(1) Global hydropheric system and the "spheres" (copy)
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
water and carbon
the earth's life support system
the two key "fuels" which enables the natural systems on earth to function
Prof Martin Evans
"the concept of the biogeochemical cycle underpins understanding of global change"
Atmosphere
= the mixture of gases around the earth
... earth's atmosphere is composed of about 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and 1% other gases

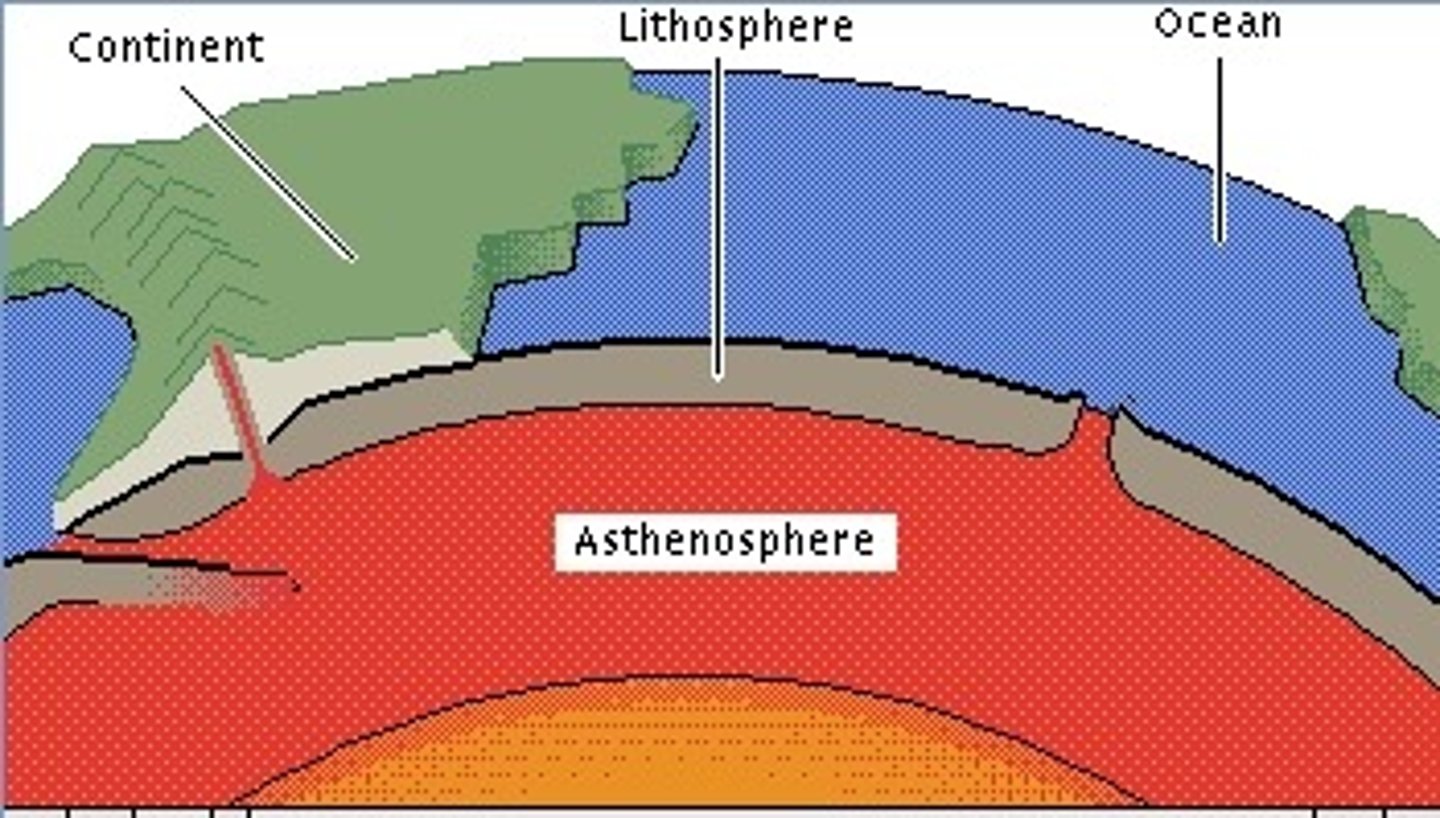
Lithosphere
= the solid outer part of the earth which includes the brittle upper portion of the mantle and the crust
(outermost layers of earths structure)
Biosphere
= the region of the earth where life can exist and grow
... constitution of the ecosystems
Hydrosphere
= the total amount of water on a planet (can be liquid, vapour, or ice)
... surface water, underground water, and water in the air

Cryosphere
= the frozen water in the earth system, including frozen parts of the ocean
... solid precipitation, snow, sea ice, lake and river ice, icebergs, glaciers, ice caps, ice sheets/shelves, permafrost

Anthrosphere
= the total presence of humans and human systems on earth
... evolutionary origins, species diversity, culture, technology, built environment, etc.

system
A group of interacting, interrelated, or interdependent elements that function together to accomplish a goal
subsystems
smaller systems that operate within the context of a larger system
i.e., the "spheres"
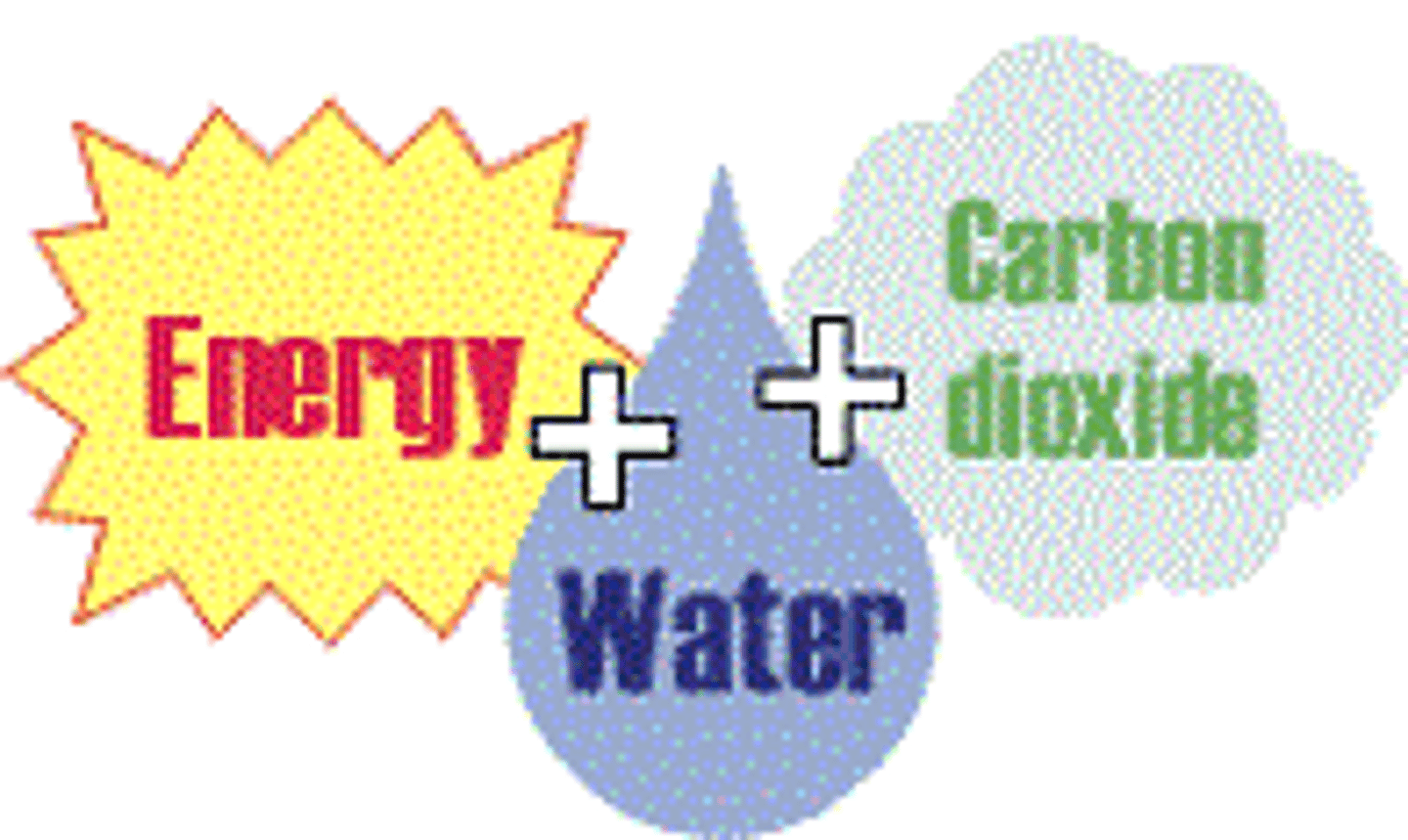
inputs
the addition of matter/energy into a system from the outside
e.g., precipitation with dissolved carbon dioxide
outputs
where matter or energy leave a system to the outside
e.g., dissolved carbon with runoff

energy
power or driving force
glucose through photosynthesis
stores/components
the individual elements/parts of a system
e.g., trees, puddles, soil, rock
flows/transfers
The links or relationships between the components
e.g., infiltration, groundwater flow, evaporation, burning
isolated system
a system with no inputs and no outputs of matter and energy
e.g., the universe

open systems
a system where there are inputs and outputs of energy and matter
e.g., coastal and river systems

closed systems
where there are inputs and outputs of energy, but the matter stays within the systems
e.g., the global hydrological cycle and drainage basin system
e.g., the global carbon cycles
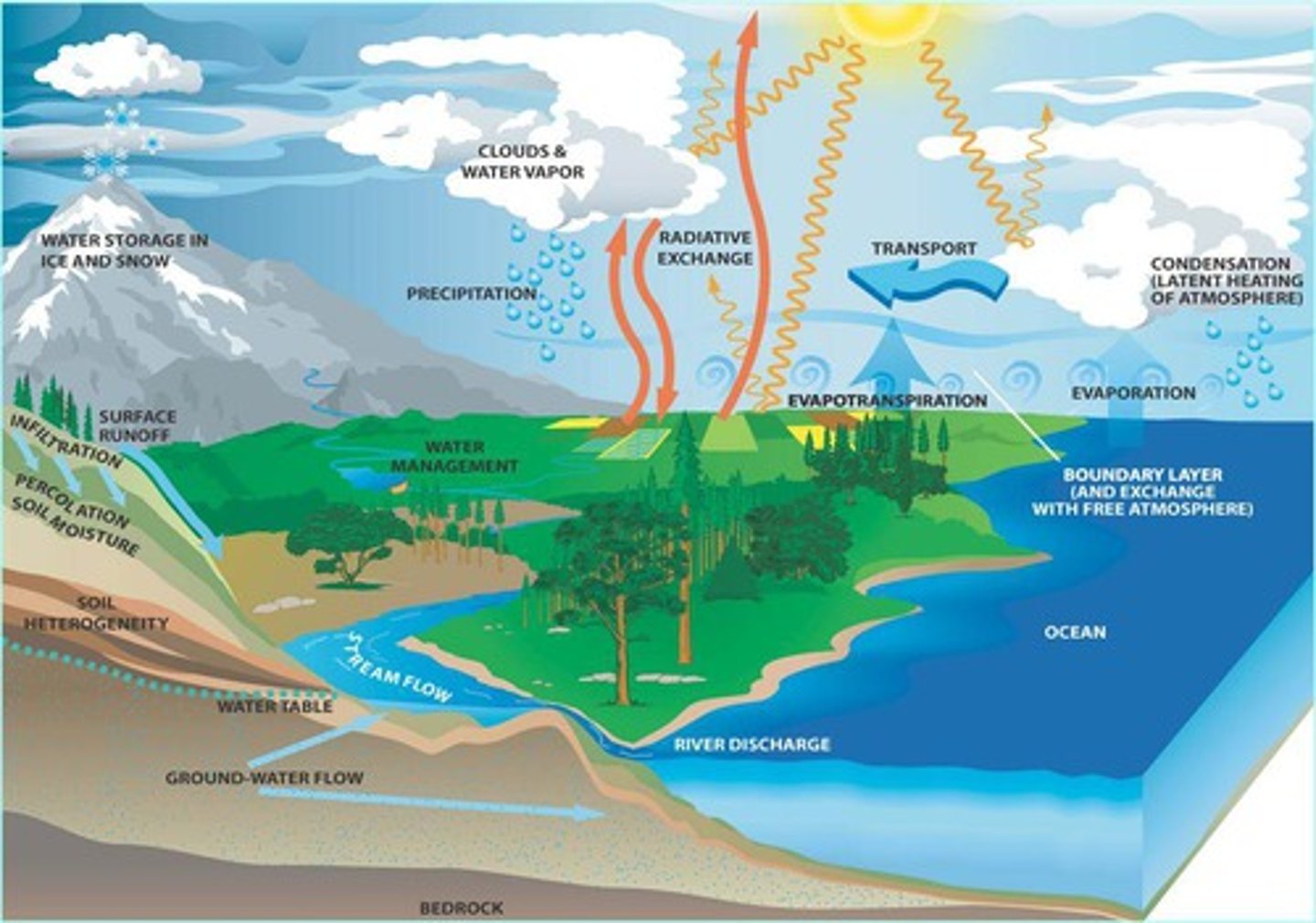
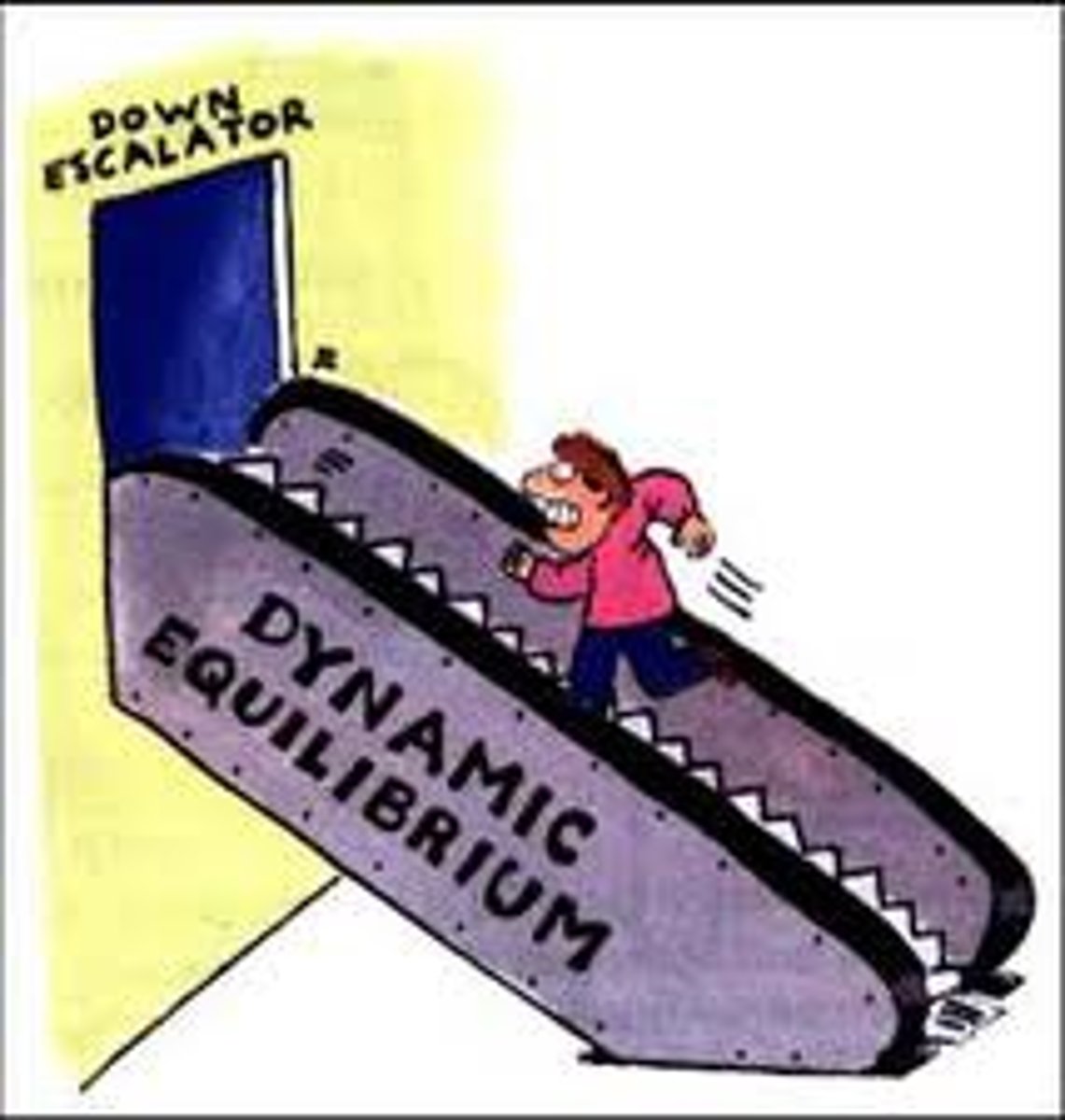
dynamic equillibirum
the balanced state of a system when inputs and outputs balance over time
... result of positive and negative feedback

negative feedback
= helps to maintain the natural environment
example of negative feedback
increased surface temperatures lead to an increase in evaporation from the oceans
this leads to more cloud cover, which reflects more radiation from the sun
...resulting in a slight cooling of surface temperatures
positive feedback
= tries to overcome the threshold to trigger a new natural state, works against the equilibrium
example of positive feedback
rising sea level due to thermal expansion and melting freshwater ice can destabilise ice shelves, increasing the rate of calving and consequently melting
... causing sea levels to rise further
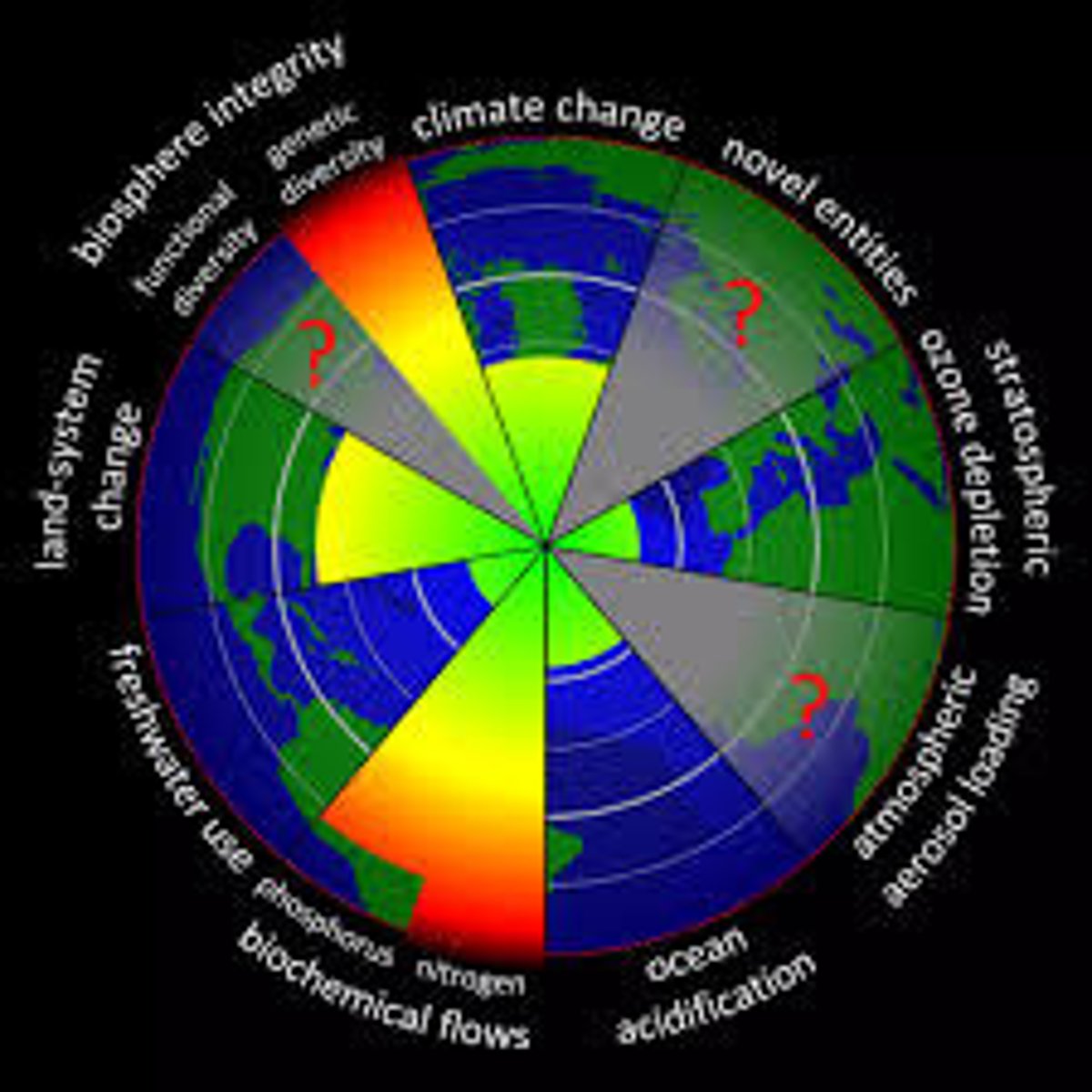
planetary boundaries 2009
Green areas represent human activities that are within safe margins
Yellow areas represent human activities that may have exceeded safe margins
Red areas represent human activities that have exceeded the safe margin
Grey areas with red question marks represent human activities for which safe margins have not been determined
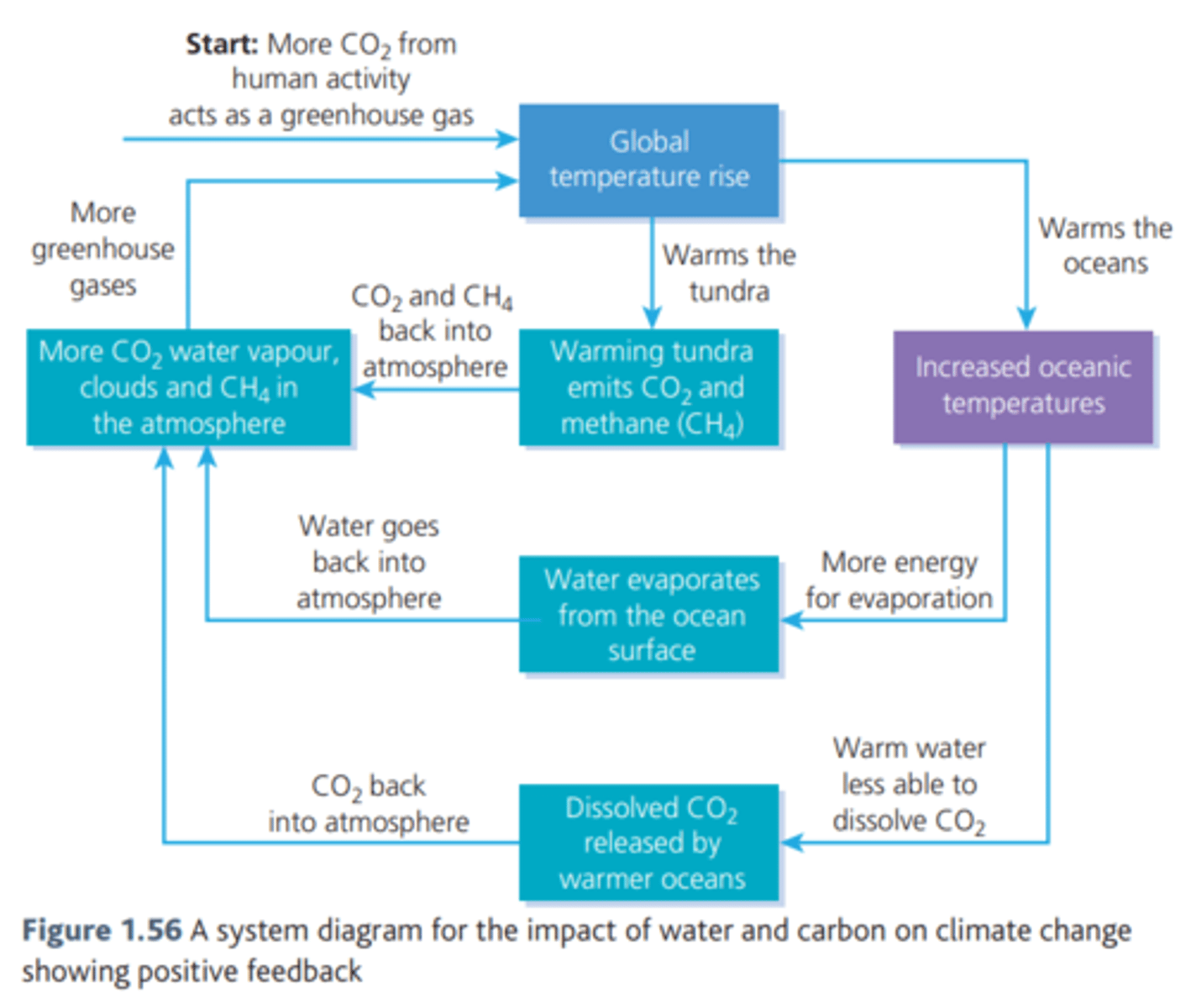
connections between flows and feedback
global temperature rise increases water vapour + evaporation (positive) so more CO2 is returned to atmosphere
Oceans remove Co2 from air (negative) so more water means more CO2 is absorbed
rising temperatures melt permafrost (positive) so less radiation is reflected back to the atmosphere and more is absorbed
Co2 back to atmosphere (positive)