biology midterm thingies
1/113
Earn XP
Description and Tags
bio bio I hate bio. This has as much as I can put into it from notes from others and some of my own.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
Carbohydrates: Function
Immediate sources of energy
Carbohydrates: Elements
C, H, O
Carbohydrates: Monomer
Monosaccharide - C6H12O6
Carbohydrates: Polymer
Disaccharide/Polysaccharide
Carbohydrates: Functional Group
Hydroxyl
Carbohydrates: Identifying Characteristics
CH2O formula
Carbohydrates: Type of Bond
Glycosidic Bond
Lipids: Function
Store energy, makes up cell membrane, chemical messengers
Lipids: Elements
C, H, O
Lipids: Monomers
Fatty acid and glycerol
Lipids: Polymer
Diglycerides and triglycerides
Lipids: Functional Groups
Hydroxyl (Glycerol) and Carboxyl (Fatty Acids)
Lipids: Identifying Characteristics
Nonpolar and does not dissolve in water
Lipids: Type of Bond
Ester Bonds
Lipids: Unsaturated
One or more double bonds between two carbons
Lipids: Saturated
Maximum number of hydrogens (All single bonds between carbons)
What are lipids found in??
Oil, Fat, Wax
Proteins: Function
Carry out/catalyze chemical reactions, transport molecules, fight diseases, restore/repair tissue, make up body parts
Proteins: Elements
C, H, O, N, Sometimes S
Proteins: Monomers
Amino Acid
Proteins: Polymers
Polypeptide
Proteins: Functional Groups
Amino group and Carboxyl Group
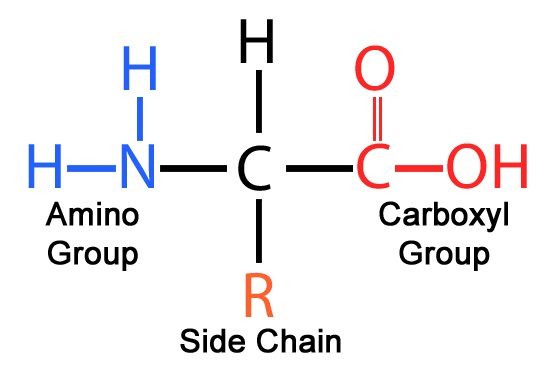
Proteins: Identifying Characteristics
Nitrogen is present
What are proteins found in??
Meat, eggs, and beans
Protein: Type of Bond
Peptide Bonds
Nucleic Acid: Function
Store and transmits genetic information
Nucleic Acid: Elements
C, H, O, N, P
Nucleic Acid: Monomers
Nucleotides
Nucleic Acid: Polymers
Nucleic Acid (DNA & RNA)
Nucleic Acid: Functional Group
Phosphate group, Amino group, hydroxyl group
Nucleic Acid: Identifying Characteristics
Phosphate group, 5 carbon rings, and nitrogen in the rings
Where are Nucleic Acids found??
Cells
Nucleic Acid: Type of bond
Posphodiester Bond
Nucleic Acid: Nitrogenous bases
Adenine, Guanine, Thymine, Cytosine, Uracil
Meaning of “Bio”
Living
Meaning of “Molecule”
Combination of atoms
What do all organic biomolecules have??
C-H Bonds
What are the four biomolecules?
Lipids, Carbohydrates, Nucleic Acid, and Proteins
Characteristics of Life
Grow and Develop, use energy, reproduce, composed of cells, respond to environment, adapt to change.
How many valence electrons does Carbon have, and how many more to be stable?
Carbon has 4 valence electrons and needs 6 more to be stable
What are the four Functional Groups?
Hydroxyl, Carboxyl, Amino Group, Phosphate Group
What are Monomers?
Smaller units of building blocks
What are Polymers?
Large molecules made by joined monomers
What is Polymerization?
The process of monomers becoming polymers
What is Dehydration Synthesis?
When molecules bond through the removal of water
On molecule gets -OH removed and the other has -H removed
What is Hydrolysis?
A molecule is broken through the addition of water.
H2O is added to separate.
What are Enzymes?
An Organic catalyst, usually a protein, that speeds up reactions in cells due to its particular shape
What is a Catalyst?
A substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction without being changed
What is a Substrate?
The reactant molecule that an enzyme works on
What is the Active Site?
The part of an enzyme where the substrate binds
How do enzymes speed up reactions?
They lower the activation energy of a reaction (the amount of energy required for a reaction to occur)
They bind the substrate in a way that allows the reaction to happen more efficiently
Factors that affect enzyme activity:
Temperature
pH levels
Concentration
Sub-optimal conditions can cause the Enzyme to lose the ability to bind with a substrate
Do Enzymes prefer higher or lower temperatures?
Generally higher temperatures, but too high temperatures can cause the enzyme to denature
What happens when an Enzyme denatures??
The enzyme’s active site loses its specific shape that allows it to bind to substrates
How does Enzyme Concentration affect reaction rates??
Generally, it will speed up the reaction but if there are too many enzymes and not enough substrate, the reaction rate will not really be affected.
Enzyme Inhibitors
Enzyme inhibitors bind to enzymes to decrease activity
Noncompetitive Inhibitor:
Inhibitor binds to the enzyme at a place other than the active site. This changes the enzyme so it is no longer able to bind to substrates
Competitive inhibition:
Inhibitor and substrate compete for the same active site of an enzyme, slowing the amount of product produced.
Phospholipid Bilayer:
The phospholipids in a cell membrane
The head of the phospholipid is hydrophilic and the tails are hydrophobic
Channel Proteins:
Trans-membrane proteins that are hydrophilic which allows specific Ions and molecules to pass through by facilitated diffusion
Carrier Proteins:
Trans-Membrane proteins that facilitate the transport of specific molecules
Diffusion:
Movement of a molecule from a high concentration area to a low concentration area
Concentration gradient:
The difference in concentration in two areas
Facilitated Diffusion:
A type of passive transport that moves large or charged molecules from high to low concentration using carrier or channel proteins but not using energy
Aquaporin:
Proteins that form pores in cell membranes to facilitate rapid passage of water
Osmosis
The movement of solvent (usually water) across a semipermeable membrane from a low solute concentration to a high solute concentration
Isotonic Solution:
Some solute concentration in a cell, no movement
Hypotonic solution
More solvent and less solute in a solution than another solution
Hypertonic solution
Higher solute concentration than another solution
Turgor Pressure:
Outward pressure by a fluid inside a plant cell against its own cell wall
Active Transport:
Movement of Ions and Molecules using enzymes and energy
Sodium-Potassium Pump:
A membrane protein that uses ATP energy to move three sodium Ions and two potassium ions against their concentration gradients
Bulk Transport:
Moving large substances across a cell membrane using membrane bound vesicles
Endocytosis:
Active transport where cell membranes engulfs external substances and forms vesicles
Exocytosis:
When a cell expels substances out of the cell by fusing a vesicle to the plasma membrane
Phagocytosis
When a cell “eats” large particles to consume and digest them
Pinocytosis:
A type of endocytosis where a cell takes in small amounts of extracellular fluid and dissolved solutes by forming a vesicle
Homeostasis:
Biological process of maintaining a stable internal environment against external forces
Negative Feedback:
When a body counteracts changes to maintain Homeostasis
Positive Feedback
A process that amplifies an initial stimulus
What is ATP - Adenosine Triphosphate
Usable energy for all cells
Active transport
Muscle Contraction
Cell signaling
What does the cell do when it needs energy from ATP?
The bond between the 2nd and 3rd phosphate groups on ATP is broken
Energy for cells is released
ADP is produced
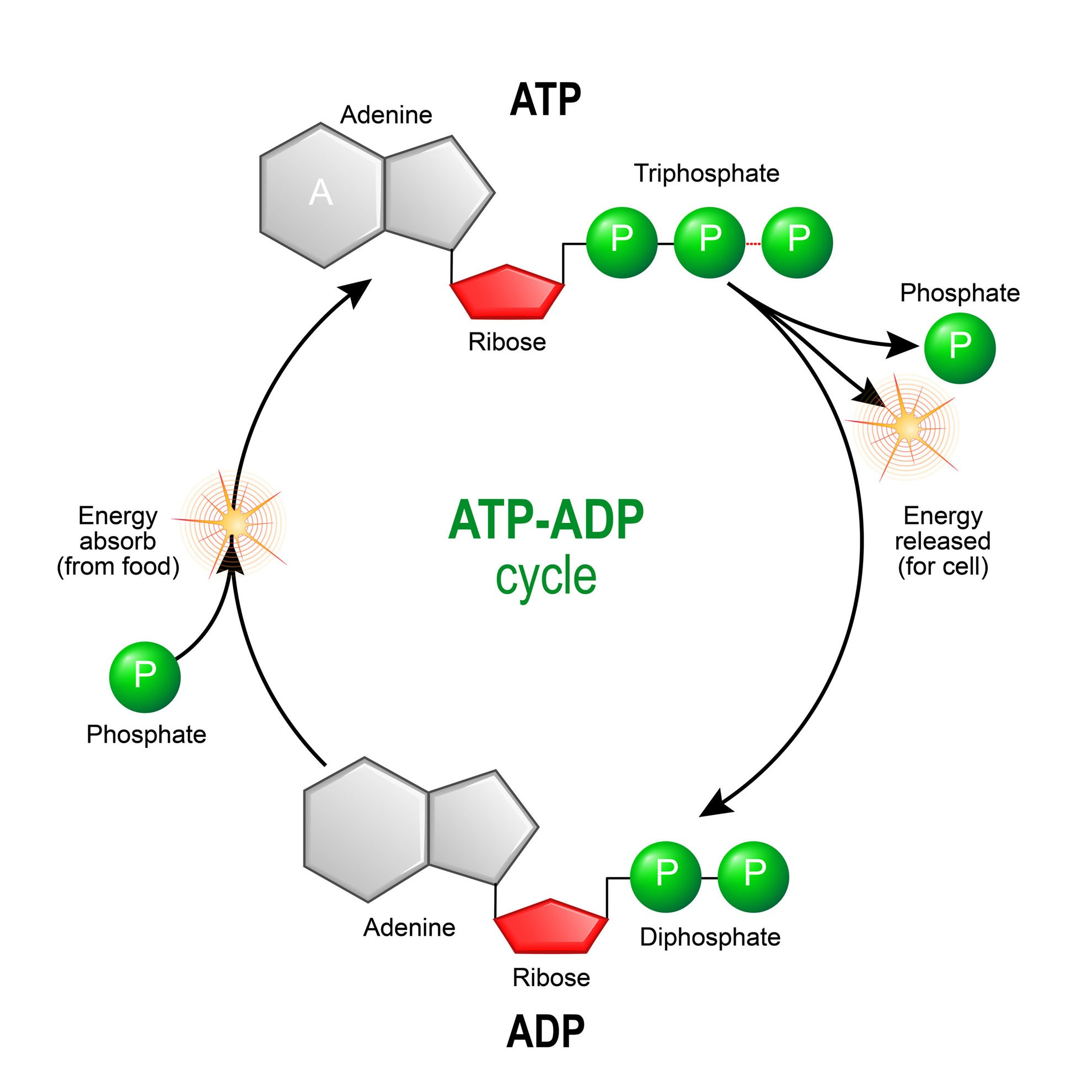
How is ATP replenished?
Cells use cell respiration to reattach a phosphate group to ADP turning it into ATP
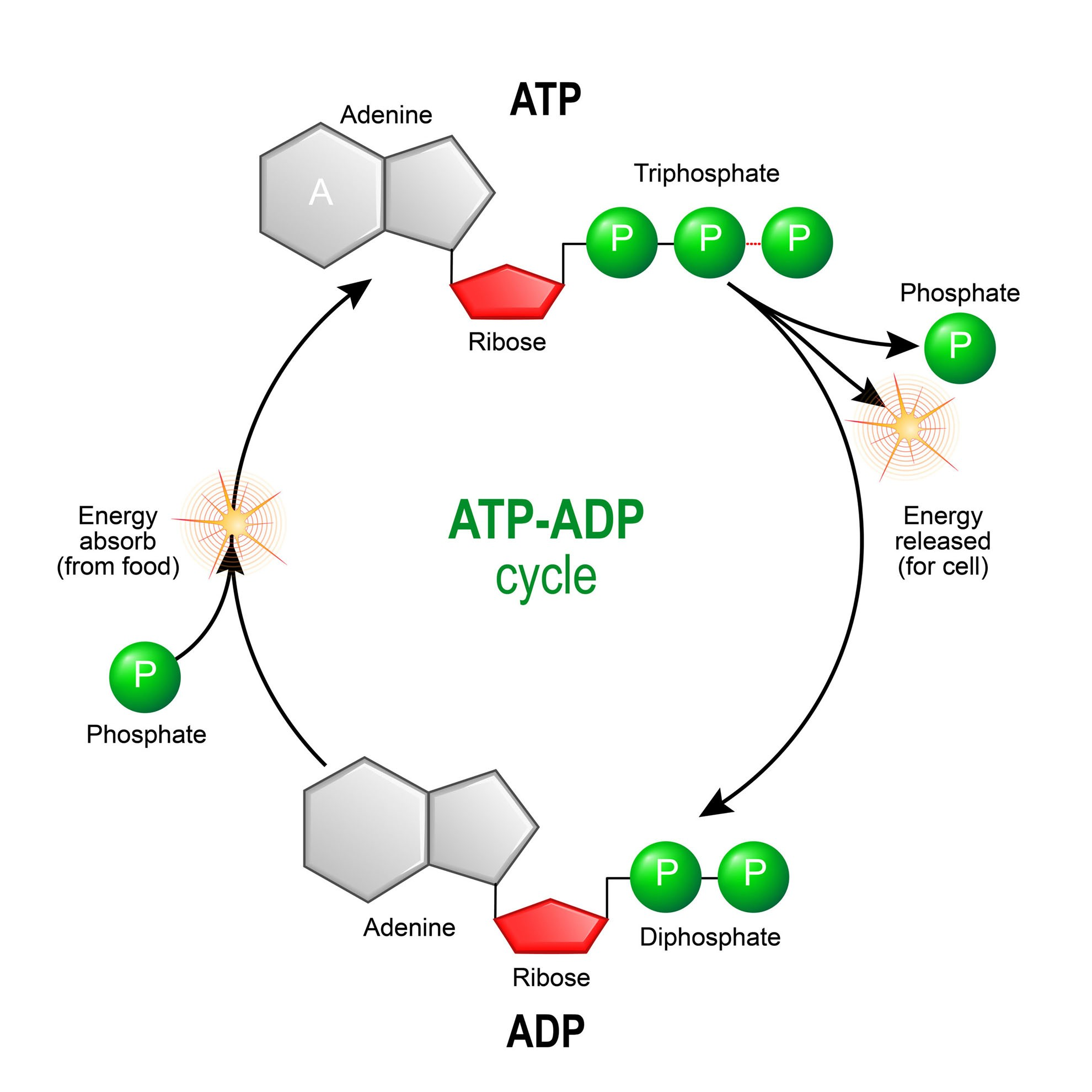
Where do cells get the energy required to turn ADP into ATP?
Converting glucose into energy using Aerobic or Anaerobic cellular respiration
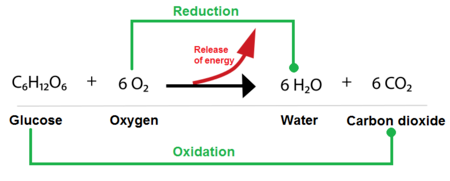
Cellular Respiration Redox reaction:
C6H12O2 + O2 = 6CO2 + 6H2O
What do NADH and FADH2 do?
They carry electrons and release them in the last step of Cellular Respiration
They turn into FAD and NAD+ after they lose their electron (Oxidized)
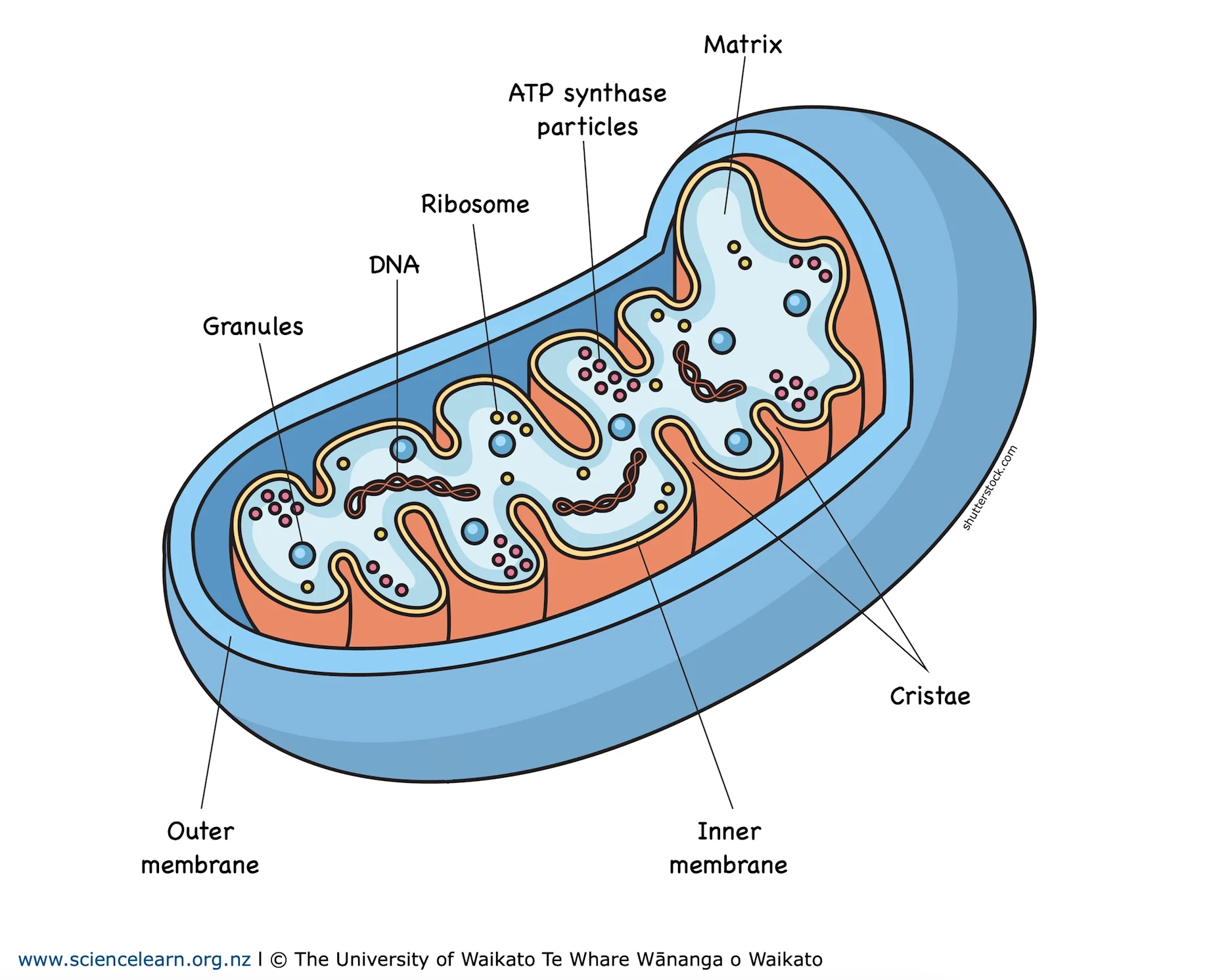
Four Mitochondrial Structures:
Outer Membrane
Phospholipid Bilayer, regulates what enters and exits the cell
Inner Membrane
Contains protein channels for H+ Ions and ATP production, freely permeable to oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water
Cristae: Folds of inner membrane, increases surface area between matrix and membrae
Intermembrane space
Region between the inner membrane and outer, important for oxidative phosphorylation
Matrix
Innermost region of the mitochondria, location of prep reactions and Krebs cycle
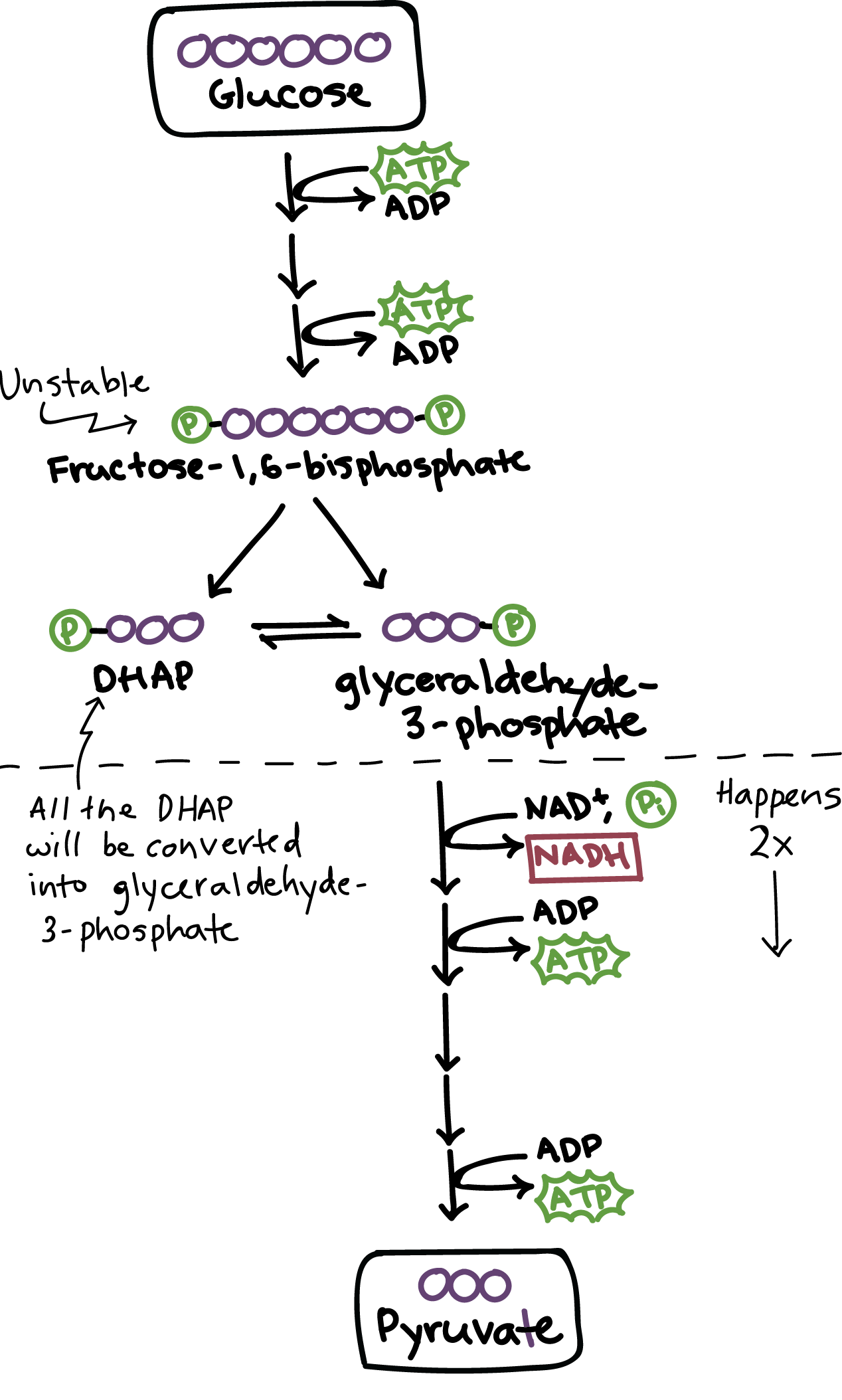
Glycolysis (Both Anaerobic and Aerobic Resp)
Occurs in cytoplasm
Energy investment steps
2 ATP are used to convert glucose into molecules of G3P
Energy harvesting steps
G3P is oxidized, creating NADH and 2ATP
Ending molecule is pyruvate
Happens 2X (once for each G3P)
Inputs: Glucose, 2 NAD+, 2 ATP
Outputs: 2 Pyruvate, 2 NADH, 2 ATP
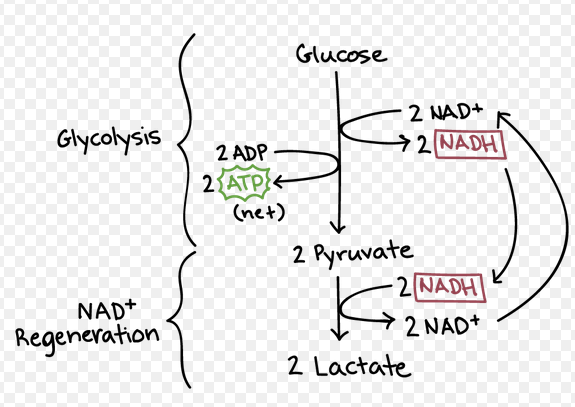
Fermentation (Anaerobic Resp)
In animal cells and some bacteria cells
Pyruvate is reduced to form lactic acid
NADH is converted to NAD+ to be reused in glycolysis
In yeast, plants, and some bacteria cells:
Pyruvate is reduced to form alcohol and CO2
NADH is converted to NAD+ to be reused in glycolysis
Fermentation requires NO extra ATP
Main goal is to replenish NAD+for glycolysis
Prep Reactions/Pyruvate Oxidation (Aerobic Resp)
Occurs in the matrix of mitochondria
Each pyruvate molecule (2) from glycolysis is oxidized, producing NADH and CO2
The remaining acetlyl group attaches to the input of coenzyme A (COA) to produce acetyl-COA
Outputs of this step are used as inputs in the remaining steps
Inputs: 2 pyruvate, 2 COA, 2 NAD+
Outputs: 2 acetyl-COA, 2 NADH, 2 CO2
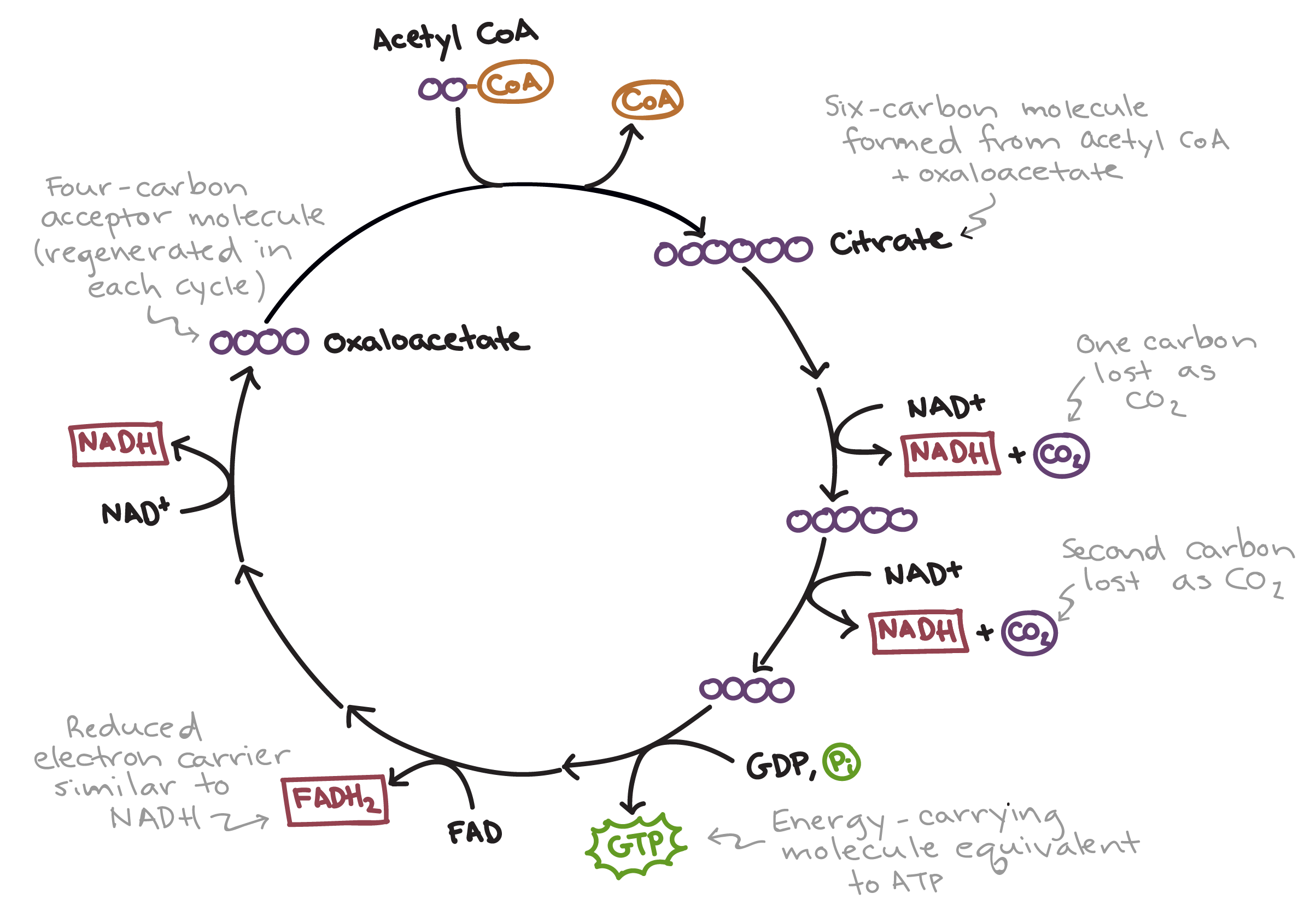
Krebs Cycle (Aerobic Resp)
Occurs in matrix of mitochondria
Acetyl-COA joins with oxaleacetate (a 4-carbon molecule) to form citric acid
Citric acid is broken down in several steps releasing 2 CO2, 3 NADH, 1 FADH2, and 1 ATP
Oxaleacetate is regenerated, ready to join with another acetyl-COA so the cycle can repeat
The Krebs Cycle happens 2X per Glucose molecule
Main goal is to genereate NADH and FADH2 which carry high-energy electrons to the electron transport chain (ETC)
Inputs: 2 acetyl-CoA, 6 NAD+, 2 FAD, 2 ADP, oxaloacetate
Outputs: 4 CO2, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2, 2 ATP, oxaloacetate
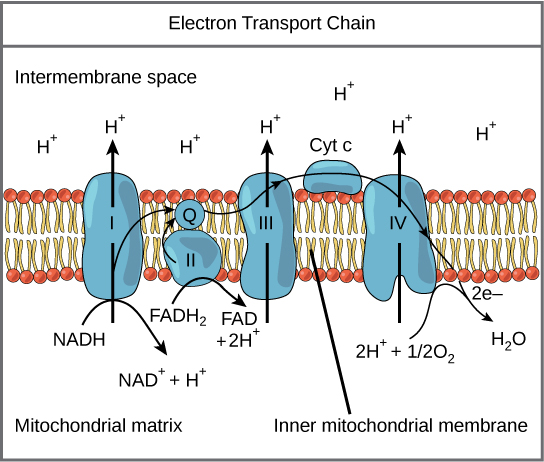
ETC and Chemiosmosis
Occurs in the inner membrane of the mitochondria
NADH and FADH2 give their electrons to protein complexes embedded in the inner membrane
As electrons move from one protein to another, they release energy
Energy is used to pump protons (H+ ions) across the membrane from the mitochondrial matrix into the intermembrane space, creating a proton gradient
At the end of the chain, electrons combine with oxygen and H+ ions to form water
Chemiosmosis: The built up H+ ions flow back through an enzyme called ATP synthase, producing high amounts of ATP
Inputs: 2 FADH2, 10 NADH, 32-34 ADP, 6 O2
Outputs: 6 H2O, 10 NAD+, 2 FAD, 32-34 ATP
Photosynthesis:
The process in which light energy is converted into chemical energy
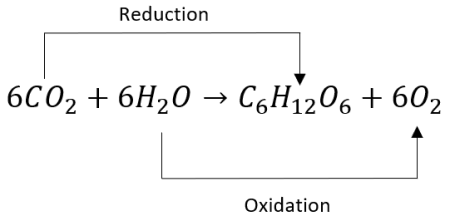
Photosynthesis redox reaction
6CO2 + 6H2O = C6H12O6 + 6O2
Autotrophs
Organisms that can make their own organic compounds for food
Photoautotrophs
Organisms that do photosynthesis
Heterotrophs
Organisms that cannot make their own organic molecules and have to consume other organisms for food
Effects of Photosynthesis on Atmosphere
Generates Oxygen and removes carbon dioxide
Where does photosynthesis occur??
Palisade mesophyll cells are the primary site of photosynthesis and spongy mesophyll has air spaces for gas exchanges
Vascular Tissues:
Xylem
Vascular tissue in plants that transport water from the roots up to the leaves and other parts of the plant
Xy to the Sky!
Ploem
Vascular tissue in plants that transport sugars and other nutrients from where they are made (usually in leaves) to other parts of the plant
Phlo to the floor