the structure and function of the sarcolemma and sarcoplasmic reticulum in skeletal muscle cells, video 2
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
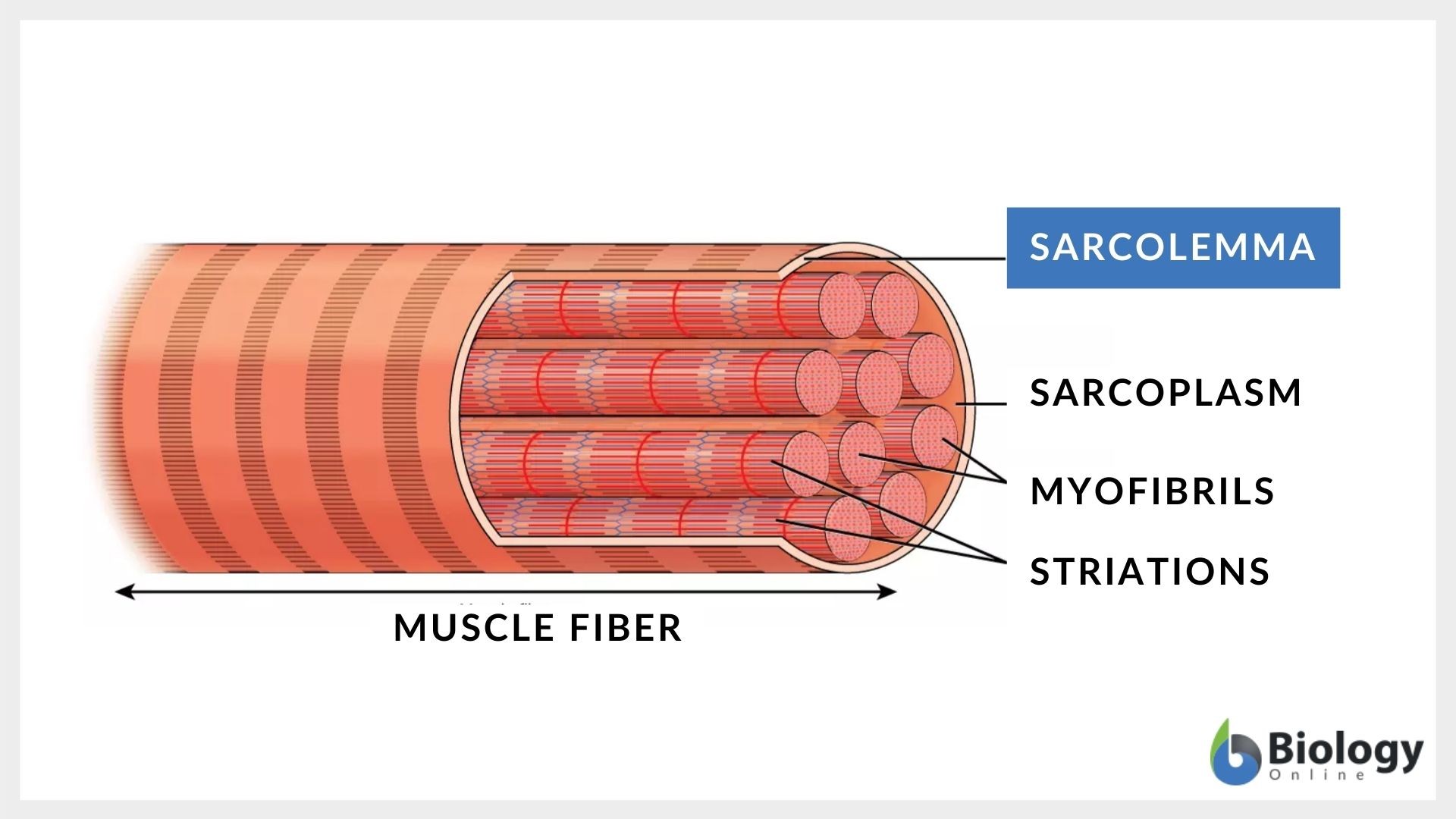
What is the sarcolemma
the specialized cell membrane of skeletal muscle cells
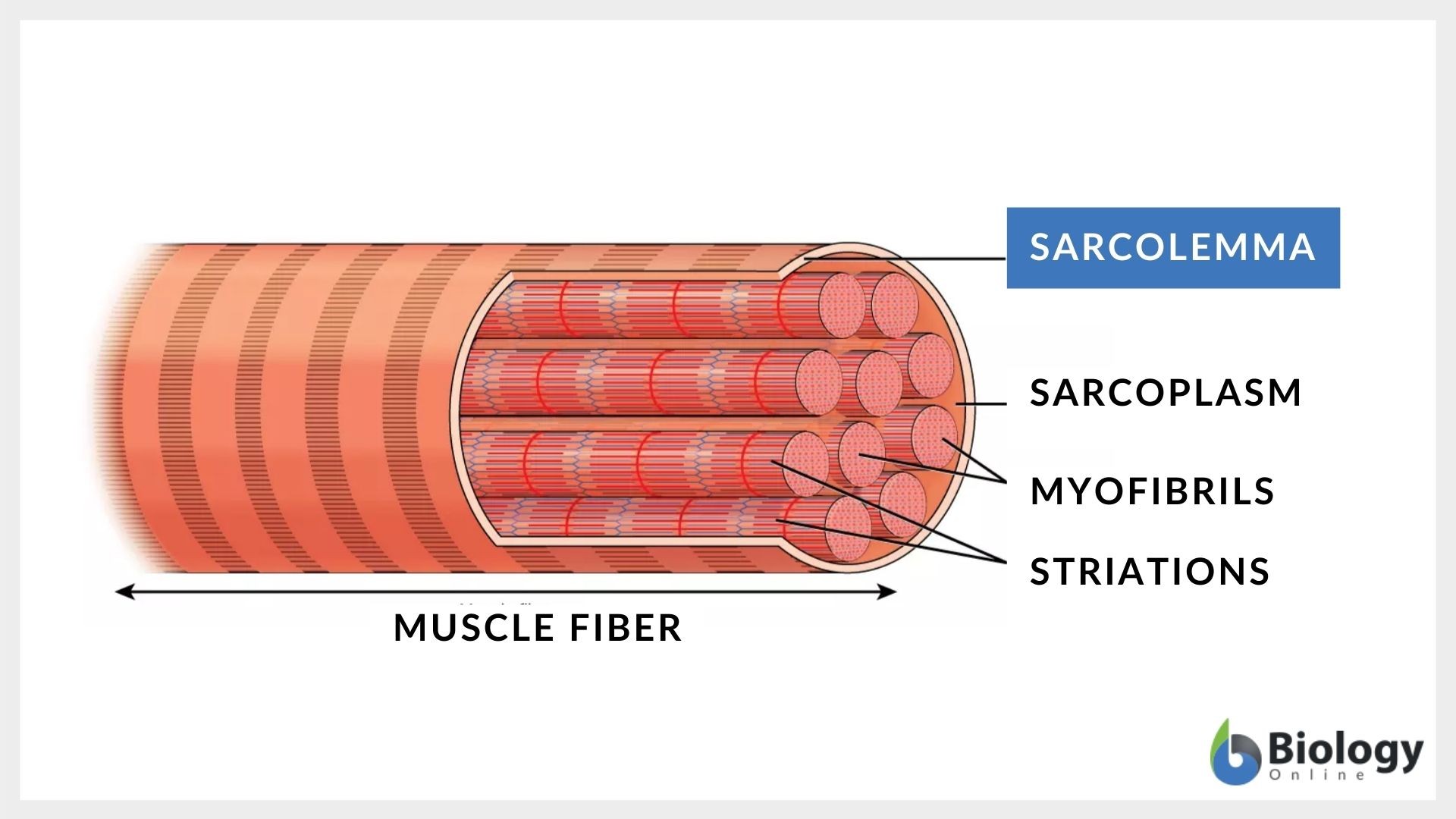
how is sarcolemma different from a regular cell membrane
Unlike regular membranes, it has modifications like T-tubules that help transmit signals for muscle contraction.
What are the unique features of the sarcolemma that assist in muscle contraction?
It contains T-tubules, is involved in generating action potentials, and has voltage-gated channels for ion flow.
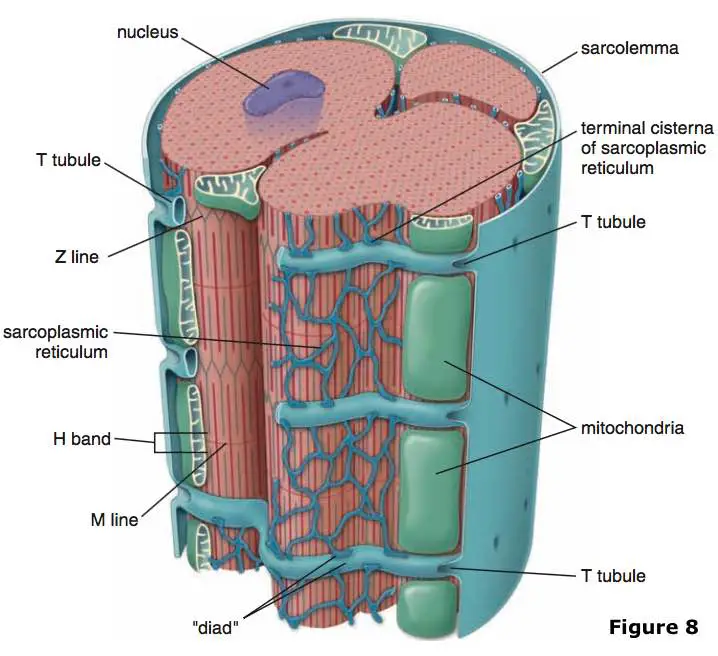
How do T-tubules contribute to muscle contraction?
They extend deep into the muscle fiber, allowing electrical signals (action potentials) to quickly reach all parts of the muscle, ensuring uniform contraction
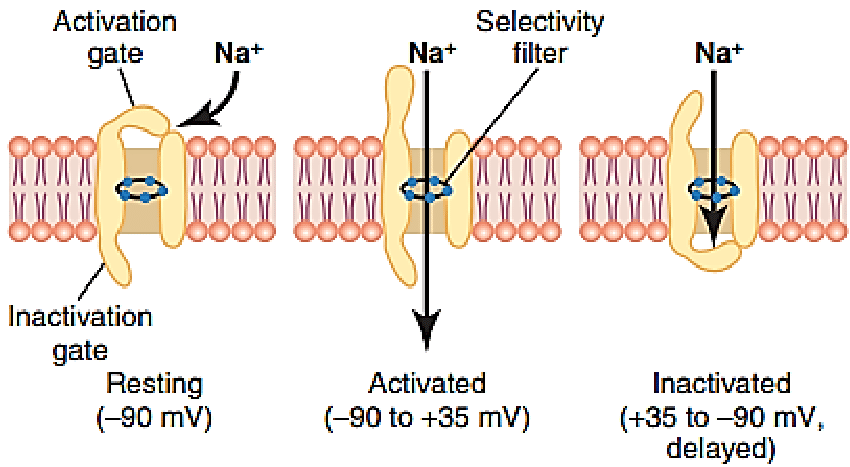
What is the role of voltage-gated sodium and potassium channels in muscle contraction?
These channels regulate membrane potential changes, allowing the transmission of action potentials that trigger muscle contraction.
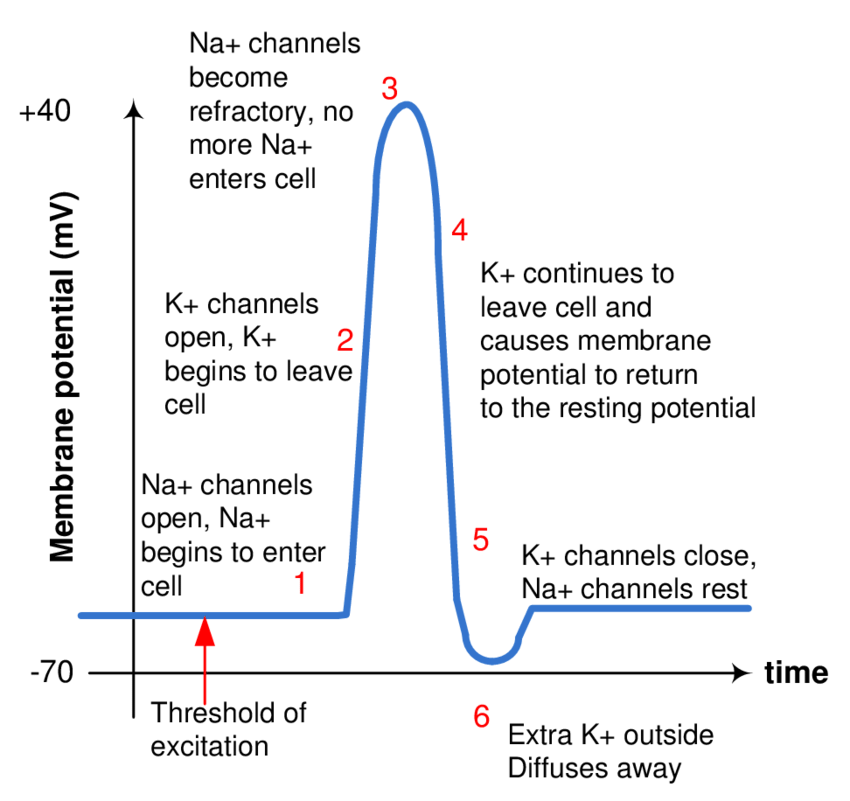
How does an action potential lead to muscle contraction?
A stimulus changes the membrane potential, opening voltage-gated sodium channels, causing depolarization. This signal travels through T-tubules and triggers calcium release for contraction.
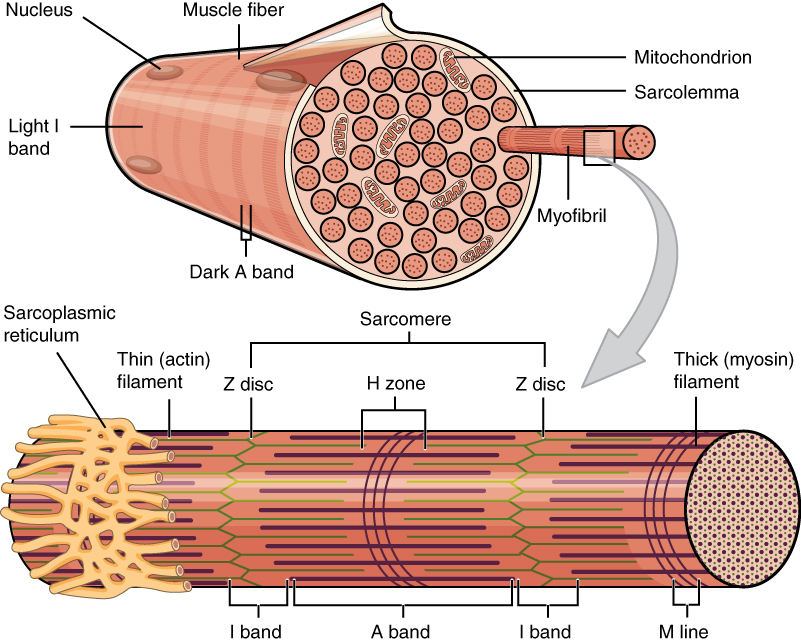
What are myofibrils
long thread-like structures inside muscle fibers made up of sarcomeres
how do myofibrils relate to muscle function?
they are the fundamental units of muscle contraction.
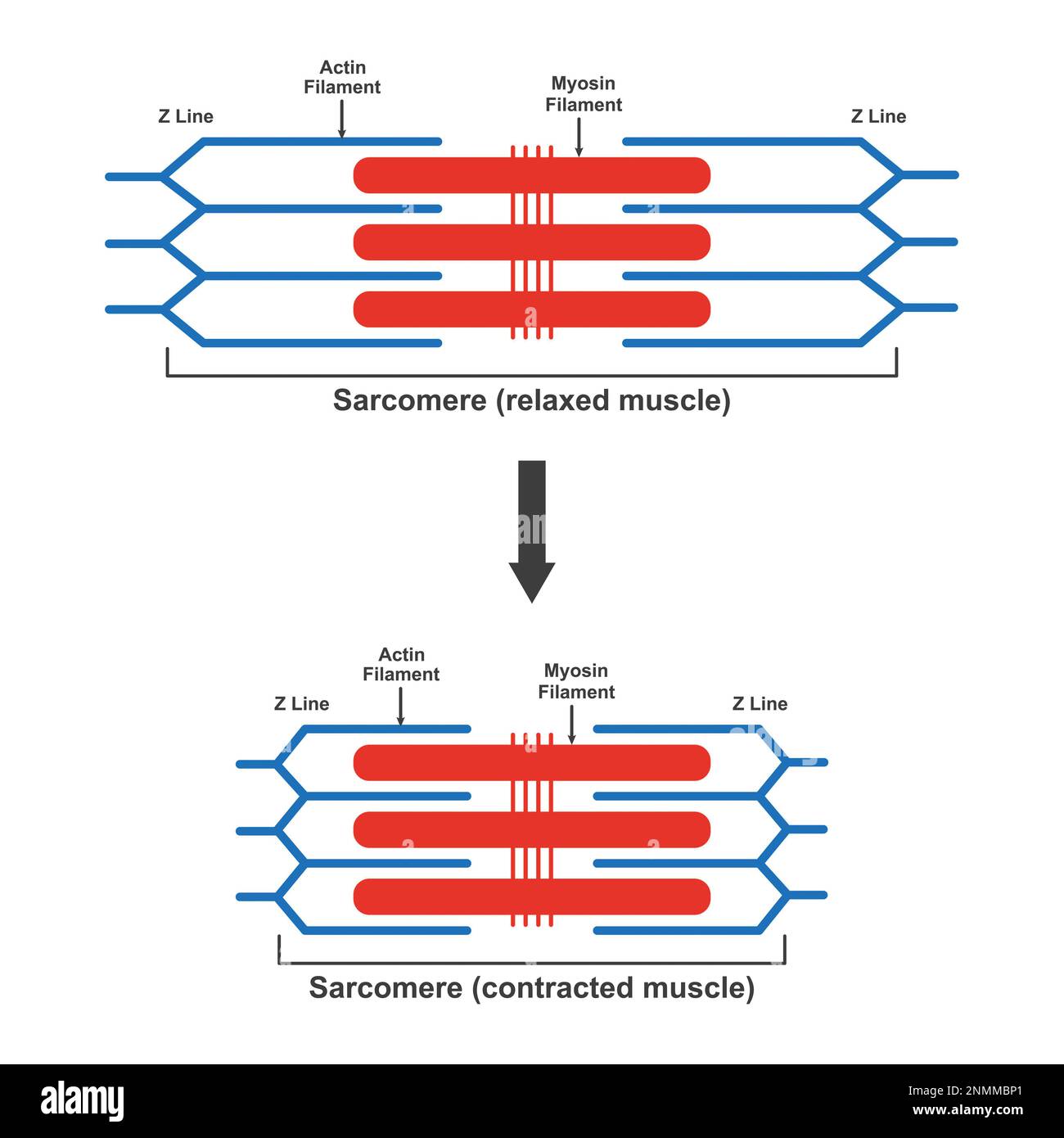
What is the sarcomere
the contractile unit of a muscle
what happens inside the sarcomere during contraction?
Actin and myosin filaments slide past each other, shortening the sarcomere and generating muscle contraction.
Actin
a protein that makes up the thin filaments in muscle cells
myosin
a protein that makes up the thick filaments in muscle cells
What proteins make up thin filaments?
Actin, troponin, and tropomyosin
tropomyosin
a regulatory protein found in thin filaments (along with actin) in muscle cells.
what role does tropomyosin play in muscle contraction
blocking the binding sites on actin when the muscle is at rest. During muscle contraction
What proteins make up thick filaments?
Myosin
How do regulatory proteins control muscle contraction?
Tropomyosin blocks actin-binding sites at rest. When calcium binds to troponin, tropomyosin shifts, allowing myosin to bind to actin and generate contraction.
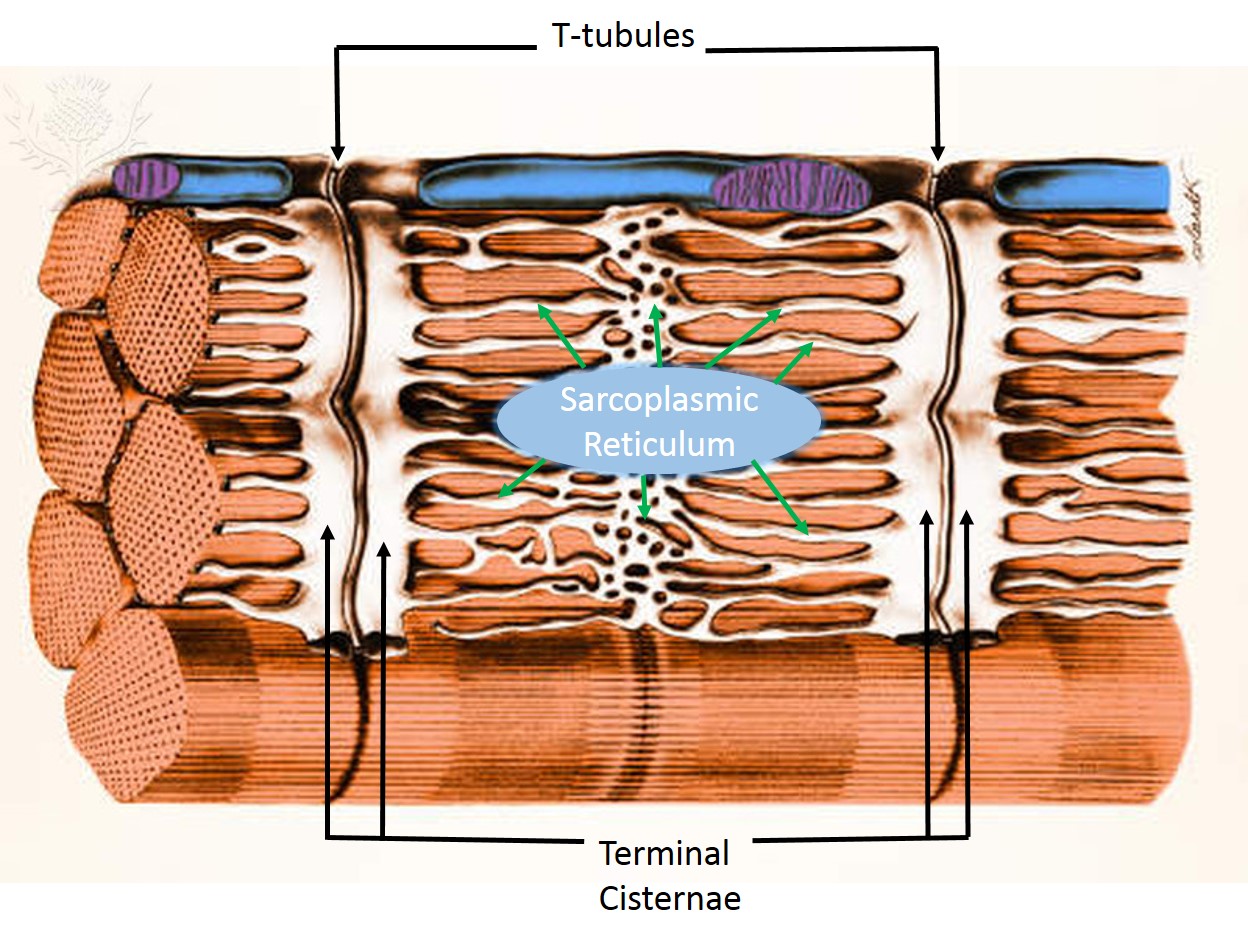
What is the sarcoplasmic reticulum
a specialized organelle in muscle cells that stores and releases calcium
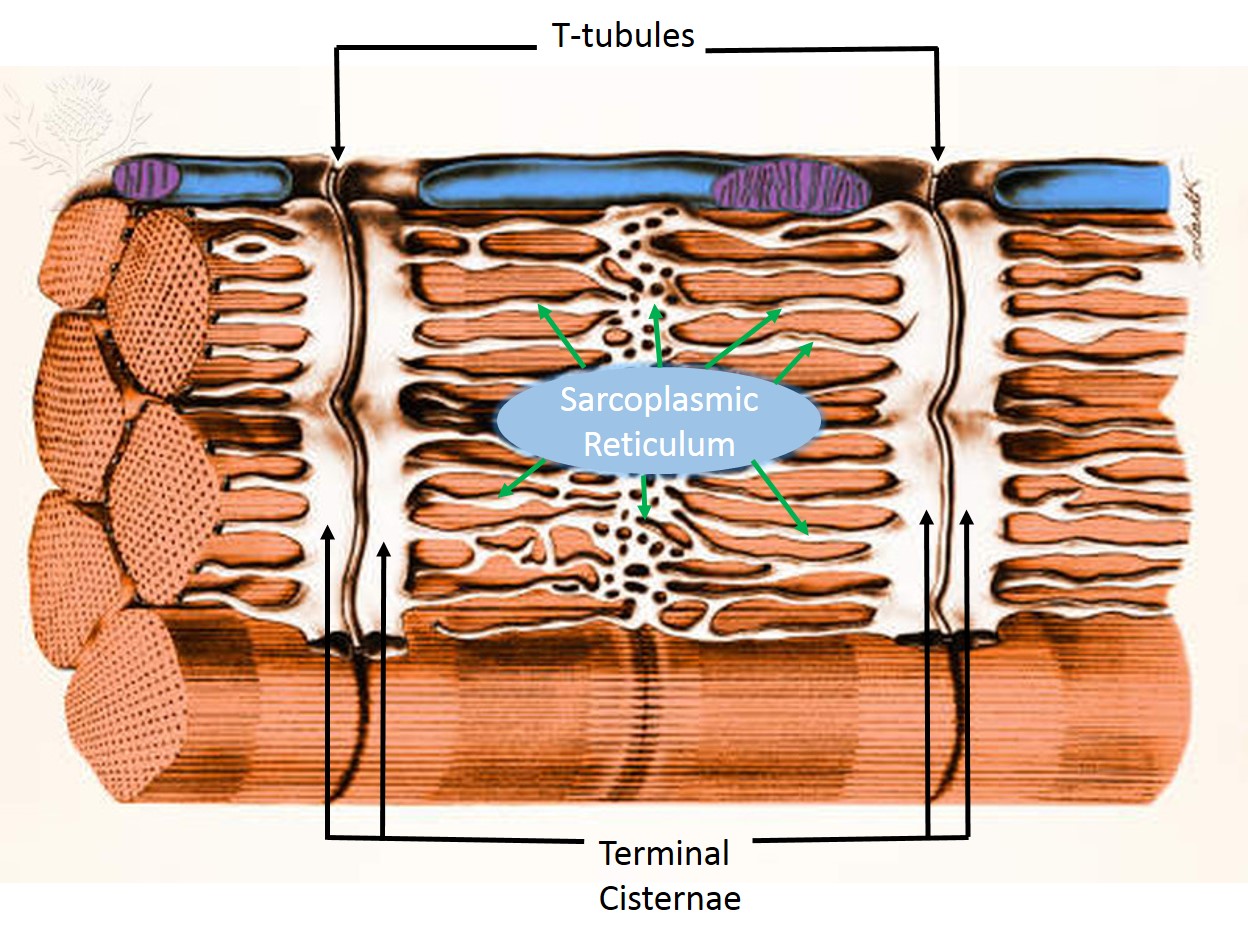
What is the role of the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
muscle contraction (role is crucial)
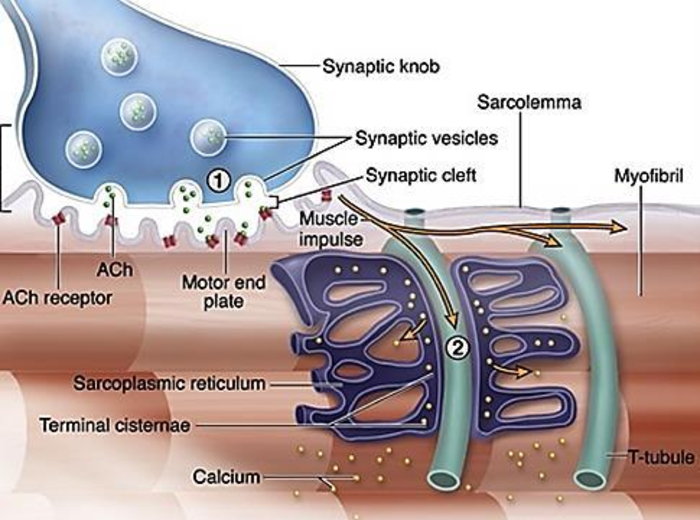
What are terminal cisternae
enlarged sections of the SR that store calcium
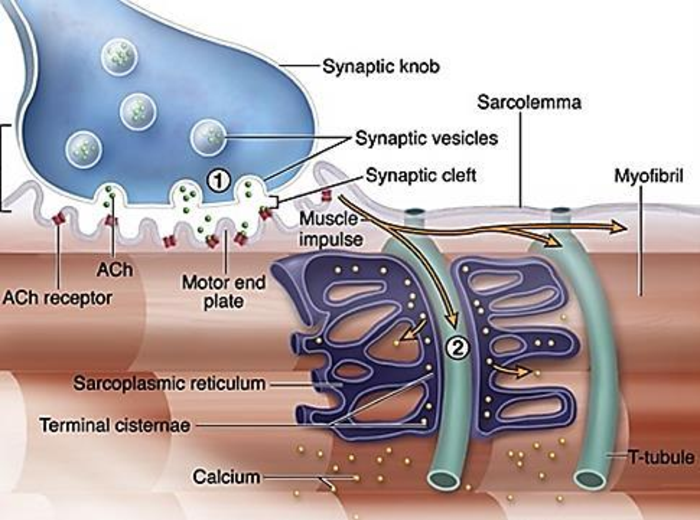
how do terminal cisternae function?
When an action potential reaches them, they release calcium into the muscle cell to trigger contraction.
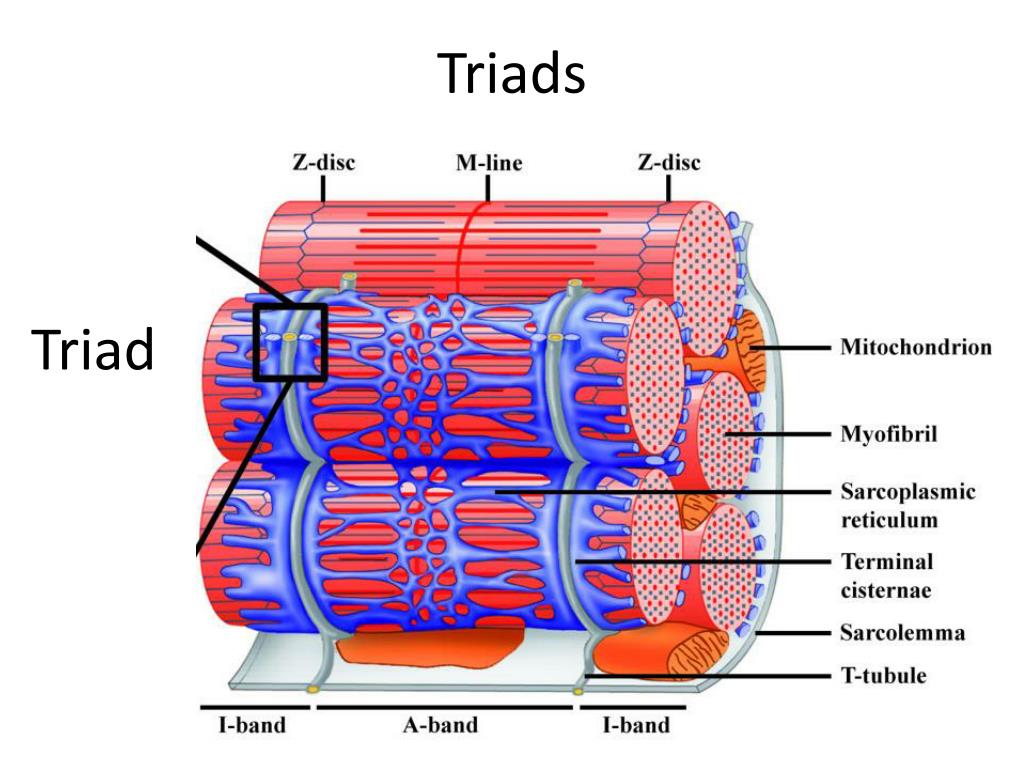
What is a triad in muscle cells?
two terminal cisternae from the sarcoplasmic reticulum and one T-tubule in the middle, forming a structure crucial for rapid calcium release and muscle activation.
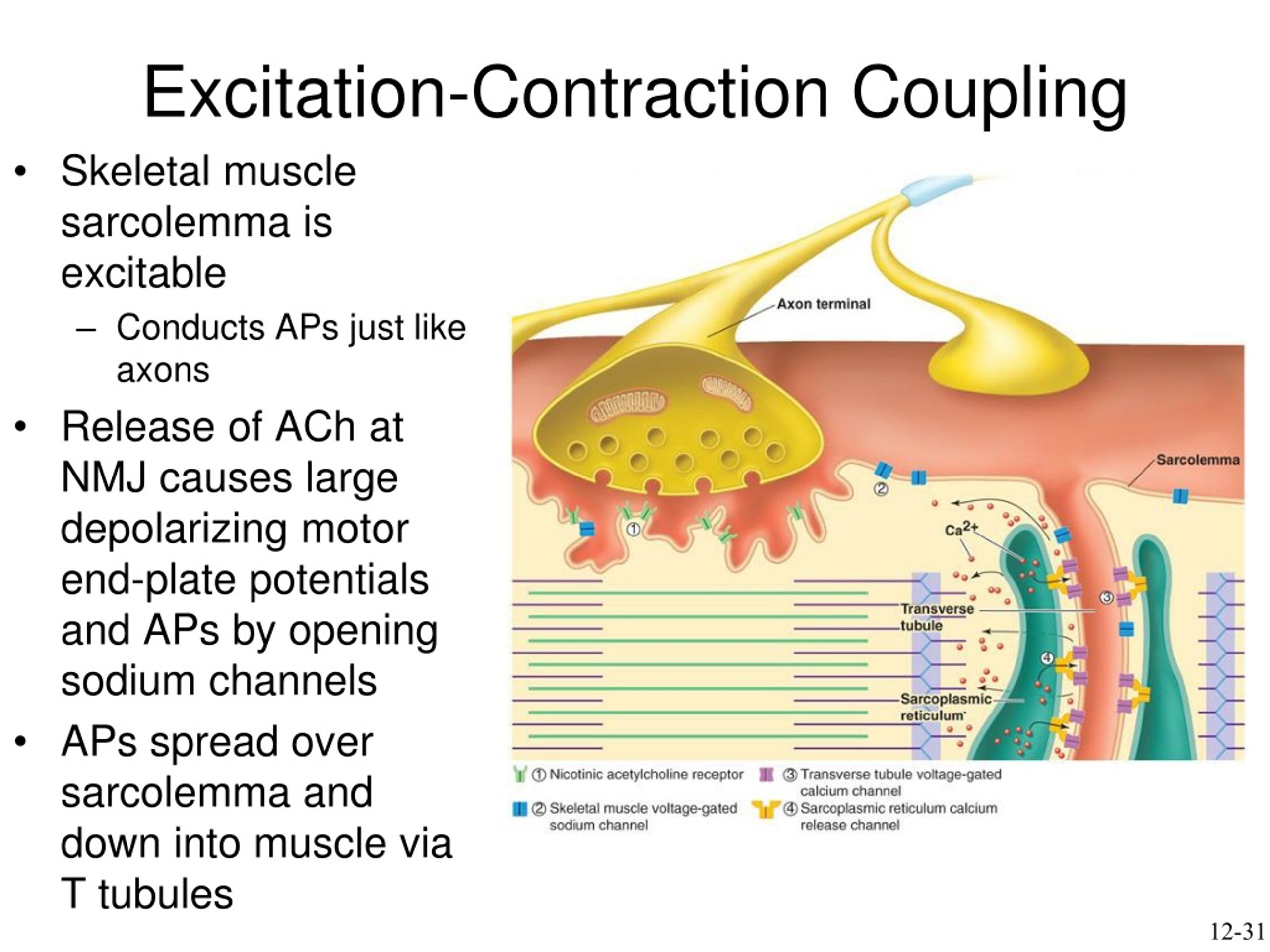
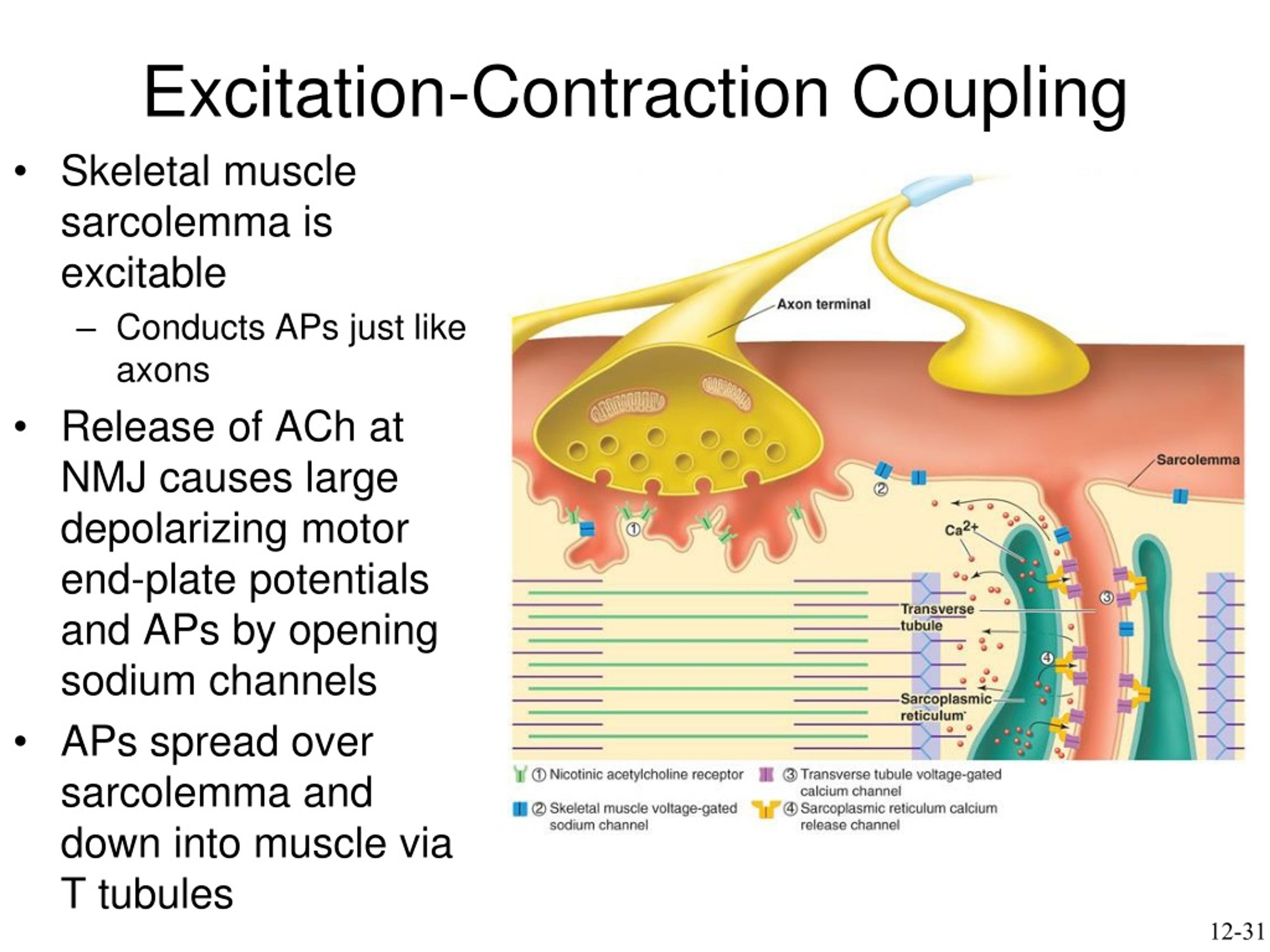
What is excitation-contraction coupling
the process where an electrical signal (action potential) travels through the T-tubules, triggering calcium release from the SR
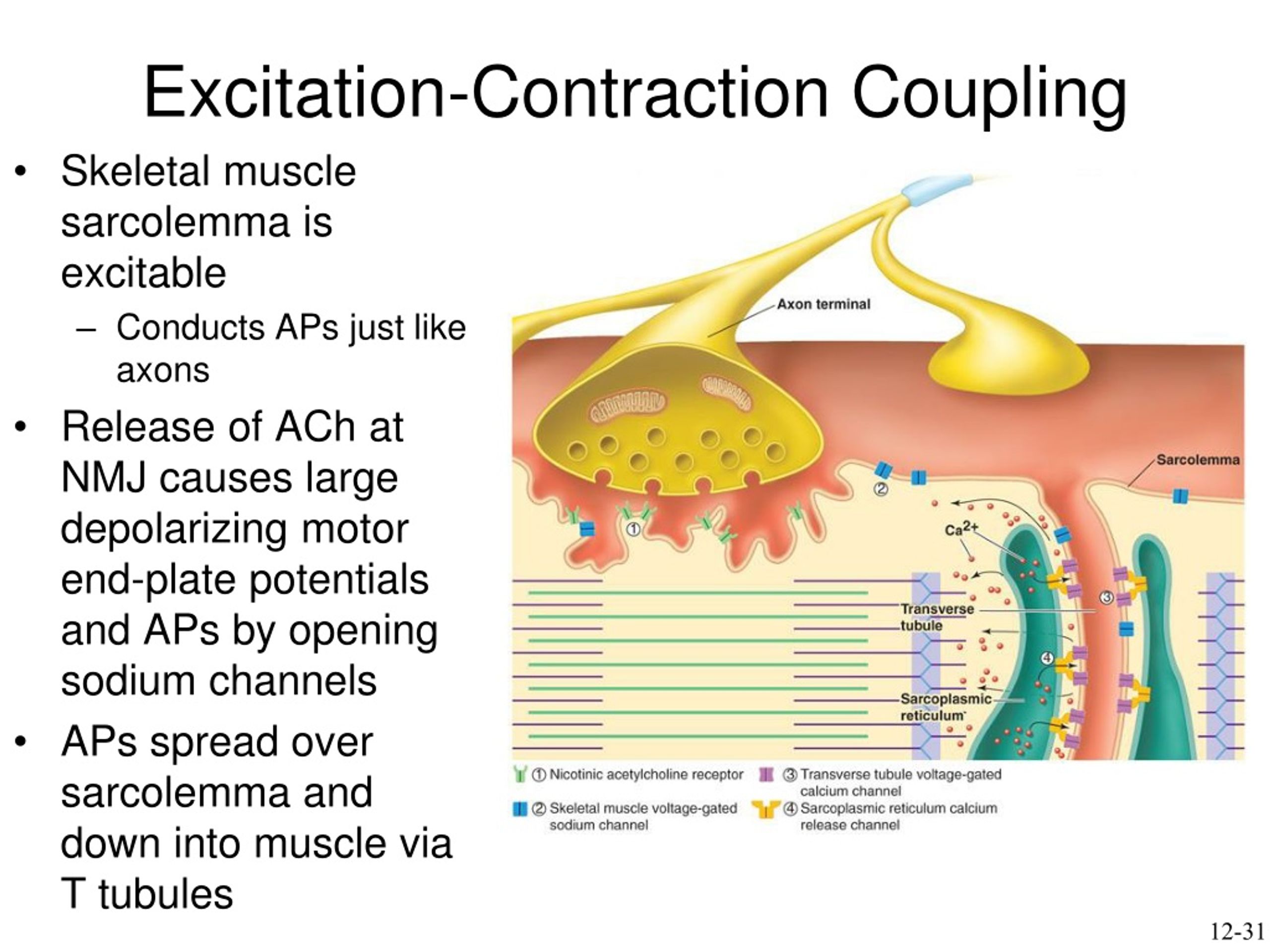
why is excitation-contraction coupling important?
leads to muscle contraction
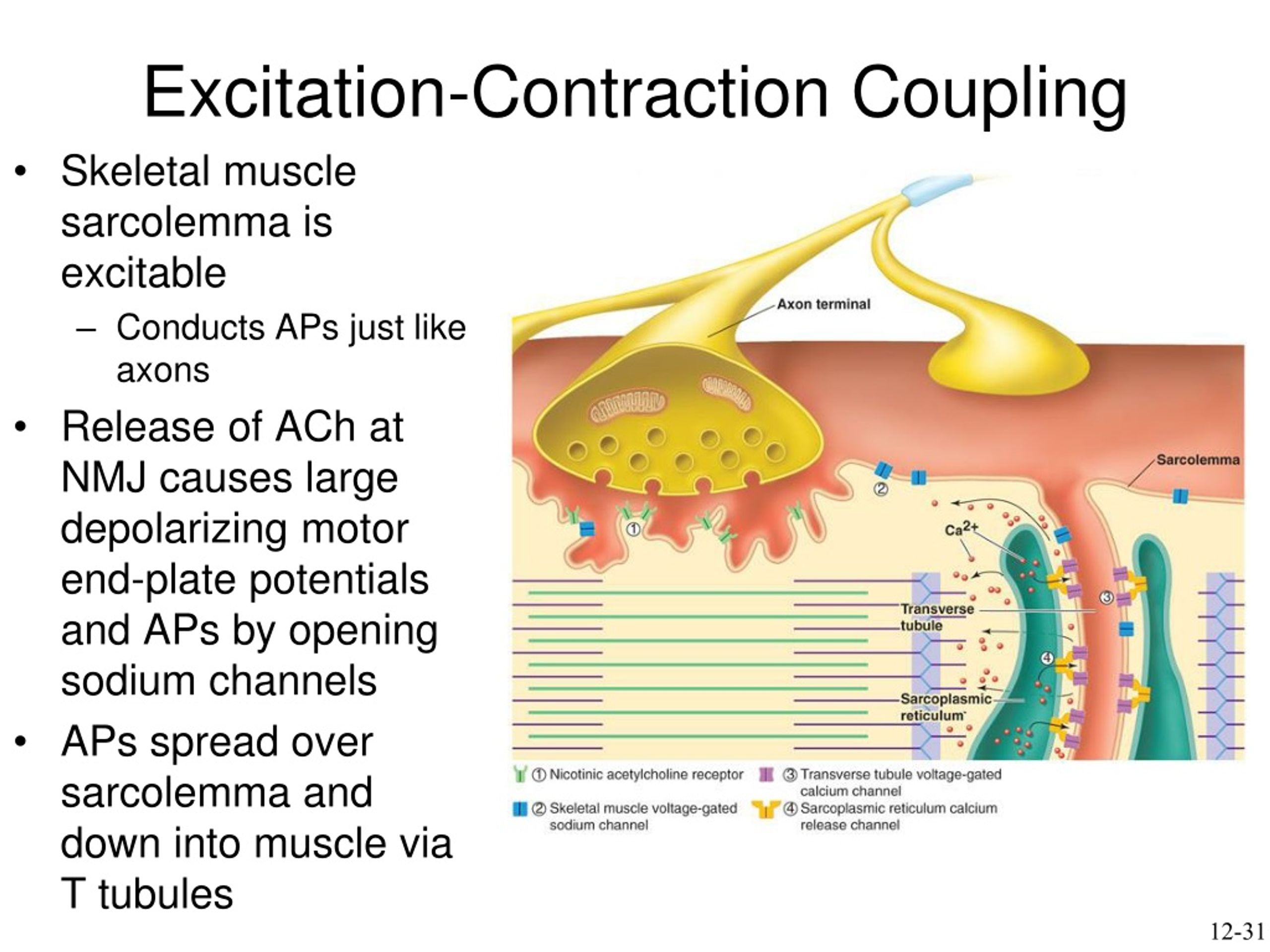
What is the first key step in excitation-contraction coupling
Action potential travels down the sarcolemma and into T-tubules.
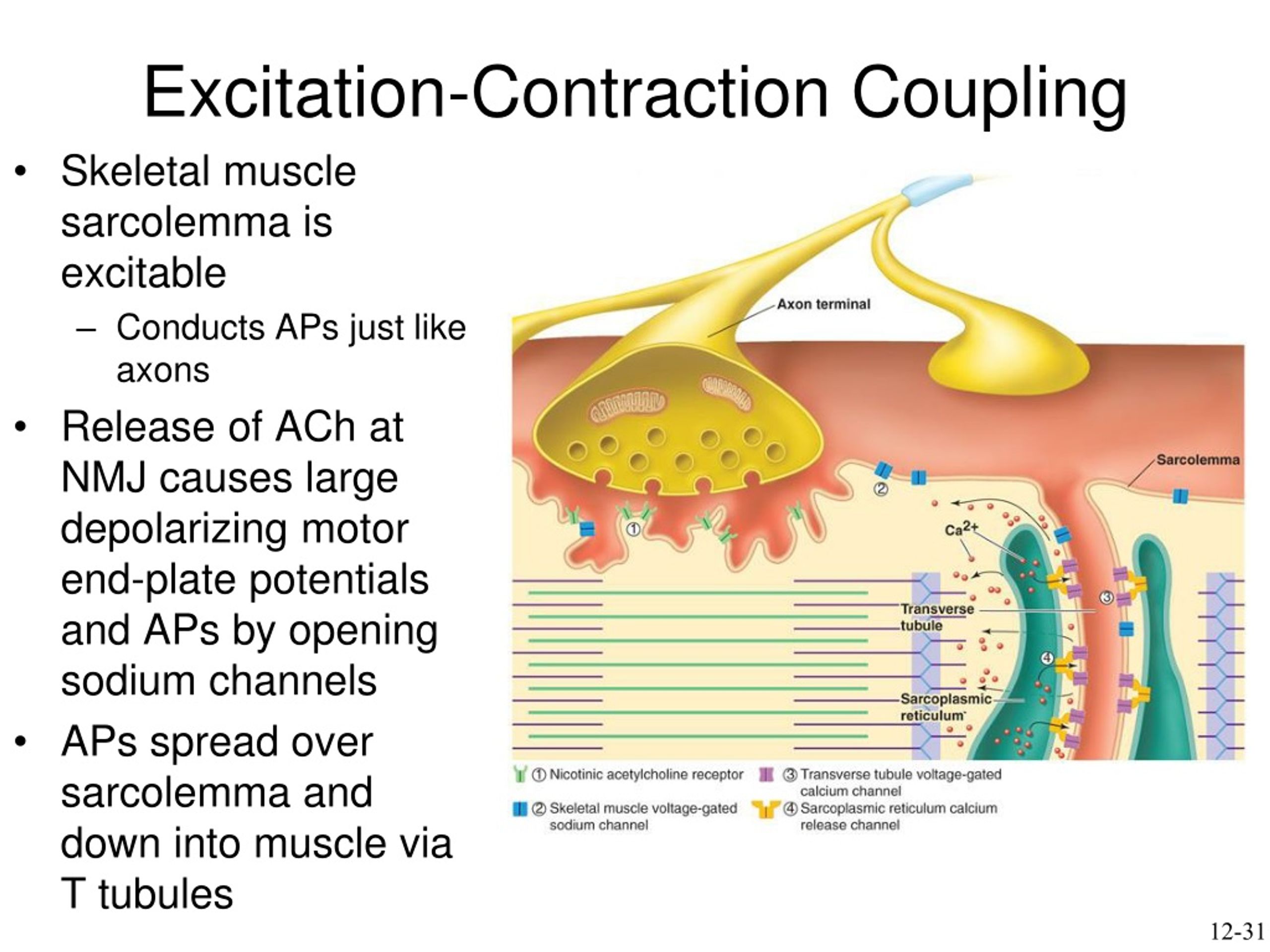
What is the second key step in excitation-contraction coupling
Voltage-gated channels in the T-tubules trigger the SR to release calcium.
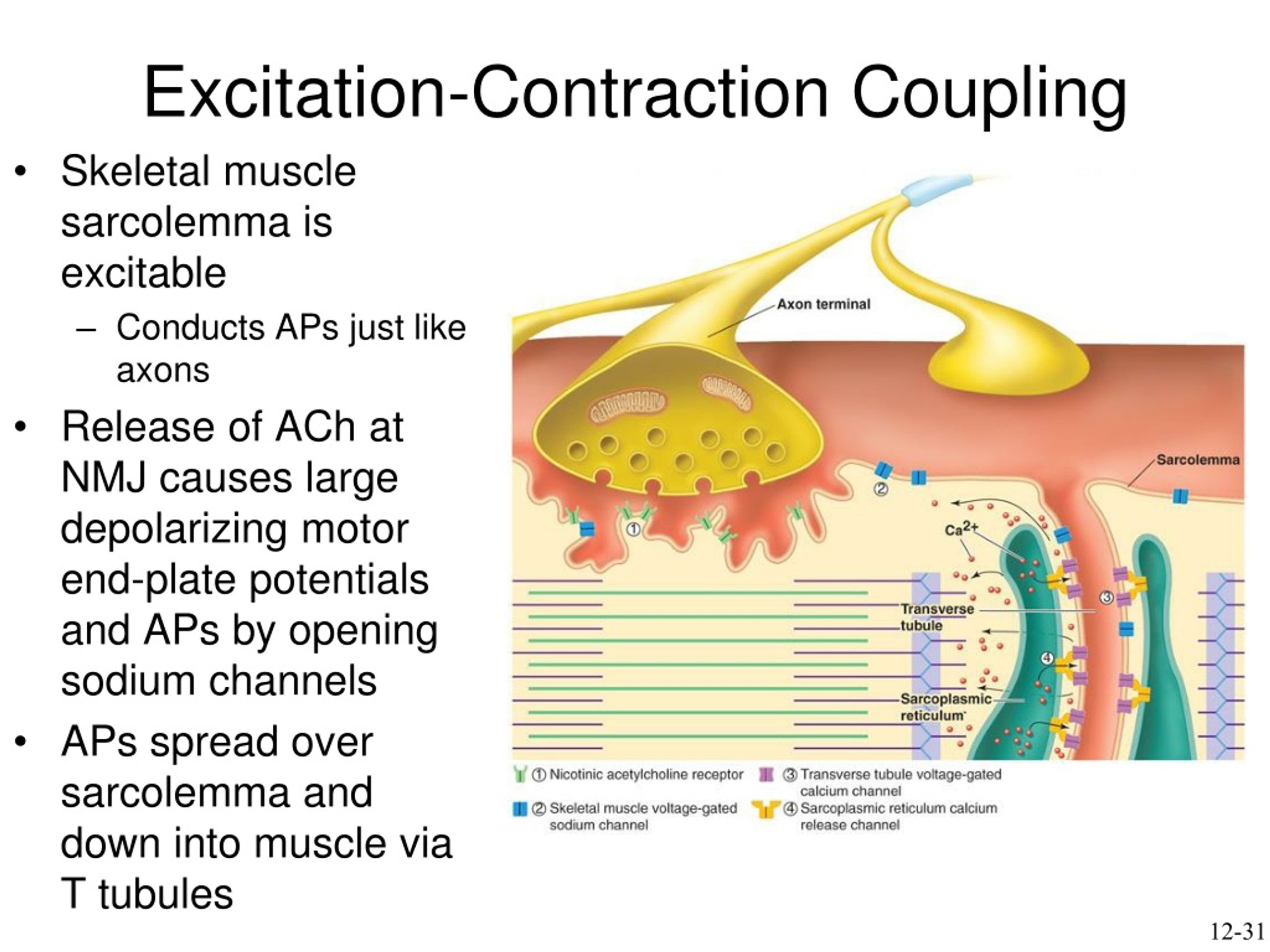
What is the third key step in excitation-contraction coupling
Calcium binds to troponin, shifting tropomyosin and allowing myosin to bind to actin.
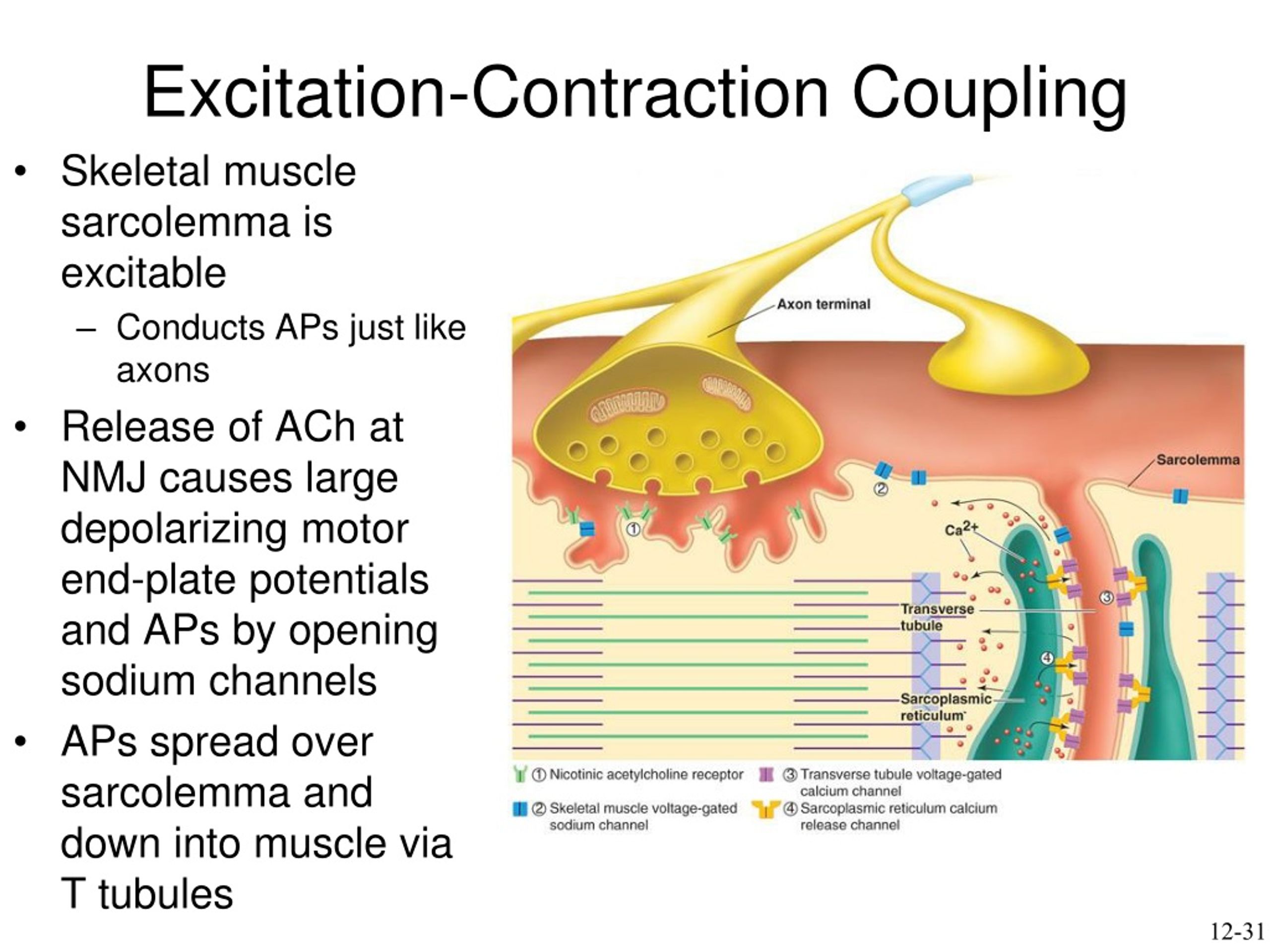
What is the fourth key step in excitation-contraction coupling
Myosin pulls actin, shortening the sarcomere (muscle contraction).
What is the fifth key step in excitation-contraction coupling
When calcium is reabsorbed into the SR, the muscle relaxes.
How does a muscle relax after contraction?
Calcium is actively pumped back into the SR, causing troponin to release calcium, which allows tropomyosin to block actin again, preventing myosin binding and stopping contraction.
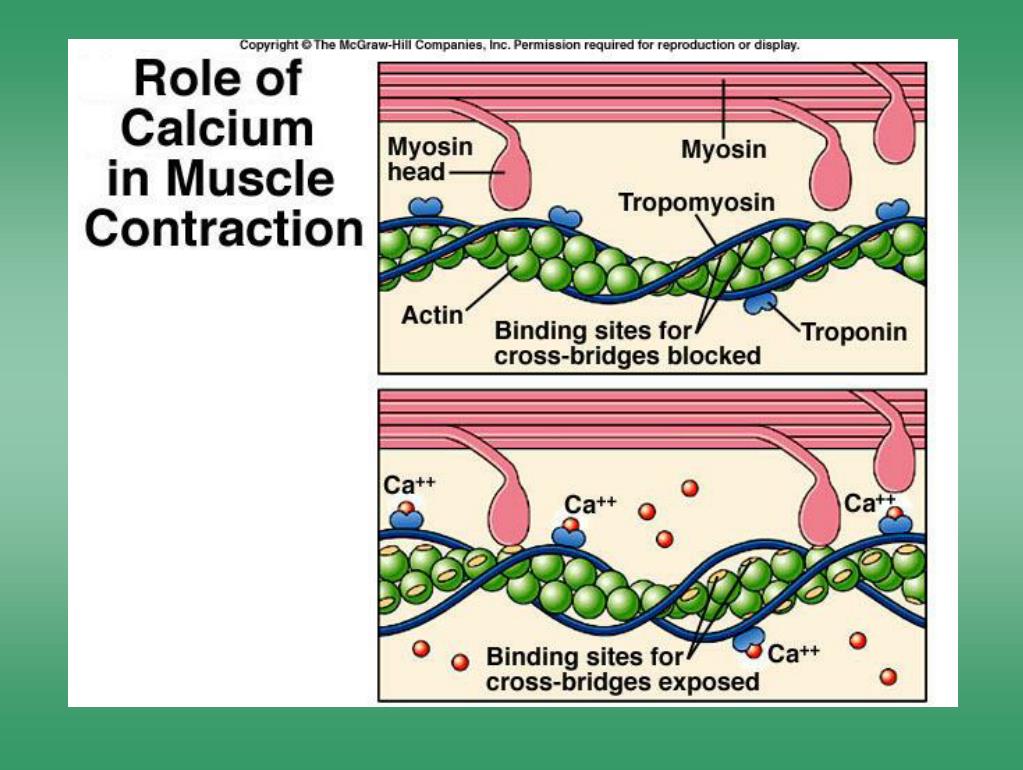
Why is calcium critical for muscle contraction?
Calcium removes tropomyosin from actin-binding sites, enabling myosin to bind and generate contraction. Without calcium, muscles remain relaxed.