Unit 9: Protein Synthesis
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/43
Last updated 12:42 PM on 2/17/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
1
New cards
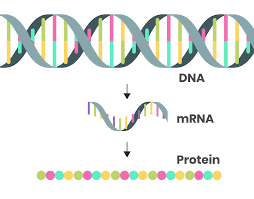
Central Dogma
DNA→RNA→Protein
2
New cards
Base pairing rules of DNA
A→T
C→G
C→G
3
New cards
Base pairing rules of RNA
A→U
C→G
C→G
4
New cards
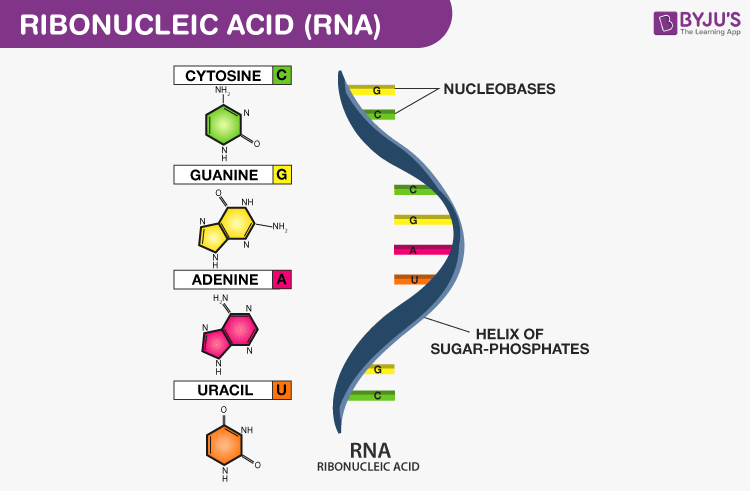
Structure and Function of **mRNA**
Structure:
* single stranded
* linear/one straight line
Function:
* copy DNA code during transcription
* carry DNA code to the ribosome
* single stranded
* linear/one straight line
Function:
* copy DNA code during transcription
* carry DNA code to the ribosome
5
New cards
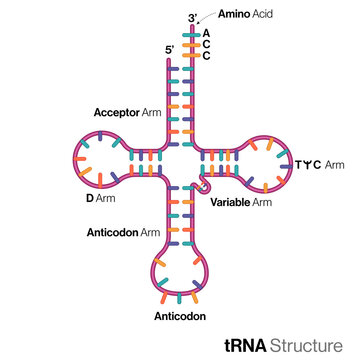
Structure and Function of **tRNA**
Structure:
* single stranded
* clover leaf shape
Function:
* carry the correct amino acids to the ribosome during translation
* single stranded
* clover leaf shape
Function:
* carry the correct amino acids to the ribosome during translation
6
New cards
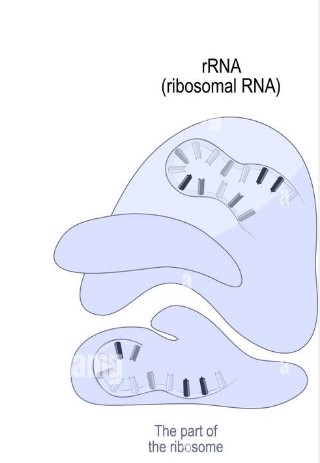
Structure and Function of **rRNA**
Structure:
* single stranded
* globular
Function:
* combine with proteins to make up ribosomes
* single stranded
* globular
Function:
* combine with proteins to make up ribosomes
7
New cards
Why do we need Central Dogma?
chromosomes have info to determine what proteins are made
* mostly enzymes
* mostly enzymes
8
New cards
Why do we need transcription?
the DNA can’t leave the nucleus and ribosomes are in the cytoplasm so DNA has to turn into mRNA to leave the nucleus
9
New cards
What is the product of transcription?
a single stranded mRNA
10
New cards
Where does transcription happen?
in the nucleus
11
New cards
Steps of Transcription
1. Initiation
2. Elongation
3. Termination
12
New cards
transcription factors
a protein that controls the rate of transcription
13
New cards
TATA box
* adenine and thymine
* promoter region
* site where transcription starts/the start of a gene
* promoter region
* site where transcription starts/the start of a gene
14
New cards
Transcription **Initiation**
1. helicase, single stranded binding proteins, and topoisomerase do their thing and keep the DNA strand open (essentially ==makes a template==)
2. transcription factors ==find the promoter region== (TATA box)
3. transcription factors tell ==RNA polymerase where to attach==
15
New cards
Transcription **Elongation**
1. RNA polymerase adds the base pairs complementary to the template strand of DNA
* RNA polymerase works 3’→5’
* mRNA = a leading strand
16
New cards
Transcription **Termination**
1. termination sequence of nucleotides signal the end of transcription
* yellow light for transcription
2. 10-35 base pairs later RNA polymerase stops
17
New cards
termination sequence
AAUAAA
18
New cards
Where does translation happen?
generally in cytoplasm but specifically in ribosomes
19
New cards
What is the product of translation?
proteins !!
20
New cards
codon?
* set of three nitrogenous bases
* ex. AUU , CGC, AGU
* every codon codes for an amino acid
* 1 codon = 1 amino acid
* ex. AUU , CGC, AGU
* every codon codes for an amino acid
* 1 codon = 1 amino acid
21
New cards
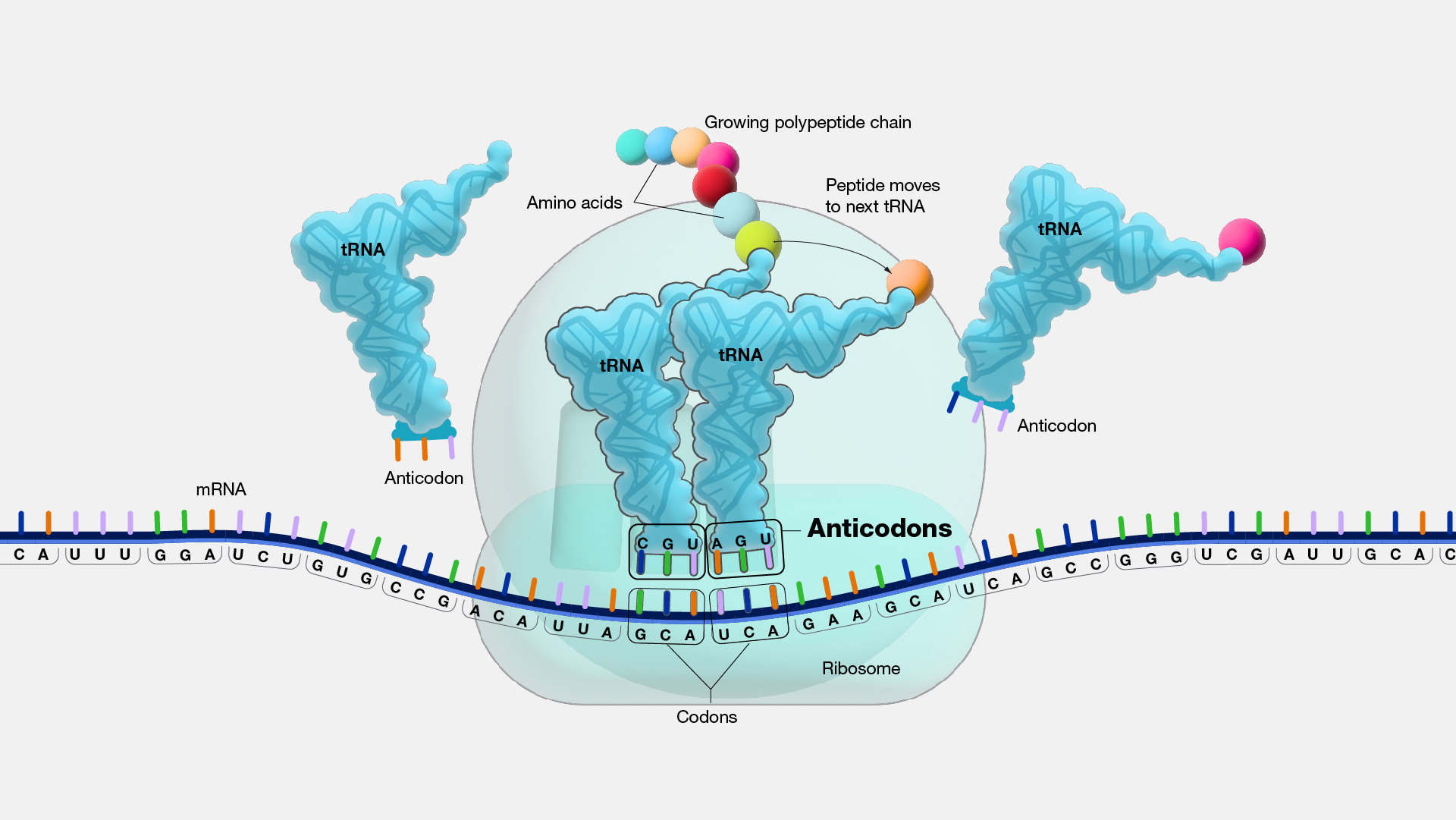
tRNA
* brings correct amino acids to the ribosomes
* has complementary anticodons that attach to the
* has complementary anticodons that attach to the
22
New cards
anticodon
* a trinucleotide
* at the end of a tRNA
* corresponds with a codon in the mRNA
* at the end of a tRNA
* corresponds with a codon in the mRNA
23
New cards
peptide bonds
* bonds that attach amino acids to the polypeptide chain
24
New cards
ribosomes
* small subunit = ground
* large subunit = wall
* func = making proteins
* large subunit = wall
* func = making proteins
25
New cards
5’ GTP cap
* guanine triphosphate (guanine nucleotide w/ 2 additional phosphates attached
* where the mRNA molecule attaches to the ribosome
* where the mRNA molecule attaches to the ribosome
26
New cards
poly-A-Tail
* 140-200 adenine nucleotides on the 3’ end
* provides stability
* provides stability
27
New cards
introns
non-coding sequences
stay in the nucleus
stay in the nucleus
28
New cards
extrons
coding sequences
exit the nucleus
exit the nucleus
29
New cards
heterogenous nuclear mRNA
uncleaved mRNA
30
New cards
what cleaves introns
* small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs) = “biological scissors”
* found in large spliceosomes
* do the cutting and putting back together of actual mRNA
* found in large spliceosomes
* do the cutting and putting back together of actual mRNA
31
New cards
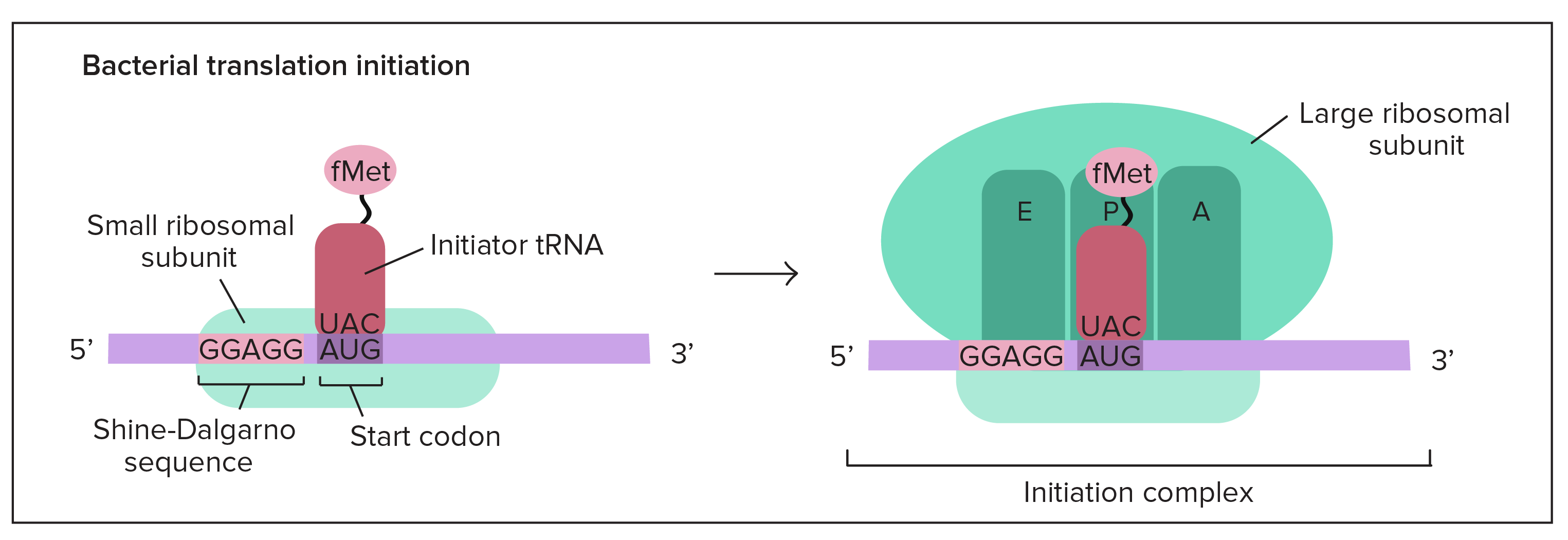
Translation Initiation
1. 5’ GTP cap attaches to the small ribosomal subunit
2. tRNA w/ the start **anti**codon (UAC) attaches to the mRNA start **codon** (AUG) at the P site
3. the large ribosomal subunit attaches to the complex which makes a complete ribosome
32
New cards
Translation Elongation
1. the next tRNA arrives at the A site
2. Methionine is removed from the tRNA at the P site
3. Methionine attaches to the new amino acid in the A site
4. everything shifts over - the mRNA moves over which switches everything over
5. the tRNA exits from the E site
6. the next tRNA goes in the A site and the cycle repeats
33
New cards
APE sites
A = attachment site
* where the next tRNA attaches to the mRNA
P site:
* holds the tRNA with the amino acid chain/ growing polypeptide
E = exit site
* where the empty tRNA can exit and attach to a new but same type of amino acid
* where the next tRNA attaches to the mRNA
P site:
* holds the tRNA with the amino acid chain/ growing polypeptide
E = exit site
* where the empty tRNA can exit and attach to a new but same type of amino acid
34
New cards
methionine
* essential in humans
* we don’t naturally make it
* have to consume through meat, fish, dairy, etc.
* we don’t naturally make it
* have to consume through meat, fish, dairy, etc.
35
New cards
Translation Termination
1. one of the stop codons (UAA, UGA, UAG) comes up in the mRNA sequence
2. a release factor comes instead of an amino acid
3. the 2 subunits of the ribosome, the last tRNA, and the completed polypeptide are released from the mRNA
4. the above components can be recycled and complete translation somewhere else in the cell
1. the protein can now fold into it’s secondary, terriatry, and quaternary structure
36
New cards
stop codons
* UAA
* UGA
* UAG
* UGA
* UAG
37
New cards
point mutations
change one base pair
38
New cards
substitution mutations
* silent
* missense
* nonsense
* missense
* nonsense
39
New cards
silent mutation
* no effect on the amino acid being created
* inserted at the “wobble” position
* there is >1 codon for each amino acid
* when you change the third base pair it doesn’t always change the amino acid
* ex. CCG and CCA both code for glycine
* inserted at the “wobble” position
* there is >1 codon for each amino acid
* when you change the third base pair it doesn’t always change the amino acid
* ex. CCG and CCA both code for glycine
40
New cards
missense mutation
* changes the amino acid being created
* can change the shape/function of entire polypeptide
* can change the shape/function of entire polypeptide
41
New cards
nonsense mutation
* creates a stop codon
* ultimately creates a nonfunctional polypeptide
* stop making protein
* amino acids get recycled
* ultimately creates a nonfunctional polypeptide
* stop making protein
* amino acids get recycled
42
New cards
frameshift mutations
* changes reading frame of code
* Insertion
* Deletion
* Insertion
* Deletion
43
New cards
Insertion mutation
A nucleotide is added to a gene
Changes all of the amino acids”downstream” of the mutation
Shifts the reading frame to the right→
Results in a non functional protein
Changes all of the amino acids”downstream” of the mutation
Shifts the reading frame to the right→
Results in a non functional protein
44
New cards
Deletion mutation
A nucleotide is removed from the gene
All of the amino acids downstream of the change are affected
Shifts the reading frame to the left
All of the amino acids downstream of the change are affected
Shifts the reading frame to the left