All Physics
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Incandescence
light emitted from a material because of the high temperature of the material
Electric Discharge
light emitted by a heated gas
Luminescence
The emission of light by a material or an object that has not been heated
Fluorescence
light that is emitted during exposure of the source to ultraviolet light. Emits immediately
Phosphorescence
light that is emitted due to the exposure of the source to ultraviolet light, and that continues to be emitted for some time in the absence of ultraviolet light.
Chemiluminescence
Light that is produced by a chemical reaction without a rise in temperature.
Bioluminescence
light that is produced by a biochemical reaction in a living organism.
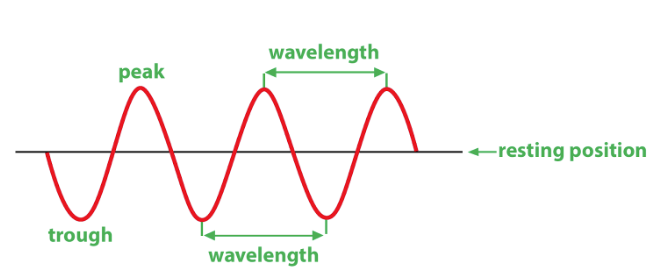
Wavelength
distance between maximums(peaks) of the spectrum
Electromagnetic Spectrum
The full range of electromagnetic radiation organized by wavelength and color.
Red on the Emag spectrum
Longest wavelength (700 nm)
Violet on the Emag Spectrum
Shortest wavelength (400 nm)
1 nm =
1 billionth m OR 1 m = 1 billion nm
Light rays off object parallel to principle axis. Concave mirror
reflects off mirror and through focal point
light ray off object through focal point. Concave mirror
reflects off mirror and parallel to principle axis
Light rays off center of curvature. Concave mirror
reflects off mirror and back through center of curvature
SALT attributes
size, attitude, location, type
Object beyond/behind center of curvature. Concave mirror
S: smaller, A: inverted, L: between center of curvature and focal point. T: real image
Object between Center of curvature and focal point. Concave mirror
S: larger, A: inverted, L: behind Center of curvature, T: real image
Object on Center of curvature. Concave mirror
S: same, A: inverted, L: on center of curvature, T: real image.
Object in front of focal point. Concave mirror
S: larger, A: same, L: through/in front of mirror, T: virtual image
Refraction (in mirror)
bending of light when it travels between two different substances or mediums. Occurs because the speed of light is different in different mediums due to their density.
Refraction in Less dense to more dense medium
Light bends towards the normal. (faster to slower)
Refraction in More dense to less dense medium
Light bends away from the normal. (slower to faster)
light parallel to PA (converging lens)
Passes through F on the other side
light through F (converging lens)
Parallel to PA on other side
Light through vertex (converging lens)
straight through vertex to other side.
Object between 2F and F (converging lens)
larger, inverted, beyond 2F, real image
Object in front of F - between F and lens (converging lens)
larger, same, between 2F and F, virtual image
Object beyond 2F (converging lens)
smaller, inverted, between 2F and F, real image
Law of reflection
angle of incident = angle of reflection