Protein maturation, Point mutations, DNA repair, & HGT
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:39 PM on 11/8/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
1
New cards
Most proteins need to
fold
2
New cards
Proteins may undergo
chemical modification, or cleavage
3
New cards
Proteins can translocated...
translocated into the periplasmic space
4
New cards
Proteins may be
secreted outside of the cell entirely
5
New cards
Mutations can be caused by __ or __
intrinsic processes (spontaneous) or external mutagens (induced)
6
New cards
Spontaneous mutations
caused by mistakes in the process of DNA replication
7
New cards
Induced mutation
caused by exposure to mutagens - chemical agents or radiation; mutagens exposure can increase the rate of mutation more than 1000-fold
8
New cards
chemical mutagens:
nucleoside analogs, modifying agents, intercalating agents
9
New cards
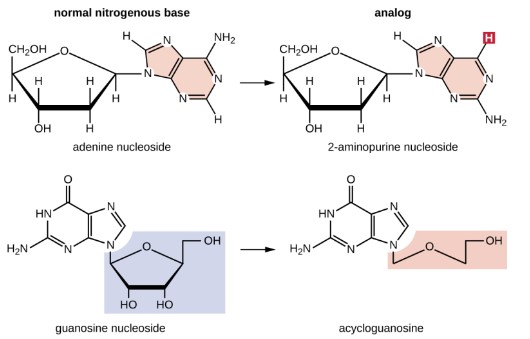
Nucleotides analog
are structurally similar to normal nucleotide bases and can be incorporated into DNA during replication. These base analogs induce mutations bec. they often have different base-pairing rules than the bases they replace
10
New cards
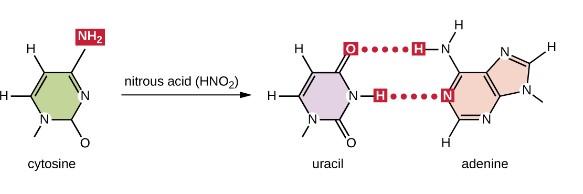
Modifying agents
modify normal DNA bases, resulting in different base-pairing rules deaminates GC base pair to an AT
11
New cards
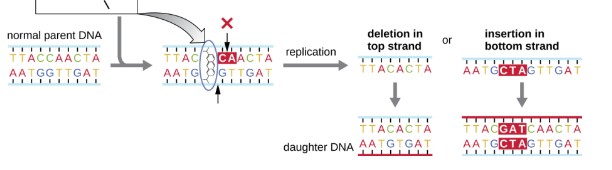
Intercalating agents
slide between the stacked nitrogenous bases of the DNA double helix, distorting the molecule and creating atypical spacing between nucleotide base pairs. This results in DNA polymerase either skipping several nucleotides (creating a deletion) or inserting extra nucleotides (creating an insertion) -> frameshift mutation
- shorten words
- bc
- own interpretation
- shorten words
- bc
- own interpretation
12
New cards
Silent mutation
due to degeneracy of the genetic code, a point mutation will commonly result in the same amino acid being incorporated into the resulting polypeptide despite the sequence change
13
New cards
Missense mutation
results in a different amino acid being incorporated into the resulting polypeptide. The effect of a missense mutation depends on how chemically different the new amino acid is from the wild-type amino acid and location
14
New cards
Nonsense Mutation
converts a codon encoding an amino acid (a sense codon) into a stop codon (a nonsense codon); this results in shortened proteins typically not functional
15
New cards
Frameshift mutation
results from insertion or deletion of 1 or 2 base pairs in the coding region of gene; can change every amino acid after the point of the mutation. The new reading frame may also include a stop codon before the end of the coding sequence; resulting proteins nearly always nonfunctional
16
New cards
Conditional mutants only have
phenotype under some conditions
17
New cards
Auxotrophic mutants are
unable to make a specific biomolecule - eg amino acid
18
New cards
how does Ames Test work?
two test tubes 1 control and other with mutagen, look at how much grows
19
New cards
What does it Ames test prove?
looks at how the end result is metabolized by the rat liver enzymes
20
New cards
The Ames Test
is a method that uses bacteria for rapid, inexpensive screening of the
carcinogenic potential of new chemical compounds. Measures the mutation rate associated with
exposure to the compound, which, if elevated, may indicate that exposure to this compound is
associated with greater cancer risk. Because many chemicals are not directly mutagenic but are
metabolized to mutagenic forms by liver enzymes, rat liver extract is commonly included at the
start of this experiment to mimic liver metabolism.
carcinogenic potential of new chemical compounds. Measures the mutation rate associated with
exposure to the compound, which, if elevated, may indicate that exposure to this compound is
associated with greater cancer risk. Because many chemicals are not directly mutagenic but are
metabolized to mutagenic forms by liver enzymes, rat liver extract is commonly included at the
start of this experiment to mimic liver metabolism.
21
New cards
Proofreading
promptly corrected by DNA polymerases through proofreading.
If an incorrect base has been added, the enzyme makes a cut to release the
wrong nucleotide and a new base is added.
If an incorrect base has been added, the enzyme makes a cut to release the
wrong nucleotide and a new base is added.
22
New cards
Mismatch Repair
shortly after the replication machinery has moved. The
enzymes involved in this mechanism recognize the incorrectly added nucleotide,
excise it, and replace it with the correct base.
enzymes involved in this mechanism recognize the incorrectly added nucleotide,
excise it, and replace it with the correct base.
23
New cards
Nucleotide excision repair
enzymes remove the pyrimidine
dimer and replace it with the correct
bases. Enzyme cuts the sugar-
phosphate backbone several bases
upstream and downstream of the
dimer, and the segment of DNA
between these two cuts is then
enzymatically removed. DNA pol I
replaces the missing nucleotides with
the correct ones and DNA ligase
seals the gap in the sugar-phosphate
backbone.
dimer and replace it with the correct
bases. Enzyme cuts the sugar-
phosphate backbone several bases
upstream and downstream of the
dimer, and the segment of DNA
between these two cuts is then
enzymatically removed. DNA pol I
replaces the missing nucleotides with
the correct ones and DNA ligase
seals the gap in the sugar-phosphate
backbone.
24
New cards
Direct repair
occurs through the
process of photoreactivation in the
presence of visible light. An enzyme
called photolyase recognizes and
breaks apart the thymine dimers,
allowing the thymines to again
correctly base pair with the adenines
on the complementary strand.
process of photoreactivation in the
presence of visible light. An enzyme
called photolyase recognizes and
breaks apart the thymine dimers,
allowing the thymines to again
correctly base pair with the adenines
on the complementary strand.
25
New cards
Horizontal gene transfer
= transfer of genes from one
independent, mature
organism to another
independent, mature
organism to another
26
New cards
what a transposable element is
DNA sequence that have the ability to change their position within a genome
diversity
diversity
27
New cards
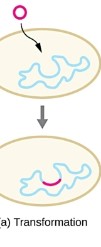
transformation
Uptake of naked DNA by a competent
cell followed by incorporation of the DNA into the recipient
cell’s genome
cell followed by incorporation of the DNA into the recipient
cell’s genome
28
New cards
transduction
Viruses that infect bacteria
(bacteriophages) may also move short pieces of
chromosomal DNA from one bacterium to another in a
process called transduction
- chromosomal DNA from the infected host bacterium is
accidentally packaged into the phage head during phage
assembly
(bacteriophages) may also move short pieces of
chromosomal DNA from one bacterium to another in a
process called transduction
- chromosomal DNA from the infected host bacterium is
accidentally packaged into the phage head during phage
assembly
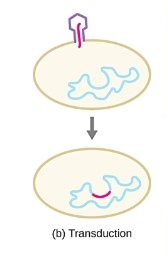
29
New cards
lytic phage
mediate generalized transduction
30
New cards
lysogenic phage
mediate specialized transduction
31
New cards
transduction phage-mediated
transfer of genetic material
32
New cards
Conjugation
DNA is directly transferred from one prokaryote to another by means of a conjugation pilus, which brings the organisms into contact with one another
- DNA transfer by direct cell-cell contact
- DNA transfer by direct cell-cell contact
33
New cards
F plasmid also called
Fertility factor
- in ecoli the genes encoding the ability to conjugate are on bacterial plasmid
- in ecoli the genes encoding the ability to conjugate are on bacterial plasmid
34
New cards
F +
DONOR = cells with F plasmid and F pilus (conjugation)
35
New cards
F -
recipient cells = cells lacking an F plasmid and F pilus
36
New cards
F plasmid integration results
in Hfr cell
37
New cards
Hfr cells can
transfer genomic material but usually not the entire F plasmid
38
New cards
F plasmids carry
other genes from the bacterial chromosome
39
New cards
High frequency of recombination
seen when recipient F - cells receive genetic information from Hfr cells through conjugation
40
New cards
The integrated F plasmid
may also be imprecisely excised from the chromosome, producing an F plasmid that carries with it some chromosomal DNA adjacent to the integration site
-high transfer of certain donor chromosomal genes
-high transfer of certain donor chromosomal genes