Lids, Lashes, Lacrimal
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
what causes dermatochalasis
weakened orbital septum with age
2 main types of blepharitis
staph and seborrheic
both can cause anterior and posterior blepharitis
what is seborrheic blepharitis associated with
seborrheic dermatitis
how does seborrheic bleph differ from staph bleph
seborrheic bleph is less inflamed and more oily/greasy, has more eyelash loss (madarosis) and misdirected lashes
2 things to ask about when patient has hordeolum or chalazion
history of acne rosacea or seborrheic dermatitis
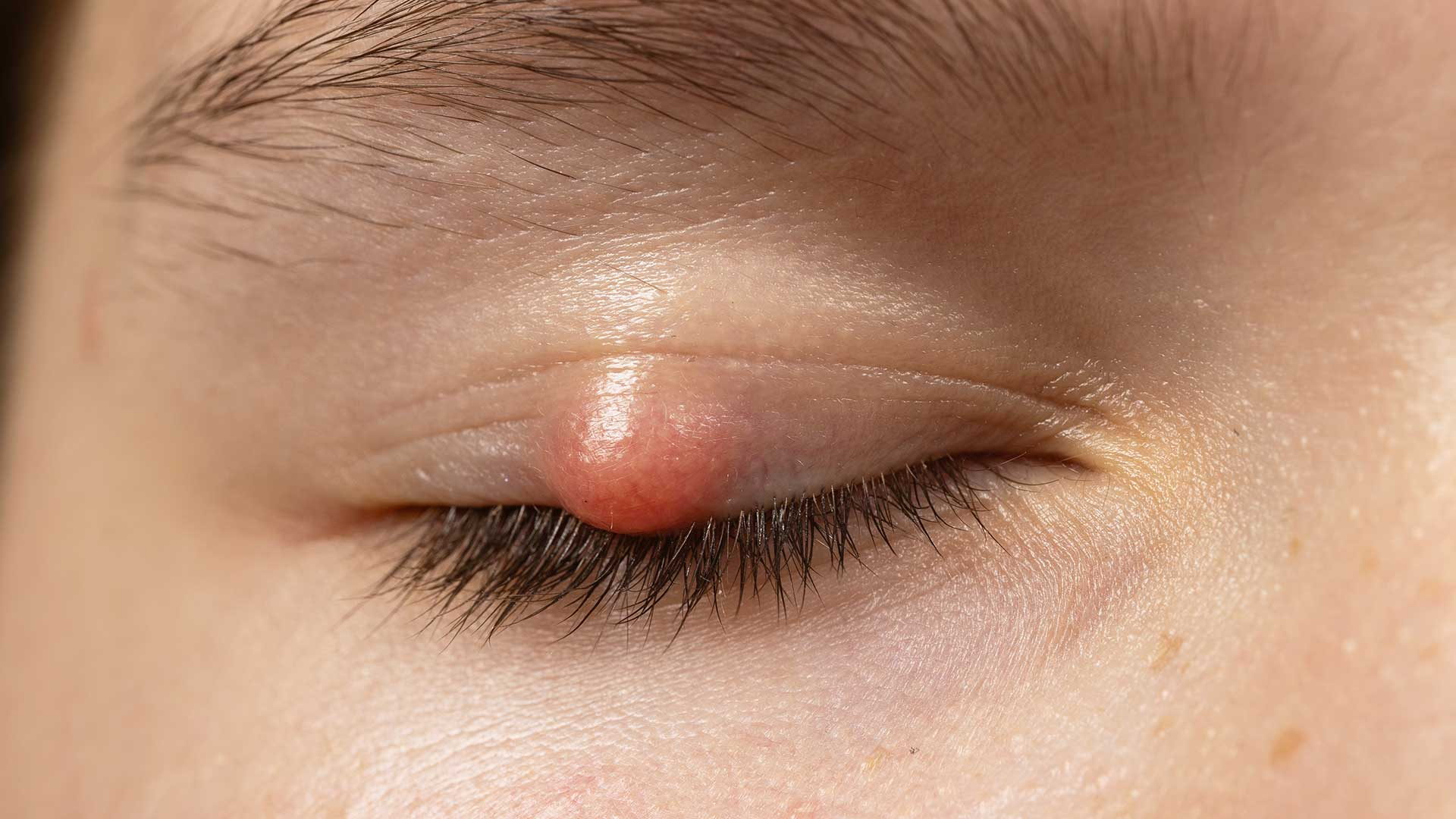
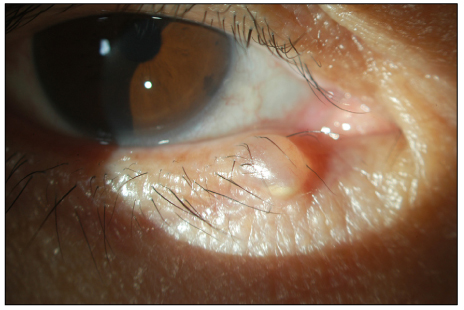
chalazion
localized sterile inflammation of an MG due to retention of secretions
chalazion prognosis
25% resolve on their own
chalazion presentation
hard, immobile, painless nodule without redness on the upper lid
concern with recurrent chalazion
malignancy, especially sebaceous gland carcinoma
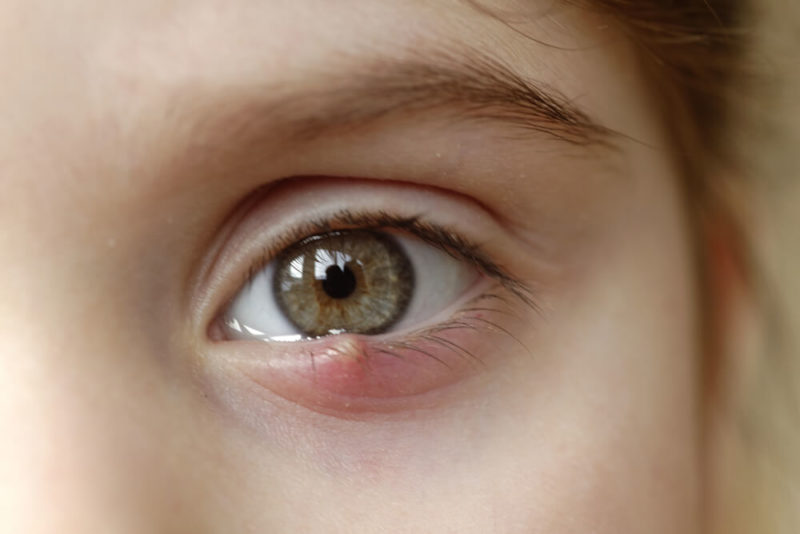
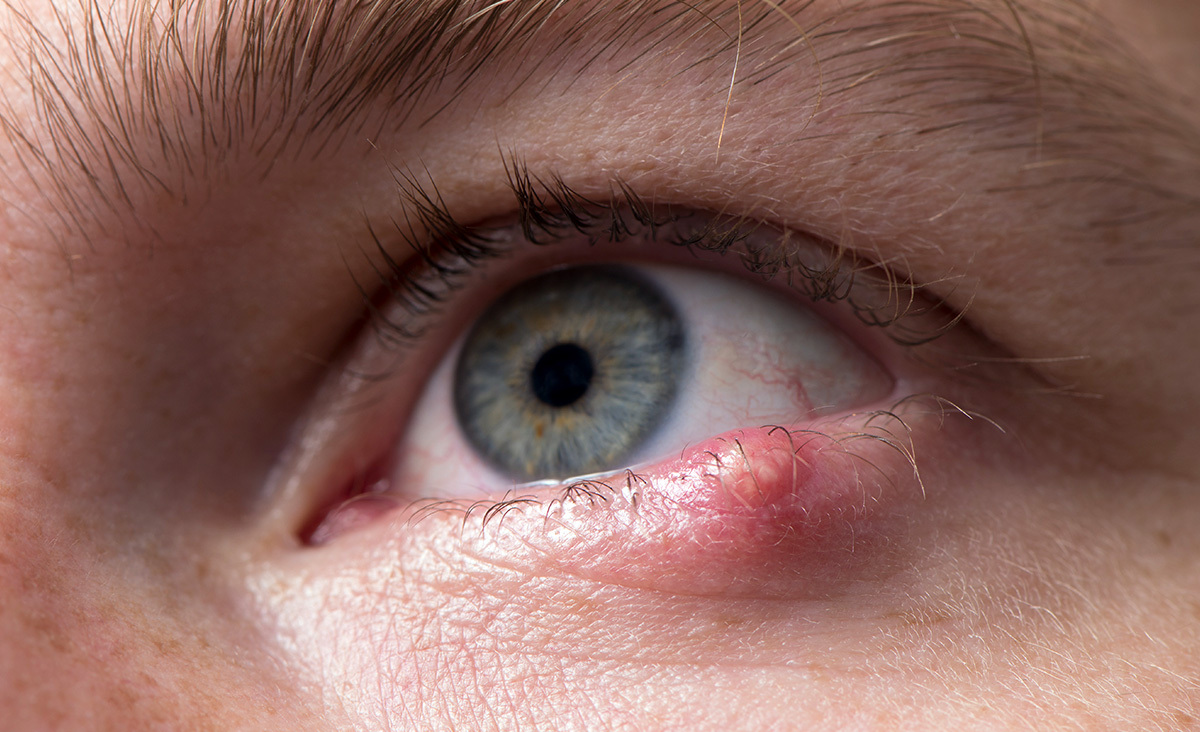
what is a hordeolum
staph infection of eyelid glands
what is a stye
external hordeolum that effects glands of zeis or moll
internal vs. external hordeolum
external: stye, affects glands of zeis or moll
internal: affects MGs
hordeolum presentation
tender, red, warm area of focal swelling on lid
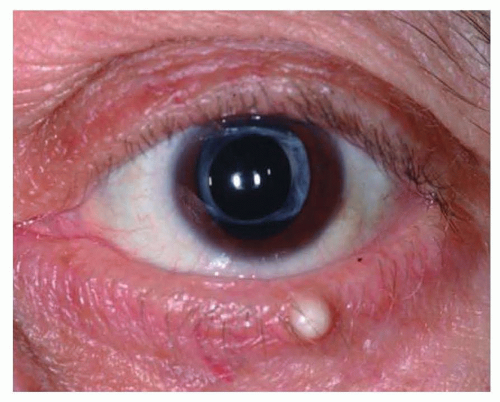
inclusion cyst
lesion from trauma or surgery that appears white due to keratinous debris accumulation
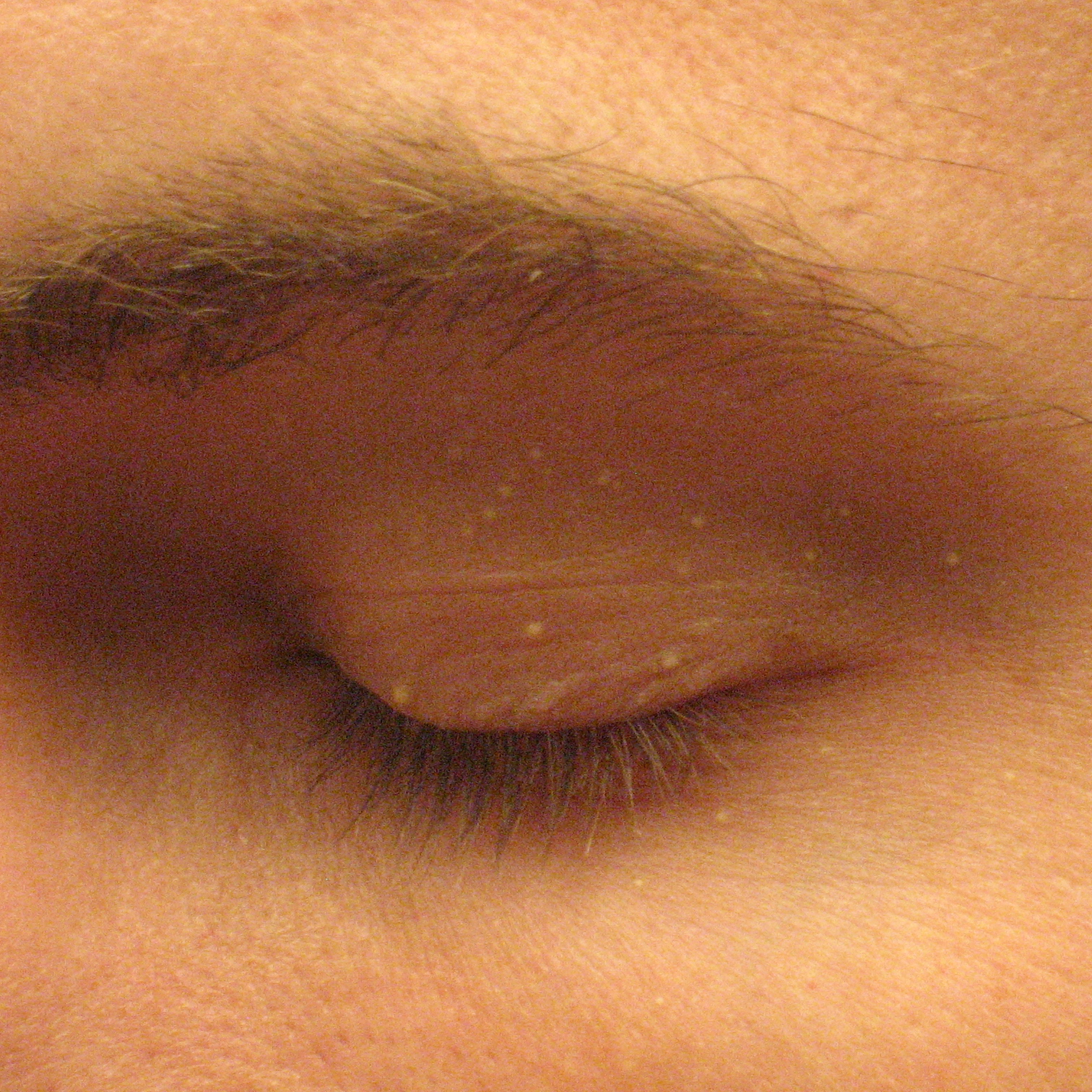
milia
white lesion from the occlusion of sweat pores or pilosebaceous follicles
dermoid cyst
firm, immobile lesion of normal tissue in abnormal location
sebaceous cyst
retention of fluid in glands of zeis or debris in MGs
yellow or opaque smooth lesions
most common cause of ectropion
age-related (involutional) loss of muscle tone of orbicularis oculi
main sign of ectropion
exposure keratopathy
main cause of ectropion
age-related (involutional)
main cause of cicatricial entropion
trachoma
cicatricial means from scarring
what can entropion do to lashes
trichiasis: posterior lash growth
distichiasis: second row of lashes
what causes blindness in trachoma
corneal ulceration from entropion and trichiasis
typical floppy eyelid syndrome patient
obese man with obstructive sleep apnea
what causes floppy eyelid syndrome
reduced elastin in tarsal plate, often seen in face down sleepers
what can friction in floppy eyelid syndrome cause
papillary conjunctivitis
3 ocular conditions that cause red eyes in the morning
floppy eyelid syndrome
RCEs
exposure keratopathy
benign essential blepharospasm
idiopathic involuntary, bilateral, repetitive blinking from spasms of orbicularis, corrugator, and procerus
meige’s syndrome
benign essential blepharospasm with lower facial abnormalities (jaw pain, jaw spasms)
50% of patients with BEB
BEB vs. myokymia
BEB: idiopathic, bilateral, 3 muscles
myokymia: classic causes, unilateral, 1 muscle (orbicularis)
what is the most common skin cancer in the US
basal cell carcinoma
what is the most common eyelid cancer
basal cell carcinoma (90% of malignancies)
pathophys of BCC
malignancy of basal layer of epidermis
can be due to increased sun exposure (especially UV-B)
BCC prognosis
less than 0.1% metastasis
BCC presentation and progression
shiny, firm, pearly nodule with superficial telangiectasia
often bleeds and does not heal
common on LL
progresses into central ulceration
2nd most common eyelid cancer
squamous cell carcinoma
more common in males
pathophys of SCC
malignancy of stratus spinosum layer of epidermis
what is the precursor to SCC
actinic keratosis
most common pre-cancerous skin lesion
SCC prognosis
more aggressive than BCC, 13-24% metastasize
presentation
like BCC without telangectasia
rough erythematous plaque that can look flat or elevated
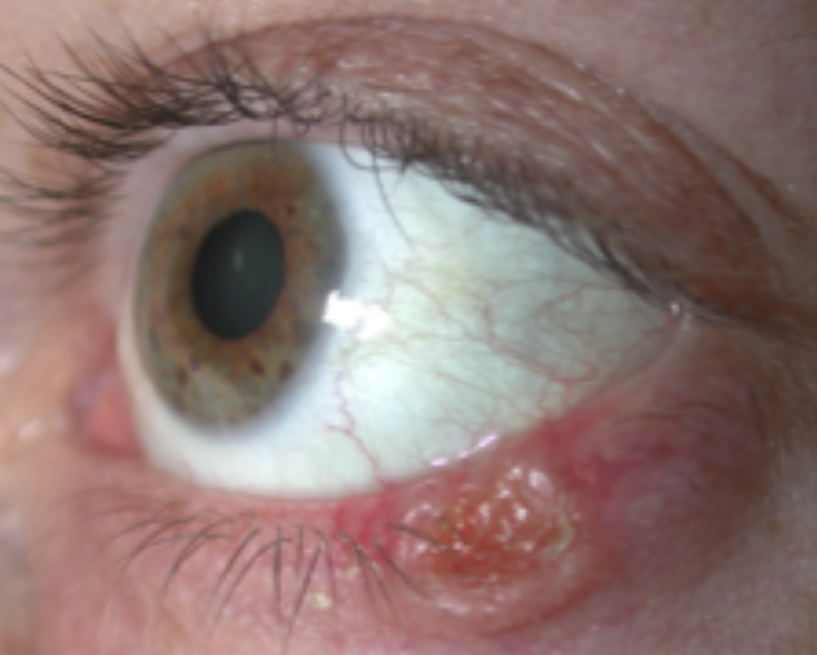
keratoacanthoma
fast growing benign tumor with central plaque or ulceration
keratoacanthoma prognosis
often grows large and then spontaneously resolves
pathophys of sebaceous gland carcinoma
neoplasm of sebaceous glands (MGs or zeis)
prognosis of sebaceous gland carcinoma
lesion greater than 2 cm has 60% mortality
overall 10% mortality rate
sebaceous gland carcinoma presentation
hard tumor with thickened, red lid margins and madarosis
often looks like chalazion
most lethal primary skin cancer
malignant melanoma
pathophys of malignant melanoma
malignancy of melanocytes (cells that produce pigment)
ABCDE of malignant melanoma suspicion
Asymmetry
Border irregularity
Color differences
Diameter (large)
Enlargement of lesion
2 most important malignant melanoma prognostic factors
depth of invasion
size of lesion
who is dacryoadenitis most commonly impacting
kids and young adults
pathophys of dacryoadenitis
inflammation of lacrimal gland (chronic or acute)
most common cause of acute vs. chronic dacryoadenitis
acute: bacteria or virus
chronic: inflammatory disease (sarcoid, TB, graves, idiopathic orbital inflammation)
what disease has 25% lacrimal gland involvement
idiopathic orbital inflammation
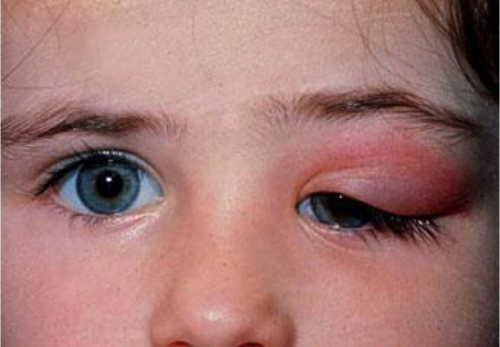
presentation of acute dacryoadenitis
S-shaped ptosis, upper lid pain, redness, swelling, preauricular lymphadenopathy, fever, elevated WBC count
presentation of chronic dacryoadenitis
temporal upper lid swelling with less redness, swelling, and pain than acute
can cause proptosis and globe displacement
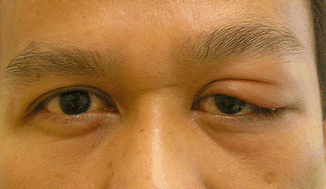
most common cause of canaliculitis
actinomyces israelii
canaliculitis caused by a. israelii has what presentation
yellow sulfur granules expressed at canaliculi
presentation of canaliculitis
pouting punctum, tenderness of nasal UL and LL, mucopurulent discharge when palpating lacrimal sac
what to ask about with dacrycystitis
concomitant ear, nose, or throat infection
pathophys of dacryocystitis
lacrimal sac infection with NLDO, causing backflow of bacteria from NLD into the lacrimal sac
dacryocystitis swelling is below:
medial canthus tendon
if swelling is located above medial canthus tendon, suspect:
lacrimal sac tumor
chronic cases of dacryocystitis should raise suspicion for what 2 diseases
epithelial carcinoma
malignant lymphoma
is dacryocystitis or canaliculitis more painful and swollen
dacryocystitis
what should you not do during acute dacryocystitis
do not attempt to irrigate or refer for surgery until treatment has been initiated
what is acquired punctal stenosis most often caused by
older age has progressive narrowing and occlusion of puncta
most common symptom of punctal stenosis
epiphora
most common cause of NLDO in older patients
involutional stenosis
most common cause of NLDO in younger patients and prognosis
membranous blockage at valve of hasner
spontaneous opening usually occurs 1-2 months after birth
NLDO often causes secondary _______
dacryocystitis
what does a positive jones 1 test indicate
patent lacrimal system
when is jones 2 testing performed
negative jones 1 result
reflex fluid out of the same punctum being injected during jones 2 indicates
canaliculus obstruction
retrograde flow through the opposite canaliculus during jones 2 testing indicates:
nasolacrimal blockage
what is the most common cause of congenital ptosis
failure of levator muscle to properly develop
plaque
palpable flat lesion on skin more than 0.5 cm
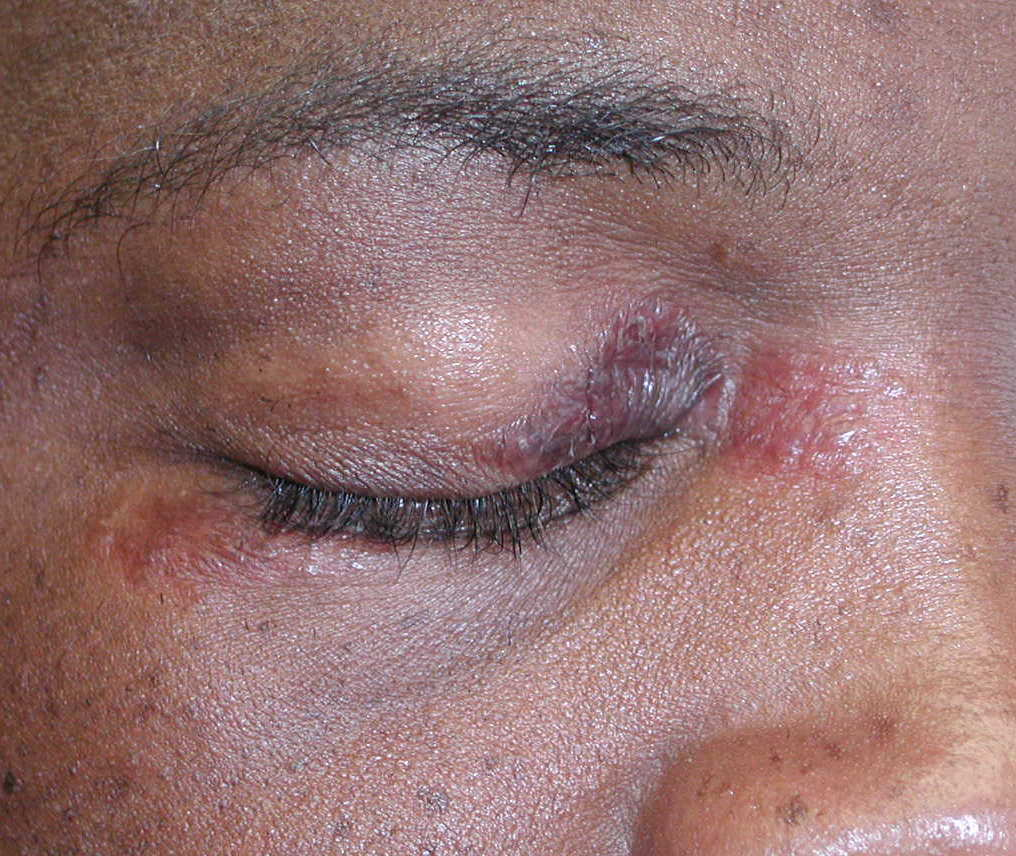
macule
localized area of color change without elevation
ex: freckle
papule
small, palpable lesion with solid elevation usually less than 0.5 cm in size
vesicle
small fluid-filled lesion
nodule
solid area of elevated skin enlarged in 3 dimensions
aponeurotic ptosis
most common, defect in levator aponeurosis
moderate ptosis with high eyelid crease and good levator function
most commonly from aging
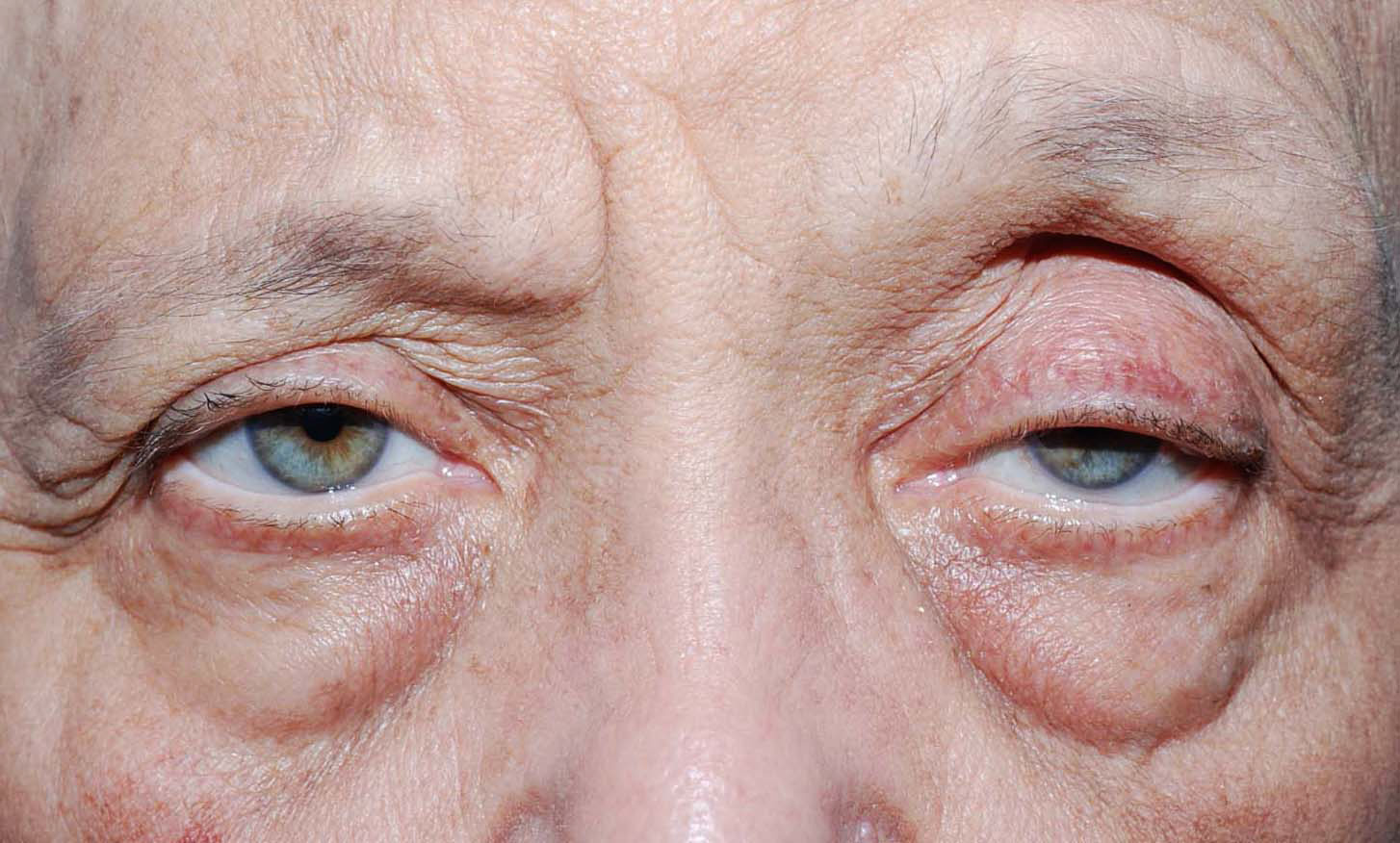
mechanical ptosis
ptosis due to mass or scarring
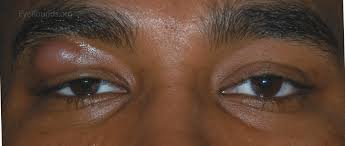
myogenic ptosis
myopathy of levator muscle
poor or absent lid crease
can be congenital or from disease (MG, myotonic dystrophy, CPEO, kearns sayre)
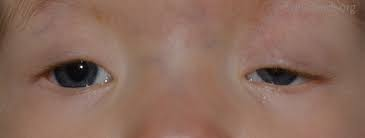
neurologic ptosis
innervational defect that leads to lid drooping
often from CN defects