Sketchy Microbiology: Clostridium Tetani
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
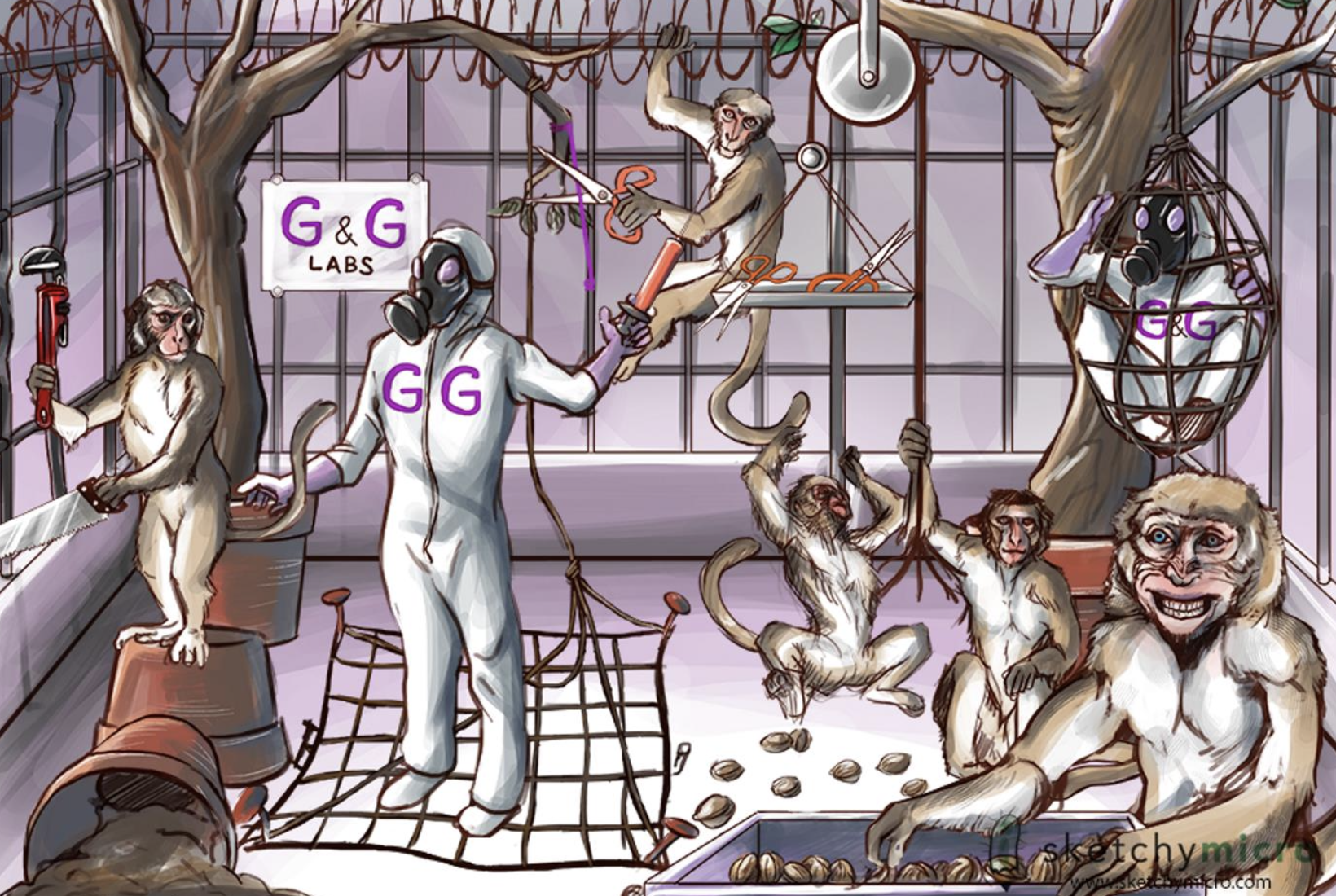

Rhesus Research Revolution — Clostridium Tetani

Purple Hues – Clostridium Genus is Gram Positive Rods

Gas mask — Clostridium Genus are Obligate anaerobes

Walnuts — Clostridium Genus are spore forming
Spores allow it to survive in harsh environments
What are the components of spores?
Chromosome
Protein synthesizing enzymes / glycolysis enzymes
What are the protective layers of a spore?
Spore membrane
Cortex
Coat
Exposporium
What are the steps of sporulation?
Asymmetric cell devision
Ingestion of a daughter cell
Coat synthesis
Exosporium synthesis
Stem cell lysis
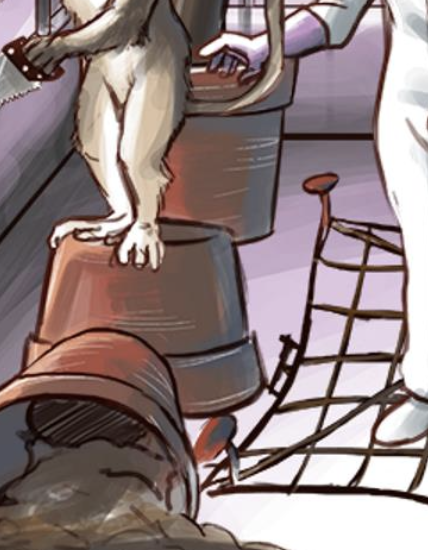

Rusty nails, barbed wire, pots of soil – Clostridium is found in the dirt and enters the body through a puncture wound
What are other charachteristics about C. Tetani?
Heat Sensitive
Motility via flagella
Spores are “Drumstick Shaped”

Smiling Rhesus monkey — Spastic paralysis leading to rigidity, rhesus (to grin) sardonicus (evil), also accompanies lock jaw

Monkey w/ arched back position — Opisthosomas
What is the pathogenesis?
1. Puncture wound occurs with tetany spores on it → spores are embedded in the flesh → the organism vegetates and stays at the wound site. It will release tetanus toxin that will cause all the symptoms
2. Tetanus toxin will travel retrograde through the motor axons to the spinal cord.
3. Tetanus toxin will cleave snare and inhibit exocytosis of the neurotransmitter into the synapse (GABA and glycine) or Renshaw cells.
4. If GABA and glycine are inhibited → uncontrolled firing of the motor neurons → spastic paralysis
5. Renshaw cells sense over activity of nearby motor neurons → they will attempt to fire and inhibit the motor neuron. So the GABA and Glycine release from these cells is inhibited → spasm

Monkey w/ a pulley with scissors on it — Tetanus toxin will travel retrograde through the motor axons to the spinal cord
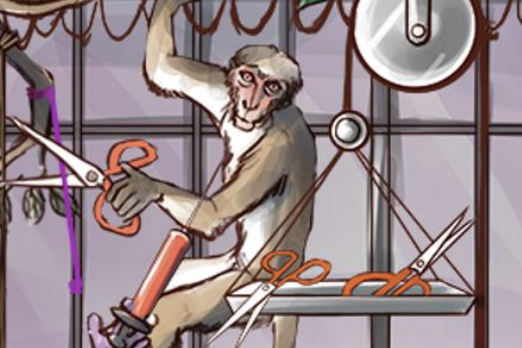
Monkey cutting the snare trap — Tetanus toxin will cleave snare and inhibit exocytosis of the neurotransmitter into the synapse (GABA and glycine) or Renshaw cells

G&G labs — 2 types of inhibitory neurons, GABA and glycine
If these are inhibited → uncontrolled firing of the motor neurons leading to spastic paralysis

Monkey with wrench and saw — Renshaw cells will sense the over activity of nearby motor neurons and when they sense this activity they will attempt to fire and inhibit the motor neuron. So the GABA and Glycine release from these cells is inhibited leading to spasm

Researcher with Vaccine in hand — Toxoid Vaccine, toxin conjugated to protein.
Antibody response to the toxin
What are other treatment options?
Stopping the toxin production
Large dose of Metronidazole, or Penicillin G
Neutralizing the toxin