Chapter 6: Number Systems
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
notation
determine how symbols can be created using strings of characters from a given alphabet
representations
show how to assign real world meaning to a given string
decimal (base 10)
system that uses ten digits (0-9) to represent numbers, where each digit's position represents a power of ten.

binary (base 2)
A number system that uses only two digits, 0 and 1, to represent values.

octal (base 8)
A number system that uses eight digits (0-7) to represent values, where each digit's position represents a power of eight.

hexadecimal (base 16)
A number system that uses sixteen distinct symbols (0-9 and A-F) to represent values, where each digit's position represents a power of sixteen.
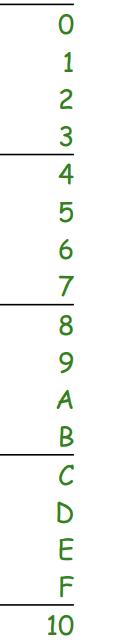
Powers of two
The values obtained by raising two to various non-negative integer exponents, commonly used in computing and binary representation.

Unsigned Integers
Non-negative whole numbers represented without a sign, where all bits are used to represent the magnitude.
Signed Integers
Whole numbers that can be either positive or negative, represented in computing with a sign bit to indicate the value's sign.
Two’s Complement
A method for representing signed integers in binary form, where the highest bit indicates the sign and the value is derived by inverting the bits and adding one to the least significant bit.
Sign and Magnitude
This signed representation (used in floating point) employs all but one bits for an unsigned magnitude. The remaining bit indicates the sign. It problems include complex arithmetic logic (since addition sometimes becomes subtraction and vice versus) and two representations of zero (+0 and -0). This may seem like a small matter. But comparison to zero is the most commonly performed conditional operation. If there are two values representing zero, this operation become more complex
One’s Complement
This signed representation has a simple negation: complement each bit. So +1 (0001) is negated to -1 (1110). This representation also introduces complexity is arithmetic. And it has two values for 0 (0000) and (1111).
Fixed Point Representation
a fixed step size (resolution), but varying accuracy.
Floating Point
a more complex representation with fixed accuracy, but a varying step size.
Sign
the leftmost bit that indicates whether a number is positive or negative in a signed number representation.
mantissa
the part of a floating-point number that contains its significant digits, representing the precision of the value.
exponent
the part of a floating point number that determines the scale or magnitude of the number, indicating how many places the decimal point should be moved.
normalization
the process of adjusting the mantissa and exponent of a floating-point number to ensure it is in a standard form, allowing for consistent representation and accuracy.
Quantitative Representation
a method for expressing numbers in a way that emphasizes their magnitude and scale, often used in scientific notation.
Symbolic Representation
The use of symbols to convey information, representing concepts, values, or instructions in a concise form, commonly used in mathematics and logic.
ASCII
A character encoding standard for electronic communication that represents text in computers, using a numerical value for each character, based on the English alphabet.