Comprehensive Guide to the Peripheral Nervous System and Cranial Nerves
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
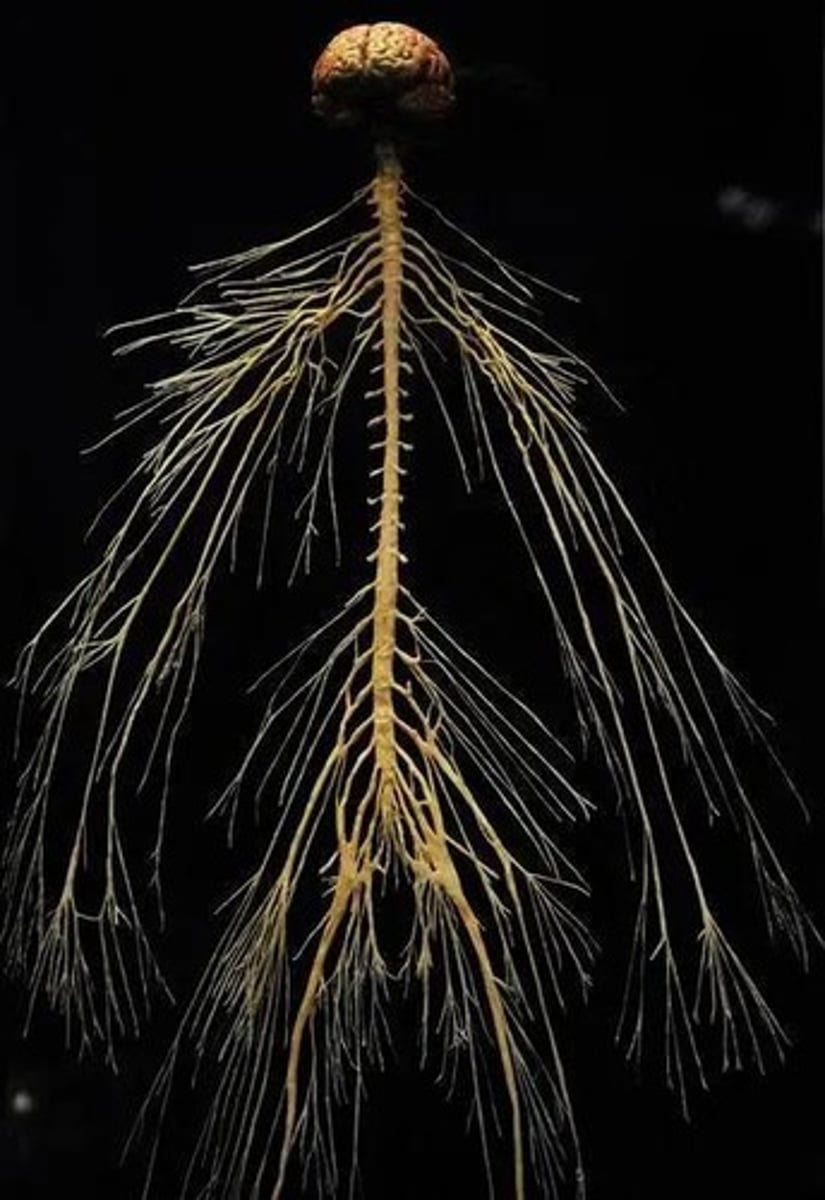
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Part of the nervous system containing all nerves outside the central nervous system (CNS) that carry information to and from the body.
Sensory Division
Carries information towards the CNS.
Motor Division
Carries information away from the CNS.
Somatic Division
Controls skeletal muscle and involves voluntary control of muscles.
Autonomic Division
Controls cardiac and smooth muscle and involuntary control of muscles.
Sympathetic Division
Controls fight or flight responses.
Parasympathetic Division
Controls rest and digest responses.
Axon
A nerve is made up of many axons that are bundled together.
Mixed Nerves
Nerves that contain both sensory (afferent) and motor (efferent) neurons.
Myelin
Areolar CT that wraps around the axon on top of the myelin sheath to protect against 'short circuiting'.
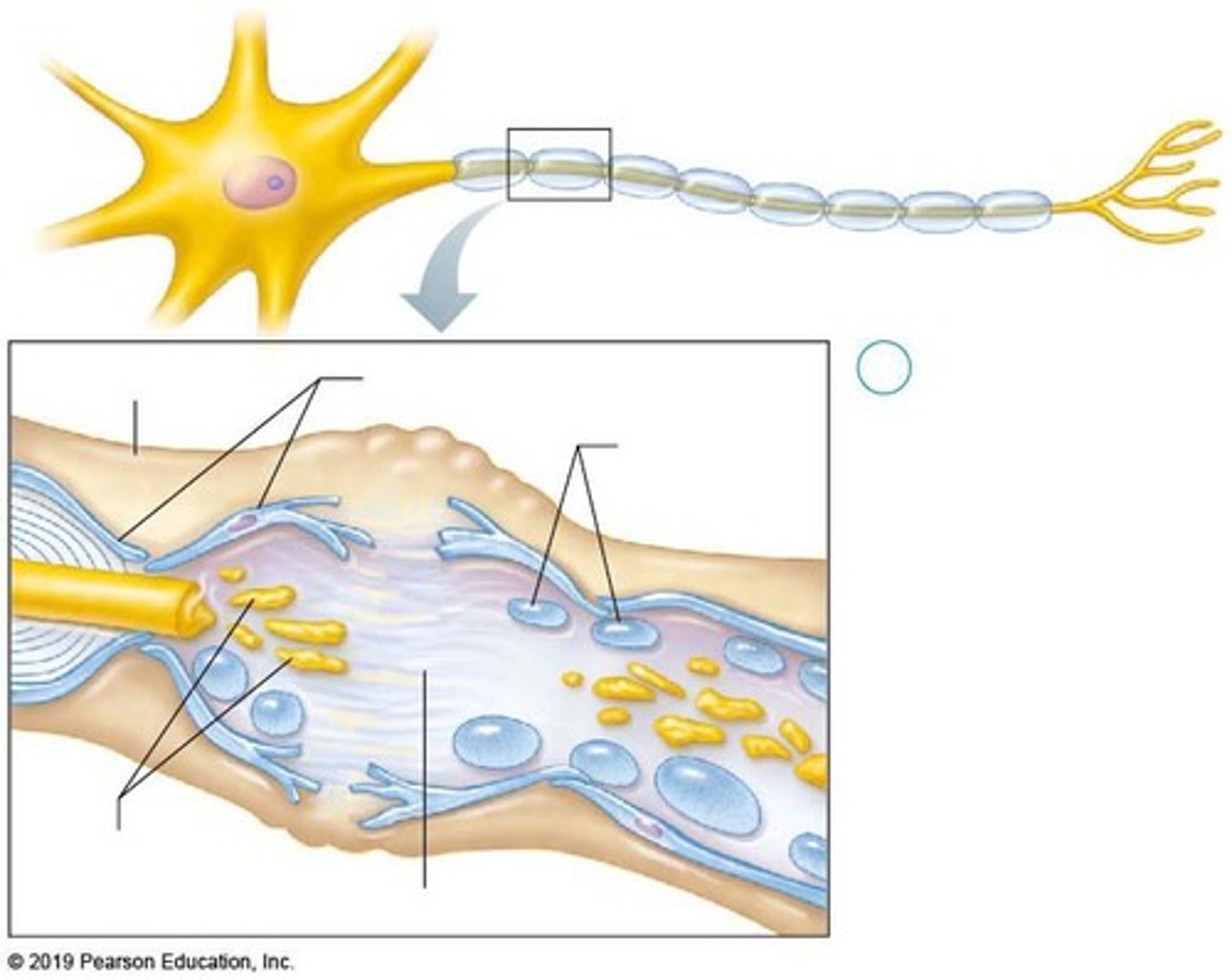
Fascicle
A bundle of axons wrapped by dense irregular CT.
Nerve
A dense irregular CT that wraps bundles of fascicles.
Cranial Nerves
Nerves that exit from the cranium and supply the head and neck.
Spinal Nerves
Nerves that exit from the spinal cord and supply the rest of the body.
Sensory Neurons
Detect sensations in the body and relay them to the CNS.
Extero-receptors
Receptors that detect external sensations.
Intero-receptors
Receptors that detect internal sensations.
Phasic Receptors
Receptors that turn off after a period of stimulation.
Tonic Receptors
Receptors that never turn off because their information is too important.
Referred Pain
Pain from an organ is experienced in a different part of the body.
Axon Regeneration
Process that can occur if the cell body remains intact and involves several steps including macrophages cleaning up debris.
Wallerian Degeneration
The process where the axon breaks down distal to the injury.
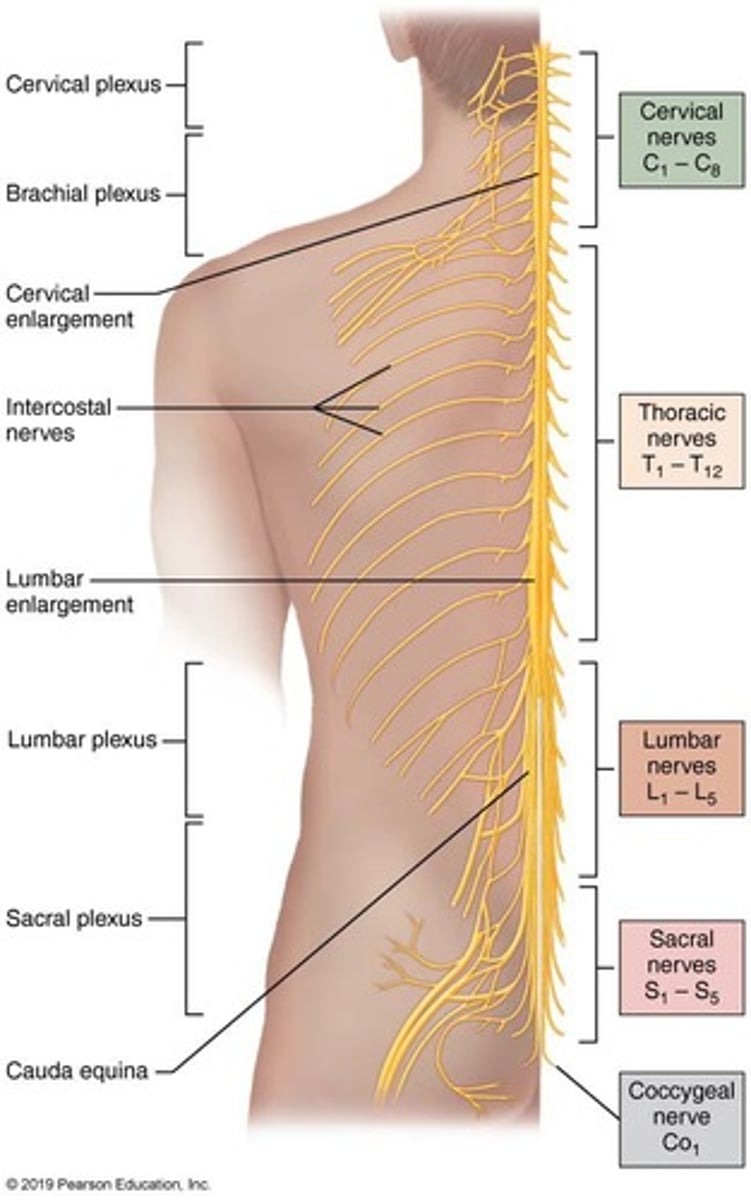
Spinal Nerve Count
There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves (62 total).
Dorsal Roots
Contain sensory neurons.
Ventral Roots
Contain motor neurons.
Dorsal Root Ganglion
Contains the cell bodies of sensory neurons.
Cervical Plexus
Formed from the ventral rami of spinal nerves C1 to C4.
Phrenic Nerve
Formed from spinal nerves C3 to C5 and is responsible for controlling the diaphragm.

Brachial Plexus
The brachial plexus is formed from the ventral rami of spinal nerves C5 to T1.
Axillary Nerve
Supplies the skin and muscles of the shoulder.
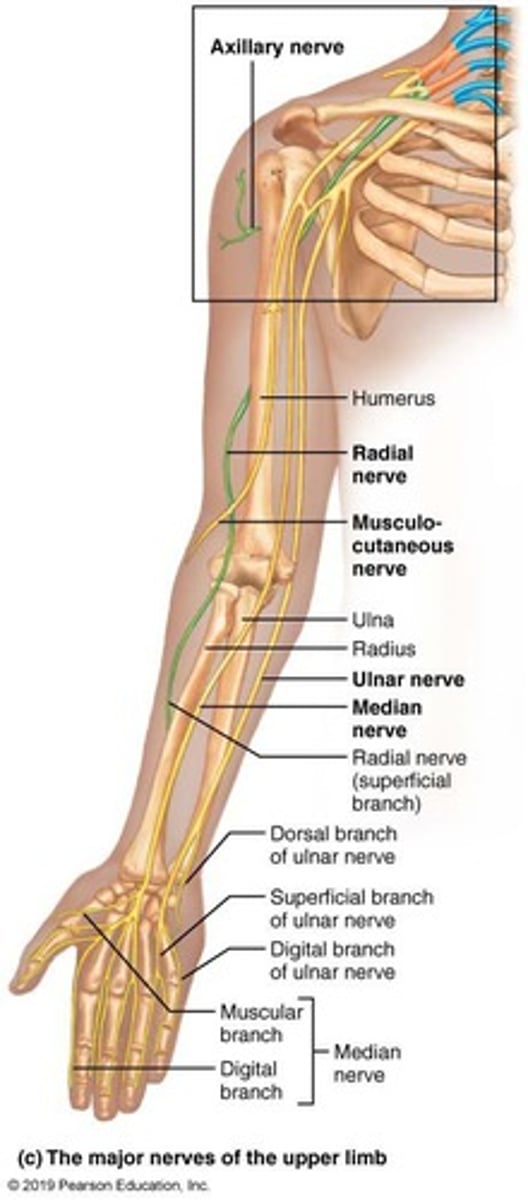
Musculo-cutaneous Nerve
Supplies the skin and muscles on the front of the upper arm.
Radial Nerve
Supplies the skin and muscles on the back of the arm.
Median Nerve
Supplies the skin and muscles of the lateral forearm and hand.
Ulnar Nerve
Supplies the skin and muscles of the medial forearm and hand.
Lumbar Plexus
The lumbar plexus is formed from the ventral rami of spinal nerves L1 to L4.
Femoral Nerve
Supplies the skin and muscles of the anterior leg.
Obturator Nerve
Supplies the skin and muscles on the medial aspect of the leg.
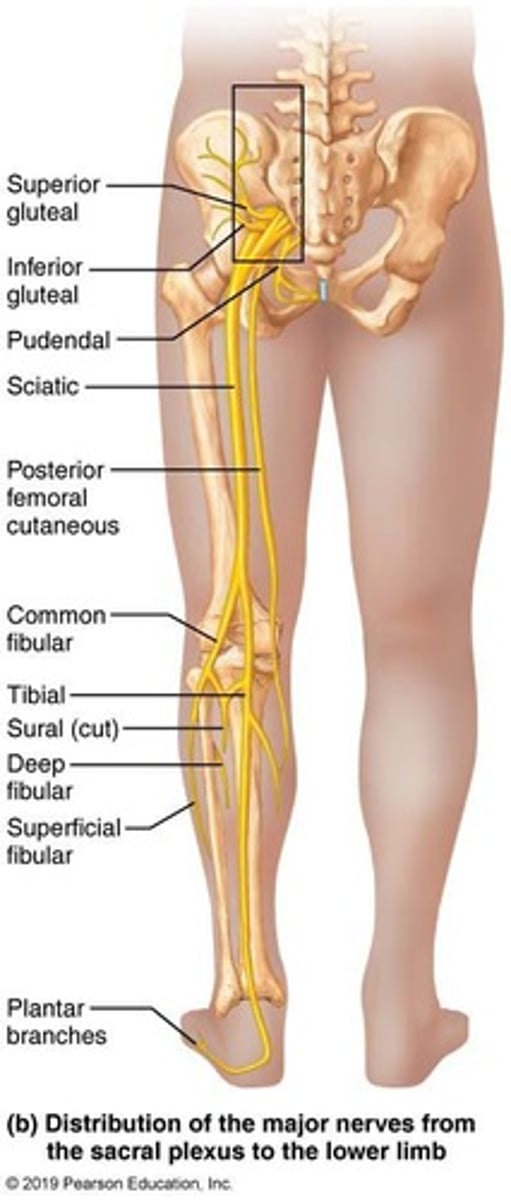
Sacral Plexus
The sacral plexus is formed from the ventral rami of spinal nerves L4 to S4.
Sciatic Nerve
Supplies the skin and muscles of the posterior leg.
Dermatome
Each spinal nerve controls a specific area of the skin called a dermatome.
Somatic Reflexes
A reflex is an involuntary movement in response to a stimulus.
Patellar Stretch Reflex
Striking the patellar tendon quickly stretches the quadriceps muscle activating the muscle spindle.
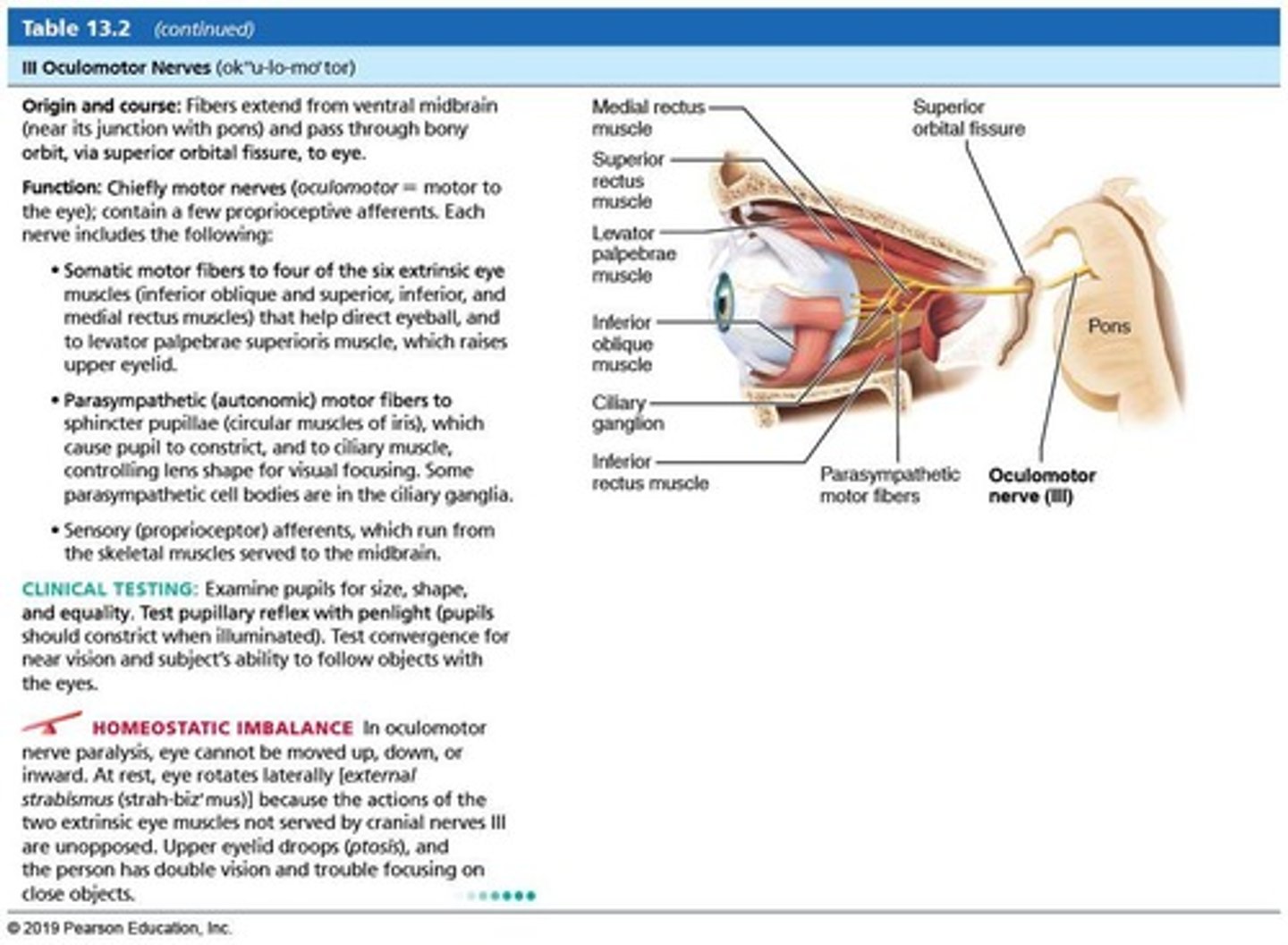
Cranial Nerve III (CN III)
Oculomotor nerve.
Cranial Nerve I (CN I)
Olfactory nerve.
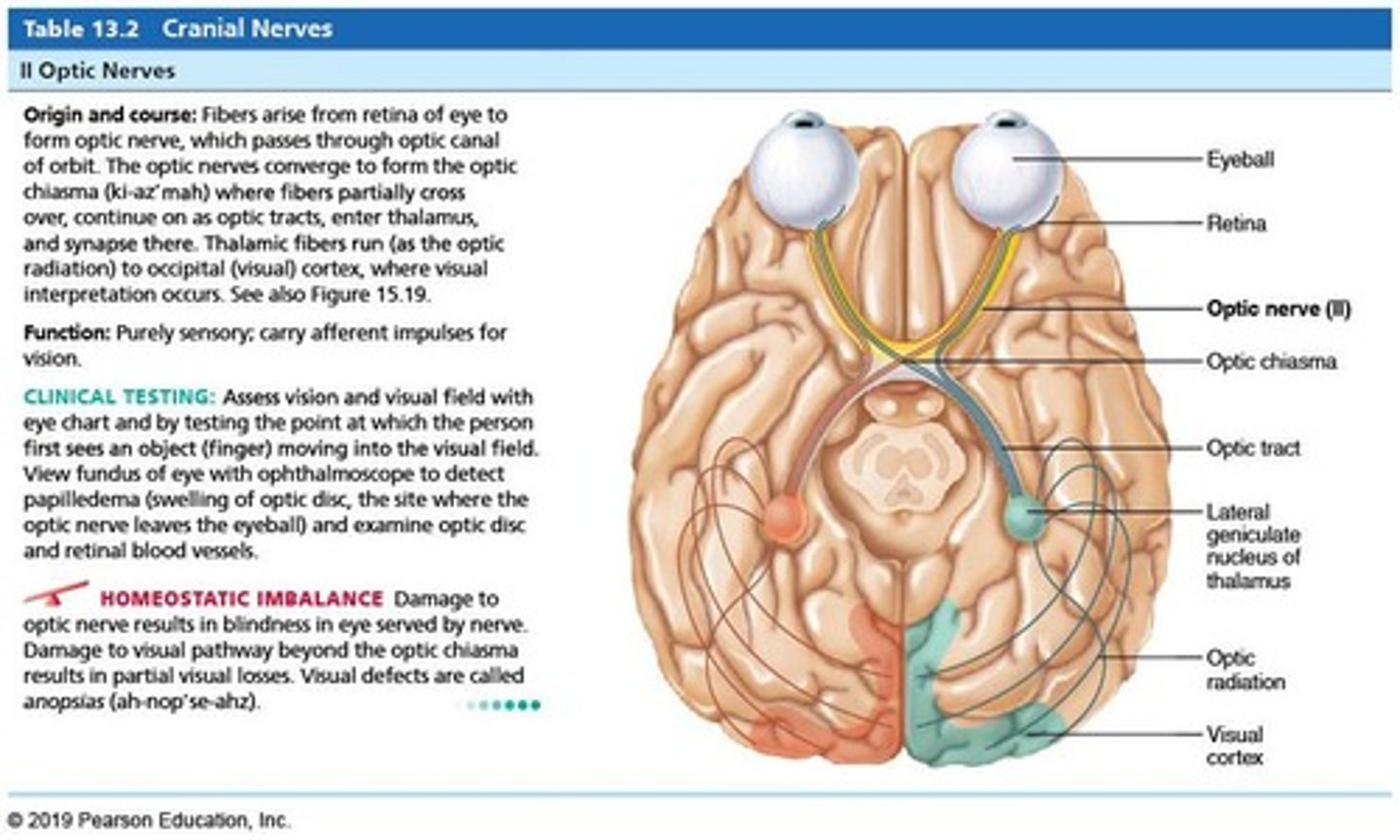
Cranial Nerve II (CN II)
Optic nerve.
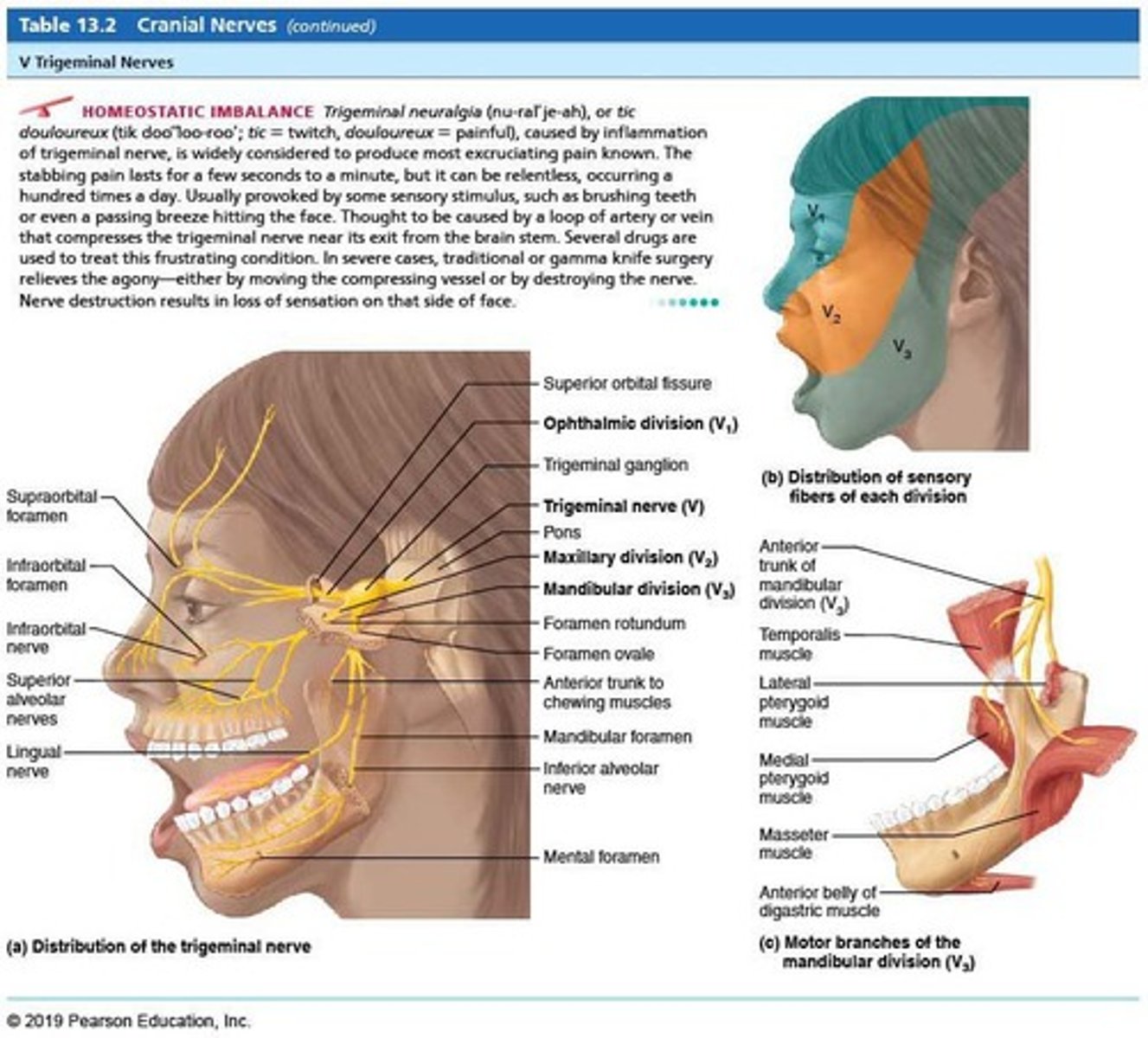
Cranial Nerve V (CN V)
Trigeminal nerve.
Cranial Nerve VI (CN VI)
Abducens nerve.
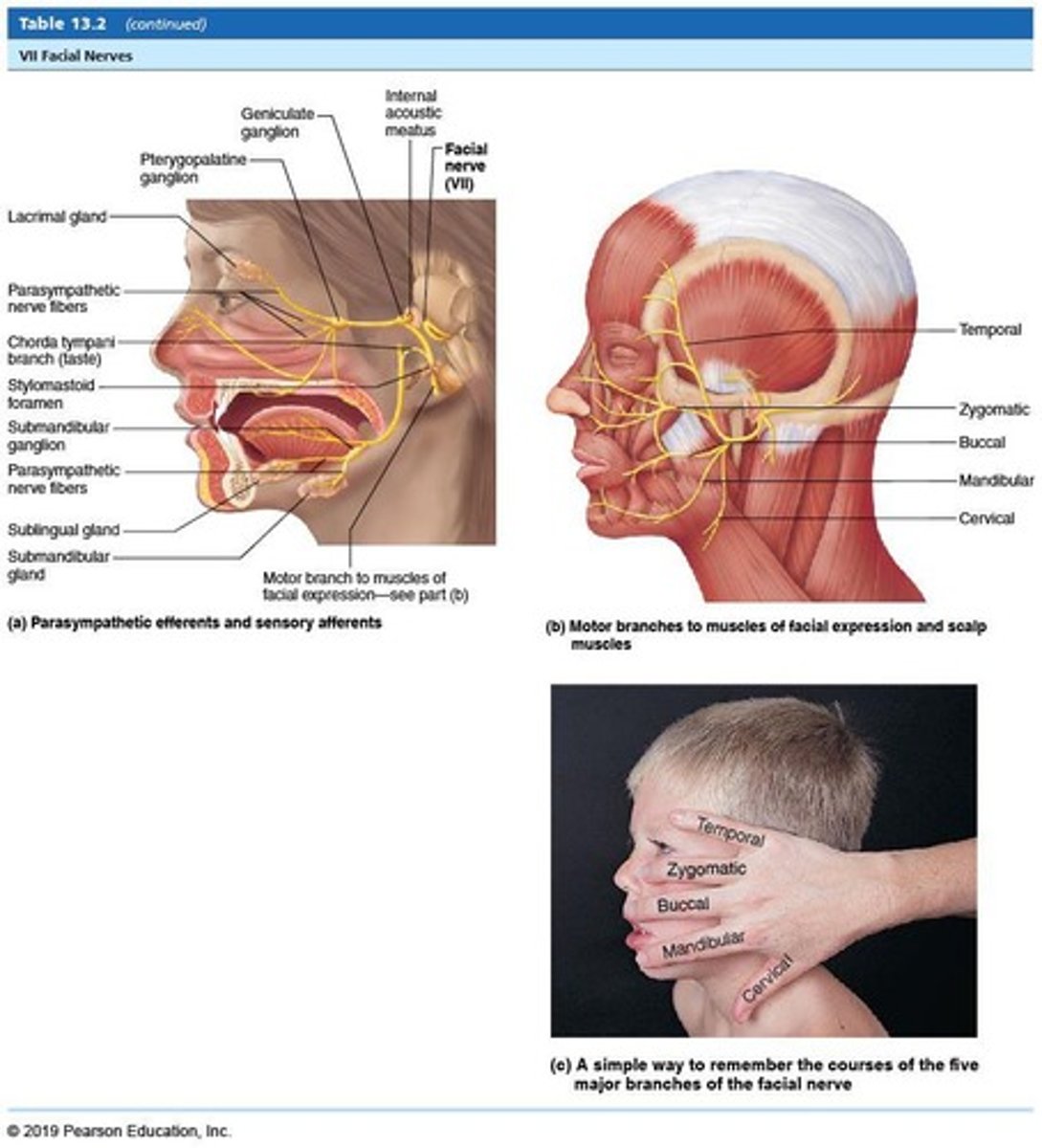
Cranial Nerve VII (CN VII)
Facial nerve.
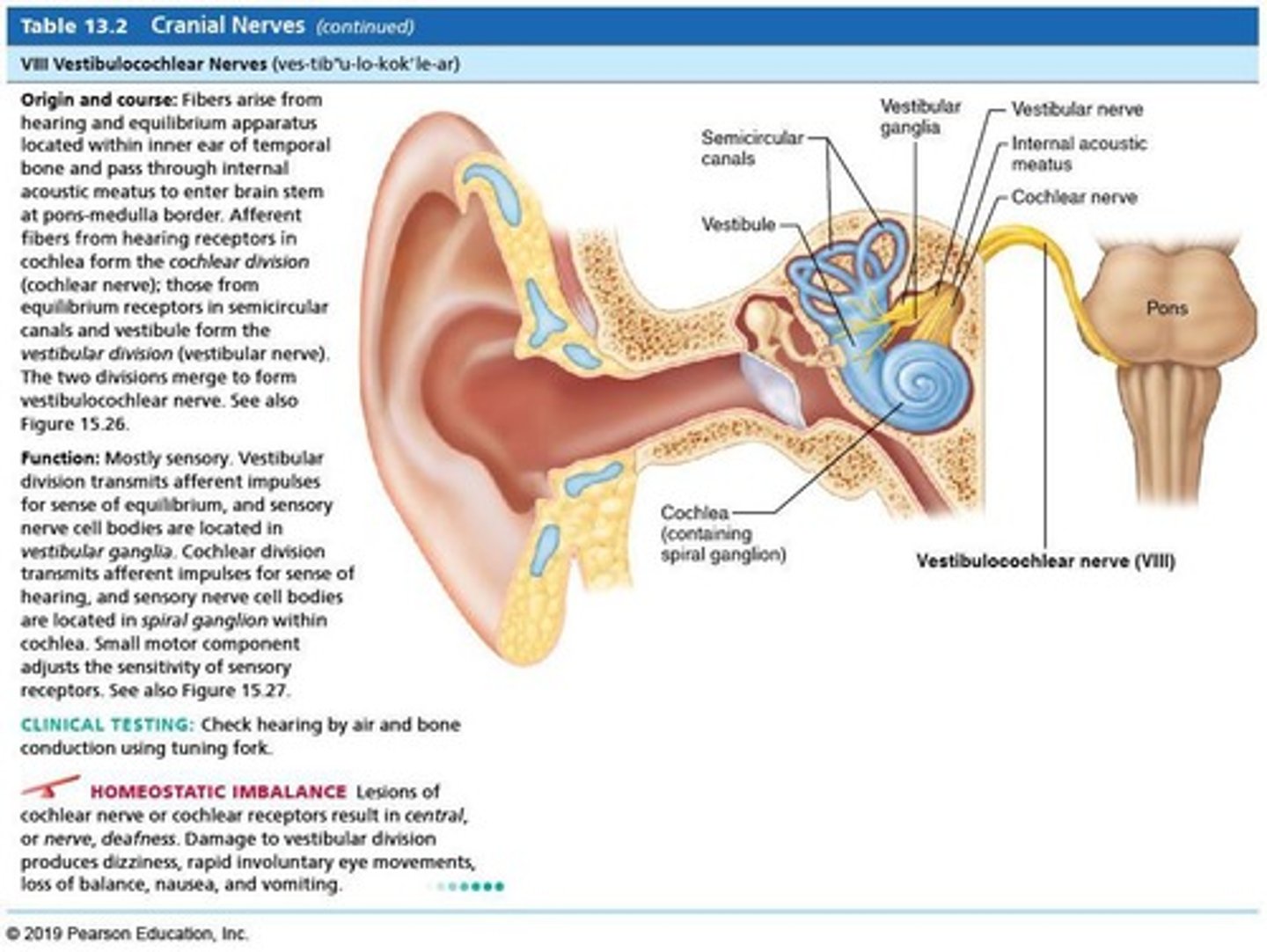
Cranial Nerve VIII (CN VIII)
Vestibulocochlear nerve.
Cranial Nerve IX (CN IX)
Glossopharyngeal nerve.
Cranial Nerve X (CN X)
Vagus nerve.
Cranial Nerve XI (CN XI)
Accessory nerve.
Cranial Nerve XII (CN XII)
Hypoglossal nerve.
Olfactory nerve
Cranial nerve I (CN I); Function: Smell; Type: Sensory only; Test: Have the patient identify different smells like coffee, vanilla, cinnamon, etc.; Damage: Loss of smell.
Optic nerve
Cranial nerve II (CN II); Function: Vision; Type: Sensory only; Test: Have a patient read an eye chart; Damage: Loss of sight.
Oculomotor nerve
Cranial Nerve III (CN III); Function: Eye movements (Moves most extraocular eye muscles (SR, IR, MR, IO)); Type: Motor only; Test: Have patient follow tip of pen (eye tracking); Damage: Double vision, eyes won't track equally, drooping eyelid (CN III).
Trochlear nerve
Cranial Nerve IV (CN IV); Function: Eye movements (Controls superior oblique muscle (eye depression + intorsion)); Type: Motor only; Test: Have patient follow tip of pen (eye tracking); Damage: Double vision, eyes won't track equally, drooping eyelid (CN III).
Trigeminal nerve
Cranial Nerve V (CN V); Function: Sensory: Face sensation (touch, pain, temp), cornea; Motor: Muscles of mastication (chewing); Type: Mixed; Test: 1. Have patient close their eyes, stroke their face with a cotton swab to see if they can feel it. 2. Have patient clench their jaw/bite; Damage: Facial numbness, difficulty chewing. Trigeminal neuralgia: Inflammation of trigeminal nerve causing severe facial pain.
Abducens nerve
Cranial Nerve VI (CN VI); Function: Eye movements (Controls lateral rectus (abducts the eye)); Type: Motor only; Test: Have patient follow tip of pen (eye tracking); Damage: Double vision, eyes won't track equally.
Facial nerve
Cranial Nerve VII (CN VII); Function: Motor: Muscles of facial expression; Sensory: Taste; Type: Mixed; Test: Have patient raise eyebrows, smile, etc.; Damage: Bell's Palsy - sagging of mouth, facial paralysis, loss of taste.
Vestibulocochlear nerve
Cranial Nerve VIII (CN VIII); Function: Balance & Hearing; Type: Sensory only; Test: Hold vibrating tuning fork near patient's ears. Have patient close their eyes and gently nudge them; Damage: Hearing loss, vertigo/loss of balance.
Glossopharyngeal nerve
Cranial Nerve IX (CN IX); Function: Sensory: Taste; Motor: Swallowing (stylopharyngeus); Type: Mixed; Test: Have patient talk, swallow or trigger gag reflex with tongue depressor; Damage: Hoarse voice, difficulty swallowing, loss of taste.
Vagus nerve
Cranial Nerve X (CN X); Function: Sensory: Taste; Motor: Swallowing (stylopharyngeus); Also... organ muscles & organ sensations; Type: Mixed; Test: Same as CN IX as they both control larynx; Damage: Hoarse voice, impaired digestion and elevated heart rate.
Spinal Accessory nerve
Cranial Nerve XI (CN XI); Function: Neck and shoulder muscles; Type: Motor only; Test: Have patient shrug shoulders; Damage: Difficulty flexing and turning head, shrugging shoulders.
Hypoglossal nerve
Cranial Nerve XII (CN XII); Function: Tongue movement; Type: Motor only; Test: Have patient stick out their tongue; Damage: Difficulty moving tongue, chewing, swallowing, and talking.