Semester AP Biology Final Exam
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
chi square analysis
use equation
add results together
compare results to critical numbers (look at degree and do one less)
confirm or deny null hypothesis (confirm is under, deny is over)
positive loop
supplements for something that the body needs
ex: stops a cut from bleeding
negative loop
bringing the body back to normal
ex: childbirth, body temperature
polar covalent bonds
stronger than hydrogen bonds
H+ and O- are being bonded together within the molecule
hydrogen bonds
not as strong as covalent bonds
bonds two molecules together
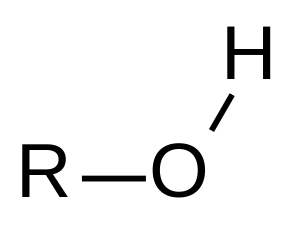
hydroxyl group
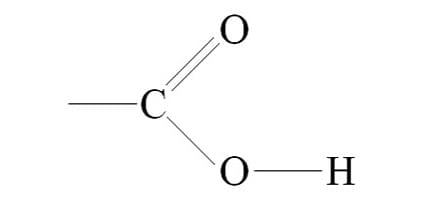
carboxyl group
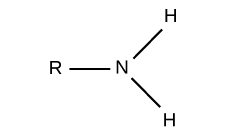
amino group
anabolic reaction
smaller molecule to bigger (poly + poly » monomer)
ex: dehydration synthase
two molecules join and H2O is lost
catabolic reaction
bigger molecule to small (monomer + H2O » poly + poly)
ex: hydrolysis
one molecule breaks down into two molecules using H2O
monomer
building block of a polymer
ex. of carbohydrates
starchs, glycogen, cellulose, chitin
what is a monosaccharide and polysaccharide
monosaccharide: simplest carb
disaccharide: polymer
polysacchardie: polymers joined together to create a carb, monomer
what is the carbohydrates role in photosynthesis?
the formation of the carbohydrates is a chemical way that the plant’s store food
provide energy for the plants
help the plant with storage
what are lipids?
made of C, H, O
do not dissolve good in water
ex: phospholipids: make up the majority of the cell membrane
what are the monomers and polymers of lipids?
monomer: glycerol and fatty acids
polymer: phospholipids and triglycerides
what is the function of a lipid?
to help with moving and storing energy
what is the structure of a lipid?
long chains for strong energy, the fats store this energy usually
phospolipids: hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail
causes them to form membranes
saturated fats: no C-C double bonds
found in meat and unhealthy
unsaturated fats: one or more C-C double bonds
found in plants and healthier
what are the monomer and polymer of proteins?
monomer: amino acids
polymer: peptide chains, proteins
what is the function of proteins?
enzymes, structure, immunity, transport, storage, hormones
what is a polypeptide chain?
formed through dehydration synthesis
it is what folds into a protein
what are the levels of protein structure?
primary: sequence of the polypeptide chain
dictates the way the protein will fold
secondary: helix or pleated sheets (flat)
prepares the chain for further folding
tertiary: bonding between R- groups
provides proteins with their specific shape
quaternary: two or more polypeptides that form a protein
arrangement of multiple proteins
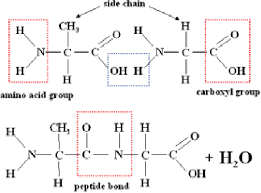
what is a peptide bond?
a bond that connects to amino acids
recognize the peptide bond
how do the properties of amino acids change the final protein structure?
the chemical properties of each amino acid is what gives the protein its structure at the secondary level
sickle cell: different amino acid bond that causes the protein to fold differently (structure), so the function of the protein is different
what is denaturing?
causes a protein to lose structure
ex: pH change, temperature, environment
all of these things can causes a hydrogen bond to change
causes the protein to fold different at different levels
different folding = different structure and function
how do you increase faster yield of products?
add more enzymes
what are the main components of the cell membrane?
phospolipids, proteins, carbohydrates
what are phospholipids in regards to the cell membrane?
core of the cell membrane
hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail
barrier that prevents things from freely moving in and out
stuff can still get through by different transport mechanisms
what are proteins in regards to the cell membrane?
integral and peripheral proteins
transport proteins: act as channels or carriers to allow ions and nutrients to pass through without going through the bilayer
what are carbohydrates in regards to the cell membrane?
usually attached to the proteins
do not help with transport, but they help the cell selectively interacts with the environment
what are the components of the cell membranes role?
allow cell to maintain stable internal environment by selectively permitting or blocking certain things from entering the cell
essential for the cells health and communication
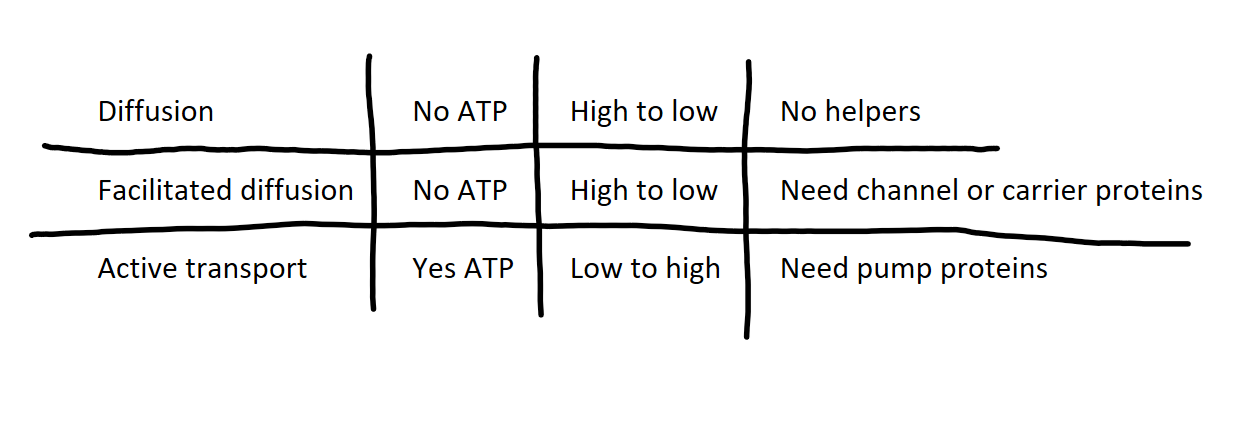
what is diffusion?
passive transport
high concentration to low concentration
does not require ATP
small, nonpolar molecules go directly through the phospholipid bilayer
does not need a helper
facilitated diffusion
passive transport
high concentration to low concentration with help from a protein
channel protein: form pores in the membrane allowing ions to go through
carrier protein: bind to specific molecule, change shape, transport across membrane
what is osmosis?
facilitated diffusion of water using aquaporins
H2O goes from high to low and needs a helper
does not require energy
what is active transport?
against gradient, low concentration to high concentration
requires energy
relies on protein pumps
ex: Na+ K+ pump
what is a Na+ K+ pump?
moves Na+ ions out of the cell and K+ into the cell
adds a phosphate and uses ATP
comparison chat between diffusion, facilitate diffusion, active transport
what is the concentration gradient?
affects movement across the membrane depending on if the ion/molecule is moving with or against the gradient
some might need energy
the goal is to reach equilibrium
what is endocytosis?
cell engulfs substances from the outside and encloses them inside the membrane in the vesicle
organelles: plasma membrane, vesicles
active transport
what is exocytosis?
cell expels substances from inside the cell to the external environment by putting it into a vesicle that becomes the membrane
organelles: plasma membrane, vesicles, golgi
active transport
what is endosymbiotic theory?
says that eukaryotic cells originated through a process in which ancestral counterparts were engulfed by cells forming a symbiotic relationship
what was engulfed turned into organelles like the mitochondria and chloroplast
shows evolution because both of the organelles are said to be from bacteria but how they help the cell
what is the 1st law of thermodynamics?
energy can not be created or destroyed
what is the 2nd law of thermodynamics?
each energy transfer/ transformation increases the randomness of the universe
how does the 1st law of thermodynamics relate to chemical equations and energy in ecosystems?
chemical: reactants have stored energy and during a reaction the energy is transformed
ecosystem: energy is converted
how does the 2nd law of thermodynamics relate to chemical equations and energy in ecosystems?
chemical: reactions increase randomness
ecosystem: loss of energy each transformation
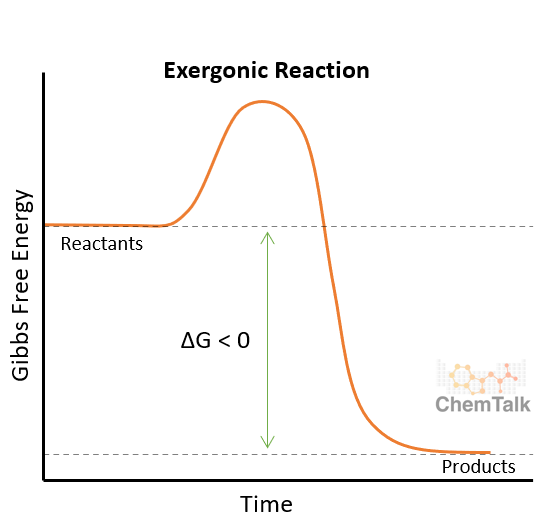
what is an exergonic reaction?
releasing energy to the surrounds
reaction is spontaneous
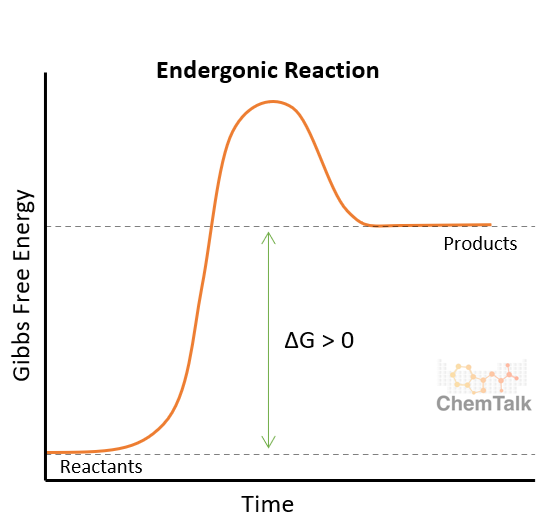
what is an endergonic reaction?
absorbing energy
reaction is not spontaneous (needs energy)
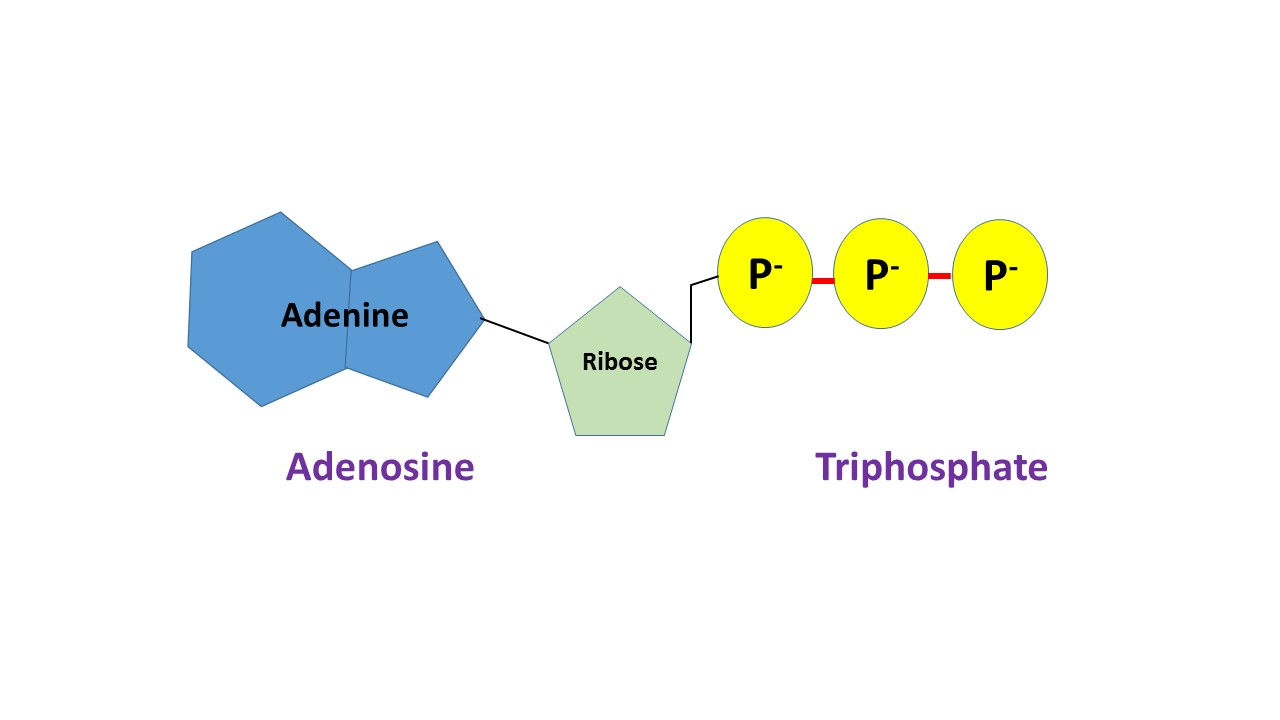
what does ATP look like?
what is phosphorylation?
transfers one phosphate group to another molecule
ATP uses enzyme to attach phosphate elsewhere
ATP is now ADP
the added phosphate gives the other molecule more reactive (more energy)
what are enzymes?
speed up chemical reactions
the substrate enters the active site and the enzyme changes shape accordingly
this is the reaction
after the reaction, the product is released
enzyme are specific (lock and key)
what is induced fit?
models how enzymes and substrates work
the enzyme adapts its shape to hold the substrate tightly - reaction will be faster
what environmental conditions on enzyme function?
temperature
low = slow; high = enzyme denatures
pH
to low or high = bad enzyme bonds
what are competitive inhibitor?
mimic the substrate and bind to the active site which prevents the enzyme from doing the reaction
no reaction
non-competitive inhibitor
binds to a different spot on the enzyme causing the enzyme to change the shape
no reaction
allosteric reaction
occurs when a regulatory molecule binds to a protein at one site and affects the protein’s function at another active site
can stimulate or inhibit the enzyme
copperativity
forms of allosteric regulation that can amplify enzyme activity
feedback loops with enzymes (graph)
once enough enzyme has been created the end product is supposed to go back up and stop it from making more products
will be an allosteric or competitive inhibitor
end-product can go on the back of the enzyme and change its shape
oxidation
loss of electrons
often gains oxygen or loses hydrogen
releases energy
reduction
gain of electrons
often loses oxygen or gains hydrogen
requires or stores energy
how are oxidation and reduction similar?
involve electrons moving and are involved in energy transfer during chemical reactions
they depend on each other
what are the steps of cellular respiration?
glycolysis, kreb cycle, electron transport chain
what are the steps in photosynthesis?
light dependent reaction, calvin cycle
what is an autotroph?
produce their own food
use sunlight for energy
performs photosynthesis and cellular respiration
plants
what is a heterotroph?
rely on consuming other organisms for food
use organic molecules for energy
only perform cellular respiration
animals
how are heterotroph and autotroph similar?
both are living
both need gluclose
both grow and reproduce