Macroeconomics - Inflation & Types of Inflation
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Inflation: Definition
a sustained increase in the average price level (APL) of an economy over time
Stable inflation is associated with growth (2-3%)
Unstable rates of inflation cause uncertainty in the economy and affect spending decisions
↑AD → ↑profits and incomes → ↑jobs → ↓unemployment
Disinflation: Definition
a slowdown in the rate of inflation, slower inflation
Prices are still increasing, but more slowly
Ex: from 4% to 2% inflation but NOT DEFLATION
Deflation: Definition
negative inflation rate; a decrease in the average price level
Often associated with recession and falling demand
Why do we LIKE inflation?
✅ Pros:
↑AD → ↑profits and incomes → ↑jobs → ↓unemployment
Why do we DISLIKE inflation?
❌ Cons:
↓Real income falls
Value increases: ↑inflation → ↑prices
↓What income gets you
Workers get demotivated over time by fall in real income 😔
Prices can fluctuate
↓Purchasing power when incomes stay fixed
↓Real income falls
For lower income people, they must spend all they have and can’t save
For middle income people, they can save a little bit but inflation causes them to save less
For higher income people, inflation is not a huge issue at 2%-4%
High and Unstable Inflation: Harmful Effect
Reduces real income: When wages don't keep up with inflation, purchasing power falls.
Uncertainty: Discourages investment due to unpredictable future costs.
Income redistribution effects: Hurts fixed-income earners and savers.
Wage pressure and strikes: Workers may demand higher wages to maintain living standards.
Potential inflationary spiral: Higher wages → higher costs → higher prices → demand for more wages.
Why do workers hate inflation?
Inflation causes…
Disincentive: workers become less productive, may protest
Discontent: unions potentially strike to raise wages
INFLATIONARY SPIRAL!
Real Interest Rate:
High inflation reduces real returns on savings.
Investors may shift to real assets (property, gold, inflation-indexed bonds).
Savings during Inflation: Effect on Economic Groups
Effect of savings due to inflation:
Low-income people: few savings, more trade-offs
Middle-income people: they have savings and can maintain their lifestyle to a point
High-income people: have a cushion and can weather the storm, more assets so asset values ↑
Inflation acts as a regressive tax, disproportionately hurting the poor
Consumer Price Index (CPI): Definition
weighted basket of typical goods and services that are bought in the economy by the typical family, used to measure changes in inflation
Measures the average change in price of a "basket" of goods and services consumed by a typical household.
Consumer Price Index (CPI): Limitations
Representative bias: Not all households have the same consumption patterns.
little information on how individuals are affected (disregards different cultures, income brackets, ages, parts of the country)
Static basket: Basket may not reflect changes in preferences or new goods.
Quality adjustments: goods and services improve in quality over time → prices of certain goods may fall. A reduction in inflation may be due to improvements in quality, but it may be misinterpreted as a bad thing or that economic activity is slowing down when it’s not
CPI may overstate inflation if it doesn’t account for quality improvements.
Does not reflect income distribution: Effects of inflation vary across income levels.
Causes of Inflation: Types
Demand-Pull Inflation = increase in aggregate demand
Cost-Push Inflation = higher costs of production
Monetary Inflation = sustained increase in the amount of money available to the economy
Inflationary Spiral = inflation compounds
(Price-Wage Inflationary Spiral)
Hyperinflation = Demand-Pull → Cost-Push Inflation spirals
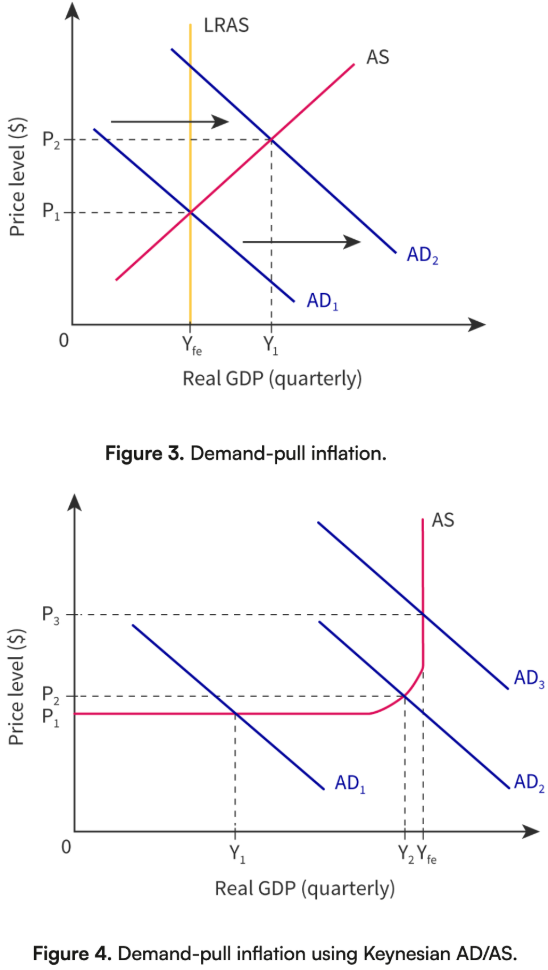
Demand-Pull Inflation: Definition
occurs when aggregate demand exceeds the economy’s productive capacity
Key features:
Driven by increases in C, I, G, or (X - M).
Likely when the economy is near or at full employment.
Supported by Keynesian and Neoclassical views:
Keynesian: Prices may not rise until full capacity is reached.
Neoclassical: Any AD increase raises prices; no permanent output gain.
Demand-Pull Inflation: Graph
Demand-Pull Inflation: Solutions 🦊
🔹 Demand-Pull Inflation
Main Issue: Excessive aggregate demand
Solutions:
Contractionary fiscal policy (reduce government spending, raise taxes)
Contractionary monetary policy (raise interest rates, reduce money supply)
Strengthen exchange rate to reduce net exports
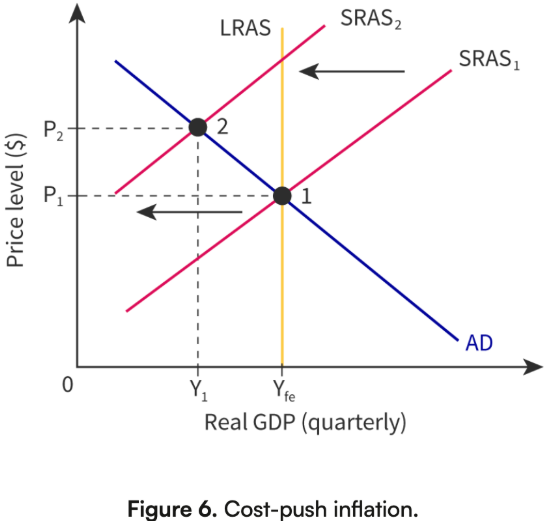
Cost-Push Inflation: Definition
Caused by increases in the cost of production that shift the short-run aggregate supply (SRAS) curve leftward
Sources:
Rising wages
Higher raw material prices (e.g., oil)
Currency depreciation (imported inflation)
Supply shocks (natural disasters, wars)
Increased regulation or taxes on firms
Cost-Push Inflation: Graph
Cost-Push Inflation: Solutions 🦊
🔹 Cost-Push Inflation
Main Issue: Rising production costs
Solutions:
Market-based supply-side policies (e.g., deregulation, reduce minimum wage, reduce production taxes)
Encourage technological innovation to boost productivity
Reduce import tariffs or secure cheaper import sources (to lower costs)
NOTE: Demand-side policies may worsen unemployment
Monetary Inflation: Definition
results from excessive growth in the money supply beyond the economy's ability to produce goods/services
Key concept:
"Too much money chasing too few goods."
Expansionary monetary policy (e.g., QE, OMO, deficit financing) increases AD, possibly triggering inflation.
Monetary Inflation: Solutions 🦊
🔹 Monetary Inflation
Main Issue: Excess money supply
Solutions:
Tight monetary policy (increase interest rates, sell government bonds, reduce QE)
Improve central bank independence to reduce political pressure for excessive money printing
Currency reform in extreme cases
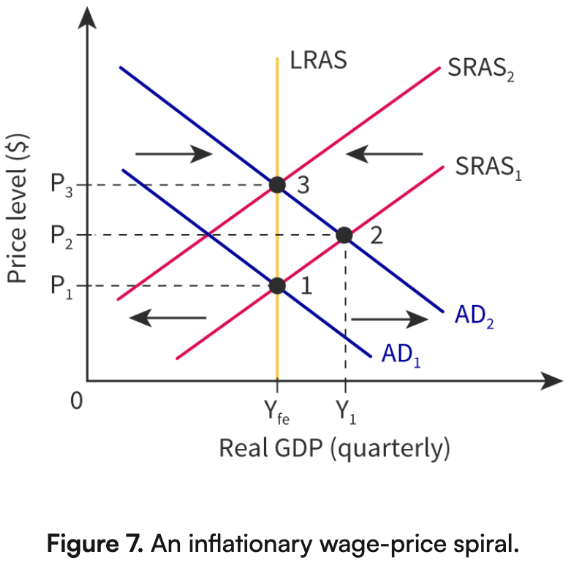
Inflationary Spiral (Price-Wage): Definition
occurs when inflation expectations lead to continuous wage and price increases:
Higher AD causes prices to rise.
Workers demand higher wages.
Higher wages increase costs for firms.
Firms raise prices again.
Cycle repeats, leading to embedded inflation.
Inflationary Spiral (Price-Wage): Graph
Inflationary Spiral (Price-Wage): Solutions 🦊
🔹 Inflationary Spiral
Main Issue: Self-reinforcing wage-price increases due to expectations
Higher AD causes prices to rise.
Workers demand higher wages.
Higher wages increase costs for firms.
Firms raise prices again.
Cycle repeats, leading to inflationary spiral.
Solutions:
Pre-emptive contractionary monetary policy to manage expectations
Implement income policies or wage guidelines
Maintain credibility of central bank to anchor inflation expectations
Short-term wage freezes or public sector wage restraint (controversial)
Hyperinflation: Definition and Impact
Definition: Extremely rapid and out-of-control inflation, often >50% per month
Causes:
Money illusion from higher inflation: higher wages and higher inflation
Demand-pull → cost-push inflation spirals into hyperinflation
Persistent demand-pull + cost-push effects
Massive money supply growth
Collapse of trust in currency
Effects:
Money loses value rapidly
Savings and pensions are wiped out
Shift to barter or foreign currency
Solutions:
Currency reform (currency swap)
Stabilization via tight monetary and fiscal policy
Restoring central bank credibility
External support (e.g., IMF loans)
Hyperinflation: Solutions 🦊
Problem: Demand Pull → solve using Contractionary Demand-Side policies
Milton Friedman Monetarist
Currency swap: replaced inflated currency with new second currency to raise faith
Hyperinflation is too difficult to solve, but inflation rates of ~8% is manageable and can be used for policies
Quantitative Easing (QE)
Introduction of new money into the money supply of an economy
Usually used to kickstart aggregate demand when the economy is stagnant
However, this can be done by government implementing government spending projects with new money or by buying back bonds and putting new money onto the market