Chapter 15: Identification of Saliva
15.1: Biological Characteristics of Saliva
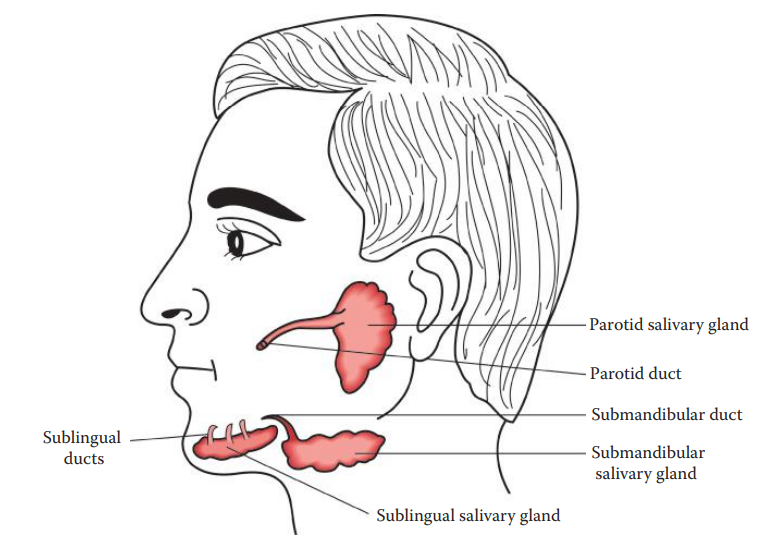
The human salivary glands produce 1.0–1.5 L of saliva daily.
About 70% of saliva is produced from the submandibular salivary glands, 25% from the parotids, and 5% from the sublingual salivary glands.
Saliva is largely water containing small quantities of electrolytes, proteins, antibodies, and enzymes.
Amylases
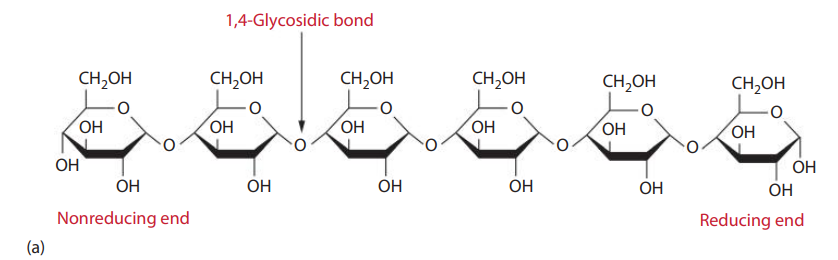
Amylases: Are enzymes that cleave polysaccharides such as starches, which are composed of D-glucose units connected by α1→4 linkages.
Starches contain two types of glucose polymers:
- Amylose consists of long, linear chains of glucose residues connected by α1→4 linkages.
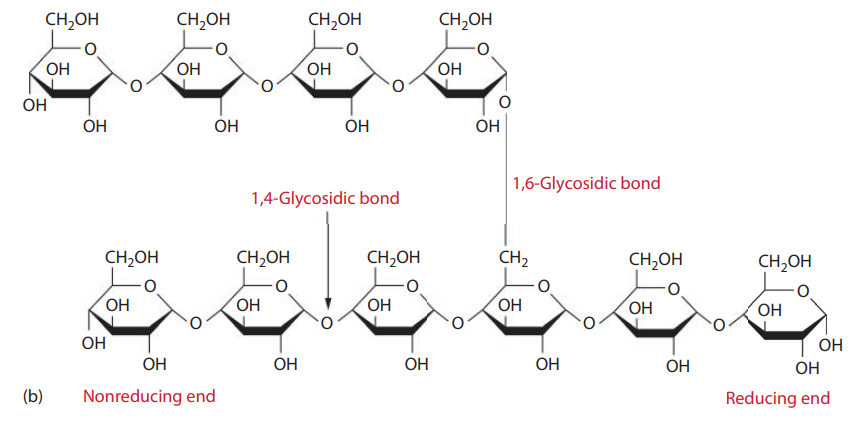
- Amylopectin is highly branched and consists of linear chains of glucose residues connected by α1→4 linkages with the branch points connected by α1→6 linkages.
Two types of amylases are characterized:
- β-Amylases found in plant and bacterial sources cleave only at the terminal-reducing end of a polysaccharide chain.
- Human α-amylases cleave at α1→4 linkages randomly along the polysaccharide chain.
Human salivary α-amylase (HSA): Encoded by the Amy1 locus, synthesized at the salivary glands and secreted into the oral cavity.
Human pancreatic α-amylase (HPA): Encoded by the Amy2 locus, is synthesized by the pancreas and secreted into the duodenum through the pancreatic duct.
15.2: Analytical Techniques for Identification of Saliva
Presumptive Assays
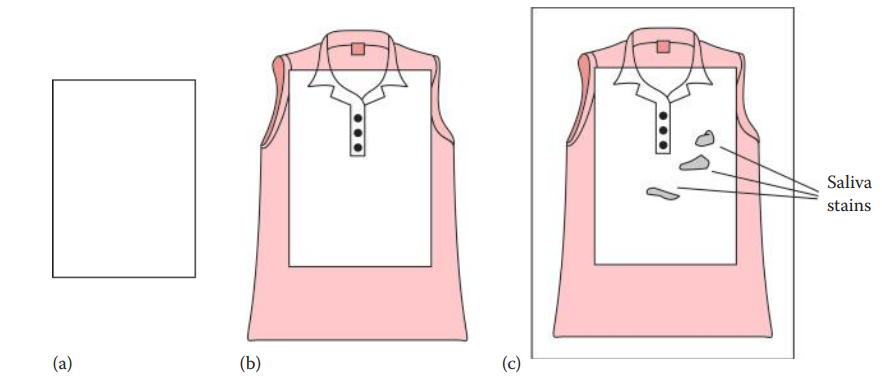
Visual Examination
- The lighting techniques used to search for semen stains can be utilized in searching for saliva stains.
- Microscopic examination with proper histological staining can also be performed to identify the buccal epithelial cells, indicating the presence of a saliva stain.
Determination of Amylase Activity
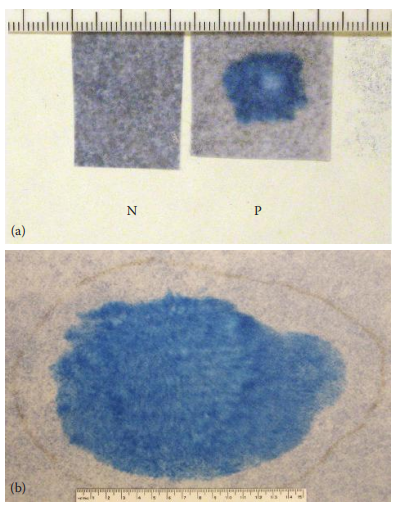
Starch–Iodine Assay
Iodine is used to test for the presence of starch.
The amylose in starch reacts strongly with iodine to form a dark blue complex, while amylopectin develops a reddish-purple color.
Colorimetric Assays
Dye-labeled amylase substrates such as dye-conjugated amylose or amylopectin are utilized.
These substrates are not soluble in water.
Confirmatory Assays
Identification of Human Salivary α-Amylase
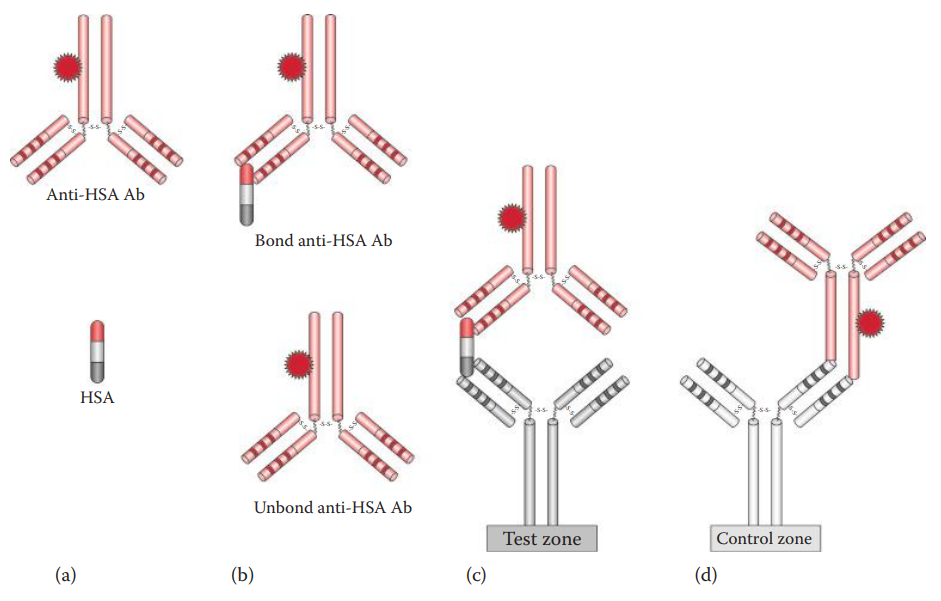
- Immunochromatographic Assays: RSID®-Saliva kit.
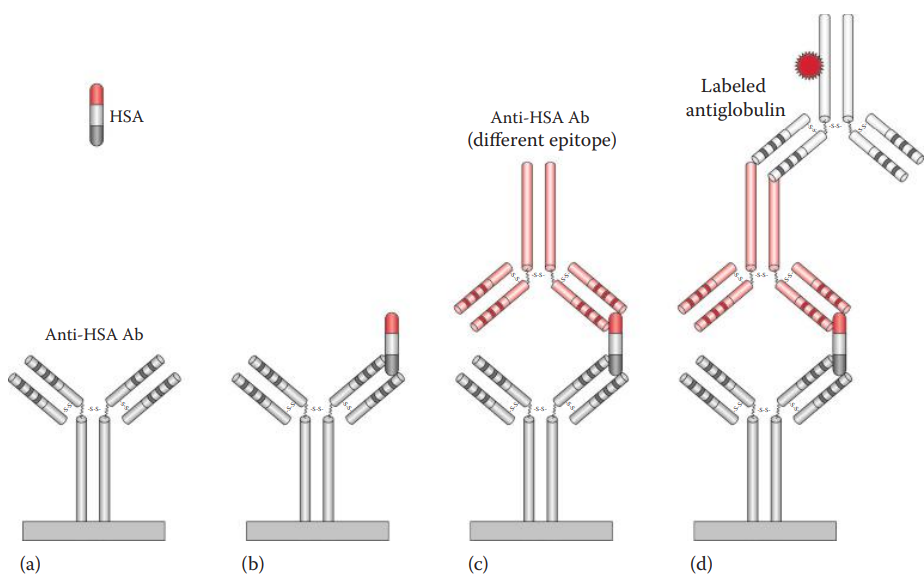
- Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA): Antibody—Antigen—Antibody Sandwich
RNA-Based Assay: These assays utilize reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction methods to detect gene expression levels of mRNAs for saliva identification.
Application of RT-PCR Assay for Saliva Identification
| Gene Symbol | Gene Product | Description |
|---|---|---|
| HTN3 | Histatin 3 | Histidine-rich protein involved in nonimmune host defense in oral cavity. |
| STATH | Statherin | Inhibitor of precipitation of calcium phosphate salts in oral cavity. |