AP Music Theory
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
homophony
texture with principal melody and accompanying harmony
heterophony
a type of texture characterized by the simultaneous variation of a single melodic line
polyphony
the style of simultaneously combining a number of parts, each forming an individual melody and harmonizing with each other.
monophony
single-line texture, or melody without accompaniment
appoggiatura
a grace note performed before a note of the melody and falling on the beat
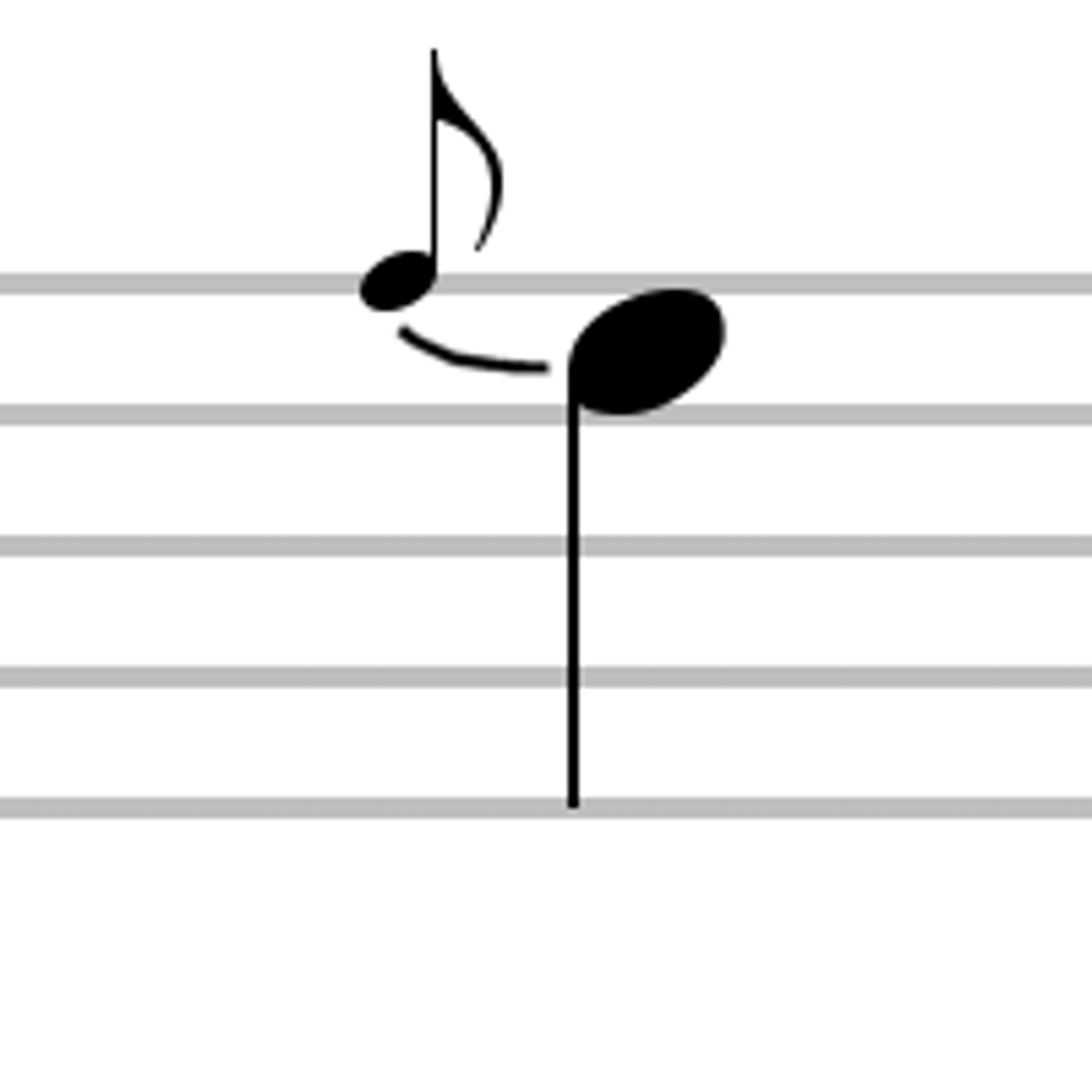

anticipation
part of a chord about to follow is introduced beforehand (approached by step)
escape tone
approached by step, resolved by skip in the opposite direction
neighbor tone
a nonharmonic tone which steps below (lower) or above (upper) the chord tones.
preparation
the consonant pitch or chord which precedes a dissonant nonharmonic tone (move from consonance to dissonance)
suspension
prolonging a note to create a dissonance with the next chord, resolves down
retardation
prolonging a note to create a dissonance with the next chord, resolves up
resolution
the move of a note or chord from dissonance to a consonance
retrograde
inversion of a motive that reverses the order of the motive's pitches
binary form
a musical form consisting of two units (A and B) constructed to balance and complement each other
rounded binary form
binary form in which the beginning or all of the first section returns in the tonic in the latter part of the second section
ternary form
a three-part musical form in which the third section is a repeat of the first
truncation
Shortening of a musical phrase
elision
a special device for joining phrases together in an overlapping manner; the final bar of one phrase is simultaneously the first bar of the next phrase
augmentation
Statement of a melody in longer note values, often twice as slow as the original
diminution
statement of a melody in shorter note values, often twice as fast as the original
melisma
a group of notes sung to one syllable of text
ostinato
a continually repeated musical phrase or rhythm
obbligato
an instrumental part, typically distinctive in effect, which is integral to a piece of music and should not be omitted in performance
rubato
a flexible tempo using slight variations of speed to enhance musical expression
tessitura
the range within which most notes lie
fragmentation
division of a musical idea (gesture, motive, theme, etc.) into segments
parallel period
when two phrases begin the same
contrasting period
when two phrases begin differently
strophic form
verse-repeating or chorus form
voice exchange
when voice parts exchange notes in order to prolong a chord: For example, a I chord moving to a I6 chord could exchange the root and the third with the bass and soprano voices
conjunct
stepwise
disjunct
a melody that moves by leaps
ionian
major scale
dorian
starting on second degree of major, close to minor
phrygian
starting on third degree of major, close to minor
lydian
starting on fourth degree of major, close to major
mixolydian
starting on fifth degree of major, close to major
aeolian
starting on sixth degree of major, same as natural minor
locrian
starting on the seventh degree of major, basically a minor scale
antiphonal
A type of music in which two or more groups of voices or instruments alternate with one another
picardy third
suddenly ending a minor composition in a major triad
phrygian half cadence
iv6 to V in minor
plagal cadence
IV-I (hallelujah)
deceptive cadence
V-vi
perfect authentic cadence
V to I; in root position; melody ends on tonic
imperfect authentic cadence
must end on I chord
half cadence
ends with the V chord
sequence
melodic phrase repeated at different levels of pitch
consequent phrase
the second phrase of a two-part melodic unit that brings a melody to a point of repose and closure
antecedent phrase
the opening, incomplete-sounding phrase of a melody with a half cadence; often followed by a consequent phrase that brings the melody to closure
cadenza
solo section
scalar variance
the use of natural, harmonic, and melodic minor within one composition
recapitulation
reiteration of the musical themes from the movement's exposition
rondo form
classical form with at least three statements of the refrain (A) and at least two contrasting sections (at least B and C); placement of the refrain creates symmetrical patterns such as ABACA, ABACABA, or even ABACADA
mordent
ornament in which the written note is played, followed by the note above and the written note again (basically a trill)
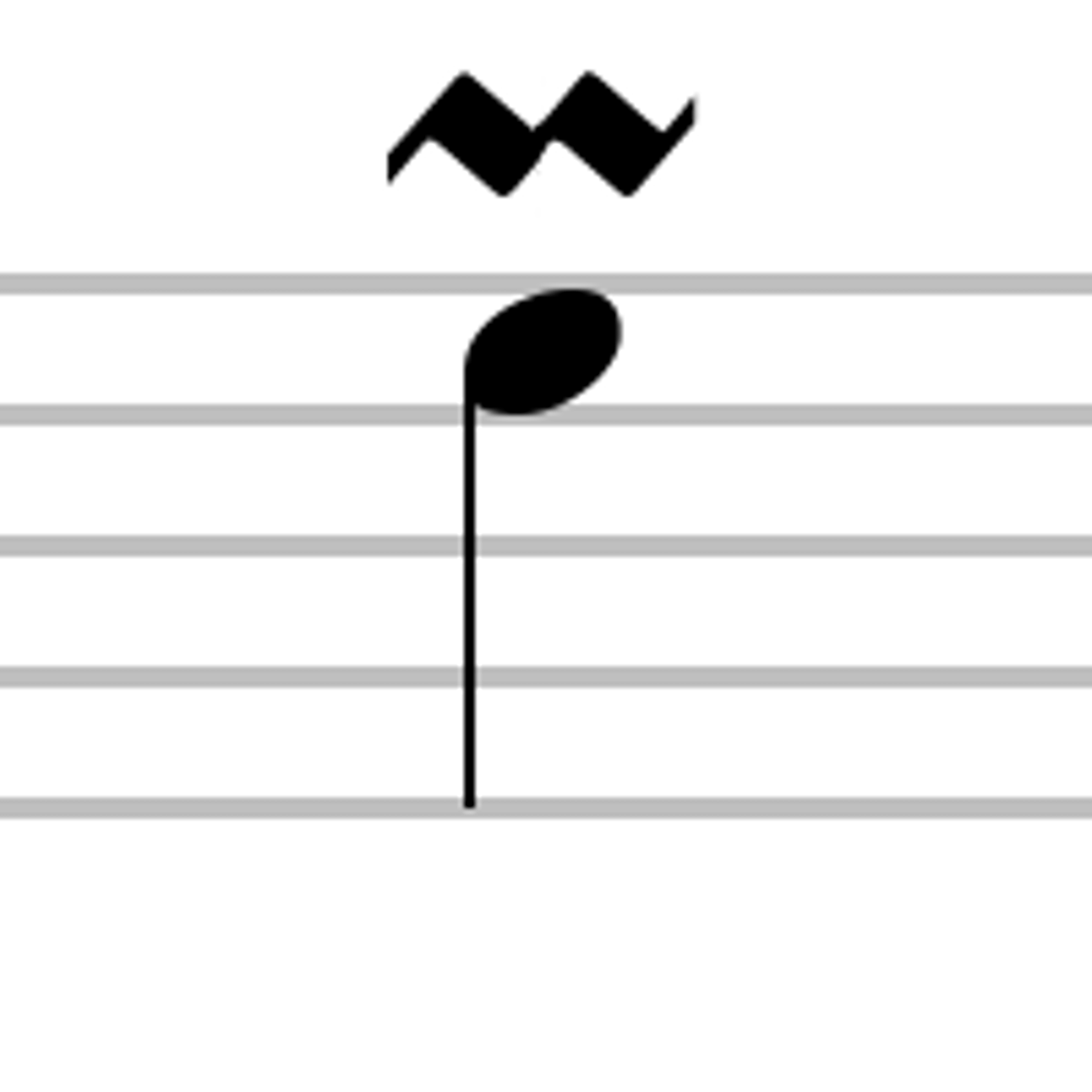
hemiola
a musical figure in which, typically, two groups of three beats are replaced by three groups of two beats, giving the effect of a shift between triple and duple meter
alla breve
cut time 2/2
stringendo
gradually faster