Biology - Chapter 6 - Plant structures and their functions
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Where does photosynthesis take place?
In the leaves within the sub-cellular structures chloroplasts which contain chlorophyll which absorb light
What is the word equation for photosynthesis?
Carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen
What is the symbol equation for photosynthesis?
6Co2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Is photosynthesis endothermic or exothermic?
Endothermic
How does photosynthesis happen?
Carbon dioxide diffuses into the leaves through the stomata, water is taken up from the soil by roots and is transported to leaves via xylem
What is cellular respiration for?
To release energy
What is cellulose for?
To strengthen cell walls
What is starch?
A long term, compact, insoluble store of glucose
What does starch do when needed?
Breaks down
What does the growth rate of plants depend on?
How fast they can photosynthesize
What do amino acids break down into?
Glucose and nitrate ions
What do glucose and nitrate ions break down into?
Proteins
What are the four factors that affect photosynthesis?
Light intensity, temperature, carbon dioxide and chlorophyll concentration
Why does temperature affect photosynthesis?
Enzymes work quickly with a greater temp causing the molecules to move faster
What are the three reasons why chlorophyll levels can vary?
Due to disease, lack of nutrients and environmental stress
What does plateaued mean?
Another factor is limiting the rate of the reaction
How can artificial conditions be created by farmers for photosynthesis?
Greenhouses, artificial lights, paraffin heaters, fertilisers, pesticides
What are the advantages and disadvantages for farmers creating artificial conditions for photosynthesis?
Increased profit from a greater yield but expensive to setup and manage
Draw and label the plant cell organisation
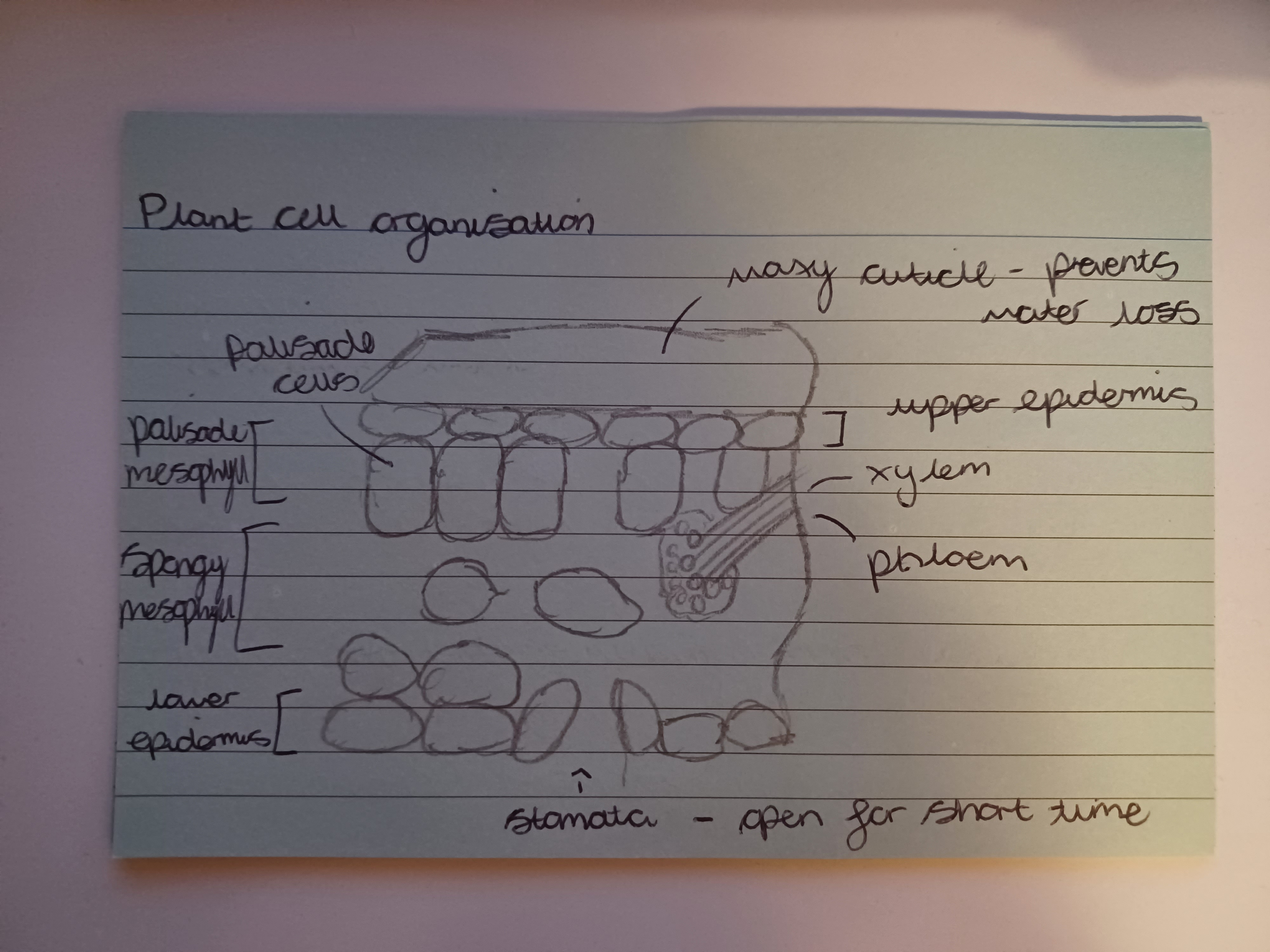
Where is the stoma located?
In-between two guard cells
How are guard cells adapted for their function?
They are turgid, making the gap larger so that more CO2 is able to diffuse through
What do guard cells do when a plant is short of water?
They become flaccid which closes the stoma to conserve water vapour
What happens to guard cells at night?
They close
Are stoma located on the shady or sunny side?
Shaded side
Why are stoma located on the shady side?
So that there is less evaporation
What is translocation?
The transporting of sugars via phloem cells
Can phloem cells transport one way or both directions?
Both directions
What do phloem cells have which allow cell sap to pass through?
Pores
What are xylem tubes made up of?
Dead xylem cellsW
What are xylem tubes strengthened by?
Lignin
What do xylem tubes transport?
Water and mineral ions
What is transpiration?
Evaporation of water from the leaves
What are the four factors affecting transpiration?
Temperature, light intensity, air flow, humidity (more humid decreases rate)
What do plant hormones do when they sense light?
Grow towards the light to maximise photosynthesis
What do plant hormones do when they sense gravity?
Grow roots downwards
What do plant hormones do when they sense touch?
Climb around objects
Do plant hormones act locally or internationally?
Locally
What do auxins control?
The growth at roots and shoots
What do auxins in shoots do?
Stimulate growth
What do auxins in roots do?
Inhibit growth
What is phototropism?
respond to light
What is gravitropism?
Respond to gravity
Where do auxins always accumulate?
On the lower, shaded sides
In terms of phototropism and gravitropism, what are shoots?
Positively phototropic, negatively geotropic
In terms of phototropism and gravitropism, what are roots?
Negatively phototropic, positively geotropic
What does gibberellin do?
Controls dormancy, flowering, grow larger fruit
What does ethene do?
Stimulate the ripening of fruit
How is ethene useful comercially?
Controls ripening process so that it can be transported and exposed to ethene when ready to be sold