L19 Trematodes Rumen Flukes Lung Flukes | Parasitology Exam 2
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
What are the hosts of Schistosoma spp.
cattle
sheep
human
What are the hosts of Heterobilharzia spp.
dog
raccoon
What are atypical about Schistosoma compared to other trematodes
dioecious
What host does Schistosoma bovis and S. nasalis infect
cattle
What hosts does Schistosoma japonicum infect (and more pathogenic to which spp)
cattle
sheep (cause more severe dz)
human
How do adult females attac in Schistosoma spp. reproduction
adult females attach in ventral grove of males
What are the egg characteristics of Schistosoma spp.
boomerang shape with terminal spine
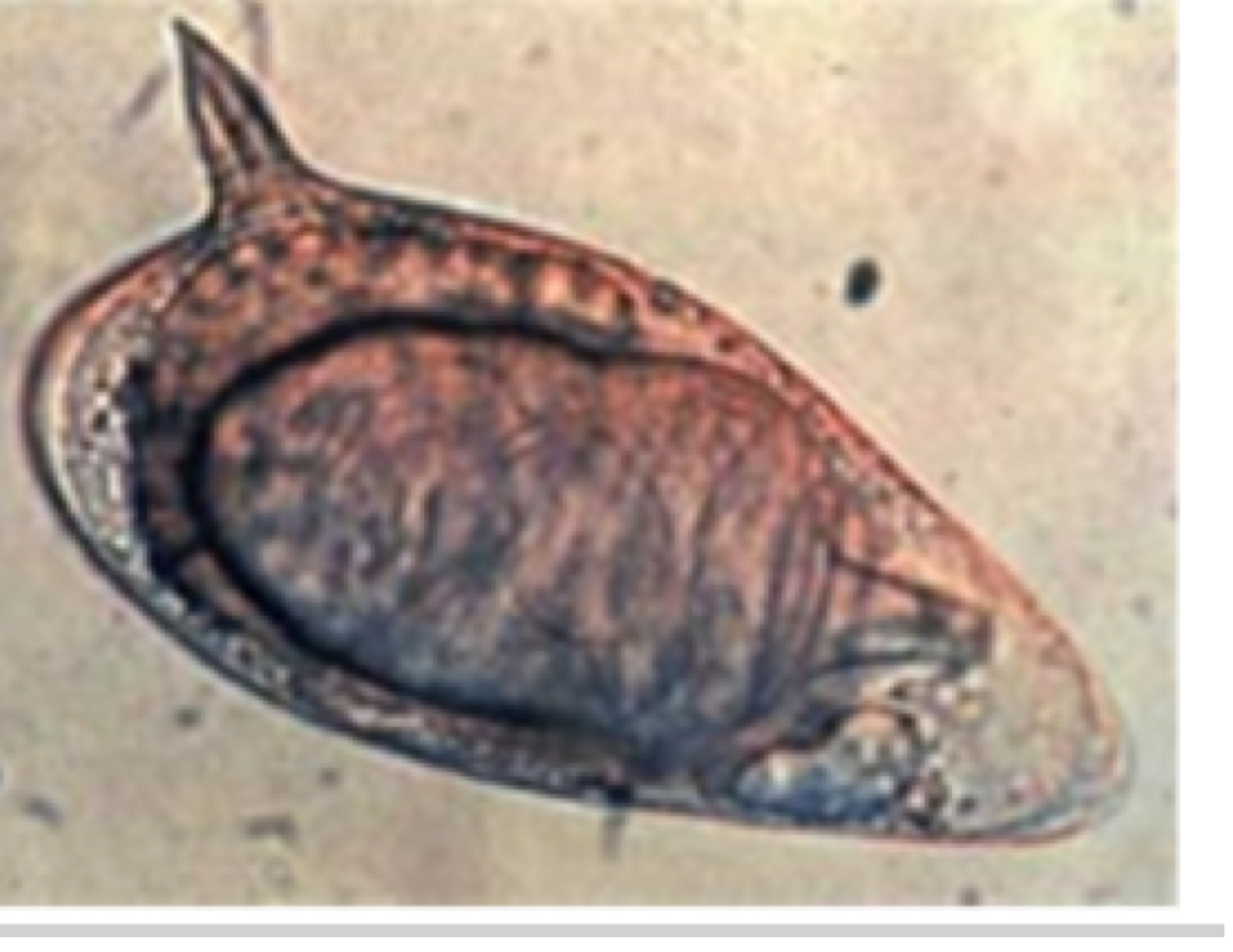
What are the predilection sites of Schistosoma spp.
portal, mesenteric, urogenital veins
What is the lifecycle of infection caused by Schistosoma bovis with juvenile flukes
Juvenile flukes travel to the heart entering the lungs
They localize in liver
then enter portal circulation from liver
What are the CS of Schistosoma bovis
irritation to gut and bladder mucosa caused by eggs
Where does Schistosoma nasalis migrate to cause CS
nasal veins
Where does Schistosoma japonicum migrate to cause CS
lungs, causing pneumonia, followed by the portal vein
What are the CS of Schisotosoma nasalis
mucopurulent nasal discharge
snoring
dyspnoea
What are the CS of Schisotosoma japonicum
dermatitis (caused by skin penetration by cercariae)
pneumonia (migration to the lungs)
In humans, what prominent CS occurs with Schistosoma mansoi (a trematode of humans)
swimmers itch (caused by irritation due to
What is the dx of Schistosoma spp.
dx by finding eggs thru sedimentation of feces
serology - Elisa kits
What is the tx of Schistosoma spp.
Praziquantel or Oxaminquine (20mg/kg)
What are atypical about Heterobilharzia Americanum compared to other trematodes
have separate sexes
Where are Heterobilharzia Americanum found and predilection site
found in coastal regions of Gulf Coast, most common in SE USA
live in mesenteric and hepatic veins
What are the DH of Heterobilharzia Americanum
dogs
raccoons
What is the lifecycle of Heterobilharzia Americanum trematode
eggs release in water hatch
snail is IH
Cercariae release from snails penetrate skin of DH
migrate to lung, liver
adults migrate to mesenteric and hepatic veins
eggs release from veins migrating through intestinal wall
passed in feces
In Heterobilharzia Americanum, when eggs are released from veins what CS does it cause
induce granulomatous inflammation of vessels
What are the CS of Heterobilharzia Americanum
diarrhea
vomiting
weight loss
lethargy
What are the egg characteristics of Heterobilharzia Americanum
thin-shelled round containing fully developed miracidium
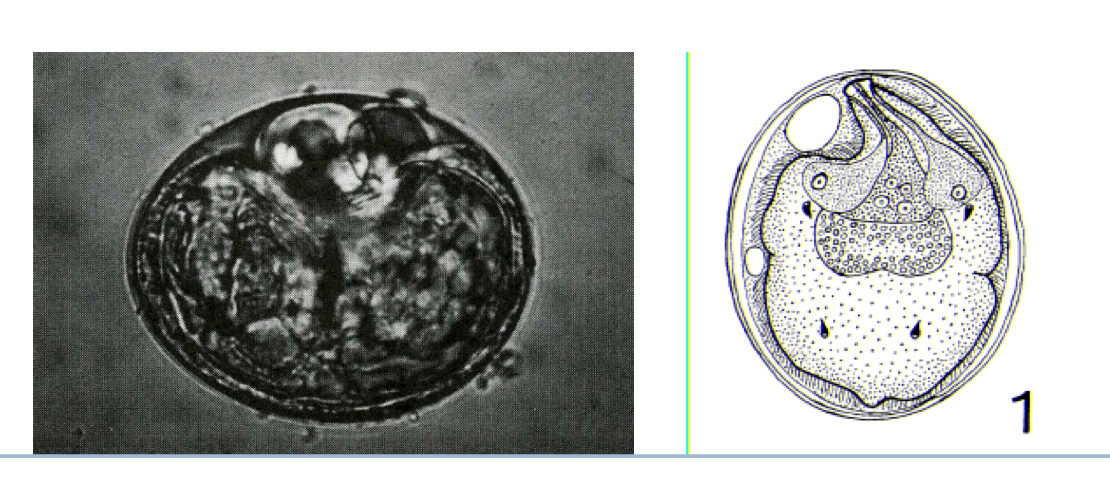
What is the dx of Heterobilharzia Americanum and the requirements for such dx
egg detection by sedimentation using normal saline (eggs will hatch when it comes in contact w water)
What are considered rumen flukes of ruminants
Paramphistomum spp.
In terms of lifecycle of Paramphistomum spp., how does the migration occur out of GIT
no migration out of GIT
What is the appearance of Paramphistomum spp.
small, conical fluke (attached to rumen mucosa)
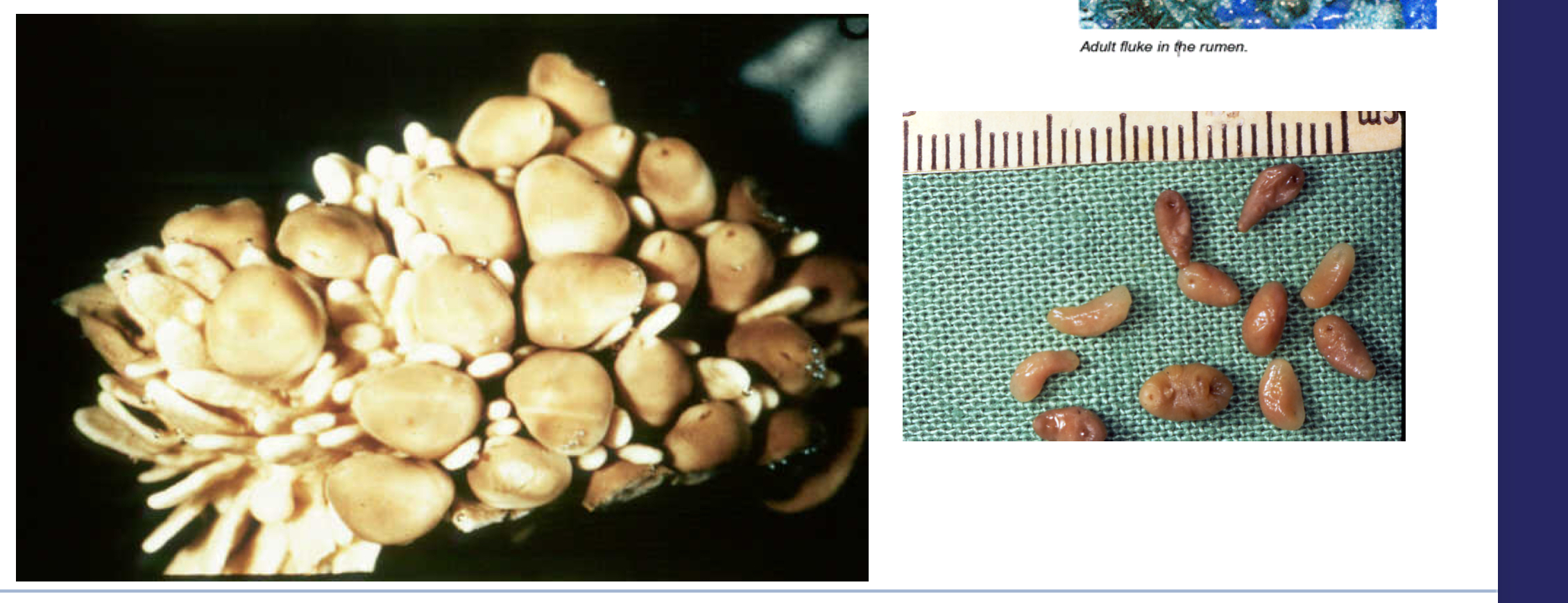
What is the pathogenicity of adult Paramphistomum spp.
nonpathogenic even in high quantities
What is larval Paramphistomiasis pathogenesis in relations to Paramphistomum spp.
juvenile stages in intestine causing infection
severe enteritis - diarrhea and anorexia
Where does larval Paramphistomiasis pathogenesis in relations to Paramphistomum spp. occur
tropics in young stock
What is the major problem of Paramphistomum spp. dx (and what is dx of paramphistomum spp.)
distinguish the egg from F. hepatica
(pointier at operculum end)
What are the hosts of Paragonimus Kellicotti (and tis secondary name)
lung fluke of carnivores
hunting dogs
outdoor cats
wild mammals
What regions are Paragonimus kellicoti found
Canada
US - midwest and Eastern USA
What are the two IH of Paragonimus Kellicotti
1st IH: snail
2nd IH: crayfish
What is the pathogenesis of Paragonimus Kellicotti from ingestion of crayfish
metacercariae penetrate intestine
move thru diaphragm into lungs
forms cysts in lung parenchyma
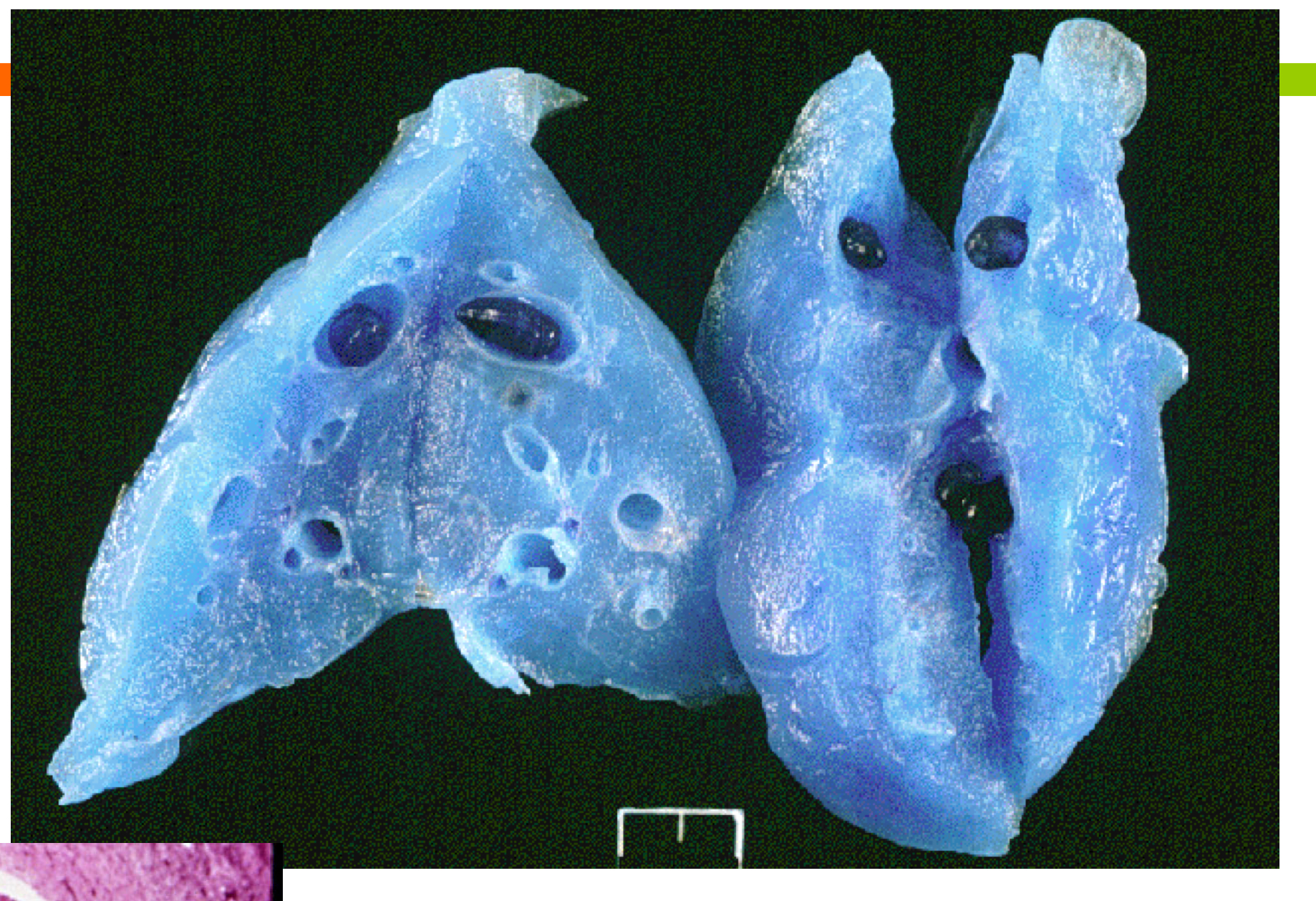
What are the CS of Paragonimus Kellicotti
chronic deep coughing (from cysts in lungs)
weakness
lethargy
hemoptysis
What is the dx of Paragonimus Kellicotti
eggs in feces thru sedimentation
What is the tx of Paragonimus Kellicotti
praziquantel (25mg/kg) for 3 days = TOC
fenbendazole (50mg/kg) for two weeks
albendazole (25mg/kg) for three weeks
What are the hosts and and predilection site of Nanophyetus salmincola
dogs
cats
humans
adult flukes in SI
What are the two IH of Nanophyetus salmincola
1st IH - snail
2nd IH - fish, metacercaria in muscle
What disease is associated with Nanophyetus salmincola infection in canines
Neorickettesia helminthoeca
What are the CS of Nanophyetus salmincola in dogs
fever, vomiting, diarrhea
enlarged lymph nodes
mortality rates of 80-90%
What is the dx of Nanophyetus salmincola
history and CS
fluke eggs in feces
postmortem histology
What are the tx of Nanophyetus salmincola
must treat fluke and rickettsia
oxytretracycle for rickettsia
praziquantel for Nanophyetus
What is the prevention of Nanophyetus salmincola
do not allow dogs to eat raw fish