4. The social determinants of health
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
according to the government of Canada, what are the most important determinants of health?
social supports and coping skills
income and social status
employment/working conditions
education
physical envrionments
access to health services
gender
culture
race / racism/ discrimination
what are health disparities?
inequalities in health (morbidity and mortality) or health care between groups
describe how health disparities exist in Canada
Health inequalities in Canada exist, are persistent, and in some cases, are growing. Many of these inequalities are the result of individuals and groups’ relative social, political, and economic disadvantages
describe why diabetes morbidity rates are different in first nations compared to Canadians
envrionmental and lifestyle factors are largely to blame
less healthy diet, lower consumption of tradition food, less physical activity due to historical changes to way of life
poverty: lower income and education contribute to increased stress and poorer health
how might diet and stress lead to diabetes?
diet → fewer healthy dietary options; reliance on processed food which are cheaper
stress → elevated cortisol levels
both cause high blood glucose → over time cause insulin resistance
describe how colonization has affected the health of indigenous people
colonization introduced new disease, loss of land, criminalization / loss of culture, genocide, and forced assimilation → higher psychological distress and higher prevalence of PTSD
what is intergenerational trauma?
trauma that is passed down to subsequent generations
what direct & indirect mechanisms may be involved in intergenerational trauma
Vicarious trauma (hearing about trauma from others that we love, increased the risk of the individual who isn’t actually affect to get PTSD)
Lack of culture & cultural identity
Marginalization & discrimination
Compromised parental functioning
Modelling of poor coping
genetic/biological vulnerabilities
what is epigenetics?
the study of changes in organisms caused by changes in gene expression due to environmental influences
what is intergenerational epigenetic effects?
epigenetic changes can be heritable via various processes; can affect multiple generations
describe the intergenerational effects of residential schools
Maternal and paternal attendance at residential schools was associated with increased childhood adversity in their adult children.
Maternal residential school attendance was also linked to increased allostatic load (a measure of cumulative physiological stress) in adult children.
how does cultural identity influence health?
historical and ongoing attacks on indigenous culture have compromised cultural identity clarity
what is resilience?
the ability to recover from a traumatic event
what is the socioeconomic gradient in health?
the pattern where health outcomes improve with each step up the socioeconomic ladder — not just between the poorest and the richest, but across all levels of income, education, and occupation.
what is the most decisive social factor that affects health?
SES
what factors mediate the SES-health relationship?
access to resources, living / working conditions
amount of chronic stress
perceived control
diet, physical activity, substance use, sleep
what is displacement aggression?
a psychological defense mechanism in which someone redirects their anger or frustration from the original source onto a safer or more convenient target — usually someone or something less threatening.
describe the status-health relationship
low status is associated with…
increased morbidity & mortality
lower QOL
but stress appears to be one key mechanism
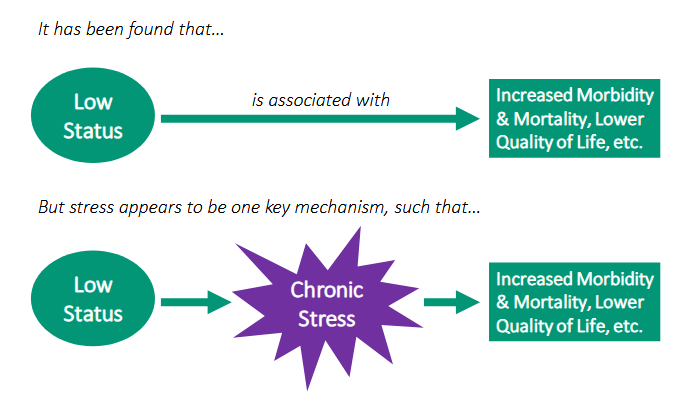
describe how low-SES individual experience stress
report more frequent stressful life events and more chronic stressors
have a tendency to interpret stressors as more threatening
cope less effectively with stress
describe the relationship between low SES and allostatic load
burden of coping with limited resources and negative life events results in increased allostatic load in those with low SES
describe the biological embedding model
childhood adversity gets programmed into the immune system through multiple mechanisms, including epigenetics
describe the shift-and-persist strategy
an approach to life for low-SES individuals to overcome those adversities that prioritizes
shifting oneself → accepting stress for what it is and adapting through reappraisals
persisting → enduring life with strength by maintaining meaning and optimism
how might inequality affect everyone, regardless of status?
status anxiety: some people look down on me because of my job situation or income
describe how status anxiety affects people of low and high income in societies of high or low inequality
Low income, regardless of inequality, have high status anxiety. But those in countries with higher inequality will still have higher status anxiety than those in lower inequality
High income, regardless of inequality, has low status anxiety, but is still affected. But those in countries with higher inequality will have higher status anxiety than those with lower inequality
describe how exactly is social inequality having a negative impact?
heightened levels of competition in a society
social evaluation anxiety — increased stress due to greater threats to self-esteem, social status, and fear of judgment
what is stigma
negative and discriminatory attitudes about a person or people based on some quality or characteristic
what is marginalization?
treatment of person or group as less important
describe the minority stress model
stigma, prejudice, and discrimination create a hostile social environment → increased stress for minorities and increased incidence of disease and illness
describe how and which population is minority stress primarily investigated in
african americans: higher rates of stroke, diabetes, perinatal disease, certain cancers, depression & substance use
2SLGBTQIA+ people: higher rates of immune dysfunction, some cancers, substance abuse, depression, anxiety, suicidal ideation
what are some of the sources of minority stress?
direct experiences of discrimination, prejudice, harassment
social stigma; internalized bias and stigma
rejection and expectations of rejection
hiding or concealing identity
describe the relationship between racism and health
racism places a substantial strain on the mental and physical health of targeted individuals
what is the mechanisms behind racism and health
institutional racism limits resources and opportunities
personal experiences of racism increases stress over time
describe resilience in black individuals after experiencing racism
racial socialization and racial identity are correlated with heightened resilience
subjective social status and perceived social support are correlated with greater resilience
racial identity clarity also matters
describe how trans stigma influence trans individuals’ health
trans people are at higher risk of suicidal ideation due to stigma and hate
in trans people, what is psychological well-being associated with?
personal control
support-seeking and social support
positive reappraisal
considering the populations discussed (indigenous, low-SES, racialized, and transgender/gender-diverse people)...
Are there any common themes that emerge (pertaining to factors in resilience)?
Control over one’s identity and autonomy
Social acceptance and support
Equality matters, more equality is better
Positive reappraisal
Identity clarity
summarize the status-health relationship
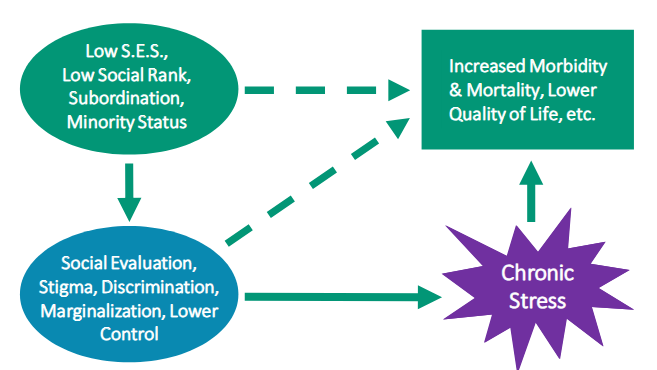
how might disease threat affect inequality, discrimination, and other sources of division
inequality is exacerbated by socioeconomic disparities in disease threat
pandemics can either worsen inequality or reduce it