MATERIAL PROPERTIES AND THEIR UNITS, GENERAL PROPERTIES, STRESS-STRAIN CURVE
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Density, ρ (Units: kg/m3, lb./ft3
• is the mass per unit volume. We measure it today as
Archimedes did: by weighing in air and in a fluid of
known density.
Price, CM (Unit: $/kg , $/lb.)
• spans a wide range, can fluctuate, and they depend on
the quantity you want and on your status as a “preferred
customer” with your chosen vendor. Despite this
uncertainty, it is useful to have an approximate price in
the early stages of material selection.
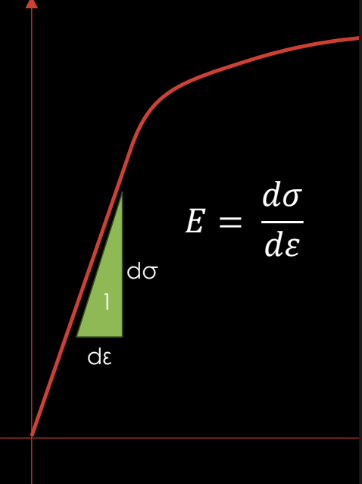
1. Elastic Moduli
2. Proportionality Limit
3. Yield Strength, Sy
4. Ultimate Strength, Sult
5. Rupture Stress, σR
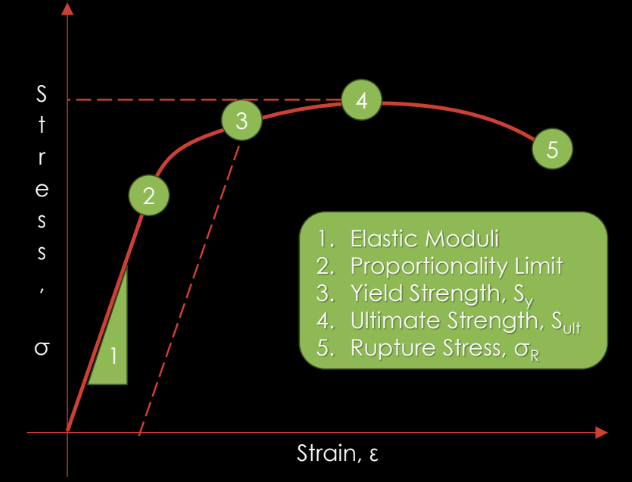
STRESS, σ
The force per unit area the specimen experiences
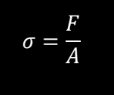
STRAIN, ε
The amount of deflection
an object experiences once stress is
applied relative to the original state
of the object.
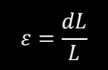
Young’s Modulus, E
ELASTIC MODULI
Describes response to tensile or compressive loading
Shear Modulus, G
ELASTIC MODULI
Describes response to shear loading
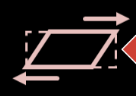
Bulk Modulus, K
ELASTIC MODULI
Describes the response to hydrostatic pressure.
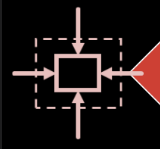
ELASTIC MODULI
Young’s Modulus, E
Shear Modulus, G
Bulk Modulus, K
ISOTROPIC
The Three Moduli are related in the following:
materials whose properties remain the same when tested in
different directions.
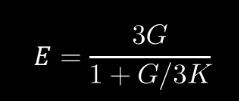
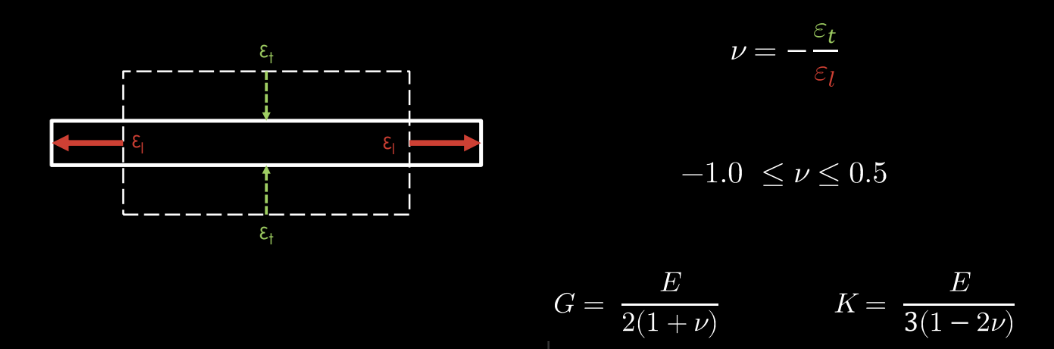
POISSON’S RATIO
Poisson’s ratio is “the ratio of transverse contraction strain to longitudinal
extension strain in the direction of the stretching force.”
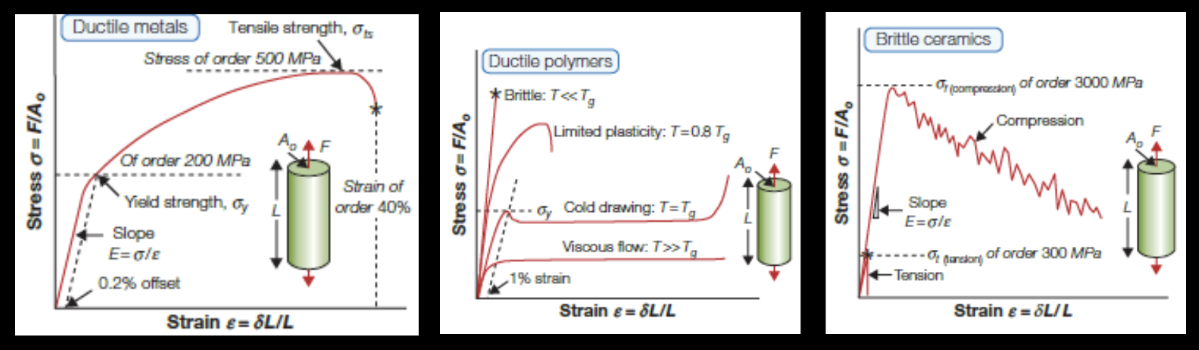
STRENGTH
• The Strength of a solid, Sf
, depends on the material.
• The Capacity of the material to handle stress.
• The stress required for a material for something interesting to occur in that
material.
• For DUCTILE Materials: Yield Strength – Sy or Ultimate Strength – Sult
• For BRITTLE Materials: Ultimate Strength – SUlt
• Units
• SI – Pa (N/m2), kPa, MPa, GPa,
• EE – psi, ksi,
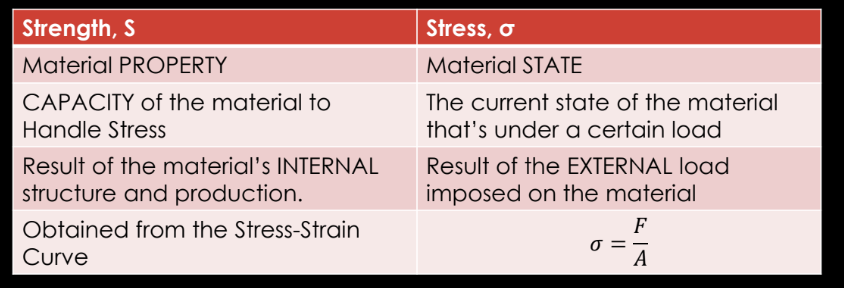
STRENGTH VS. STRESS
FACTOR OF SAFETY
• We want to design a component to withstand its
operating environment to be able to function
and to be able to function for a certain life.
• The performance criteria and the determination
of what is failure is typically determined by both
the design engineer and the program that
they're working on.
• So, what engineers do is they calculate
something called a factor of safety and what a
factor of safety does is it acts as a safeguard to
failure and it gives you a certain amount of
margin.
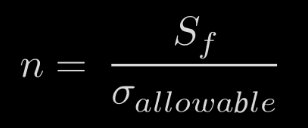
σ allowable
This is the maximum stress
that is set by the design
engineer that the
component must hold.
Sf
This is the Strength of the
material the component
is designed.