Exam 2- Gen bio
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/113
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:36 PM on 12/3/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
1
New cards
kinetic energy
energy of movement, breaking bonds
2
New cards
potential energy
energy stored in the bonds
3
New cards
law of conservation of energy
energy cannot be created or destroyed, but can be changed from one form to another
4
New cards
law of thermodynamics
energy cannot be transferred from one form to another without the loss of usable energy
5
New cards
total energy
unusable energy + usable energy
6
New cards
enthalpy
free energy (usable G) + (entropy (unusable) x absolute temp)
7
New cards
orient substrate
a way enzymes can lower activation energy by putting molecules in the right position to bond them
8
New cards
induce physical strain
lowering activation energy- stretching bonds to be able to produce chemical reactions
9
New cards
alter chemical charge of substrate
lowers activation energy
10
New cards
negative delta G
free energy is release
11
New cards
positive delta G
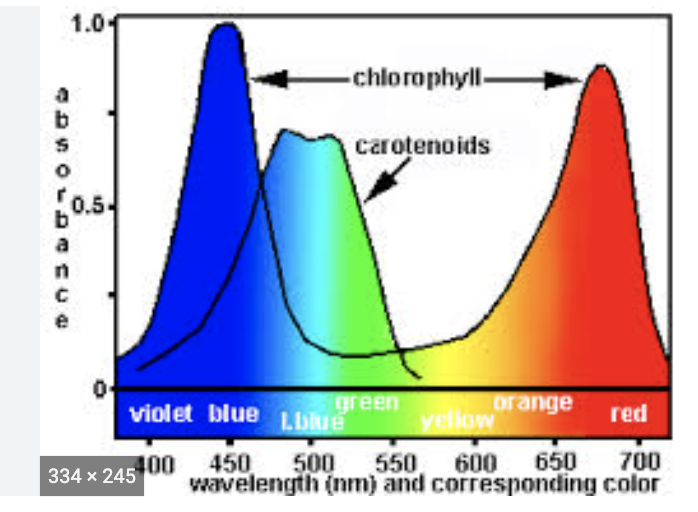
energy has been added
12
New cards
what affects enzyme regulation
environment, factors and inhibitors
13
New cards
environment regulation
pH and temperature
14
New cards
factor regulation
inorganic ions
coenzymes- carbon containing molecules
prosthetic- permanently bound (hemoglobin)
coenzymes- carbon containing molecules
prosthetic- permanently bound (hemoglobin)
15
New cards
irreversible inhibitors
covalently bonds with enzyme and shuts off activity
16
New cards
competitive reversible inhibitors
competes for the same active site with substrate
17
New cards
non-competitive reversible inhibitor
inhibitor binds somewhere other than the active site, changes the shape of the active site so substrate cannot bind
18
New cards
cellular respiration equation
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H20 + energy
19
New cards
oxidation
loss of an electron
20
New cards
reduction
gaining an electron
21
New cards
what do enzymes do in releasing free energy
helps to not lose as much energy to heat (stair graph example)
22
New cards
redox reactions
one compound getting oxidized, one compound getting reduced
23
New cards
two co-enzymes
1. NADH
2. FADH
2. FADH
24
New cards
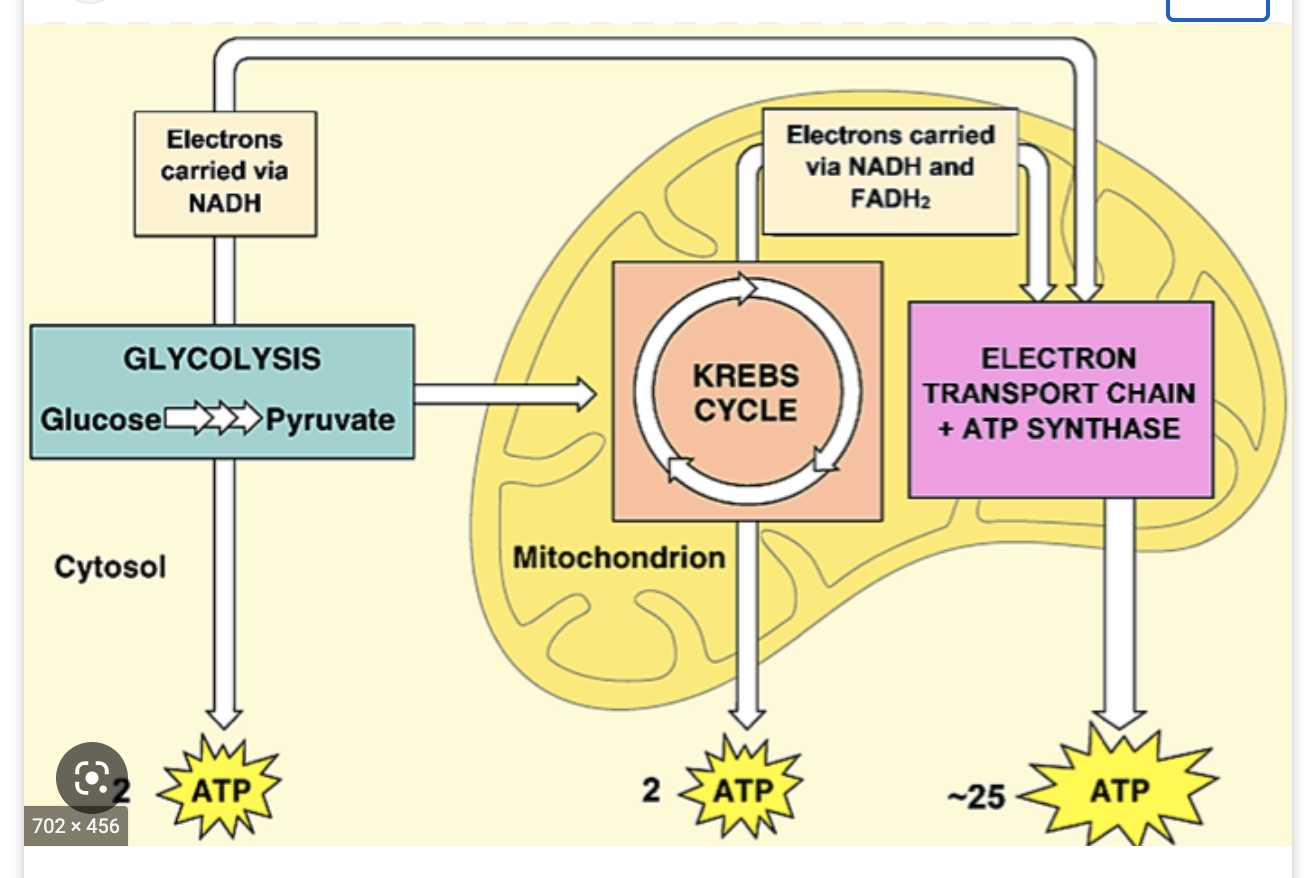
glycolysis
1. energy investment phase
2. energy harvesting phase
2. energy harvesting phase
25
New cards
energy investment phase
glucose is oxidized and an investment of two ATP molecules to result in 2 glyceraldehyd 3-phosphate and 2 ADP
26
New cards
energy harvesting phase
4 ADP+ NAD+ (reduced)+ 2G3P ---> 2 pyruvate + 4 ATP + 2 ADP
27
New cards
how much ATP is yielded after glycolysis
2 ATP
28
New cards
substrate level phosphorylation
taking a phosphate and adding it to something else (adding a phosphate from G3P to ADP to form ATP)
29
New cards
steps of cellular respiration
1. glycolysis
2. pyruvate processing
3. krebs/citric acid cycle
4. electron transport chain
2. pyruvate processing
3. krebs/citric acid cycle
4. electron transport chain
30
New cards
pyruvate processing equation
2 Pyruvate + 2 NAD+ + 2 CoA → 2 Acetyl-CoA + 2 NADH + 2CO2
-NAD+ is reduced to NADH
-NAD+ is reduced to NADH
31
New cards
krebs cycle equation
2acetylCoA + 6NAD+ + 2FAD + 2ADP --> 4Co2 + 6NADH + 2FADH2 + 2ATP
32
New cards
What does the Krebs cycle produce
4 ATP and lots of NADH
33
New cards
NADH
a high energy molecule that can be converted to energy in a later process
34
New cards
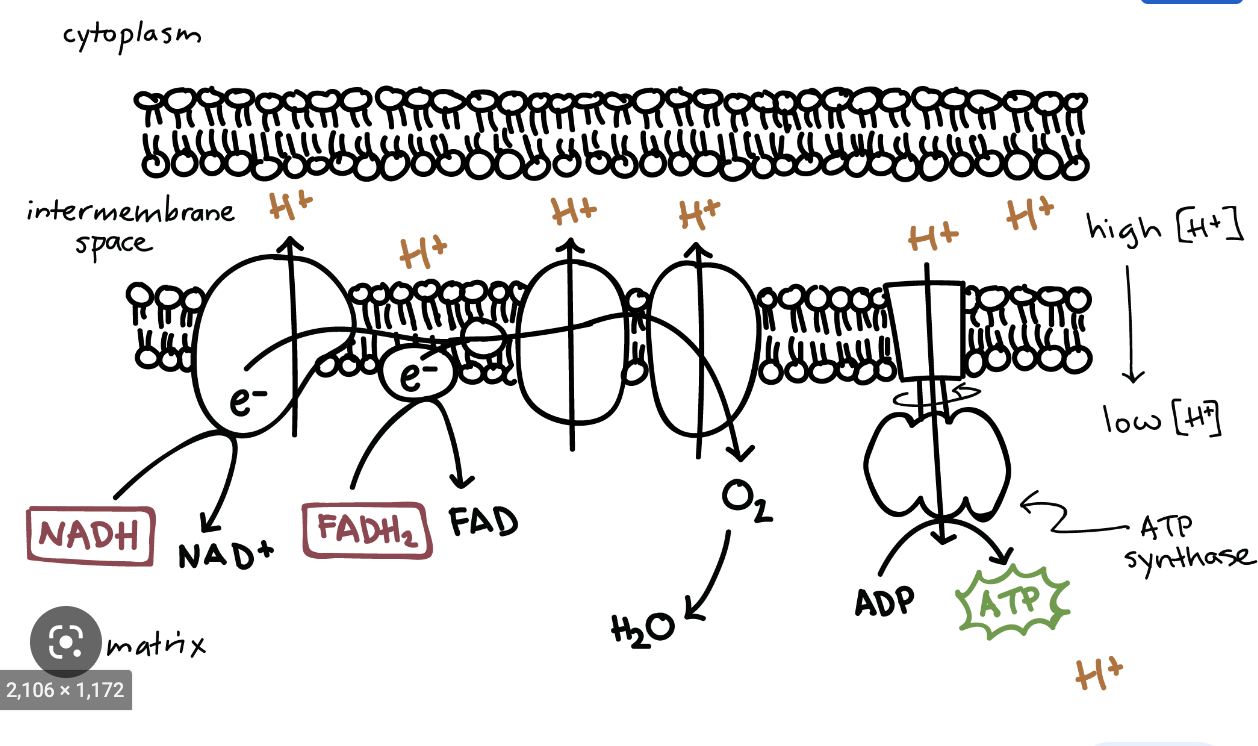
electron transport chain
a series of four protein complexes that couple redox reactions, creating an electrochemical gradient that leads to the creation of ATP in a complete system named oxidative phosphorylation.
35
New cards
where does all the oxygen go at the beginning of cellular respiration?
in the electron transport chain
36
New cards
ATP synthase
a system that pumps hydrogen back into the cell through an ion gradient to create ATP from ADP+ Pi
37
New cards
oxidation phosphroylation
oxidizing NADH and FADH, electrons go down to phosphorylate ADP+ Pi to ATP
38
New cards
how much ATP is yielded from electron transport chain
about 32 ATP
39
New cards
ATP yielded from cellular respiration
about 36 ATP
32 ATP from electron transport chain, 4 ATP from glycolysis
32 ATP from electron transport chain, 4 ATP from glycolysis
40
New cards
Two types of Fermentation
lactic acid fermentation and alcohol fermentation
41
New cards
lactic acid fermentation
pyruvate converted to lactate (cheese, yogurt, buttermilk, sour cream)
42
New cards
alcohol fermentation
Pyruvate converted to acetaldehyde by pyruvate dehydrogenase
acetaldehyde converted to ethanol by alcohol dehydrogenase
occurs in some bacteria and fungi
loses CO2
acetaldehyde converted to ethanol by alcohol dehydrogenase
occurs in some bacteria and fungi
loses CO2
43
New cards
fermentation vs respiration
goal: covert glucose into energy
respiration: 32 ATP, needs oxygen
fermentation: 2 ATP, occurs when there is a lack of oxygen
respiration: 32 ATP, needs oxygen
fermentation: 2 ATP, occurs when there is a lack of oxygen
44
New cards
Fermentation
Anaerobic- Life without air
NADH transfers electrons back to pyruvate
recycles NAD+ to be used again in glycolysis
NADH transfers electrons back to pyruvate
recycles NAD+ to be used again in glycolysis
45
New cards
photosynthesis equation
light energy + 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
46
New cards
autotrophs
produce their own energy
47
New cards
heterotrophs
get energy from another source
48
New cards
light reactions
converts light energy into usable energy (ATP+ NADPH)
happens in the inner membrane of the chloroplasts in the stroma
happens in the inner membrane of the chloroplasts in the stroma
49
New cards
light independent reactions
uses ATP and NADPH and CO2 from light reactions to make carbohydrates
50
New cards
chloroplasts
where photosynthesis occurs, 2 membranes and has its own DNA
51
New cards
electromagnetic radiation
- light
- gamma rays
- x-rays
- infrared
- radio waves
- gamma rays
- x-rays
- infrared
- radio waves
52
New cards
Photon interaction with a molecules (scattered)
photon bounces off
53
New cards
Photon interaction with a molecules (transmitted)
photon passes through
54
New cards
Photon interaction with a molecules (energy is absorbed)
molecule gains more energy, moves electrons out to another shell to hey to a higher energy level
55
New cards
pigments
absorb visible light
56
New cards
once molecule raised to another energy level...
1. releases energy as heat/ light
2. transfers molecules to another molecule
3. used for a chemical reaction
2. transfers molecules to another molecule
3. used for a chemical reaction
57
New cards
absorption spectrum
58
New cards
Non- cyclic electron transport chain
-occurs in the inner membrane of the chloroplast
- photosystem II absorbs so much light it gives electrons to another molecule (oxidizing agent) takes e- from H2O to make O2
- then given to photosystem I which is also absorbing light
- electron is eventually sent to where NADP+ is reduced to NADPH
- hydrogen is pumped back in through ATP synthase to produce ATP
- photosystem II absorbs so much light it gives electrons to another molecule (oxidizing agent) takes e- from H2O to make O2
- then given to photosystem I which is also absorbing light
- electron is eventually sent to where NADP+ is reduced to NADPH
- hydrogen is pumped back in through ATP synthase to produce ATP
59
New cards
cyclic transport chain
- only uses photosystem I
- e- always goes back to photosystem I
- can only produce ATP
- ATP synthase can still pump H+ back in to produce ATP
- e- always goes back to photosystem I
- can only produce ATP
- ATP synthase can still pump H+ back in to produce ATP
60
New cards
Calvin cycle reactions
1. CO2 fixation
2. CO2 reduction
3. regeneration of RUBP
2. CO2 reduction
3. regeneration of RUBP
61
New cards
CO2 fixation
RuBP + CO2 = 2(3PG)
Plants fix atmospheric carbon to form organic compounds
Plants fix atmospheric carbon to form organic compounds
62
New cards
rubisco
enzyme used in CO2 fixation.
it is a carboxylase and oxygenase to fix carbon and oxygen (x10 affinity for CO2)
it is a carboxylase and oxygenase to fix carbon and oxygen (x10 affinity for CO2)
63
New cards
CO2 reduction
oxidation reduction reaction- ATP to ADP+Pi and NADPH to NADP+
- generates glycealdehyde 3- phosphate a high energy molecule that is easy for plant cells to generate carbohydrates
- generates glycealdehyde 3- phosphate a high energy molecule that is easy for plant cells to generate carbohydrates
64
New cards
regeneration of RuBP
G3P converted to RuBP
65
New cards
every 3 turns of the calvin cycle produce...
1 G3P which is easily converted to fructose and other sugars
66
New cards
photorespiration
a metabolic pathway that occurs in photosynthetic organisms and releases carbon dioxide, consumes oxygen, and produces no chemical energy or food.
when hot- plant will lose water but stomata will stay close blocking CO2, concentration of CO2 will go down and oxygen concentration will increase
when hot- plant will lose water but stomata will stay close blocking CO2, concentration of CO2 will go down and oxygen concentration will increase
67
New cards
C3 plants
roses, wheat, rice, soy
CO2+ RuBP---> 2 G3P
- requires a wet, cool environment
- hot conditions have a lot of photo respiration
CO2+ RuBP---> 2 G3P
- requires a wet, cool environment
- hot conditions have a lot of photo respiration
68
New cards
C4 plants
corn, sugar cane
- separated CO2 fixation by space
CO2+ PEP ---> oxaloacerate
- separated CO2 fixation by space
CO2+ PEP ---> oxaloacerate
69
New cards
CAM plants
Cacti
separated CO2 fixation based on time
Night: stroma is open CO2 is fixed to PEP by PEP carboxylase, taking in as much CO2 as possible
Day: stroma closes CO2 is released
separated CO2 fixation based on time
Night: stroma is open CO2 is fixed to PEP by PEP carboxylase, taking in as much CO2 as possible
Day: stroma closes CO2 is released
70
New cards
steps of the cell cycle
1. reproductive signal
2. replicate DNA
3. genome segregation
4. cytokinesis
2. replicate DNA
3. genome segregation
4. cytokinesis
71
New cards
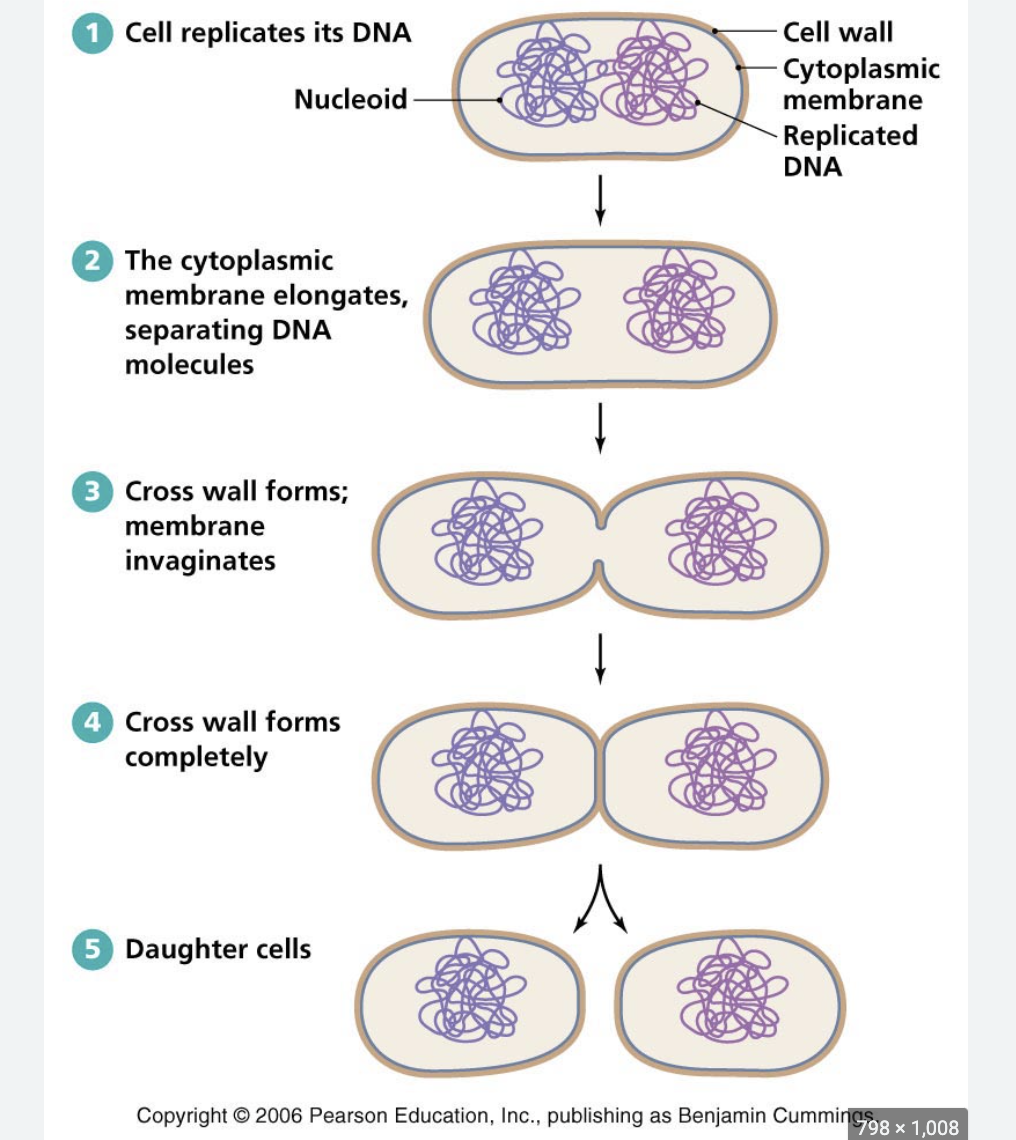
binary fission
the process in which prokaryotic cells divide
72
New cards
conditions for binary fission
ideal temperature, pH, energy source for a reproductive signal
73
New cards
prokaryotic cells
-single celled organisms
-circular DNA
- exponential growth
-circular DNA
- exponential growth
74
New cards
origin of replication in Prokaryotic Cell
- only one
- used to pull the chromosome to once side of the cell and splits the DNA
- used to pull the chromosome to once side of the cell and splits the DNA
75
New cards
Eukaryotic cell division/ check points
G1, synthesis, G2, metaphase
- cannot pass to another checkpoint without passing the previous one
- cannot pass to another checkpoint without passing the previous one
76
New cards
G1 phase/ synthesis
Growth and synthesis of DNA
77
New cards
G2 phase
ask: is all the DNA replicated?
more growth and development
more growth and development
78
New cards
metaphase
ask: are all the chromosomes aligned?
mitosis and cytokinesis occur
mitosis and cytokinesis occur
79
New cards
cyclin dependent kinase
protein required to progress through each checkpoint
adds phosphate groups to Rb (tumor suppressor gene)
adds phosphate groups to Rb (tumor suppressor gene)
80
New cards
unphosphorylated Rb
- active
- blocks DNA synthesis
- no phosphate groups are attached
- blocks DNA synthesis
- no phosphate groups are attached
81
New cards
phosphorylated Rb
-inactive
- DNA is synthesized
- phosphate groups are attached
- DNA is synthesized
- phosphate groups are attached
82
New cards
cancer
constant phosphorylation can cause constant replication and unwanted growth (tumor/retinoid blastoma)
83
New cards
oncogenes
promotes cancer
example: HER 2 receptors are hyperactive which causes breast cancer
example: HER 2 receptors are hyperactive which causes breast cancer
84
New cards
mitosis
cell division resulting in two daughter cells with the same DNA as the parent cell
85
New cards
DNA packaging
each strand of DNA wraps around a histones (protein complex) in a tight coil to form a chromosome
86
New cards
centromere
a specialized condensed region of each chromosome that appears during mitosis where the chromatids are held together to form an X shape
87
New cards
cohesion
proteins that hold sister chromatids together
88
New cards
interphase of Mitosis
G1, S, G2
cell is growing
cell is growing
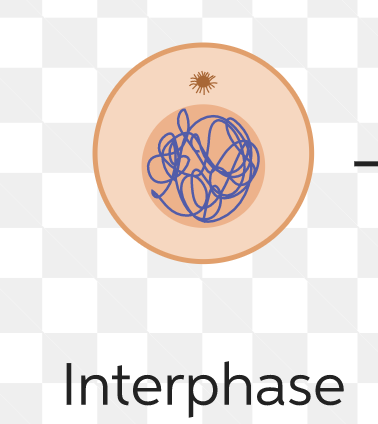
89
New cards
centrosome
microtubule organization center
a cell in interphase has one centrosome
centrosomes double in the G2 phase
a cell in interphase has one centrosome
centrosomes double in the G2 phase
90
New cards
prophase
microtubule spindles form
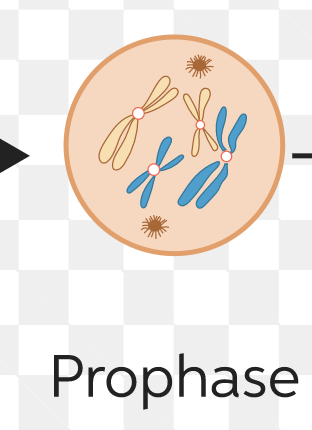
91
New cards
prometaphase
nuclear membrane breaks down
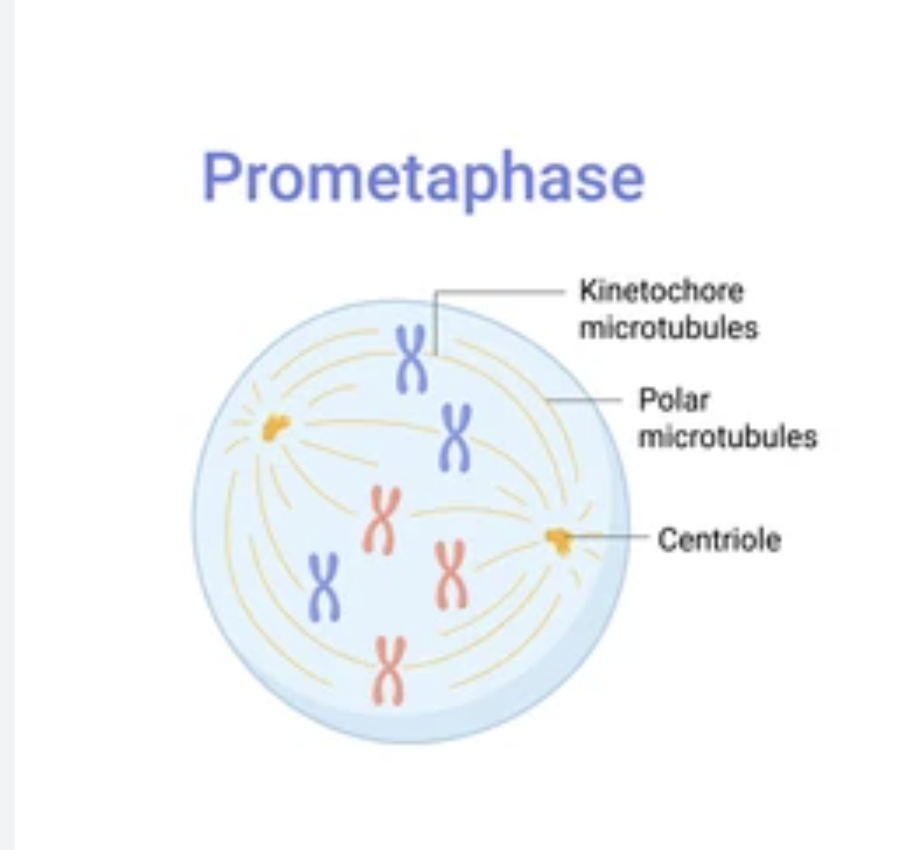
92
New cards
metaphase
chromosomes line up at metaphase plate
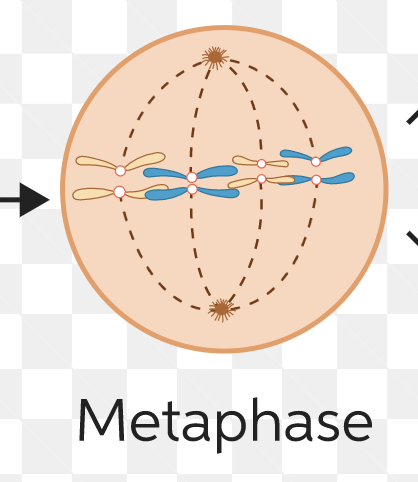
93
New cards
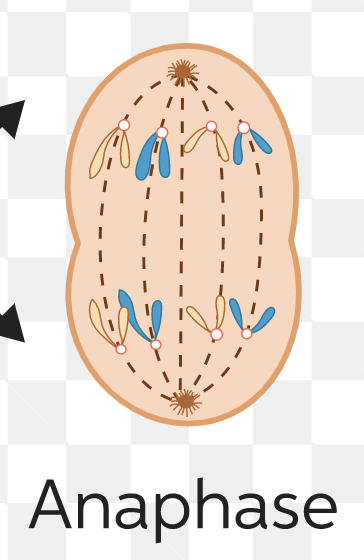
anaphase
separating of sister chromatids
94
New cards
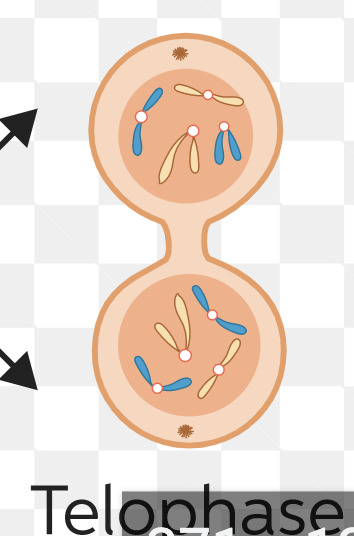
telophase
-nuclear envelope reforms
-chromosomes de-condense
-triggers cytokinesis
-chromosomes de-condense
-triggers cytokinesis
95
New cards
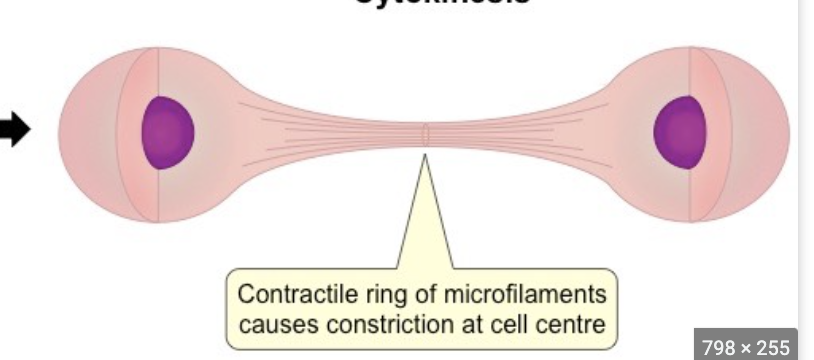
cytokinesis
pulls membranes together to split into two cells
- uses myosin and actin filaments
- uses myosin and actin filaments
96
New cards
separase
cleaves the proteins that hold the sister chromatids together
97
New cards
meiosis
generates gametes (egg or sperm cells)
cells are not identical to the parent cell
cells are not identical to the parent cell
98
New cards
somatic cells
any other cell in the body not including sex cells
2 sets of chromosomes, diploid (2n)
2 sets of chromosomes, diploid (2n)
99
New cards
how many chromosomes do humans have?
- 46 chromosomes, 23 pairs
22 autosomes, 1 pair of sex chromosomes
22 autosomes, 1 pair of sex chromosomes
100
New cards
gametes
sex cells
1 set of chromosomes, haploid cells
1 set of chromosomes, haploid cells