Unit 4: Systems Exam
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/19
Last updated 8:06 PM on 9/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
1
New cards
What is **amylase?**
It’s an enzyme (found in saliva) that breaks down **starch into disaccharides -** only activated when eating carbohydrates
2
New cards
What causes **gastric juice** to be released?
The nerves in the submucosa **release** a hormone called **gastrin** into the bloodstream where it then **causes** the cells of the mucosa to release **gastric** **juice** (submucosa → gastrin -→ bloodstream → mucosa → gastric juice)
3
New cards
What does the **stomach** do?
* partially digests proteins
* does not digest lipids and carbohydrates
* nerves initiate the release of the hormone, gastrin, into the blood stream so that it signals the release of gastric juice
* does not digest lipids and carbohydrates
* nerves initiate the release of the hormone, gastrin, into the blood stream so that it signals the release of gastric juice
4
New cards
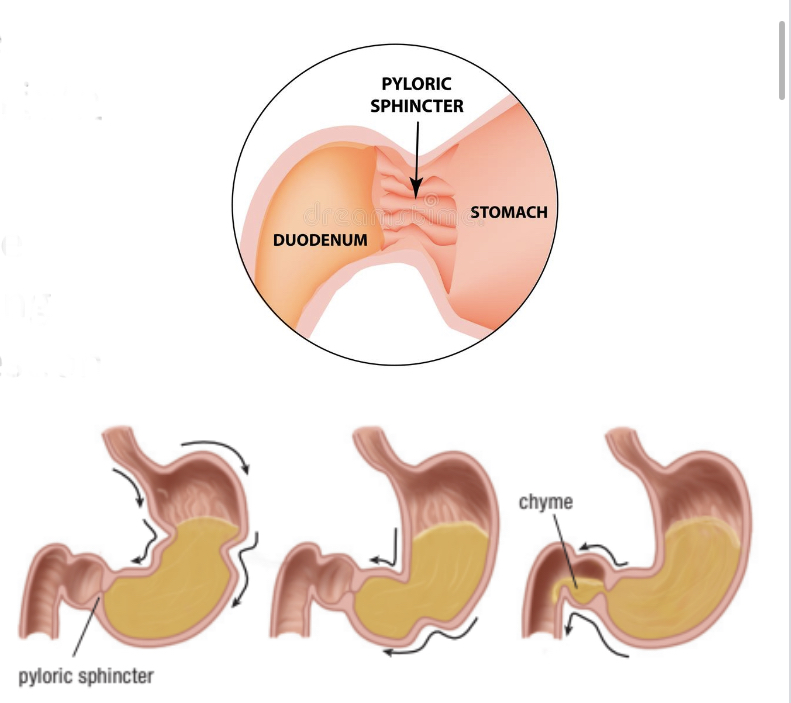
What are **sphincters?**
‘Valves’ with muscles instead of flaps - gastrpesophageal, pyloric, anus
5
New cards
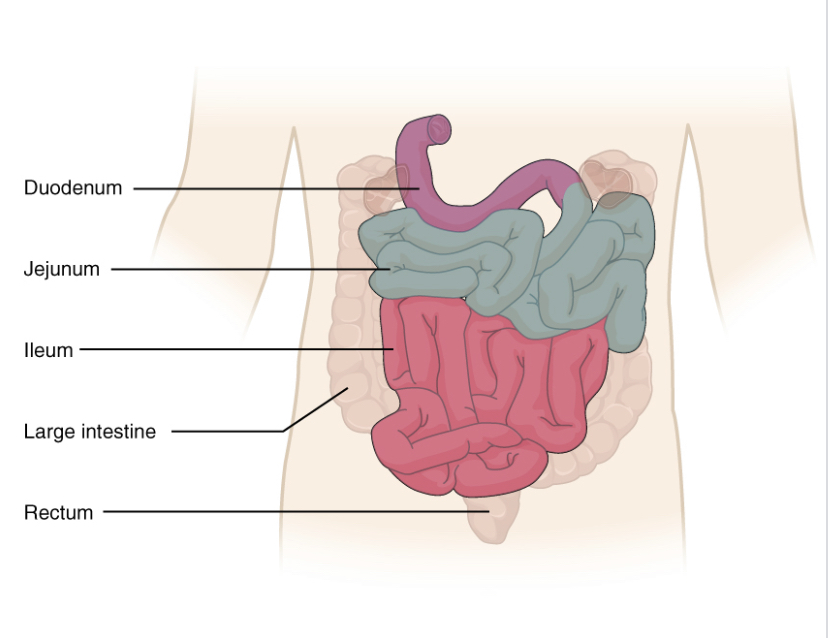
What does the **small intestine do?**
**Chemical digestion** of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins and signals w/ cholecystokinin (CKK) for __gallbladder to release bile__;
* **duodenum** (secretes hormones for accessory organs to secrete juices; __gallbladder__ - bile, __pancreas__ - trypsin, amylase, lipase)
* **jejunum** (digestion finishes → absorption)
* **ileum** (absorbs most nutrients)
* **duodenum** (secretes hormones for accessory organs to secrete juices; __gallbladder__ - bile, __pancreas__ - trypsin, amylase, lipase)
* **jejunum** (digestion finishes → absorption)
* **ileum** (absorbs most nutrients)
6
New cards
What does the **pancreas do?**
Secretes digestive enzymes when signalled by cholecystokinin (CCK) through special pancreatic duct
* **trypsin**: proteins - active form of trypsinogen
* **amylase**: carbohydrates - especially starch/disaccharides
* **lipases**: lipids/fats
* **secretin**: triggered by chyme and stimulates secretion and creation of enzymes and bile
* **trypsin**: proteins - active form of trypsinogen
* **amylase**: carbohydrates - especially starch/disaccharides
* **lipases**: lipids/fats
* **secretin**: triggered by chyme and stimulates secretion and creation of enzymes and bile
7
New cards
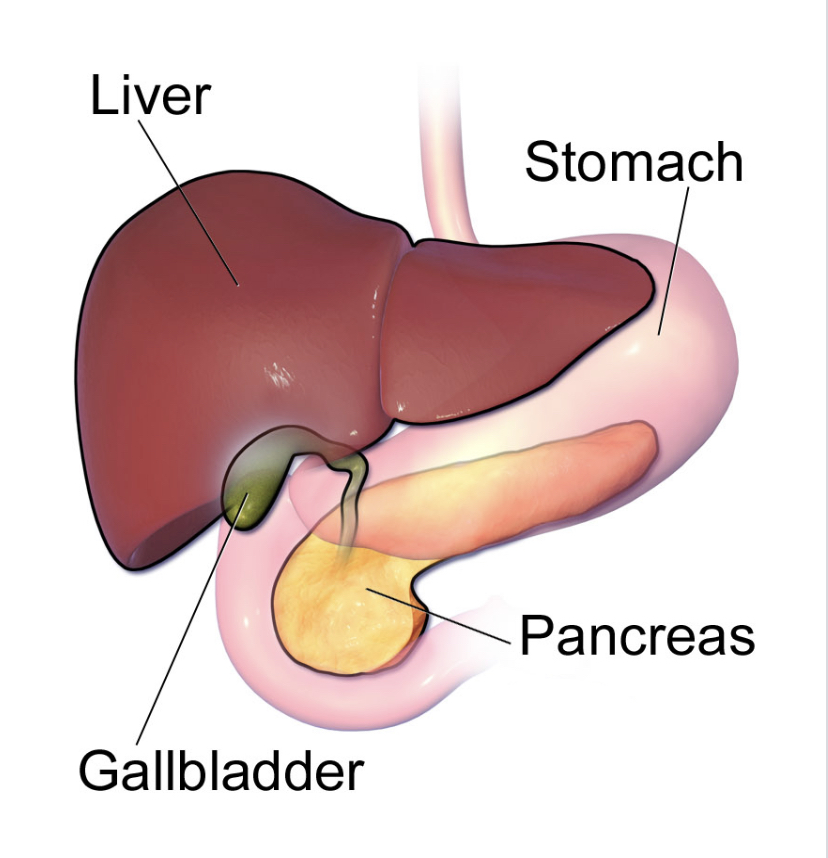
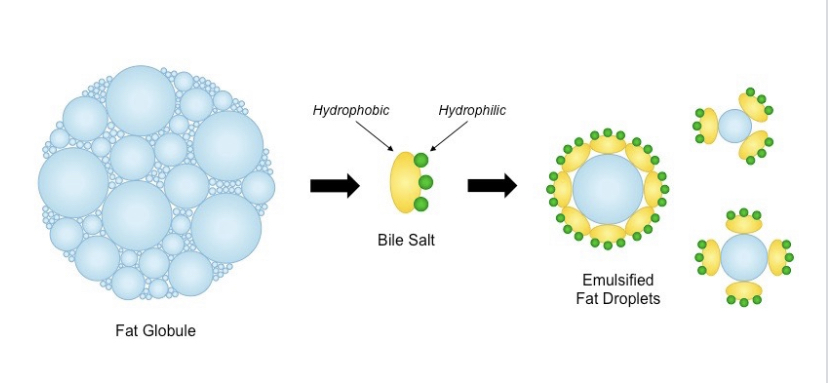
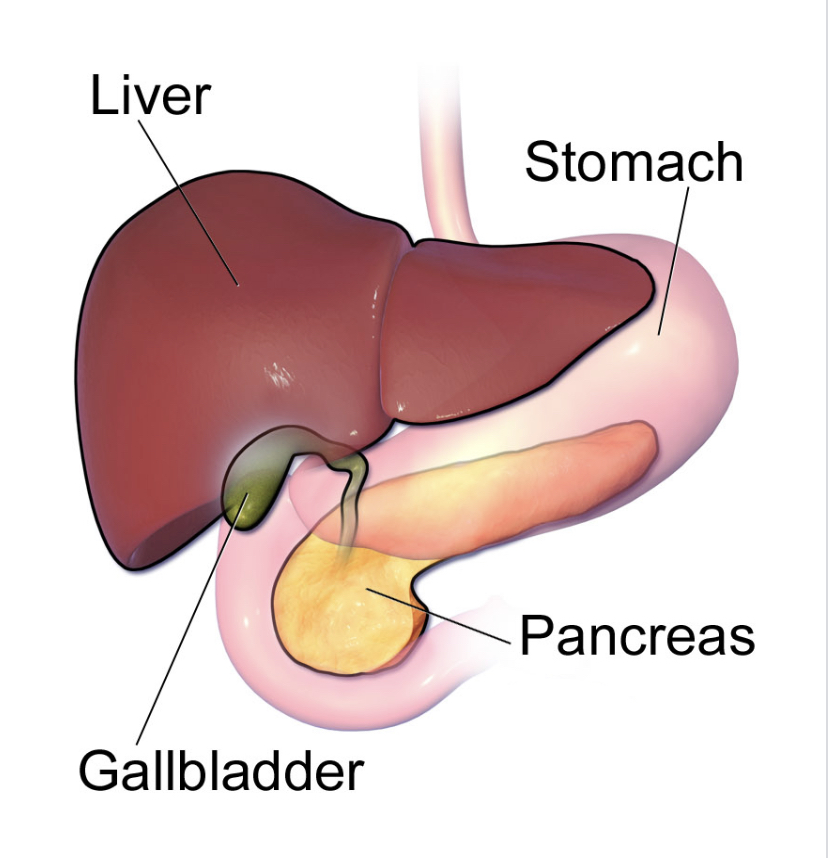
What does a **liver do?**
**Secrets bile** which emulsifies lipids and breaks them into micelles
8
New cards
What does the **gallbladder do?**
**Stores bile** and secretes to duodenum through special bile duct
9
New cards
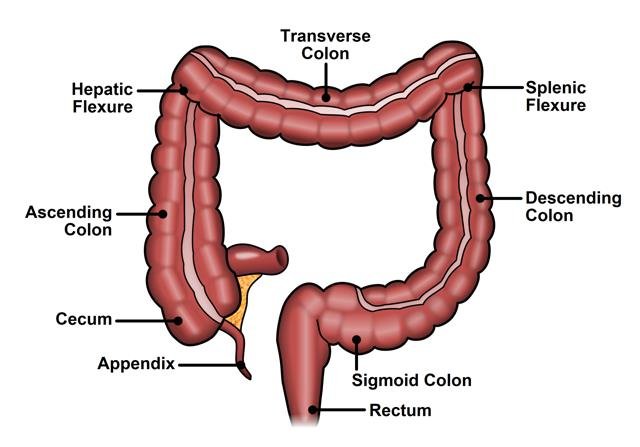
What does the **large intestine do?**
**Absorbs water** and stores food waste
10
New cards
What is **respiration?**
It’s the **movement of gases** between the outside environment and cells within tissues, there are three types: **external, internal, and cellular**
* **External**: gas exchange between air and blood; alveoli
* **Internal**: gas exchange between tissues and blood
* **Cellular**: creates ATP/energy in Mitochondria; consumes O2 and releases CO2
* **External**: gas exchange between air and blood; alveoli
* **Internal**: gas exchange between tissues and blood
* **Cellular**: creates ATP/energy in Mitochondria; consumes O2 and releases CO2
11
New cards
**Statistics** regarding **cellular respiration**
* 64% energy created is released as thermal energy (maintain body heat)
* 34% stores in molecules called adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
* 34% stores in molecules called adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
12
New cards
What do **internal intercostal muscles** do?
**Expiration: Internal intercostal muscles** lower the chest downwards which **limits volume** but increases pressure
13
New cards
What do **external intercostal muscles** do?
**Inspiration: External intercostal muscles** raise the chest upwards which creates more volume and lower pressure
14
New cards
What do **internal intercostal muscles** do?
**Expiration: Internal intercostal muscles** lower the chest downwards which limits volume but increases pressure
15
New cards
What is a **residual/reserve volume (RV)?**
It’s the **leftover air** in the respiratory system after maximum exhalation
16
New cards
What is **expiratory reserve volume (ERV)?**
It’s the **maximum** amount of air of forced exhalation in **normal breaths**
17
New cards
What is **inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)?**
It’s the **maximum amount** of air of forced inhalation in **normal breaths** (when breathing normally, how much as possible can be let out)
18
New cards
What is **vital capacity (CV)?**
It’s the **maximum amount** of air that can be exhaled after a **maximum inhalation**
19
New cards
What is **tidal volume (TV)?**
It’s the **volume of air** in a **normal involuntary** breath
20
New cards
What are the **three main functions** of the **circulatory system?**
* A **fluid** that transports (circulates) materials through the body
* A **network of tubes** in which the fluid circulates
* A **pump** that pushes the fluid through the tubes
* A **network of tubes** in which the fluid circulates
* A **pump** that pushes the fluid through the tubes