t = (-k)(t) + Ln[A]0, slope Ln[A]t/time
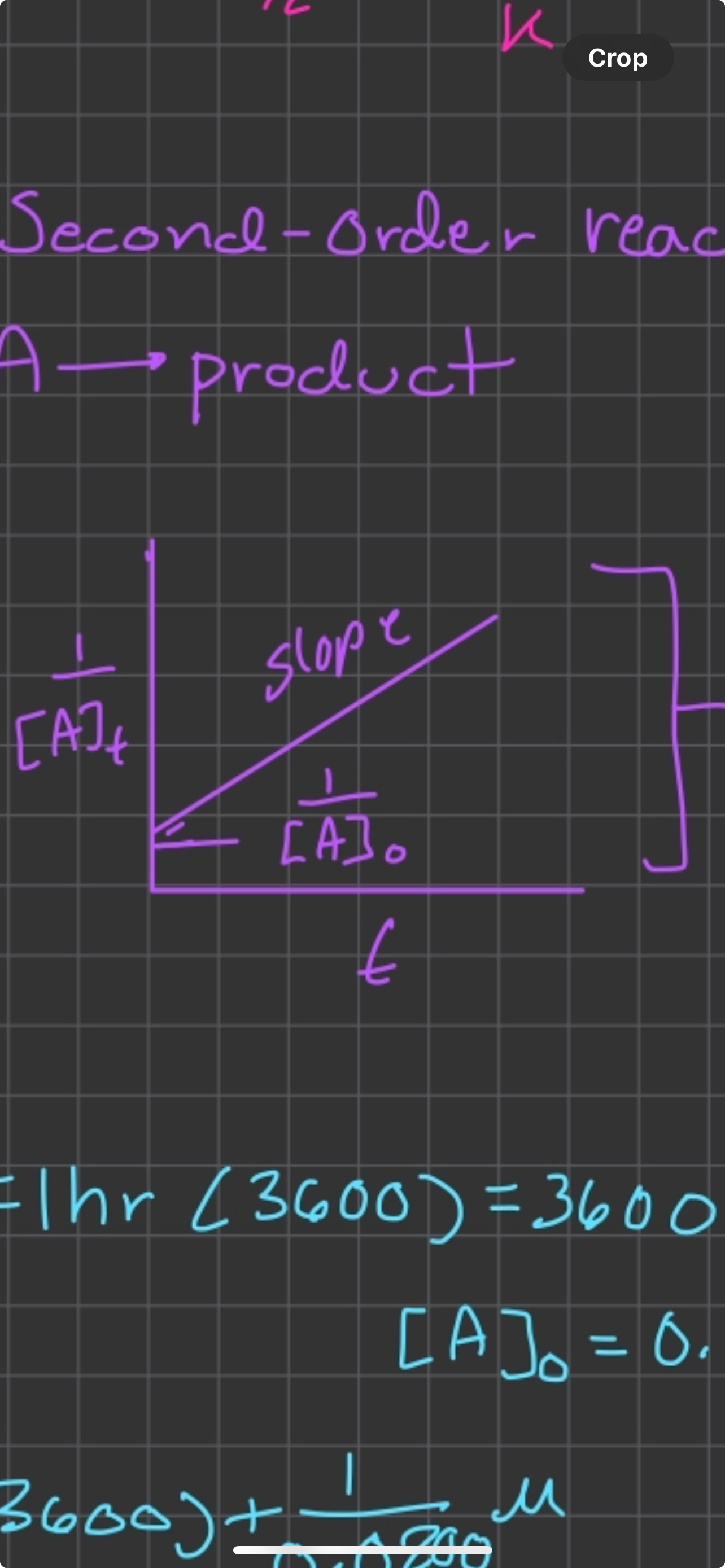
Integrated rate law second order
1/[A]t= kt + 1/[A]0
1st order half life equation
t1/2= Ln(2)/k
Reaction rate and temperature
more collisions, equals faster rate
Arrhenius Equation (Ea)
Ln(k2/k1)=( -Ea/R(8.314) )(1/T2- 1/T1) temp in k
elementary reactions
happens in one step
unimolecular
one reactant molecule
bimolecular
two reactant molecules
termolecular
three reactant molecules
Rate law for overall reaction
depends on the slowest step
reaction intermediate
1st seen as a product, used up later, not in overall reaction