Ch. 10 - Properties of Solutions
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
nu , mu
solute (u)
nv , mv
solvent (v)
Molarity (M)
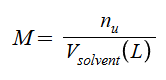
Normality (N)
N = M * (# equivalent)
# equivalent:
1 HCl ——→ 1 H+ + 1 Cl- # equiv = 1
1 H2SO4 ——→ 2 H+ + SO42- # equiv = 2
Mole Fraction (X)
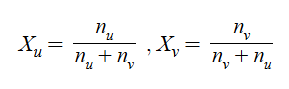
Mass Percent (P)
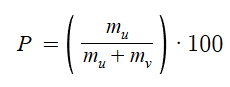
Molality (m)
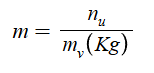
Mass of solution
msolution = mu + mv
Density of Solution
be careful with units…
Can be g/mL or g/cm3
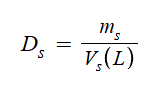
Concentration Conversion
M —→ assume 1 L
m -→ assume 1 Kg
X —→ assume 1 mole
m% —→ assume 100 g
Make denominator 1 or 100 if other information not given
To solve concentration questions….
Identify Key Words
Write out Question (Q)
Write out what you know - Data (D)
Solution Formation
ΔHsolution = ΔHsolute + ΔHsolvent + ΔHmix
ΔHsolute + ΔHsolvent
hydration energy
ΔHmix
lattice energy
hydration E > lattice E
ΔHsolution < 0
EXOTHERMIC
T increases
hydration E < lattice E
ΔHsolution > 0
ENDOTHERMIC
T decreases
Liquid-liquid solution
Like dissolves like
hydrophilic: NH, OH
hydrophobic: C, H, halides (F, Cl, Br, I, At)
Solid-liquid solution
polar solid dissolves in H2O
Factors that affect solubility
Temperature and Pressure
Temperature affect on solubility
Solid: T increases, solubility increases
Gas: T increases, solubility decreases
Pressure affect on solubility
Gas: P increases, solubility increases
Henry’s Law
Cg = KH * Pg
Cg = conc. of dissolved gas
KH = constant
Pg = partial pressure of gas solute above the soln.
Colligative Properties
boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, vapor pressure lowering, and osmotic pressure
Vapor pressure lowering (colligative property)
the colligative property where the vapor pressure of a solvent decreases when a non-volatile solute is added
The amount of vapor pressure lowering is directly proportional to the mole fraction of the solute and can be calculated using Raoult's Law:
Psolution = Xsolvent * P°solvent
Raoult’s Law
Psolution = Xsolvent * P°solvent For NON-VOLATILE
Psolution = ∑ (Xsolvent * P°solvent) For VOLATILE
Psolution - vapor pressure of solution
Xsolvent - mole fraction of solvent
P°solvent - vapor pressure of pure solvent
Freezing Point Depression (colligative property)
ΔTf = i*Kf*msolute
m = MOLALITY
Boiling Point Elevation (colligative property)
ΔTb = i*Kb*msolute
m = MOLALITY
Tbp = Tnormal bp + ΔTb (ALL IN KELVIN)
Osmotic Pressure (colligative property)
Π = iMRT
R = 0.082 L*atm/mol*K
T = KELVIN
Π = in ATM
As [solute particle] ↑
v.p and f.p ↓
b.p and o.p ↑
i
van hoff’s coefficient
CH3OH —→ i = 1 (non-electrolyte)
NaCl —→ i = 2
CaCl2 —→ i = 3
nsolute particles (other)
nsolute particles = nsolute * i