CBL 13: The Horse with Colic
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
When do the 01 (central) deciduous teeth come through?
6d
When do the 02 (middle) deciduous teeth come through?
6w
When do the 03 (corner) deciduous teeth come through?
6m
When do the 01 (central) permanent teeth come through?
2.5y
When do the 02 (middle) permanent teeth come through?
3.5y
When do the 03 (corner) permanent teeth come through?
4.5y
How many incisors do horses have?
3
How many canines do horses have?
1 (commonly extracted)
How many premolars do horses have?
3 (4 if has wolf tooth)
How many molars do horses have?
3
hypsodont teeth
teeth with high crowns
What are some features of hypsodont teeth that make them beneficial to horses?
large crown for wear protection
premolars & molars larger and flatter to grind down plant matter & aid digestion
large grinding surface
What are dental focal overgrowths caused by?
lack of attrition to crown of tooth
What does lack of attrition to the crown of horse tooth cause?
dental focal overgrowths
What can cause dental focal overgrowths (due to lack of attrition to crown of a tooth)?
if opposite occlusal surfaces don’t meet
differences in eruption times of cheek teeth
tooth loss
differences in timing of cap shedding
high starch/low fibre diet
What impacts can dental focal overgrowths have on a horse?
infection of supporting bones/maxillary sinus
quidding
weight loss
abnormal head carriage, resistance to the bit and head shaking during work
colic
diastemas (if overgrown tooth wears away from another tooth excessively)
What are the paranasal sinuses in close association with?
roots of cheek teeth
What is the maxillary sinus divided by & into?
by a thin septum into caudal and rostral sinuses
What tooth does the rostral maxillary sinus have the root of?
first maxillary molar
What paranasal sinus is the root of the first maxillary molar associated with?
rostral maxillary sinus
What teeth does the caudal maxillary sinus have the root of?
second and third molars
What paranasal sinus is the second and third molars associated with in the horse?
caudal maxillary sinus
What nerves are the teeth innervated by?
branches of the trigeminal nerve
What nerves are involved in the neural supply of the teeth?
trigeminal nerve
infraorbital nerve
inferior alveolar nerve
What does the infraorbital nerve enter & innervate?
enters maxillary foramen and innervates the upper incisors and maxillary premolar teeth
What does the inferior alveolar nerve enter and supply?
enters mandibular foramen and supplies mandibular teeth
What is the major blood supply to the teeth?
maxillary artery
Where does the major palatine artery run?
rostrally from major palatine foramen to incisive foramen along lateral border of hard palate
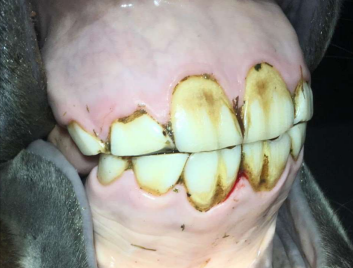
How old is this horse?
3y
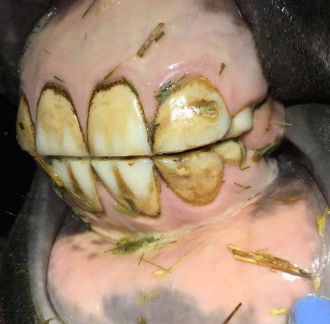
How old is this horse?
4y
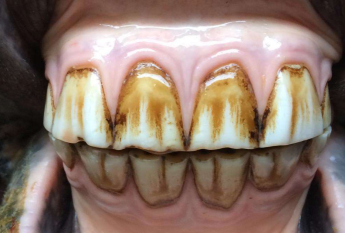
How old is this horse?
>6y
What type of tooth keeps growing/erupting?
hypsodont
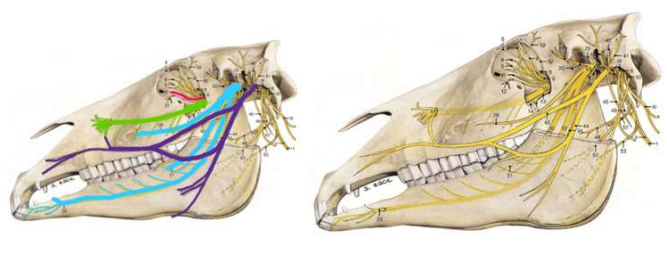
What nerve does the red/pink line show?
trigeminal nerve
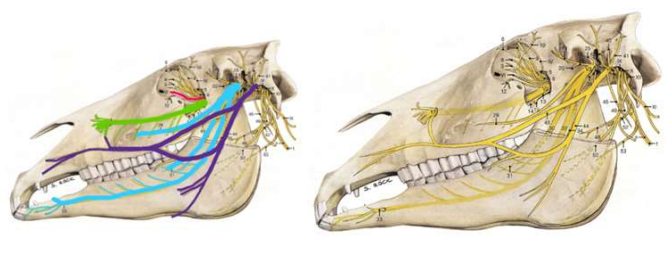
What nerve does the green line show?
maxillary
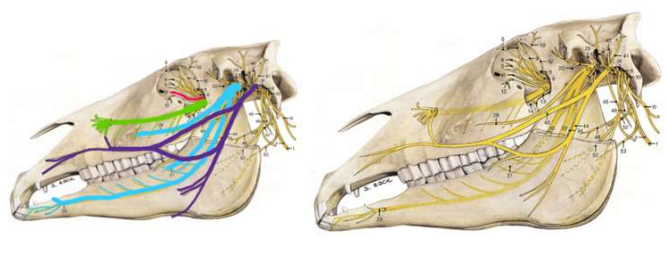
What nerve does the light blue line show?
mandibular
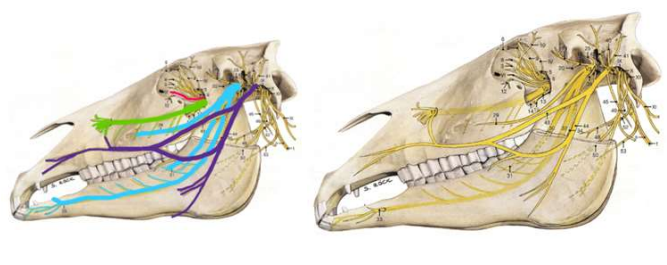
What nerve does the dark blue/purple show?
facial
Which vessels supply the mandibular CT dental arcades?
inferior alveolar artery
maxillary artery
mandibular artery mental artery
What structures should be palpable per rectum in horses?
uterus, ovaries or inguinal rings
LDC, LVC
bladder
left kidney
pelvic flexure, nephrosplenic ligament
abdominal aorta
descending colon
spleen - caudal border
caecum
What are the 2 types of gut motility?
segmentation
peristalsis
Segmentation
alternative contractions squeeze material back and forth - no net movement
What does segmentation do/increase?
increase rate of digestion and absorption
Peristalsis
initiated at a point
contraction of circular muscle on oral side
relaxation of circular muscle aboral side
moves gut contents along GI tract
What does local distension cause? (enteric control)
oral propagation excitation
aboral propagating inhibition
produces peristaltic movement aborally
What does extrinsic control cause? (gut motility - segmentation & peristalsis)
parasympathetic increases peristalsis (stronger)
sympathetic decreases peristalsis (weaker)
What is the motility in the SI like?
slow waves frequently
What is the motility in the LI like?
slow waves less frequent than SI
What is the secretion in the SI like?
mucosa has small circular folds with villi & microvilli
produces digestive enzymes
What is the secretion in the LI like?
thick mucosal layer
mucus secreting glands
What percentage of nutrients does the SI absorb?
90%
What does the LI absorb?
water & remaining nutrients
What is hindgut fermentation?
a process of anaerobic digestion that relies on the metabolic action of bacteria and other microorganisms to break down molecular substrates
At what sites does hindgut fermentation occur?
caecum and colon
What species rely on hindgut fermentation for digestion?
horses and rabbits
What are paraprofessionals?
allied veterinary professionals that work alongside vets by providing specialised care to equids
Name examples of paraprofessionals involved in equine care
equine dental technicians
farriers
musculoskeletal therapists
Name examples of musculoskeletal therapists
chiropractor
osteopath
physiotherapists
How do you build and maintain interprofessional relationships with paraprofessionals to try to safeguard the welfare of animals?
find one you trust
set up good referral process
communication
keep updated medical records
provide progress reports
manage client expectations for both parties
What is abdominal ultrasound useful to determine?
gut position
gut wall thickness
gut distension
gut motility
gut content
free fluid
need for emergency surgery
What is the ‘interface’ in ultrasounds?
point of apposition between neighbouring structures
How does a pocket of peritoneal fluid appear on ultrasound?
anechoic
How does the equine large colon appear on ultrasound?
hyperechoic
How does the bovine rumen appear on ultrasound?
hyperechoic
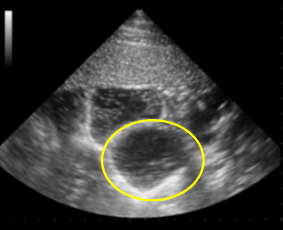
Which structure is circled?
SI distended loop
What is the normal ultrasonographic appearance of the liver?
homogeneous, mildly granular echotexture
What is the normal ultrasonographic appearance of the spleen?
homogenously echoic with a fine echotexture
What is the normal ultrasonographic appearance of the lumen of the GI tract?
variable depending on luminal contents
What is the normal ultrasonographic appearance of the mucosa of the GI tract?
hyperechoic with variable thickness
What is the normal ultrasonographic appearance of the submucosa of the GI tract wall?
hyperechoic and relatively narrow
What is the normal ultrasonographic appearance of the muscularis of the GI tract?
hypoechoic with variable thickness
What is the normal ultrasonographic appearance of the serosa of the GI tract?
thin hyperechoic layer, clear identification often difficult
What is the normal ultrasonographic appearance of the stomach?
variable appearance depending on luminal content
What is the normal ultrasonographic appearance of the capsule of the kidney?
thin hyperechoic line
What is the normal ultrasonographic appearance of the cortex of the kidneys?
hyperechoic, fine and uniform echotexture
What is the normal ultrasonographic appearance of the medulla of the kidneys?
hypoechoic to anechoic in comparison to the outer cortex
What is the normal ultrasonographic appearance of the sinus of the kidneys?
hyperechoic structure situated centrally in the kidney
What is the normal ultrasonographic appearance of the bladder?
outer: hyperechoic
middle: hypoechoic with 3 smooth muscle layers
What is the normal ultrasonographic appearance of the inner submucosal smooth muscle layer of the bladder?
hyperechoic
What is the normal ultrasonographic appearance of the innermost mucosal layer of the bladder?
hypoechoic
Acoustic enhancement
below structures transmit sound well
reduces impedance
deep to this, structures appear more clear
Acoustic shadowing
below structures which transmit sound poorly
increases impedance
deep to this the structures appear less clear
Does acoustic enhancement reduce or increase impedance?
reduce
Does acoustic shadowing reduce or increase impedance?
increase
What is an ultrasound artefact?
something that is observed on an ultrasound image but is not actually there, is in another place or looks different from what it actually looks like
What happens when ultrasound waves hits pleura?
reverberation
What is peritoneal tap also known as?
abdominocentesis
What are the 2 techniques of abdominocentesis (peritoneal tap)?
needle
trocar
At what location do you do abdominocentesis with a needle?
4” caudal to xiphoid
4” to right of midline
What location do you do abdominocentesis with a trocar?
4” caudal to xiphoid
midline
What abdominal structure might be avoided by the site 4” caudal and to the right of the midline when doing abdominocentesis?
spleen
What structure do you pass through in the ventral midline 4” caudal to the xiphoid when doing abdominocentesis?
linea alba
What physical factor will keep the peritoneal fluid in the abdomen rather than dripping out of your needle? (abdominocentesis)
surface tension
What is the normal colour of peritoneal fluid?
straw coloured, clear fluid
What is the function of peritoneal fluid in horses?
act as lubricant reducing friction when digesting
What is lactate?
ionised form of lactic acid (byproduct of anaerobic metabolism)
What is plasma lactate?
lactate in the bloodstream
Why is measuring blood plasma lactate levels useful?
in horses with colon increasing BLC can indicate worsening prognosis
assist in determining severity of conditions and need for intensive care
Colic
abdominal pain
Ileus
temporary slowing of GI motility
What are the risks associated with examining teeth in a horse?
injuries
improper handling
stress and anxiety
sedation risks
further injuries/trauma from equipment
Which type of colic is associated with tapeworms, large strongyles, cyathostomins and ascarid worm?
parasitic colic