AP Government [MCQs] - Law Making Process
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
e.
The agenda-setting function of the media refers to the power to
a. endorse specific candidates for political office
b. favor the position of one interest group over another
c. counter the censorship activities of media watch groups
d. mobilize economic interests
d.
Which of the following situations is an example of the president using the bully pulpit as a tool for agenda setting?
a. President Clinton invoking executive privilege in resisting a subpoena by the United States Senate during the Whitewater investigation
b. President Bush issuing a signing statemen in the Detainee Treatment Act of 2005 that considerably weakened its provisions
c. President Obama issuing an executive order delaying the deportation of at least five million undocumented immigrants
d. President Reagan delivering a televised address urging a reduction in federal taxes
e.
Generally, when is a president most likely to get congressional approval of proposed policies?
a. After midterm House elections
b. In the second term rather than the first
c. When public opinion is sharply divided over policy
d. In social policy areas rather than in economic policy areas
e. In foreign affairs rather than in domestic affairs
a.
Which of the following is an action a president can take to rally public support for the administration’s legislative agenda?
a. Use the State of the Union Address to pressure Congress to pass a bill lowering income taxes
b. Hold private meetings with key members of Congress to promote a compromise on the budget
c. Forge an executive agreement with another country regulating the safety of consumer products
d. Sign a bill into law that would increase aid to college students
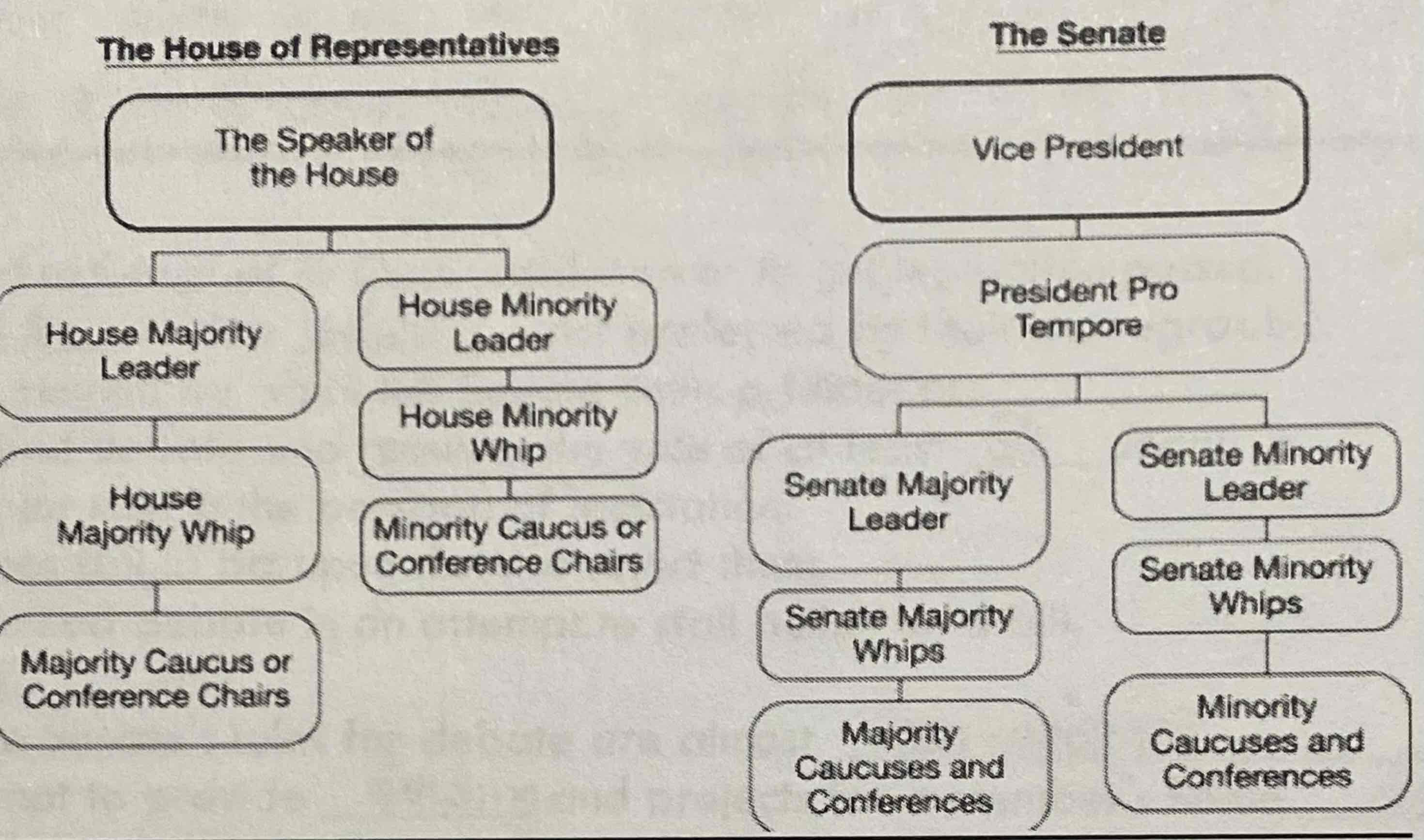
c.
A new-elected president ran on a campaign of lowering taxes and reducing spending on discretionary programs but now must work with Congress to ensure legislation passes which achieves those goals. Which of the leaders in the diagram plays the most crucial role in shaping the legislation that the president wants passed?
a. President pro-tempore
b. Vice president
c. Speaker of the House
d. Vice president
d. House majority leader
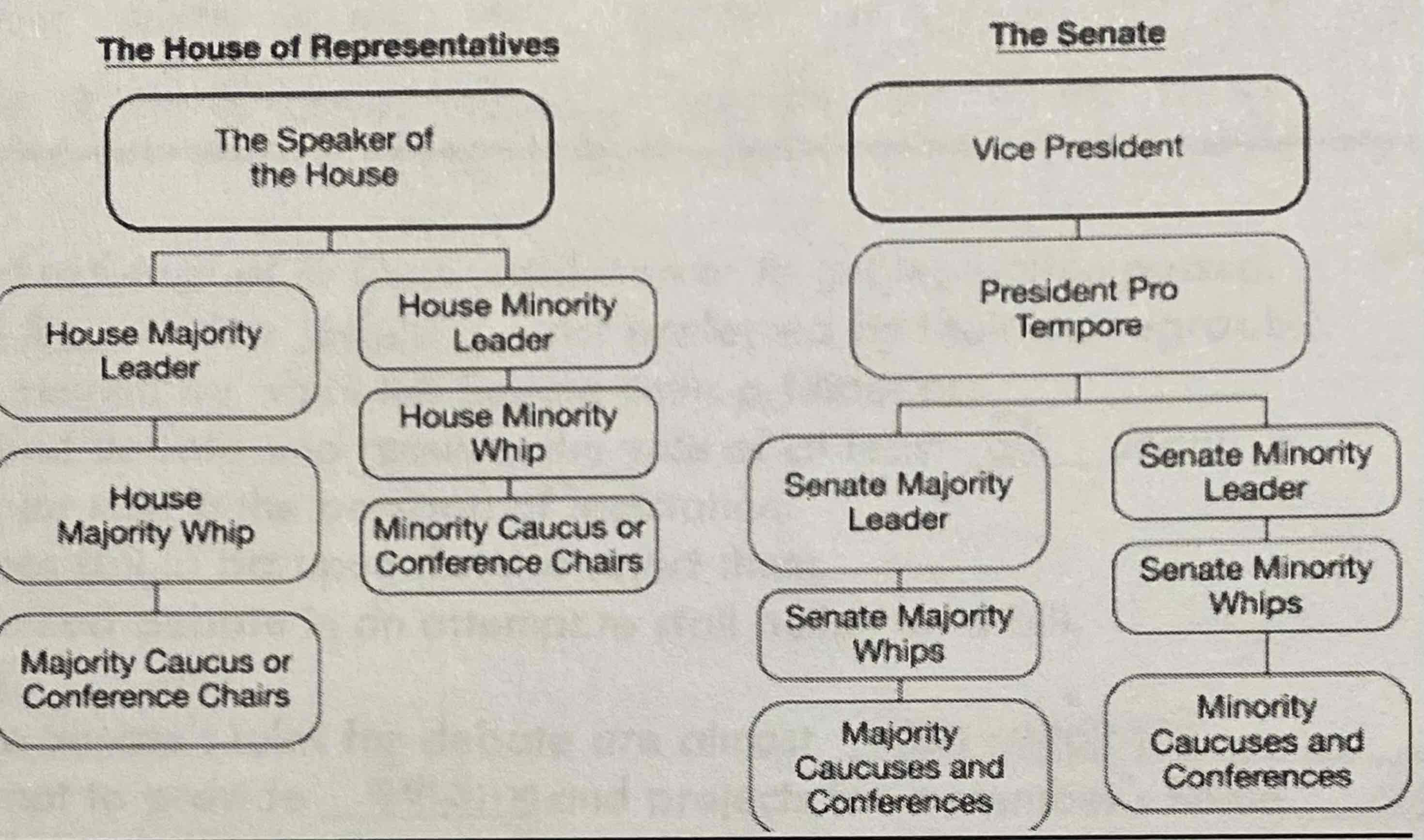
a.
Based on your knowledge and the diagram, which of the following is rue regarding the leadership structure of Congress?
a. The role of the minority leader in the House of Representatives and the Senate is to coordinate a strategy for the minority party
b. The vice president is responsible for creating and setting the legislative agenda for the Senate
c. The speaker of the House has very little power to control members of the majority party in the House of Representatives
d. The majority leaders in both chambers work to ensure that a bipartisan agenda is passed in the Congress
d.
Congressional standing committees are best described as
a. specially appointed investigative bodies
b. joint committees of the two houses of Congress
c. committees created for each session
d. permanent subject-matter committees
e. advisory staff agencies
c.
Most of the bills introduced in the House and the Senate are then
a. passed by one chamber but not the other
b. passed by both chambers but vetoed by the president
c. referred to a committee but never sent to the full Congress
d. voted down during the amendment stage of the floor debate
e. killed in the Rules Committee
d.
The committee chair in the House of Reps. is always
a. the member with the longest service on the committee
b. the member with the longest service in the House
c. a representative of the Speaker
d. a member of the majority party in the chamber
e. a trusted ally of the President
e.
Most of the legislating work in Congress takes place in
a. joint committees
b. ad job committees
c. select committees
d. conference committees
e. standing committees
b.
Which of the following statements about Congress is true?
a. Members of Congress only occasionally are interested in and pay attention to constituents
b. The legislative process is frequently lengthy, decentralized, and characterized by compromise and bargaining
c. Lobbyists and political action committees (PAC’s) successfully induce most members of Congress to trade their votes for campaign contributions
d. The growth in the size of Congress as an organization is the principal cause of growth in the federal budget deficit
e. Debate in both houses is structured by elaborate rules enacted by leaders of the majority party
d.
Which of the following identifies the formal procedure for ending a filibuster?
a. Oversight
b. Logrolling
c. Pocket veto
d. Cloture
e. Discharge petition
c.
Which of the following statements about the Senate is true?
a. Each state is represented in the Senate according to its population
b. The Senate, unlike the House, has a Rules Committee
c. Individual senators can exercise substantial influence over the legislative process
d. The Senate has a strict time limit on debate
e. The Senate is more responsible than the House for initiating appropriations legislation
c.
The power of the Rules Committee in the House of Representatives rests on its authority to
a. choose the chairs of other standing committees and issue rules for the selection of subcommittee chairs
b. initiate all spending legislation and hold budget hearings
c. place a bill on the legislative calendar, limit time for debate and determine the type of amendments allowed
d. determine the procedures by white nominations by the President will be approved by the House
e. Choose the president if no candidate wins a majority in the electoral college
c.
A member of the House of Representatives who whishes to be influential in the House itself would most likely seek a place on which of the following committees?
a. Agriculture
b. international Relations
c. Rules
d. Transportation and Infrastructure
b.
A “cloture motion” passed in the Senate does which of the following?
a. Returns a bill to committee
b. Cuts off debate on a bill
c. Criticizes a senator guilty of improprieties
d. Removes a President who has been impeached by the House
e. Brings a bill directly to a vote without formal committee approval
d.
Which of the following statements about motions for cloture is true?
a. They force a bill out of committee sot hat the full House can vote on it
b. They are applied to bills that failed in the previous session of Congress
c. They are applied to only appropriation bills
d. They are used by senators to end a filibuster and bring a bill to a vote
e. They occur whenever a bill is reported out of committee
c.
Which of the following is a unique power held by members of the Senate?
a. Control of the veto
b. Control of the appropriations process
c. The ability to filibuster
d. The ability to impeach the president
e. The ability to work with a clearly defined constituency
e.
if Congress adjourns during the ten days the President has to consider a bill passed by both houses of Congress, but which the president has not yet signed, what is the result?
a. Line-item veto
b. Legislative veto
c. Executive veto
d. Judicial review
e. Pocket veto
a.
When a bill passes the House and the Senate in different versions, the bill is resolved by which of the following types of committee?
a. Conference
b. Select
c. Reconciliation
d. Rules
e. Standing
d.
The committee that resolves differences between House and Senate versions of a bill is called a
a. joint committee
b. select committee
c. special committee
d. conference committee
e. standing committee
d.
Which of the following is true about divided party control of the presidency and Congress?
a. it is a natural occurrence due to the constitutional system of checks and balances
b. It rarely occurs in United States elections, because of straight-ticket voting
c. It promotes quick action by the President and Congress on such issues as the federal budget
d. It reflects a frequent election pattern over the past three decades
e. It results from the reapportionment of House seats after the decennial census
c.
Which of the following is the most likely consequences of divided government?
a. Reorganization of the federal bureaucracy
b. Conflicts between states
c. Delays in confirmation of federal court nominees
d. Conflicts between national government and states
e. Elimination of the seniority rule in Congress
d.
Which of the following situations best illustrates the meaning of divided government in the United States political system?
a. The majority of Supreme Court justices are from one party, but the president is from another
b. The majority of governors are from one party, but the president is from another
c. The president and a majority of members of Congress are from one party, but the majority of governors are from another
d. The majority of senators and the majority of representatives are from one party, but the president is from another
e. The majority of Supreme Court justices is from one party, but the majority of senators and representatives are from another
d.
All of the following statements pertaining to the presidential veto are true EXCEPT:
a. Congress overrides fewer than ten percent of presidential vetoes
b. A vetoed bill is often revised and passed in another form
c. Presidents often threaten to veto bills to increase their leverage with Congress
d. A President may veto part of a bill
e. Congress often places provisions the President wants into a bill the President dislikes to make a veto less likely
d.
The term “pork barrel” refers to legislation specifically designed to
a. encourage a balanced federal budget
b. ensure the careful inspection of farm goods and other foodstuffs
c. distribute excess produce to the poor
d. provide funding for local projects that are intended to benefit constituents
e. equalize presentation between farming and farming states
a.
The president cannot veto which of the following
a. Joint resolutions that propose constitutional amendments
b. Laws overturning United States Supreme Court decisions
c. Legislation regulating congressional salaries
d. Legislation affecting foreign policy
e. Bills that originate in the Senate
c.
Which of the following scenarios best illustrates a member of Congress supporting pork-barrel legislation?
a. A senator from a coal-producing state voting against a job-training program for coal miners
b. A member of the House voting for urban renewal in exchange for increased funding for roads
c. A senator from an agricultural state amending legislation to establish a potato research institute in his or her state
d. A member of the House Armed Services Committee marking up a bill that will increase funding for military bases
c.
On February 9, 2016. President Barack Obama released his budget proposal for the 2017 fiscal year. Facing a Republican Congress, many declared the plan “dead on arrival.” Among the cited issues was Obama’s request for $582.7 billion in discretionary spending for defense, which many Republicans believed was not enough. Which of the following most accurately explains the interaction between the president and the Congress regarding the defense budget?
a. The Congress has the enumerated power to raise revenue, but it is forced to work with the president because the president has the power to determine spending for each department in the upcoming fiscal year.
b. The president can create a budget for defense spending, but Congress has the power to execute laws and operate the government, which can affect how much money is spent
c. Congress passes a budget for the entire federal government, including defense, but it must consider the president’s proposal because the president may veto the bill
d. The president introduces a specific budget bill for defense spending, but Congress uses its power of legislative oversight to set up a negotiation process with the president
b.
Which of the following actions by a congressional representative is an example of “pork barreling”?
a. Misusing campaign contribution
b. Directing federal funds into the representative’s district through legislatio
c. Accepting money from a political action committee (PAC)
d. Attempting to kill a bill with unacceptable amendments
e. Voting for a salary increase
b.
“Pork barrel” legislation helps the reelection chances of a member of Congress because such legislation
a. gives the member of Congress national standing and coverage on national television news
b. helps earn the member of Congress a reputation for service to his or her district
c. attracts campaign contributions from ideological political action committees (PACs)
d. prevents other candidates from claiming that the member of Congress is too liberal for his or her district
e. requires the member of Congress to travel extensively
d.
Which of the following best describes pork barrel politics?
a. The Office of Management and Budget negotiates with Congress to get the president’s budget proposal passed
b. Senators from states with agricultural economies promote farm price supports
c. Voters in rural areas support different issue positions than do voters in metropolitan areas
d. Members of Congress negotiate bills so that individual districts get money for projects that do not benefit the nation as a whole
e. Members of the Senate Judiciary Committee refuse to endorse the president’s nominees to the federal courts
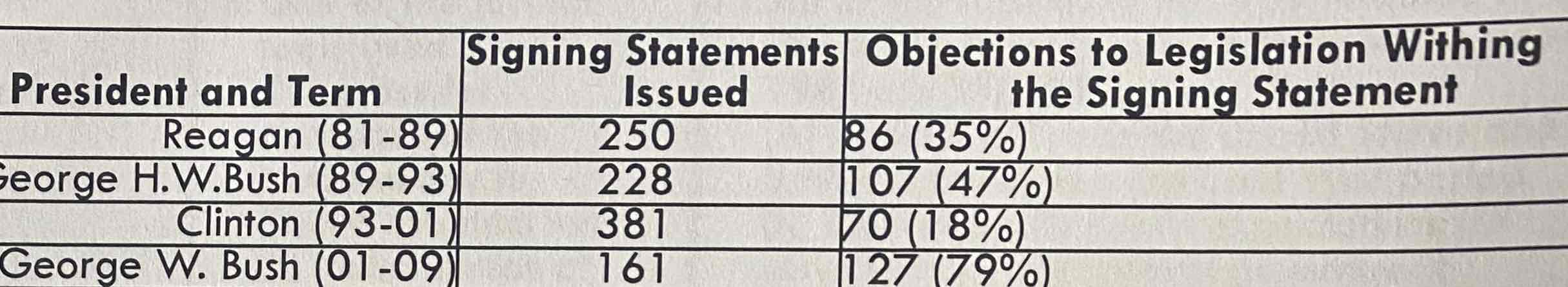
b.
Which of the following statements is most accurately supported by the data in the table?
a. President Clinton greatly reduced the use of presidential signing statements compared with his predecessors
b. While President George W. Bush issued fewer signing statements than President Clinton, his included more objects than President Clinton’s
c. President Clinton’s brief access to the power of the line-item veto allowed him to issue fewer signing statements that raised concerns about legislation
d. President George W. Bush was forced to issue more signing statements as a direct result of the terrorist attacks of September 11, 2001
a.
Which of the following best explains a reason that a president might use a signing statement to express displeasure with a bill as opposed to issuing a veto?
a. The president may have objections to provisions of a bill but does not want to risk Congress overriding a veto
b. Congress has severely curtailed the power of the president to withhold funds for bills that have been adopted
c. The Supreme Court is hesitant to acknowledge the president’s power to veto legislation
d. The president wants to ensure executive agencies do not spend the money appropriated by Congress
c.
The United States Fish and Wildlife Service will spend money appropriated by Congress to maintain wildlife refuges. This action is an example of
a. the power of the filibuster
b. congressional oversight of the bureaucracy
c. bureaucratic implementation of law
d. an unfunded mandate
e. an independent expenditure
d.
Independent regulatory commissions are created primarily for the purpose of
a. supporting and helping cabinet-level departments
b. proposing policy alternatives during periods of crisis
c. regulating the activities of other bureaucratic agencies to ensure that they act in a fair and objective manner
d. regulating certain industries to protect the public interest
e. increasing the President’s patronage powers
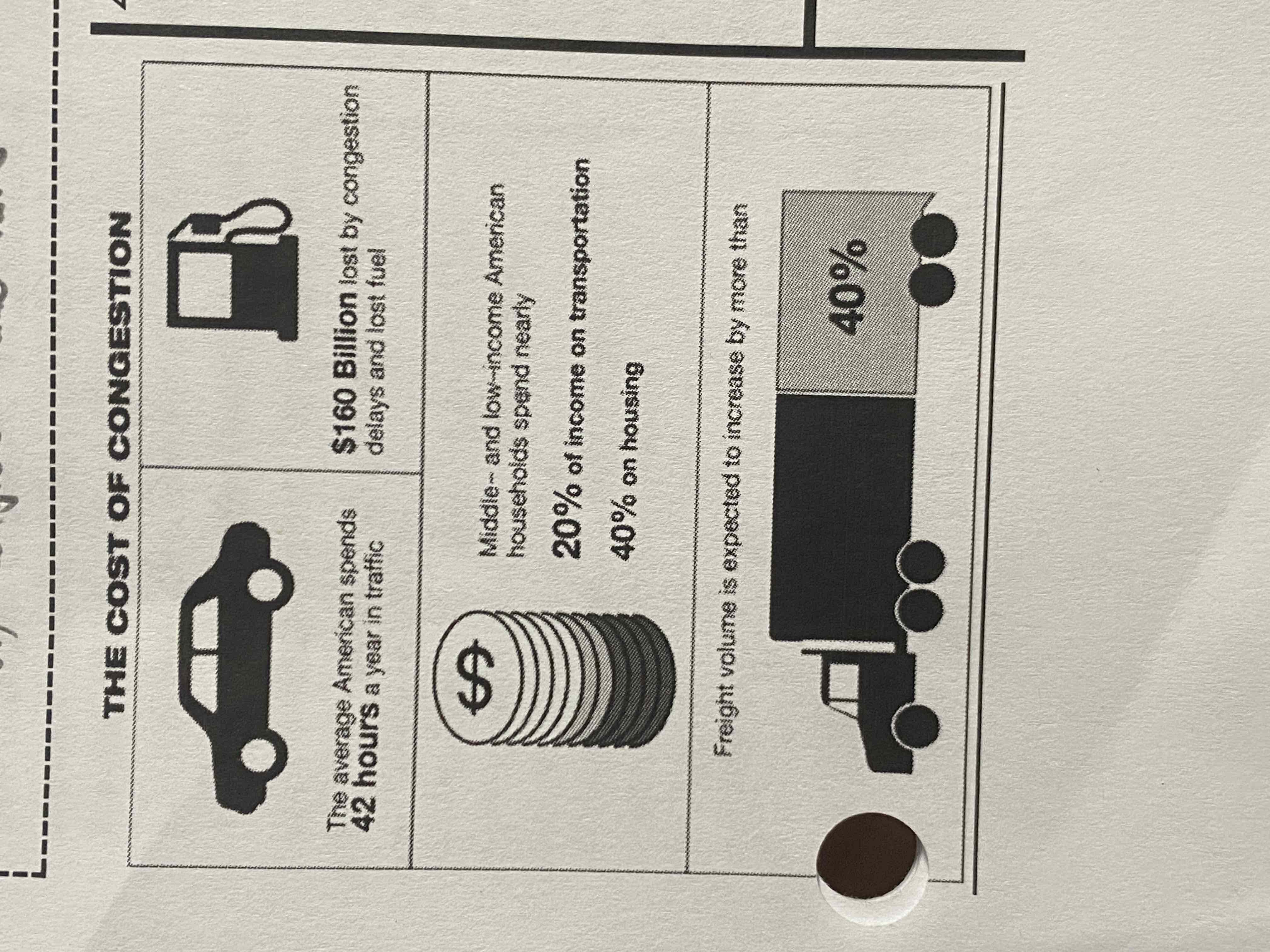
d.
Which of the following possible actions illustrates a way Congress interacts with the bureaucracy to address the problem shown in the infographic?
a. Congress could raise money through gasoline taxes to address the issues shown in the infographic
b. Congress could request that an iron triangle be formed to ensure that all bureaucratic solutions are heard prior to taking action
c. Congress could remove the members of the cabinet who work on issues related to transportation
d. congress may have members for the Department of Transportation testify before a committee to discuss the issue and potential solutions
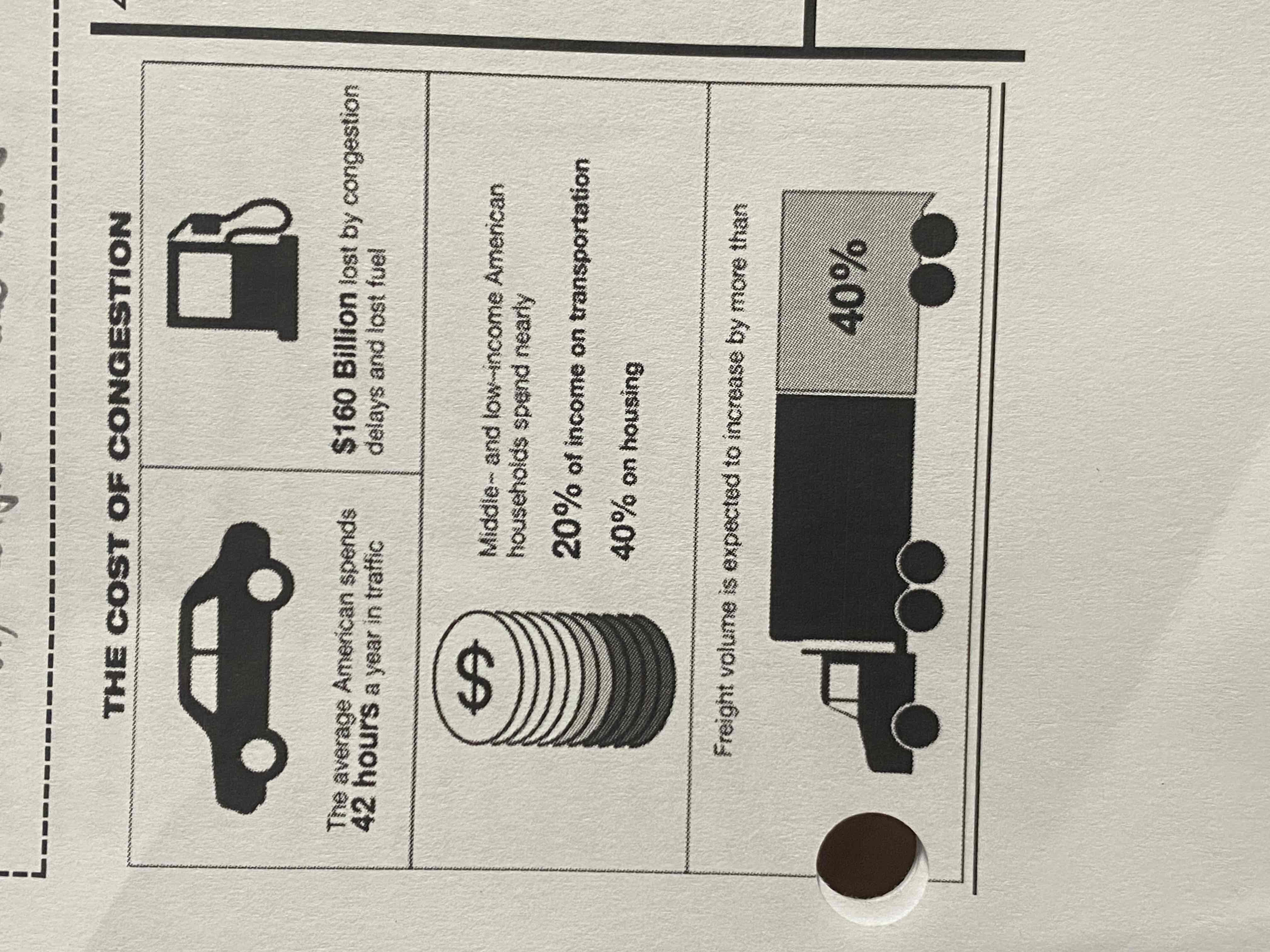
a.
Which of the following explains how the bureaucracy can address a problem shown in the infographic?
a. The Department of Transportation can write stronger regulations on freight volume
b. The president can negotiate a treaty that would allow for increased imports of oil
c. The House Committee on Energy and Commerce can hold a hearing on the cost of fuel
d. The Supreme court can overturn laws that regulate fuel economy
e.
Rule and regulations created by an agency such as the Federal Communications Commission are called
a. constitutional law
b. statutory law
c. common law
d. equity law
e. administrative law
c.
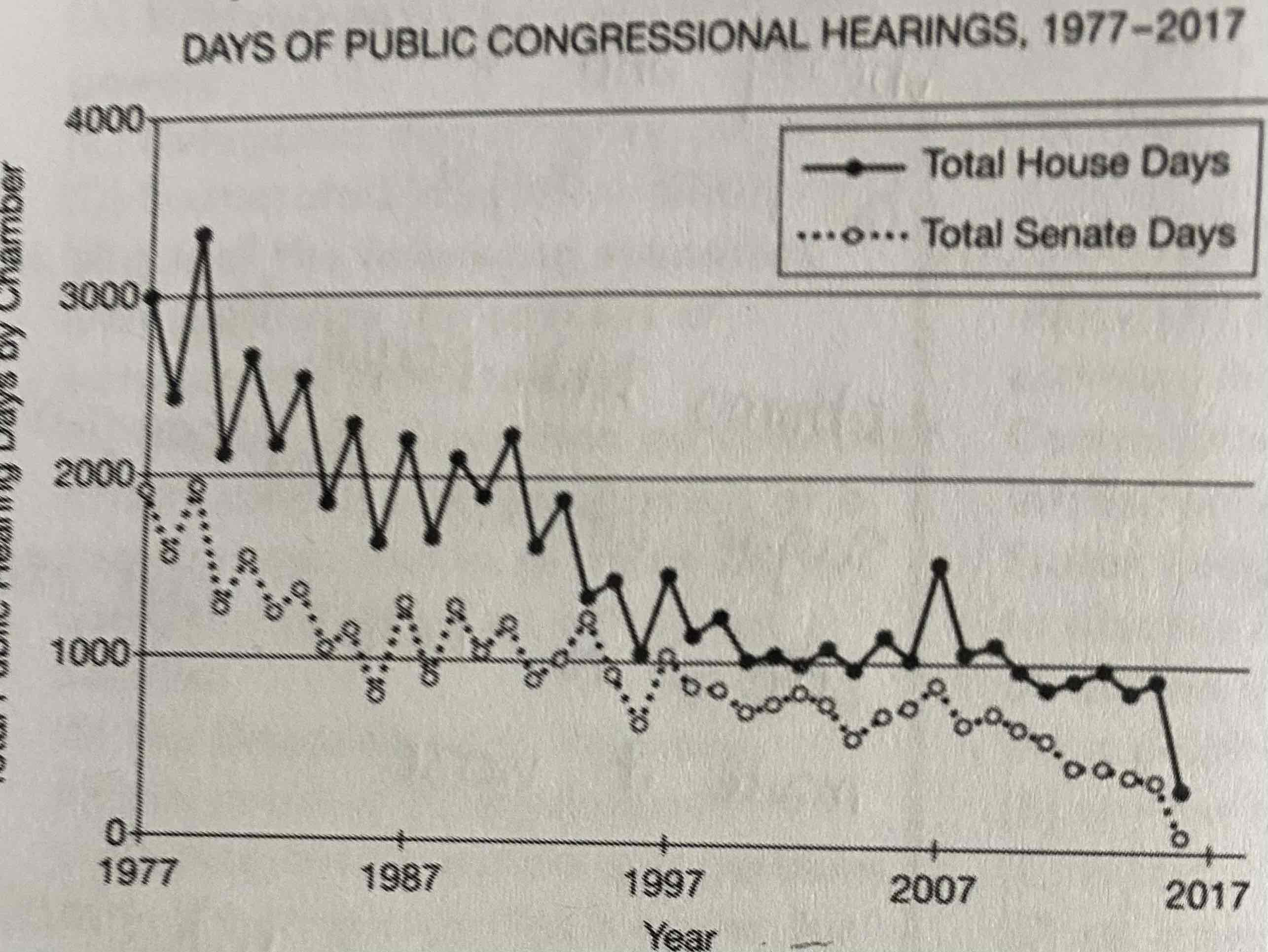
Which of the following is most likely an effect of the trend in the line graph?
a. An increase in accountability of the bureaucracy
b. A decrease in the length of regulatory bills passed by Congress
c. A decrease in congressional oversight as a mechanism to control the bureaucracy
d. An increase in the authority of the House of Representatives over the bureaucracy
c.
All of the following help to explain the President’s difficulty in controlling cabinet-level agencies EXCEPT
a. Agencies often have political support from interest groups
b. Agency staff often have information and technical expertise that the President and presidential advisers lack
c. The President can only fire appointees before they have been confirmed by the Senate
d. Civil servants who remain in their jobs through changes of administration develop loyalties to their agencies
e. Congress is a competitor for influence over the bureaucracy
e.
Which of the following form an “iron triangle?”
a. President, Congress, Supreme Court
b. President, House majority leader, Senate majority leader
c. Interest group, Senate majority leader, House majority leader
d. Executive department, House majority leader, President
e. Executive department, Congressional committee, interest group
e.
Lobbyists try to influence legislators mainly through
a. “wining and dining” legislators
b. orchestrating petition drives and letter-writing campaigns
c. placing persuasive advertisements in the media
d. threatening to help the legislator’s opponent in the next election
e. providing legislators with information on technical issues
d.
In the process and structure of public policy-making, “iron triangles” refer to the
a. bargaining and negotiating process between the President and Congress about the direction of domestic policy
b. dominance of corporate power in setting the national policy agenda for economic expansion
c. interrelationship among federal, state, and local levels of government in the policy process
d. networks of congressional committees, bureaucratic agencies, and interest groups that strongly influence the policy process
e. group of presidential advisers who formulate the President’s foreign policy agenda
b.
In the United States judicial system, when a judge decides a case based on decisions rendered in similar cases in the past, the judge is following the principle of
a. amicus curiae
b. stare decisis
c. justiciability
d. diversity
e. certiorari
b.
The doctrine of stare decisis is significant for which of the following reasons?
a. It establishes the jurisdiction of federal courts in litigation involving two or more states
b. It is the principle that affirms that courts are bound by prior decisions
c. it is the policy by which the Supreme Court decides which of the appellate cases it will hear
d. It directs states to provide a lawyer for people who cannot pay for their own legal defense
e. It holds high courts responsible for determining the constitutionality of proposed legislation before it becomes law
b.
The Supreme Court upholds a law passed by Congress as constitutional. The chief justice states in the majority opinion that previous decisions supporting Congress’ power to make laws based on the commerce clause of the Constitution were the basis of the decision. Which of the following legal concepts did the chief justice apply in writing the opinion?
a. Compliance monitoring
b. Stare decisis
c. Overlapping jurisdiction
d. Judicial activism
a.
Which of the following scenarios best illustrates the concept of a case being decided based on precedent?
a. The Supreme Court bases its decision in a case involving the commerce clause on one of its earlier decisions involving the commerce clause
b. The Supreme Court overturns a lower court decision in a case dealing with voter identification laws
c. A state passes a law which contradicts federal law, causing the Supreme Court to rule in favor of the federal government
d. The chief justice of the Supreme Court disagrees with the majority of the other justices and decides to declare a law passed by Congress as unconstitutional
d.
Which of the following actions can Congress take if the Supreme Court finds a federal law unconstitutional?
a. Appeal the Court’s decision to the district of Columbia’s Court of Appeals
b. Formally request the President to veto the Court’s decision
c. Remove certain members of the Court and replace them with new members
d. Try to amend the Constitution
e. Reenact the same law
d.
The Supreme Court issued a ruling that was unpopular with a majority of Americans. The president and Congress might be able to lessen the impact of the decision by
a. reducing the pay of the justices to pressure them to reverse their decision
b. overruling the Supreme Court’s decision by a two-thirds vote in Congress
c. impeaching the justices in the majority
d. refusing to actively enforce the decision
b.
In which ways of the following ways could the president try to limit the impact of a Supreme Court decision?
a. Calling for the removal of a Supreme Court justice
b. Instructing the Department of justice to not enforce a provision of the decision
c. Passing legislation that overrides the Court’s opinion
d. Changing the jurisdiction of the Supreme Court
e.
Which of the following is true of the seniority system of Congress in relation to committee leadership and committee staffing?
A. Members of Congress with the longest continuous service are assured the chairmanship of major congressional committees.
B. Members of Congress must be elected from safe seats to accrue seniority.
C. Members of congressional committees are the most senior members of the body’s majority party.
D. The oldest members of Congress have the most seniority.
E. The chairs of congressional committees tend to be senior members of the body’s majority party.
c.
The legislative process at the national level reflects the intent of the framers of the Constitution to create a legislature that would
A. be less powerful than the executive.
B. involve as many citizens as possible.
C. be cautious and deliberate.
D. ensure that all groups be equally represented.
E. allow majorities virtually unlimited control over policy.
d.
Debate of a bill in the House of Representatives under a “closed rule” means that
A. the bill can only be amended by section.
B. debate on the bill will consist of five-minute speeches, pro and con.
C. only senior members are allowed to participate.
D. amendments to the bill cannot be offered.
E. the bill must be approved by two-thirds of the House.
d.
Which of the following are differences between the legislative process in the House of Representatives and that in the Senate?
I. Debate is more restricted on the House floor than on the Senate floor.
II. The amendment process is more restricted in the House than in the Senate.
III. Bills are more likely to bypass committee consideration in the House than in the Senate.
IV. A Rules Committee sets the guidelines for floor debate in the House but not in the Senate.
A. I only
B. I and II only
C. II and IV only
D. I, II, and IV only
E. I, II, III, and IV
c.
The House Rules Committee is an important part of the legislative process because it
A. determines ethics rules for members’ conduct.
B. determines whether a bill should be referred to a policy committee for consideration.
C. determines the terms and conditions of debate when a bill goes to the House floor.
D. negotiates compromises on bills with the Senate Rules Committee.
E. develops a calendar to determine which bills will be debated by the House.
a.
When a bill passes in both the House and the Senate but contains different versions of the bill, which of the following provides greater leverage to a senator than to a member of the House to block passage of the bill?
A. The Senate allows for unlimited floor debate that can hold up a vote, while the House has strict limits on debate.
B. The Senate is more collegial than the House, so members can easily gain support from the opposing party.
C. The Senate allows for discharge petitions that force the bill out of committee, while the House does not.
D. The Senate is much less likely than the House to have party-line votes, so nonpartisan coalitions are more likely to form.
d.
A person claiming that the House can pass legislation with a simple majority, but the Senate is unlikely to pass legislation unless a bill has the support of a 60-vote supermajority is most likely to cite which of the following institutional differences as the cause of this trend?
A. The House has fewer legislative committees than the Senate does.
B. Members of the House often represent a much narrower constituency than senators do.
C. Party leadership in the House is highly formalized, while leadership in the Senate is much more informal.
D. The House has strict limits on debate, while the Senate allows unlimited debate.
d.
The government depicted to the left is best described by which of the following terms?
A. Nonpartisan government
B. Unicameral government
C. Unitary government
D. Divided government
E. Dealigned government

d.
In vetoing a bill, the President does which of the following?
A. Rejects only a part of the bill without rejecting it entirely.
B. Prevents any further action on the bill.
C. Sends the bill back to conference committee.
D. Rejects all sections of the bill.
E. Decides the bill’s constitutionality.
c.
Which of the following is true about the pocket veto?
A. It is used to strike down a provision of a bill that the President finds disagreeable.
B. It may be overridden by a two-thirds vote in Congress.
C. It occurs when the President takes no action on a bill for ten days during which Congress is adjourned.
D. It is used when the President expects to reach a compromise with Congress about how a bill should be modified.
E. It is used when both houses of Congress pass separate versions of the same bill.
e.
The role of a conference committee in Congress is to
A. hold hearings on proposed legislation.
B. oversee the actions of the executive branch of the government
C. decide which bills should be considered by the full Senate
D. conduct hearings that make information available to the public
E. reconcile differences in bills passed by the House and Senate.
a.
Which of the following is true of a presidential veto of a piece of legislation?
A. It is rarely overridden by Congress.
B. It is not binding unless supported by the cabinet.
C. It can only be sustained on revenue bills.
D. It is automatically reviewed by the United States Supreme Court.
E. It is subject to approval by a congressional committee.
c.
The practice in Congress whereby Representative A promises to vote for Representative B’s legislation, provided that Representative B will support Representative A’s legislation, is referred to as
A. personal casework and services
B. partisan discipline
C. logrolling
D. pork-barrel legislation
E. filibustering
A
Federal budget entitlements refer to spending
A) to provide individual benefits established by legislation
B) by legislators on trips to home states to confer with constituents
C) by congressional staff while traveling on official business
D) on behalf of life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness
E) targeted to benefit residents of specific congressional districts
A
The activities of the Federal reserve Board have the most direct influence on
A) bank interest rates
B) government spending
C) oil prices
D) troop-strength levels of the armed services
E) price of scarce minerals
C
Policy that describes the impact of the federal budget (including taxes, spending, and borrowing) on the economy is referred to as which of the following?
A) Monetary policy
B) Trade policy
C) Fiscal policy
D) Antitrust policy
E) Capitalist policy
B
Which of the following is likely public policy result of the [Top Priority] data on the line graph?
A) Public policies that create jobs but increase the deficit, such as tax cuts or infrastructure spending, will likely be prioritized decreasing the national debt
B) Bills that create an economic stimulus through public works projects will pass with bipartisan support
C) A program to extend unemployment benefits to more people will likely pass in 2018
D) Public policies that pay down the deficit but are harmful to economic growth will likely pass during the next Congress
![<p><strong>Which of the following is likely public policy result of the [Top Priority] data on the line graph?</strong></p><p>A) Public policies that create jobs but increase the deficit, such as tax cuts or infrastructure spending, will likely be prioritized decreasing the national debt</p><p>B) Bills that create an economic stimulus through public works projects will pass with bipartisan support</p><p>C) A program to extend unemployment benefits to more people will likely pass in 2018</p><p>D) Public policies that pay down the deficit but are harmful to economic growth will likely pass during the next Congress</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ecb248df-cc83-4f85-828d-181241c1c945.jpg)
B
Which of the following best explains the [Top Priority] data in the line graph?
A) Between 2012 and 2018, the economy did not grow enough to make economic issues a top priority
B) Voters care more about job than the budget deficit because the there has been an increase in unemployment between 2010 and 2018
C) The economy is likely the most important issue because it is a broader category that is more open to individual interpretation than both jobs and the budget deficit.
D) Budget deficits receive little focus in the media even though citizens care deeply about them
![<p><strong>Which of the following best explains the [Top Priority] data in the line graph?</strong></p><p>A) Between 2012 and 2018, the economy did not grow enough to make economic issues a top priority</p><p>B) Voters care more about job than the budget deficit because the there has been an increase in unemployment between 2010 and 2018</p><p>C) The economy is likely the most important issue because it is a broader category that is more open to individual interpretation than both jobs and the budget deficit.</p><p>D) Budget deficits receive little focus in the media even though citizens care deeply about them</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ffeb613a-013c-4e09-ab10-8d1abea68b56.jpg)