PAS 604 Medically Important Parasites & Fungi
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
126 Terms
non-mutual relationship between species
where one species (the parasite)
benefits and or survives
at the expense of the other (the host)
What is a parasite?
- Stool ova and parasite (O&P)
- Antigen serology
- Molecular/genetic identification
What testing is done for parasites?
- Wet mount
- Trichrome stain
What is looked at in a Stool ova and parasite (O&P) test>
- PCR
- NAAT
What are examples of molecular/genetic identification testing for parasites?
Amoebiasis
What disease does Entamoeba histolytica (ameba) cause?
- asymptomatic intestinal colonization
- invasive intestinal colitis (amebic dysentery
- invasive extra-intestinal forms (liver or pleuropulmonary abscesses)
What are the three forms of Amoebiasis?
Human reservoir - chronic carriers
What is the habitat of Entamoeba histolytica (ameba)?
Ingestion from fecal contaminated food, water, hands, or sexual contact
How is Entamoeba histolytica (ameba) transmitted?
stool O&P for cysts, serologic (EIA, PCR, GI pathogen panel)
How is Entamoeba histolytica (ameba) diagnosed?
Entaomeba histolytica
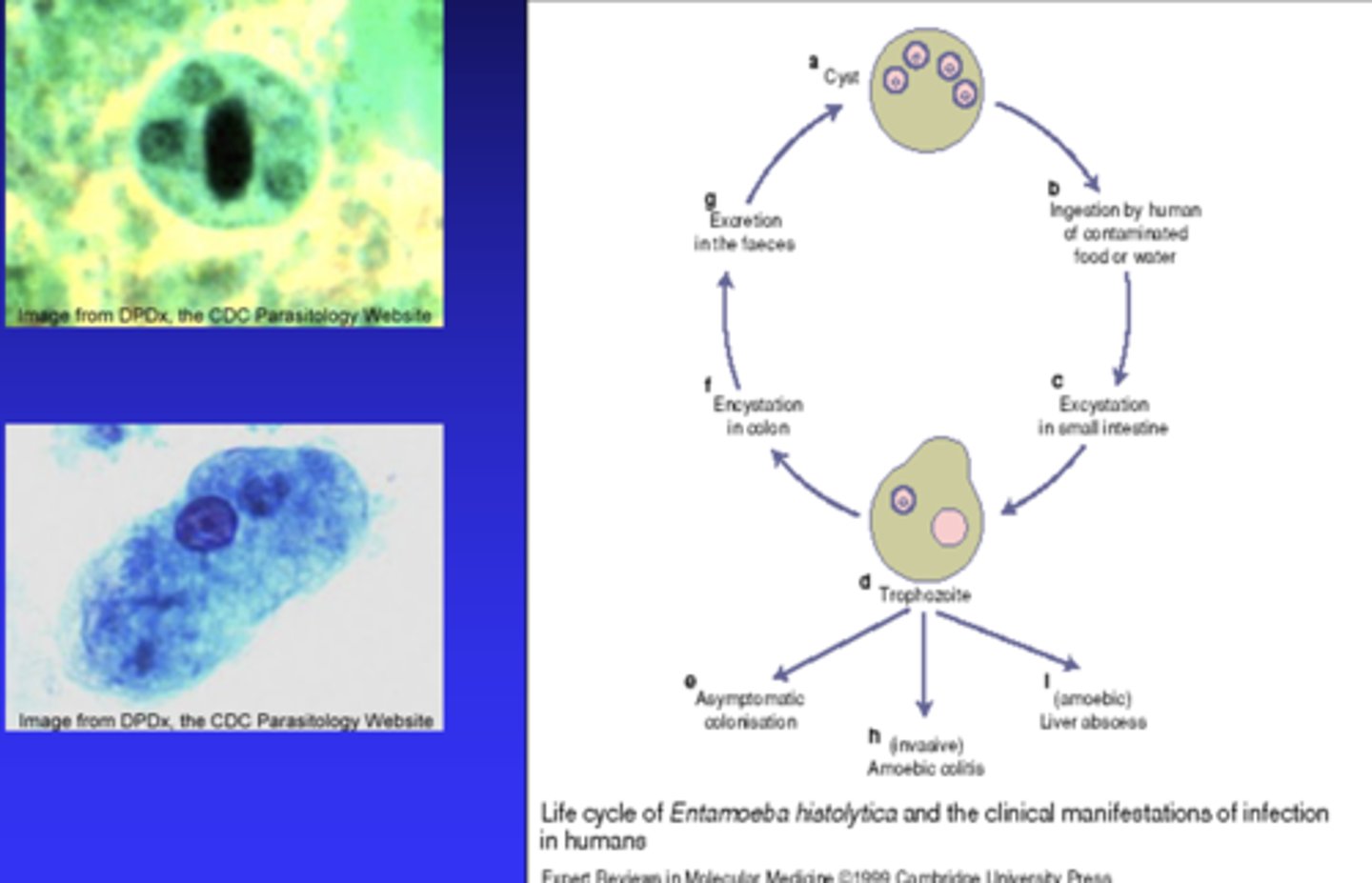
Giardiasis
What disease does Giardia Lamblia (flagellate) cause?
Incubation 1-14 days, sudden onset watery diarrhea, GI symptoms - abd pain/N/V/D
What are the symptoms of giardiasis?
Giardiasis
What is the most common diagnosed parasitic intestinal disease in the US?
- freshwater streams, daycare outbreaks
What is the habitat of Giardia Lamblia?
- Cyst ingestion from fecal contaminated food or water
- Animal reservoirs (cats, dogs, deer, beavers), person - person
How is Giardia Lamblia transmitted?
stool O&P; serologic Giardia antigen by ELISA or DFA, PCR available to speciate subtypes
How is Giardia Lamblia diagnosed?
Cryptosporidiosis
What disease does Cryptosporidium parvum (sporozoan) cause?
- asymptomatic/mild in immunocompetent host
- watery diarrhea m/c symptom
- severe GI symptoms immunocompromised
- infect intestinal epithelium - wt loss/abd pain, N/V/fever
What are the symptoms of Cryptosporidiosis?
- cyst ingestion from fecal contaminated food or water
What is the habitat of Cryptosporidium parvum?
- domestic or farm animals, person-person at the POOL
How is Cryptosporidium parvum transmitted?
modified Acidfast stain (Kinyon), serologic antigen detection by ELISA, PCR testing available
How is Cryptosporidium parvum diagnosed?
Cryposporidium
What is the leading cause recreational water related disease outbreaks?
Trichomoniasis
What disease does Trichomonas Vaginalis casue?
- Vaginitis/cervicitis
- purulent d/c, pain, dyspareunia
- urethritis, epididymitis, prostatitis
What are symptoms of Trichomoniasis?
Humans only known host
What is the habitat for Trichomonas Vaginalis?
sexual contact or via birth canal in infants
How is Trichomonas Vaginalis transmitted?
- DNA probe, PCR, NAAT (high sensitivity)
How is Trichomonas Vaginalis diagnosed?
Malaria
What disease does Plasmodium species (falciparum, vivax, ovale, malariae) cause?
- Travel hx important in endemic areas!!!
- Fever/chills, malaise, myalgia's, anemia, splenomegaly - depend on species and patient immune status
What are symptoms of malaria?
infected female anopheles mosquito bite, infected blood contaminated needles, blood transfusions, congenital transmission
What is the habitat of Plasmodium species (falciparum, vivax, ovale, malariae)?
migrate to liver and invade RBCs
How is Plasmodium species (falciparum, vivax, ovale, malariae) transmitted?
- Thin/thick blood smears - detection via Giemsa staining (purple top tube)
- RDT's (rapid diagnostic tests) by serologic antigen detection available but need confirmation by microscopy
How is Plasmodium species (falciparum, vivax, ovale, malariae) diagnosed?
Babesiosis
What disease does Babesia microti cause?
- Most cases asymptomatic
- similar to malaria- fever/chills, myalgia's, fatigue, hepatosplenomegaly
What are the symptoms of Babesiosis?
2 hosts - tick & rodent needed to reproduce - human dead-end host
What is the habitat of Babesia microti?
- bite from infected Ixodes scapularis tick
- blood transfusion
How is Babesia microti transmitted?
Thin/thick blood smears, serologic antibody detection IFA or IgM antibody titers, molecular diagnosis by PCR
How is Babesia microti diagnosed?
Toxoplasmosis
What disease is caused by Toxoplasma gondii?
- Manifest in body fluids, brain, eye and muscles
- Immunocompetent infection asymptomatic or benign, severe in immunocompromised or congenital
What are the symptoms of Toxoplasmosis?
distributed worldwide in vertebrates, definitive host/reservoir common house cat/other felines-
What is the habitat of Toxoplasma gondii?
feces contamination, transplacental transmission, or blood transfusion
How is Toxoplasma gondii transmitted?
- serologic testing IgG /IgM antibodies, new fluorescent stains for direct detection (IFA)
- PCR in blood, CSF, amniotic fluid
How is Toxoplasma gondii diagnosed?
Chagas Disease -American Trypanosomiasis
What disease is caused by Trypanosoma cruzi?
- Found in the Americas, endemic in Latin America, increasing incidence in US
- Acute/chronic infections may be asymptomatic result in cardiac/intestinal complications
What are the symptoms of Chagas Disease -American Trypanosomiasis?
Vector borne from triatomine insects
What is the habitat of Trypanosoma cruzi?
- Vector borne from triatomine insects (kissing bugs) biting human faces, blood or organ transfusion, congenital transmission
How is Trypanosoma cruzi transmitted?
- Acute - Giemsa stained blood smears
- Chronic - serologic detection of T. cruzi (ELISA, IFA) and PCR for congenital cases
How is Trypanosoma cruzi diagnosed?
Chagas Disease -American Trypanosomiasis
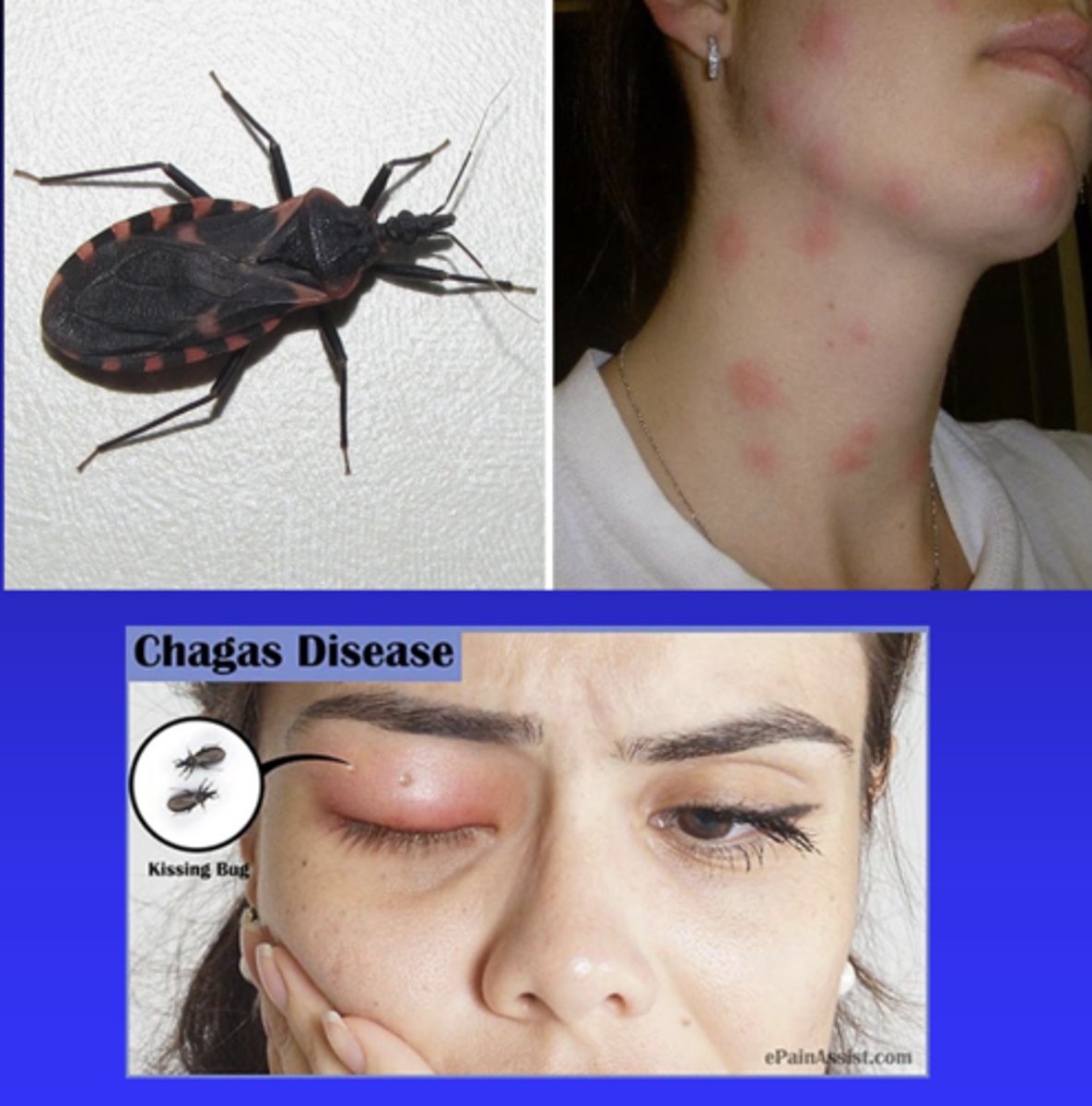
- Taeniasis
- Cysticercosis
What disease do Cestodes (flatworms/tapeworms) cause?
- Taenia saginata (beef)
- Taenia solium (pork)
What are the types of cestodes (tapeworms) and where do they come from?
intestinal - asymptomatic or mild GI symptoms w/passage of proglottids (from ingestion of adult form in pork/beef as cysterci) GB complications due to migration of parasite
What are the symptoms of Taeniasis?
(extraintestinal)- T. solium only - infection by larval cysts due to ingestion of eggs from contaminated feces. Burrow into blood, travel into muscle, brain, eye and form cysticerci - cause seizures, HA
What are the symptoms of Cysticercosis?
flatworms, tapeworms
What are cestodes?
roundworms
What are nematodes?
ingestion of infected undercooked meat containing adult tapeworm
How is taeniasis transmited?
ingestion of T. solium eggs from contaminated food/water or fecal-oral route
How is Cystercercosis transmited?
- Stool O & P (proglottids may be seen in stool)
- serologic antibody testing of tissue, blood or muscle biopsy
- PCR testing
- MRI/CT scan of brain for neurocystercercosis
How are cestodes diagnosed?
only T. solium
What causes Cysticercosis?
Both T. solium and T. saginata
What causes Taeniasis?
Taenia solium
What casues Neurocysticercosis?
Diphyllobothriasis
What disease does Diphyllobothrium latum cause?
Diphyllobothrium latum (30 feet)
What is the largest human tapeworm?
- Most infections asymptomatic/long lasting
- Abdominal pain, V/D, weight loss
- Resides in small intestine
What are symptoms of Diphyllobothrium latum?
Vit B12 deficiency, intestinal obstruction, GB disease (proglottids migrate)
What are complications of Diphyllobothrium latum?
freshwater fish
What is the habitat of Diphyllobothrium latum?
ingestion of raw or undercooked freshwater fish
How is Diphyllobothrium latum transmitted?
- Molecular PCR
- Eggs or segments of tapeworm in stool
How is Diphyllobothrium latum diagnosed?
Roundworms, Hookworms, Pinworms, Threadworms
What are nematodes?
hookworms
What are Necatur Americanus, Ancylostoma duodenale?
Itching/rash @ infection site, range from asymptomatic to mild diarrhea/abd pain can progress to anemia (IDA), delayed growth & development
What are the symptoms of hookworm disease?
humans sole host/no person-person
What is the habitat of hookworms?
- contact w/soil contaminated w/human feces through bare feet or ingesting contaminated soil
- larvae forms infective (children at high risk)
- larvae migrate to lungs, coughed up, swallowed to small intestine , attach to wall and suck blood
How are hookworms transmitted?
stool O&P for detection of eggs, earlier detection with ELISA antigen availability
How are hookworms diagnosed?
roundworms
What are Ascaris lumbricoides?
Ascariasis
What disease is caused by Ascaris lumbricoides?
- Intestinal w/abdominal pain - may cause obstruction in small intestine OR
- Pulmonary manifestation as pneumonia
What are the symptoms of Ascariasis?
humans sole host
What is the habitat of Ascaris lumbricoides?
1. Enterobius vermicularis (pinworm)
2. Ascaris lumbricoides (roundworms)
What is the most common type of parasite in humans?
ingestion of eggs in soil contaminated with human feces, they hatch and enter blood circulation and travel to lungs, coughed up and re-enter intestines for maturation
How is Ascaris lumbricoides transmitted?
- stool O&P for detection of eggs
- early detection with ELISA antigen availability
How is Ascaris lumbricoides diagnosed?
Enterobiasis
What disease is caused by Enterobius vermicularis?
- ingestion of eggs fecal oral route with reinfection & family exposure common
How is Enterobius vermicularis transmitted?
humans only host
What is the habitat of Enterobius vermicularis?
- Scotch tape test
- worms visible in stool or perianal area
- Serology not available
How is Enterobius vermicularis diagnosed?
pruritis ani
What are the symptoms of Enterobiasis?
Strongyloides stercoralis
What causes threadworm disease?
Strongyloidiasis
What disease is caused by Strongyloides stercoralis?
- GI - abd pain/diarrhea
- Pulmonary manifestations, lead to septicemia
What are the symptoms of Strongyloidiasis?
soil contaminated by feces via direct skin penetration into bloodstream to lungs, coughed up and swallowed into GI tract
How is Strongyloides stercoralis transmitted?
stool O&P for larval forms - examine stool for adult worms, antibody detection by EIA
How is Strongyloides stercoralis diagnosed?
Humans, cats, dogs as definitive hosts
What is the habitat of Strongyloides stercoralis?
yeast and mold
What are the two forms of fungi?
fungi
_______ are dimorphic
yeast form in one environment mold form in another (due to variances of CO2 and temperature)
What does dimorphic mean?
- superficial mycoses (opportunistic)
- deep mycoses (systemic infections)
What are skin fungal infection types?
true pathogens (can infect healthy & immunocompromised)
What are deep mycoses?
opportunistic pathogens (only infect immunocompromised
What are superficial mycoses?
Candidiasis
What disease is caused by candida species?
albicans, tropicalis, glabrata
What are common Candida species?
- Thrush (mouth), vaginitis (F), balanitis (M)
- can become systemic (need blood cultures)
What are the symptoms of candidiasis?