HNSC 2170: Unit 8
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
What are the health habits that women should adopt to prepare for a healthy pregnancy?
Maintain a balanced diet, exercise regularly, avoid smoking and alcohol.
What are the risks of entering pregnancy underweight or overweight?
Increased risk of complications, such as gestational diabetes or preterm birth.
Which nutrients are of special interest when a woman is pregnant?
Folic acid, iron, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids.
What are the optimal weight gain recommendations during pregnancy?
25-35 pounds for women with a normal BMI.
What are the components of weight gain during pregnancy?
Baby's weight, placenta, amniotic fluid, increased blood volume, breast tissue, and maternal fat stores.
What are common nutrition-related concerns during pregnancy?
Nausea, constipation, and food cravings.
What are the strategies to alleviate nutrition-related concerns during pregnancy?
Eat small, frequent meals, increase fiber intake, and choose healthy snacks.
What are the health concerns that can result during pregnancy?
Gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and anemia.
What practices should be avoided while pregnant?
Smoking, alcohol consumption, and certain medications.
What is Health Canada's recommendation for the duration of breastfeeding?
Exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months, followed by continued breastfeeding with complementary foods for up to 2 years or longer.
What are the nutrition recommendations for breastfeeding women?
Increase calorie intake, consume a variety of nutrient-dense foods, and stay hydrated.
What practices should be avoided or used cautiously while breastfeeding?
Excessive caffeine intake, alcohol consumption, and certain medications.
What is the nutritional composition of breast milk?
Contains carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, and antibodies.
Why are supplements needed during infancy?
To ensure adequate intake of certain nutrients, such as vitamin D and iron.
What are the different types of infant formula available in Canada?
Ready-to-use, concentrated, and powdered infant formula.
What are the proper preparation methods for infant formula?
Follow the instructions on the packaging, use clean water, and sterilize bottles and nipples.
What are the recommendations for introducing food to infants?
Start with iron-rich foods at around 6 months, gradually introduce a variety of foods, and avoid added salt and sugar.
What are the roles and responsibilities during mealtime for children and parents?
Parents provide nutritious meals, set a positive example, and create a pleasant eating environment.
What are the steps for healthy eating for children and adolescents?
Eat a variety of foods, limit sugary drinks and snacks, and engage in regular physical activity.
What are the concerns associated with energy drink consumption?
Increased risk of caffeine overdose, dehydration, and negative effects on heart health.
What lifestyle components play a role in life expectancy and quality of life?
Healthy diet, regular physical activity, adequate sleep, and stress management.
What are the physical changes of aging that affect nutrition?
Decreased appetite, reduced sense of taste and smell, and changes in digestion.
Which nutrients are of concern for older adults?
Calcium, vitamin D, vitamin B12, and fiber.
What are the strategies to combat poor nutrient intake in older adults?
Choose nutrient-dense foods, consider supplements if necessary, and seek assistance with meal preparation if needed.
What is the impact of nutrition on pregnancy?
Nutrition can affect fertility and pregnancy outcomes.
Why should women establish healthy eating practices before pregnancy?
To ensure a healthy pregnancy.
What are the risks associated with being underweight during pregnancy?
Negative effects on fertility and pregnancy outcomes.
What are the risks associated with being overweight during pregnancy?
Negative effects on fertility and pregnancy outcomes.
When should women start taking prenatal vitamin and mineral supplements?
Before becoming pregnant.
What is the purpose of taking prenatal supplements?
To ensure folate needs are met.
What are the nutrient needs during pregnancy?
A healthy balance of carbohydrates, protein, and fat.
Are high protein supplements recommended during pregnancy?
No, as they may cause negative outcomes for the fetus.
Do calorie requirements increase during the first trimester of pregnancy?
No, additional calories are not required.
When do calorie requirements increase during pregnancy?
As the pregnancy progresses.
What are the recommendations for protein intake during the second and third trimester?
Slightly higher than during the first trimester.
- RDA calls for 25 grams per day more than non-pregnant women
Should women continue to consume prenatal supplements throughout pregnancy?
Yes, it is recommended.
Which vitamins and minerals have increased DRI recommendations during pregnancy?
Most vitamins and minerals.
What is the optimal intake of folate during pregnancy?
600 micrograms per day
To reduce the risk of neural tube defects in the fetus.
What is a neural tube defect?
A birth defect affecting the brain, spine, or spinal cord.
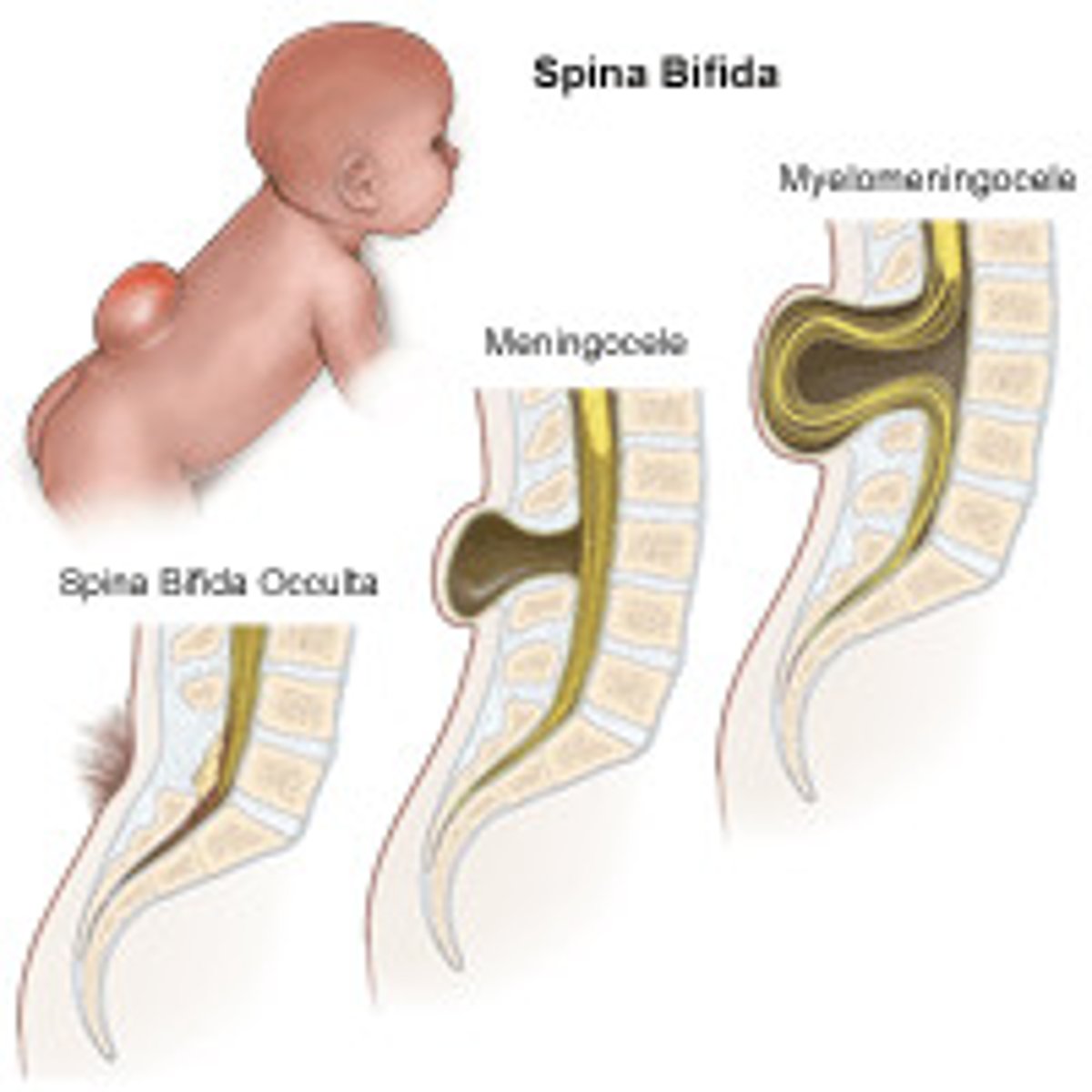
What is spina bifida?
A specific type of neural tube defect.

What is the purpose of the DRI recommendations for pregnant women?
To ensure adequate nutrient intake for a healthy pregnancy.
What is the role of Vitamin B12 during pregnancy?
Deficiency can cause irreversible nervous system damage in the fetus.
What is the role of Vitamin D during pregnancy?
Plays a role in calcium metabolism in the fetus.
Why is calcium important during pregnancy?
Optimal intake ensures proper bone and teeth development in the fetus.
Why is iron supplementation recommended during pregnancy?
Difficult to achieve iron needs through food intake.
What are the consequences of zinc deficiency during pregnancy?
Problems with fetal growth and development.
Is weight loss recommended during pregnancy?
No, weight loss is not recommended.
What is pica?
Craving non-food items like soil, clay, or ice.

What is the consequence of Vitamin B12 deficiency during pregnancy?
Irreversible nervous system damage in the fetus.
What is the role of Vitamin D in the fetus?
Plays a role in calcium metabolism.
Why is calcium intake important during pregnancy?
Ensures proper bone and teeth development in the fetus.
Why is iron supplementation recommended for pregnant women?
Difficult to meet iron needs through food alone.
What are the consequences of zinc deficiency in pregnancy?
Problems with fetal growth and development.
Is it recommended to lose weight during pregnancy?
No, weight loss is not recommended.
What should pregnant women discuss with their healthcare provider regarding physical activity?
Safety of activities during pregnancy.
What are food cravings and aversions during pregnancy?
Cravings or aversions to certain foods, not caused by physiological need.
What is morning sickness?
Nausea and vomiting caused by hormonal changes in early pregnancy.
When does morning sickness occur?
It can occur at any time of day, not just in the morning.
What causes heartburn during pregnancy?
Pressure on the stomach from the growing fetus pushing acid into the esophagus.
What can help alleviate constipation during pregnancy?
Consuming fluids, fiber, and engaging in regular physical activity.
How can I alleviate constipation during pregnancy?
Consume plenty of fluids, fiber, and engage in regular physical activity with approval from a health professional.
What are the common discomforts during pregnancy?
Morning sickness, heartburn, and constipation are common discomforts during pregnancy.
What is pre-existing diabetes?
Diabetes that a person has before becoming pregnant.
What is gestational diabetes?
Diabetes that develops during pregnancy and usually goes away after birth.
What are the risks of gestational diabetes?
Increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
What are the risks of hypertension during pregnancy?
Risks for the mother and fetus.
What is gestational hypertension?
Onset after 20 weeks of gestation without proteinuria, return of normal B/P in postpartum
What is preeclampsia?
High blood pressure and protein in the urine during pregnancy.
What are the risks of preeclampsia?
Great risk to the mother and can cause preterm delivery.
What are some practices to avoid during pregnancy?
Smoking, medicinal drugs, herbal supplements, and street drugs.
What is methyl mercury?
A contaminant that can be passed from a pregnant woman to her fetus.
How does methyl mercury affect unborn babies?
It can accumulate in their blood and cause neuropsychological deficits.
How is mercury transferred to nursing infants?
Through breast milk.
What are the potential effects of chronic maternal fish consumption?
IQ deficits, abnormal muscle tone, reduced motor function, and lower attention span.
What age group of children may display neuropsychological deficits following prenatal exposure to methyl mercury?
Children aged seven years.
What is a potential health effect of prenatal exposure to methyl mercury?
Increased blood pressure in children.
What should pregnant women avoid to reduce the risk of listeriosis?
Unpasteurized juices, unpasteurized dairy products, hotdogs, deli meats, undercooked meats, fish, poultry, eggs, unwashed vegetables and fruit, refrigerated pates, and smoked fish.
What problems can listeriosis cause during pregnancy?
Miscarriage, stillbirth, and severe infection in the fetus.
How should hotdogs, deli meats, and luncheon meats be consumed to reduce the risk of listeriosis?
They should be heated until steaming hot.
How should meats, fish, poultry, and eggs be cooked to reduce the risk of listeriosis?
Thoroughly cooked, and eggs should be cooked until completely firm.
What should pregnant women avoid in terms of vegetables and fruit to reduce the risk of listeriosis?
Unwashed vegetables and fruit.
What should pregnant women avoid in terms of pates and fish to reduce the risk of listeriosis?
Refrigerated pates and smoked fish.
Where can you find Table 10-9: Tips to Prevent Listeriosis?
In the document 'Safe Food Handling for Pregnant Women' on the Government of Canada website.
What is the document called that provides safe food handling guidelines for pregnant women?
'Safe Food Handling for Pregnant Women'.
What is the potential risk of consuming unpasteurized juices and dairy products during pregnancy?
Contracting listeriosis.
What is the potential risk of consuming undercooked meats, fish, poultry, or eggs during pregnancy?
Contracting listeriosis.
What is the potential risk of consuming unwashed vegetables and fruit during pregnancy?
Contracting listeriosis.
What is the potential risk of consuming refrigerated pates and smoked fish during pregnancy?
Contracting listeriosis.
What are the risks of high doses of vitamin or mineral supplements?
Unknown, potential harm.
What is restrictive dieting?
A diet that severely limits calorie intake.
What are the acceptable daily intake levels for approved sugar substitutes?
Government of Canada guidelines.
What are the risks of excessive caffeine intake during pregnancy?
Increased risk of miscarriage and fetal death.
What are the risks of alcohol consumption during pregnancy?
Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASD).
What is the recommended duration of breastfeeding according to the Government of Canada?
First six months exclusively, two years or longer with complementary foods.
When is breastfeeding not recommended?
Certain health conditions (e.g. active tuberculosis and HIV).
How many additional calories do women require during lactation?
About 330 calories per day.
True or False: A large reduction in weight during the post-partum will not inhibit lactation
False, too loarge of a weight reduction can inhibit lactation
Does changes in weight due to healthy eating and physical activity affect milk production during lactation?
No, it is safe and does not affect milk production.
What type of activity should pregnant women choose?
Low impact activites and avoid sports that increase risk for falls

Which is more likely to be affected by nutritional deficiencies during lactation: quantity or quality of breast milk?
Quantity of breast milk.