Ethers, Ketones, aldehydes
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Physical properties of ethers
They have no H’s on the oxygen, so theres no hydrogen bonding
They also have low melting and boiling points
Ether as a solvent
They can dissolve polar, non polar and hydrogen bonding compounds
What wont ether react with
bases, reducing agents, nucleophiles and dilute acids
What will ether react with
strong and hot acids, oxidizing agents
What is the industrial (first) preparation of ethers
reacting a primary alcohol with an acid (ex: h2so4). need to signify that you have 2 of the starting material
Why can only primary alcohols be used in the industrial (first) style of making ethers
Because it is an sn2 mechanism. using secondary or tertiary alcohols will lead to dehydration
What is the industrial (first) style of preparing ethers useful for
it’s useful for making symmetrical ethers, otherwise it results in mixtures
What is the name of the second style of preparation for ethers
Williamson ether synthesis
What is the williamson ether synthesis
its when an alcohol reacts with a strong base in the presence of an alkyl halide or alkyl tosylate
What is the mechanism for the williamson ether synthesis
the base deprotonates the alcohol and makes an alkoxide ion. then it reacts with the alkyl halide to add an alkyl group onto the alkoxide ion
What are the limitations of the alkyl halide in the williamson ether synthesis?
it needs to be a primary alkyl halide or else it will be eliminated
What is the third way to prepare eithers
Alkoxymercuration/demurcuration
What is Alkoxymercuration/demurcuration in terms of making an ether
it’s when an alkene reacts with Hg(OAc)2,ROH followed by NaBH4 to create an OCH3 group
What is the mechanism for an Alkoxymercuration/demurcuration to prepare an ether?
A OCH3 group is placed onto the molecule
Acidic cleavage of ethers
ethers can be cleaved by treated them with hot strong acid
Mechanism for acidic cleavage of ethers
the ether reacts with a strong hot acid. it cleaves at either end of the oxygen.
one side gains the halide (halide attacks the less substituted carbon) and the other side gains an OH.
after a while, excess acid attacks again, turning the OH into water, and then the halide takes its place
How do you prepare epoxides industrially
by using O2,heat/Ag2O
Why is making epoxides industrially not common
they’re expensive and may oxidize other groups
Mechanism for making epoxides industrially
What is the halohydrin formation for making epoxides
you treat a halohydrin with a base to induce an sn2 reaction
what is the mechanism for the halohydrin formation of an epoxide
an alkene is treated with a halogen/water
this places an OH and a halogen on the alkene respectively
treat it with a base like OH and it turns into an epoxide
What is peroxyacid epoxidation
its when you turn an alkene directly into an epoxide
what is the mechanism for peroxyacid epoxidation
What are the reagents for peroxyacid epoxidation
MCPBA/CH2Cl2
What is the grignard way of opening an epoxide ring
you use R-MgBr/Et2O (attacks the less hindered side)
the O of the epoxide becomes an OH
the R group attached to the mgbr gets added
reacts with h3o+ to form an OH
What is the reaction of epoxides with NaOEt/EtOH
EtO- attacks the epoxide and opens it (attacks less hindered side)
the O of the epoxide goes one way while theres an ethyl group formed with an ether
What is the acidic ring opening for the reaction of epoxides
its when a poor nucleophile (such as ROH/H) reacts with an epoxide
the epoxide reacts with the H+
the attack occurs at the more substituted carbon
Crown ethers
can make ionic salts soluble in non polar organic solvents
Formula for a crown ether
(# of atoms)-crown-(#r of oxygens)
rules for aldehyde nomenclature
pick the longest chain with the CHO group
the aldehyde carbon is #1
drop the e in the parent alkane and add al “hexanal”
what is the parent name of an aldehyde on a ring
cyclo*alkane*carbaldehyde
rules for ketone nomenclature
pick the longest chain with the C=O group
give the carbonyl the lowest number possible
drop the e in the parent alkane and add one along with a number (heptan-2-one)
name for aldehyde as a substituent
formyl
name for ketone as a substituent
oxo
oxidization of secondary alcohols
can use any oxidizing agent to turn an OH into a carbonyl
Oxidization of primary alcohols
use PCC,pyr/-2H to turn a alcohol into a aldehyde or carboxylic acid
Cleavage of an alkene using O3/(CH3)2S
makes a ketone and aldehyde
cleavage of an alkene using KMNO4 hot and concentrated
makes a ketone and carboxylic acid
What is a reagent you can use to put a aldehyde on a benzene
CO,HCl/CuCl,AlCl3 aka the gattermann koch reaction
What is 1,3-dithiane
a protecting group for ketones and aldehydes
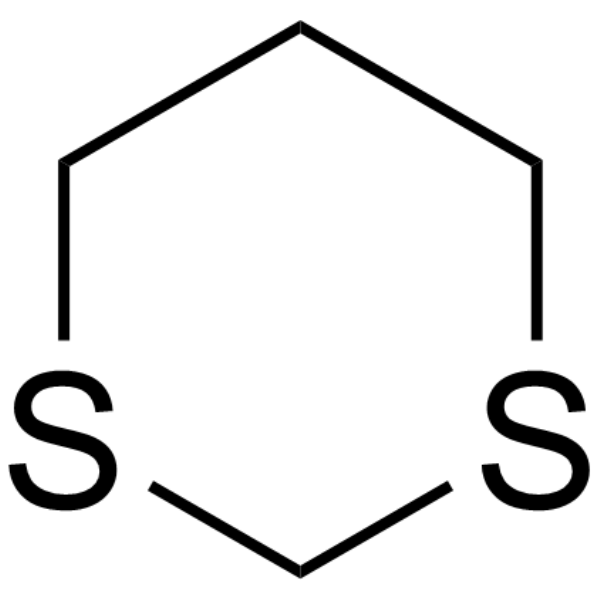
How do you deprotect a carbonyl from thioacetal
H,HgCl2/H2O
Acid catalyzed mechanism for addition of water
adds two alcohols in place of a carbonyl
needs a driving force (use excess of water)
Base catalyzed mechanism for addition of water
What are acetals
protecting group for aldehydes and ketones that have two ethers
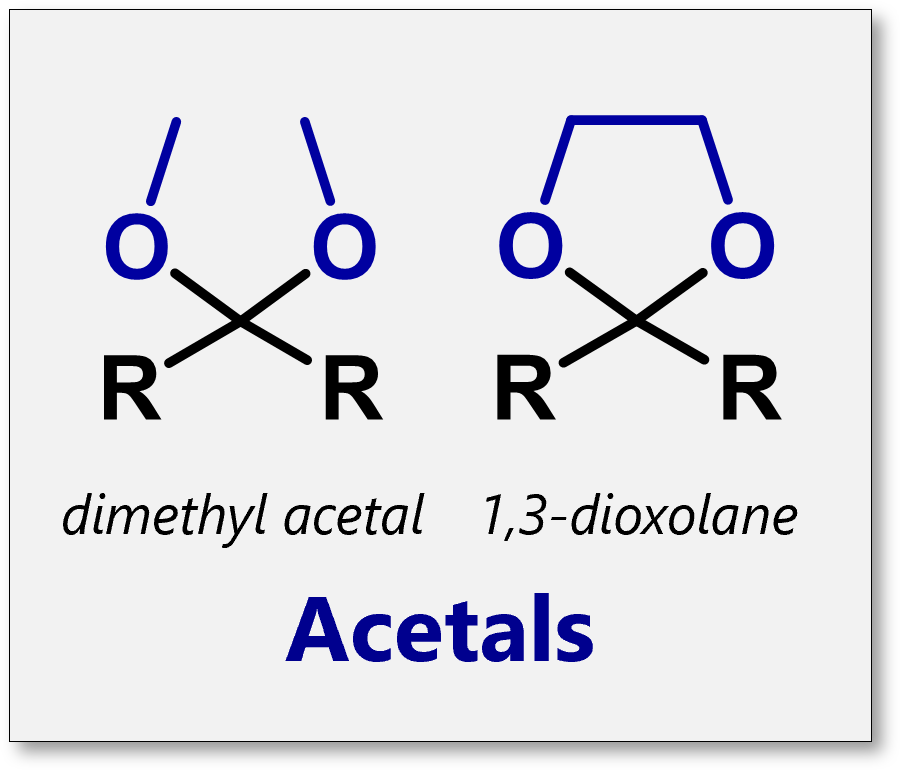
How do you get rid of an acetal
H+,H2O
What are the reagents for forming an acetal
2 equivalence of an ethyl with an OH/H+
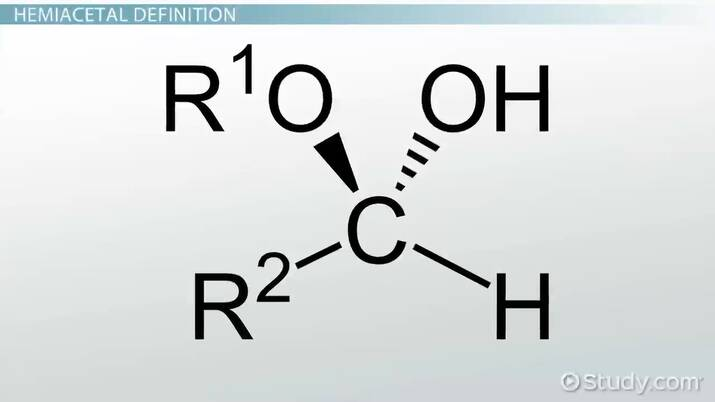
hemiacetal
Addition of HCN
Addition of grignards to ketones
What is the requirement for mclafferty rearrangement
need at least on hydrogen on the gamma carbon (also needs to have an aldehyde)
Cleavage between beta and gamma carbons of an aldehyde/ketone
cation is stabilized by enol, look for a double bond that is touching the oxygen
What is the wittig reaction
turns a carbonyl into an alkene
Wittig reaction mechanism
What do you get when you react a carbonyl with a primary amine
imine
What do you get when you react a carbonyl with a secondary amine
enamine
Imine formation
Enamine formation
Reducing agent LiAlH4
very reacting, can reduce a lot of things
LiAlH4,ether/H3O
Reducing agent NaBH4
less reactive, only reduces ketones and aldehydes
NaBH4/CH3OH
Reduction by using hydrogen/metal
can use H2/RN
turns carbonyl into an alcohol
What happens if the carbonyl is on a benzene during a Hydrogen reduction?
instead of turning into an alcohol, it will reduce completely
Clemmonson reaction
completely removes a carbonyl
Wolff Kishner reduction
reduces carbonyls into alkanes by using NH2-NH2