2.1 Cell Structure
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
structure of a eukaryotic cell
Large and have a nucleus bonded by nuclear membranes (nuclear envelope), dna associated with histone proteins, membrane bound organelles, 80s ribosomes
Animal and plant cells.
describe how a sample of chloroplasts could be isolated from leaves
Break open cells and filter
In cold, isotonic, buffered solution
Centrifuge/spin and remove nuclei/cell debris
spin at higher speed, chloroplasts settle out
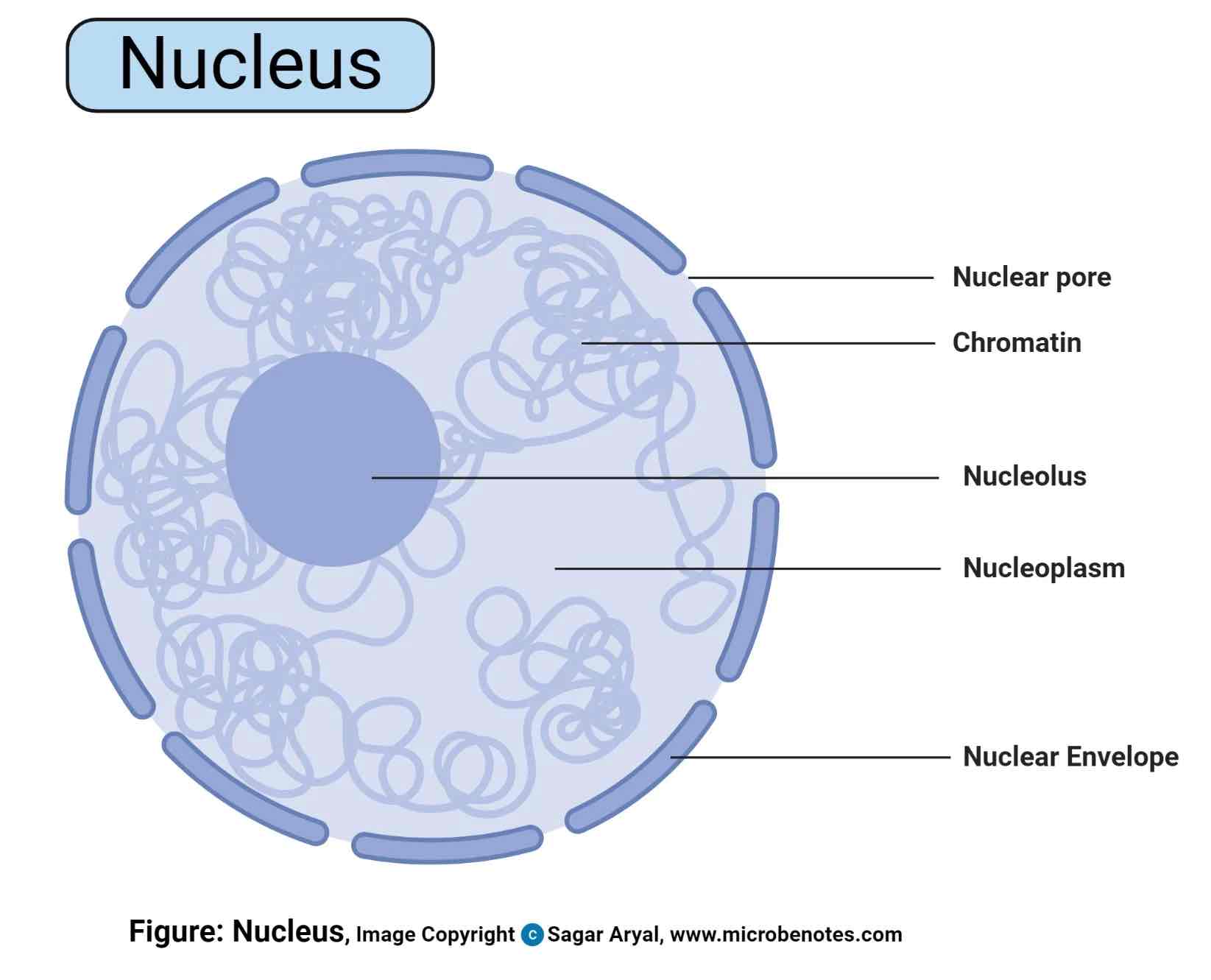
Nucleus
Found in eukaryotic cells
structure- nuclear envelope and pores. chromatin. nucleolus
Function- stores genetic material for polypeptide production. dna replication. production of mrna
structure of prokaryotic cells
Small, lack nucleus, 70s ribosomes, plasmids may be present, cell wall made of murien. No membrane bound organelles
differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells
80s vs 70s ribosomes, membrane/ no membrane bound organelles, no plasmids/ possible plasmids
structure of virus particles
genetic material, capsid and attachment proteins
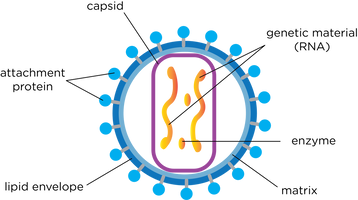
role of capsid and attachment protein
Capsid- helps to protect the virus from the host's immune system and to deliver the viral genetic material into the host cell.
Attachment proteins- bind to host cells in order to infect them.
give one feature of the chloroplast that allows protein to be synthesised inside the chloroplast and describe one difference between this feature in the chloroplast and similar features in the rest of the cell
ribosomes- 70s in chloroplast ,, 80s in cytoplasm
why are viruses described as acellular and non - living
no cell surface membrane
non-living, have no metabolic reactions
can not respire / replicate
no nutrition
outline the role of organelles in the production, transport and release of proteins from eukaryotic cells
dna in the nucleus codes for proteins
ribosomes/ RER produce proteins
mitochondria produce atp for protein synthesis
golgi body packages and modifies
vesicles transport
relate the structure of of a virus to its replication in cells
a virus uses attachment proteins on its surface to bind to complementary receptor proteins on the surface of a host cell. The virus then injects its DNA or RNA into the host cell. The host cell then uses its nucleic acid and protein-building machinery (ribosomes) to produce new viral particles.
how does an optical microscope work
Visible light passes through the specimen and is bent through the lens system
This creates a magnified image
The lenses in the microscope magnify the image by refracting the light and the focussing knobs are used to focus the light on the retina
limitations of an optical microscope
Advantages: minimal preparation
Disadvantages: low resolution because long wavelength
how does a transmission electron microscope work
Prepare a thin slice of specimen & place in vacuum chamber
Fire an electron beam down through the specimen from a giant gun
An electromagnetic coil (first lense) concentrates the electrons into a more powerful beam.
Another (second lense) focuses the bean onto a certain part of the specimen.
The beam passes through the specimen and pick up an image of it
The projector lense magnifies
Image becomes visible when beam hits fluorescent screen.
Image can be viewed directly through viewing portal, binoculars at the side or on a tv monitor
Specimen is treated with heavy metals
advantages and limitations of a transmission microscope
Advantages: High resolution, living organisms can be viewed
Disadvantages: expensive, 2D image
how does a scanning electron microscope work
Electron gun shoots electron beam down at the specimen
A positively charged electrode (anode) attracts the electrons and accelerates them into an energetic beam
An electromagnetic coil brings down the electron beam to a very precise focus, much like a lense
Another coil lower down steers the beam from side to side
The beam systematically scans across the object being viewed
Electrons of the beam hit the surface of the object and bounce off it
A detector registers these scattered electrons and turns them into a picture
A highly magnified image of the object is displayed on a tv screen
advantages and limitations of a scanning electron microscope
Advantages: high resolution, 3D image, can contain artefacts
Disadvantage: can’t observe living specimens, expensive, size
difference between magnification and resolution
Magnification: This tells you how many times bigger the image is than real life.
Resolution: The ability to see two structures very close together as separate structures.
process of homogenisation
sample tissue must be placed in cold isotonic buffered solution. cold- reduce enzyme activity. isotonic-prevent osmosis. buffered- prevent enzymes denaturing
the solution is then homogenised using a homogeniser, breaking plasma membrane and releasing organelles into a solution called homogenate
the homogenate goes through filtration- filtering out large debris leaving filtrate
ultra-centrifugation
filtrate is placed into the centrifuge
first spun at a low speed for a long period of time causing the heaviest organelles to settle at the bottom. this called the pellect
other organelles stay suspended in the solution above the pellet
this solution is also known as the supernatant
supernatent is placed in another tube and span at a faster speed for a shorter amount of time
organelle order of mass
nucleaus
chloroplast
mitochondria
lysosomes
endoplasmic reticulum
ribosomes
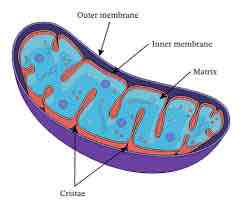
Mitochondria
Found in eukaryotic cells
Surrounded by a double membrane, inside is a fluid matrix containing ribosomes and a loop of DNA
Function- Produce ATP during aerobic respiration
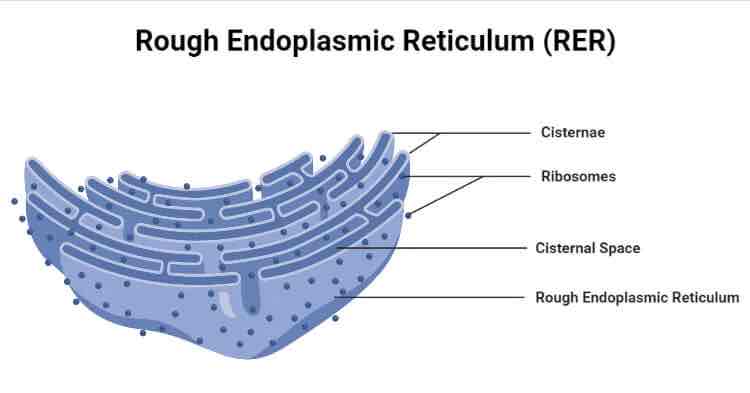
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
Found in eukaryotic cells
Consists of a series of flattened membranes bounds sacs (cisternae) that are linked to the nuclear envelope. This type of ER has ribosomes studded into its membranes
Site of protein synthesis and used a transport system for proteins
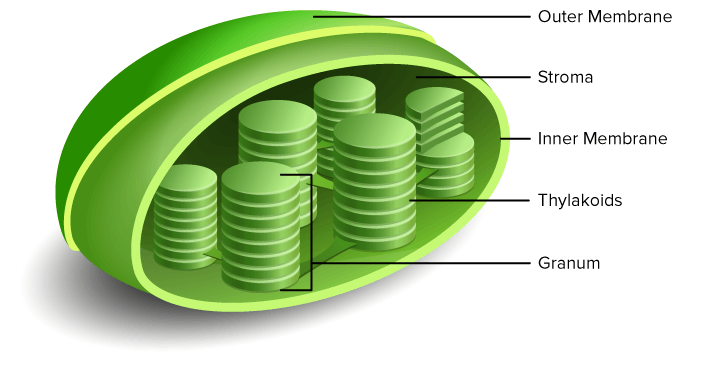
Chloroplast
Found in eukaryotic cells
Large organelle surrounded by a double membrane. Contains a gel-like fluid called the strong and internal membranes called thylakoids: these contain chlorophyll
function- site of photosynthesis
Cell Wall
Found in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells
In plants it is made of cellulose. In prokaryotic cells it is made of murein. These structures also have pores called plasmodesmata, that allow the cytoplasm of adjacent cells to connect.
function- supports herbaceous plants and acts as a temporary food store.
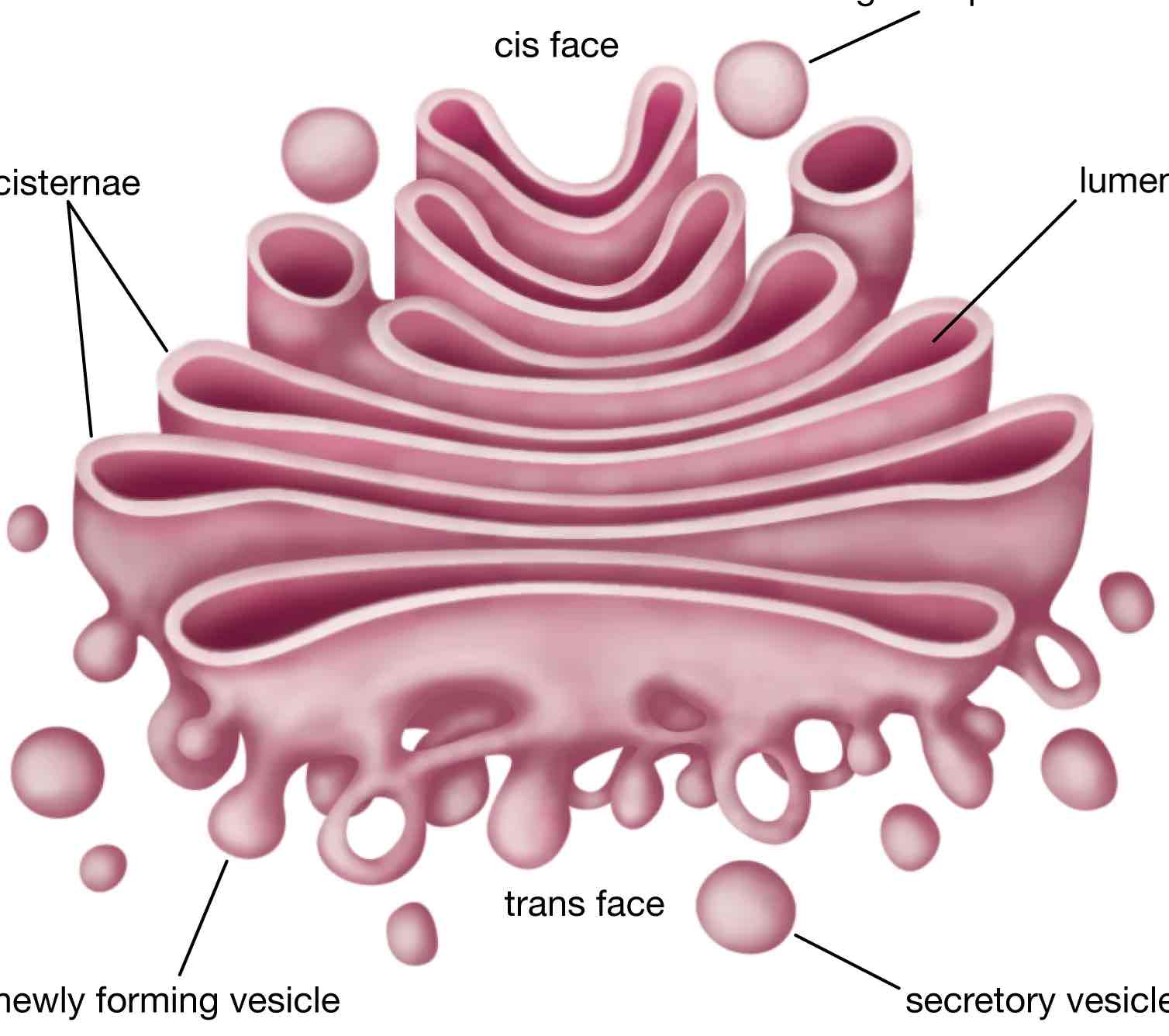
Golgi Apparatus
Found in eukaryotic cells
A crescent shaped stack of flattened membrane bound sacs called cisternae, vesicles
Function- chemically modifying & packaging proteins and lipids to be exported from the cell
forms vesicles and lysosomes
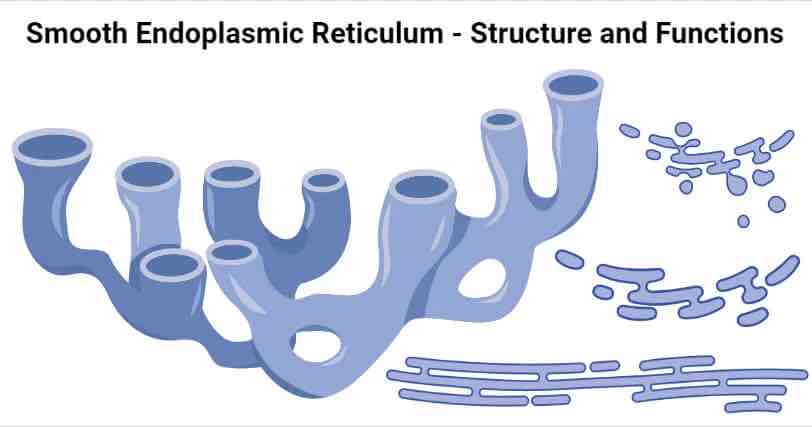
Smooth Endoplasmic Recticulum
Found in eukaryotic cells
Consists of a series of flattened, membrane bound sacs (cisternae) that are linked to the nuclear envelope.
Function- synthesises, stores and transports lipids and carbohydrates
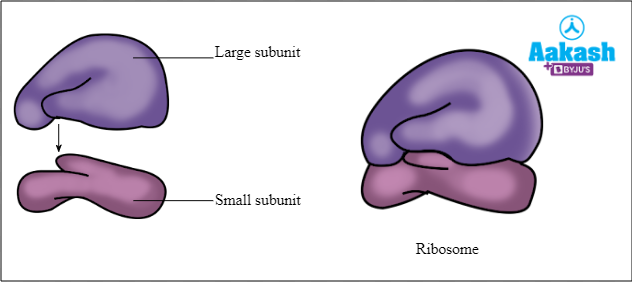
Ribosomes
Found in eukaryotic (80s) and prokaryotic (70s) cells
Made of a type of RNA and protein. Consists of a large subunit and a small subunit
Function- site of protein synthesis
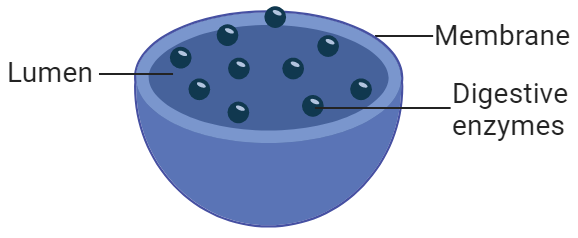
Lysosome
Found in eukaryotic cells
Consists of a lumen, surrounded by a single membrane and contains hydrologic enzymes.
Function: Digests unwanted material in the cell
Vacuole
Found in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
A single membrane called a tonoplast, containing a solution of mineral salts, sugars, amino acids, wastes and sometimes pigments
Function- provides mechanical strength and support. Stops the cell bursting in dilute solution I.e prevents osmotic lysis
Describe the role of plasmids, capsules and flagella.
Plasmids- replicate and move between cells so that genetic information can be shared.
Capsule- Protective slimy layer which helps the cell to retain moisture and adhere to surfaces
Flagella- help the cell move
tem vs optical
TEM use electrons and optical use light;
2. TEM allows a greater resolution
3. (So with TEM) smaller organelles/named cell structure can be observed OR greater detail in organelles/named cell structure can be observed
4. TEM view only dead/dehydrated specimens and optical (can) view live specimens
5. TEM does not show colour and optical (can);
6. TEM requires thinner specimens
7. TEM requires a more complex/time consuming preparation
8. TEM focuses using magnets and optical uses (glass) lenses