Medical Assisting: Respiratory System
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/78
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
1
New cards
Respiratory System (Pulmonary System)
a network of organs and tissues that help the body take in oxygen and expel gas
2
New cards
Parts of the Upper Respiratory Tract
Nose, Nasal cavity, Sinuses, Pharynx, and Larynx (voice box)
3
New cards
Parts of the Lower Respiratory Tract
Trachea, Bronchial tree, Lungs
4
New cards

What is pulmonary ventilation?
the physical act of breathing
5
New cards
Primary Function of the Respiratory System
1. Breathing/ Pulmonary Ventilation
2. Regulating gas exchange
3. Producing audio
4. Maintaining body temperature
5. House sensory neurons
6. External and Internal Respiration
6
New cards
What are the 3 processes used to ensure oxygen is provided to the body and corbon dioxide is removed?
Pulmonary Ventilation, Respiration, Oxygenation
7
New cards
What are the 3 major respiratory muscles?
Diaphragm, External Intercostal Muscles, and Internal Intercostal Muscles
8
New cards
Diaphragm
a dome-shaped muscle below the lungs that separate the thoracic and abdominal cavity
9
New cards
External Intercostal Muscles
pull ribs upwards and outwards
10
New cards
Internal Intercostal Muscles
pull ribs downwards and inwards
11
New cards
Breathing
the involuntary inhaling and exhaling of air
12
New cards
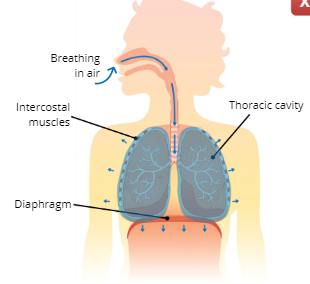
Inhalation (inspiration)
the process of breathing in air
13
New cards
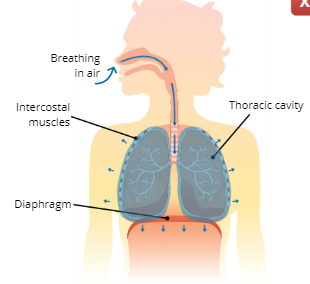
Explain the Process of Inhalation (Inspiration)
The intercostal muscles and diaphragm contract, this causes the thoracic cavity to expand which increases lung volume, the increase in lung volume creates a suction that pulls air into the lungs
14
New cards
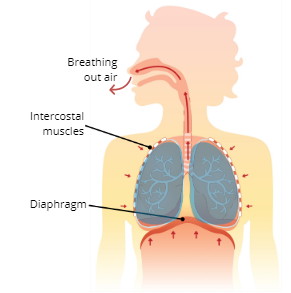
Exhalation (Expiration)
the process of breathing out air
15
New cards
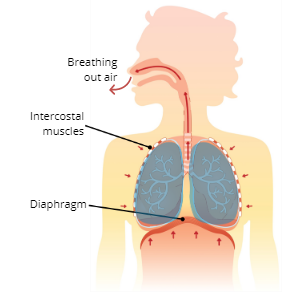
Explain the Process of Exhalation (Expiration
The intercostal muscles and diaphragm relax, which causes the thoracic cavity to reduce in size which decreases lung volume, this then creates pressure that pushes air out of the lungs
16
New cards
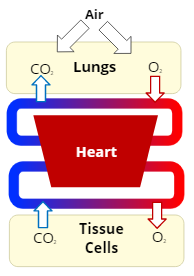
Respiration
the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the body
17
New cards
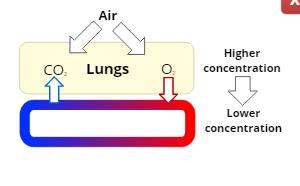
External Respiration
the exchange of the gases, oxygen and carbon dioxide, between the air in the lungs and the bloodstream
18
New cards
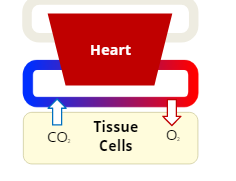
Internal Respiration
the exchange of the gases, oxygen and carbon dioxide, between the bloodstream and cells in the body's tissues
19
New cards
In the cells, what is oxygen used for?
Cellular respiration
20
New cards
What is formed when hemoglobin combines with oxygen?
oxyhemoglobin
21
New cards
What is formed when hemoglobin combines with carbon dioxide?
carbaminohemoglobin and carboxyhemoglobin
22
New cards
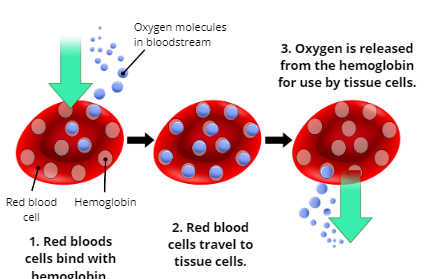
Oxygenation
the process of supplying oxygen to the body’s tissue cells
23
New cards
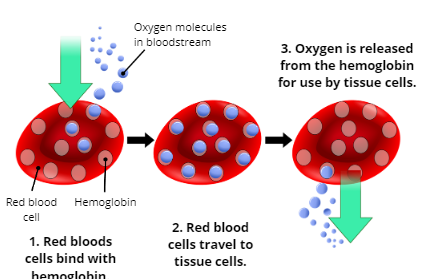
Explain the Process of Oxygenation
1. Oxygen molecules in the bloodstream enter red blood cells and bind with hemoglobin
2. Red blood cells travel to tissue cells
3. Oxygen is released from the hemoglobin for use by tissue cells
24
New cards
Nose
primary passageway for air into and out of the respiratory system
25
New cards
Cilia
nasal hair that filters out foreign materials and moves mucous from nasal cavity into pharynx to be swallowed into stomach
26
New cards
Nostrils
entrance of nose
27
New cards
Mucous Membranes of Nose
filters out foreign bodies
28
New cards
Mouth-breathing
allows the respiratory system to meet increased oxygen demands during high stress or extreme circumstances. It can lead o an increased risk of dental and gum diseases and respiratory infections
29
New cards
Nasal cavity
primary passageway for air in and out of the respiratory system
30
New cards
Nasal septum
cartilage that divides the nasal cavity into two
31
New cards
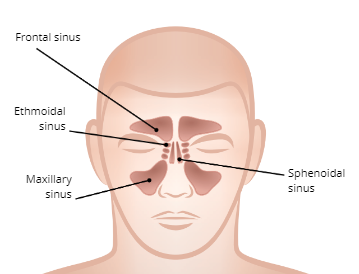
SInuses
four pairs of hollow spaces in the skull that open into the nasal cavity
32
New cards
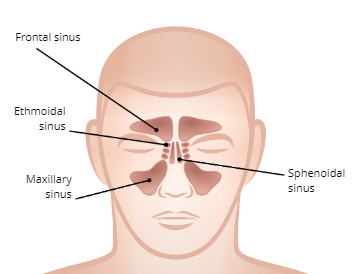
Functions of the Sinuses
1. Moistens and filters air
2. Regulate air temperature
3. Provide voice resonance
33
New cards
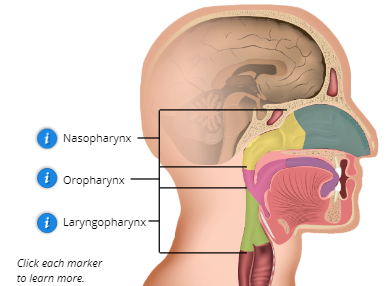
Pharynx
located behind the nasal cavity and mouth; connects nose, mouth, and larynx; functions as a passageway for air moving from the nasal cavity to the larynx and food moving from the mouth to the esophagus
34
New cards
Name the 3 Parts of the Pharynx
Nasopharynx, Oropharynx, and Laryngopharynx
35
New cards
Tonsils
part of the immune system that aids in infection control
36
New cards
What are the 3 different tonsils?
Pharyngeal, Palatine, and Lingual Tonsils
37
New cards
Function of Tonsils
Acts as a passageway for air moving from the nasal cavity to the larynx, food moving from the mouth to the esophagus, and helps form specific phoenetic sounds
38
New cards
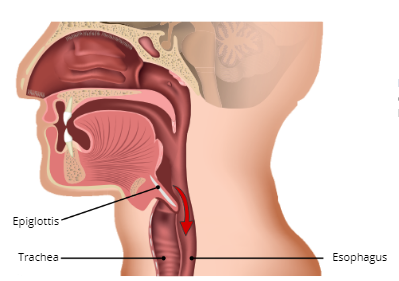
Epiglottis
a small, leaf-like flap of cartilage at the bottom of the laryngopharynx that prevents food from entering the trachea or lungs
39
New cards
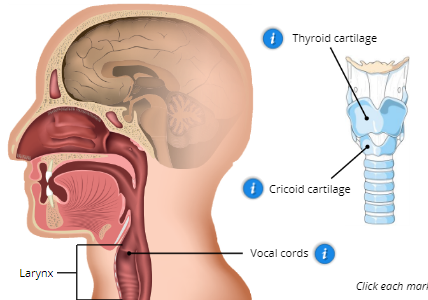
Larynx (voice box)
contains vocal cords and the thyroid and cricoid cartilage
40
New cards
Vocal cords
1. Upper: False Cords
2. Lower: True Vocal Cords
3. Glottis: opening between vocal cords that produce vocal sound
41
New cards
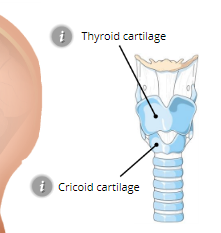
Thyroid Cartilage
Adams apple
42
New cards
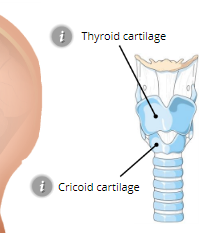
Cricoid Cartilage
expands to allow large amounts of food to be swallowed
43
New cards
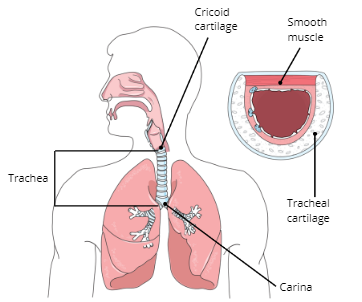
Trachea
AKA windpipe is a C-shaped ringed cartilaginous tube
44
New cards
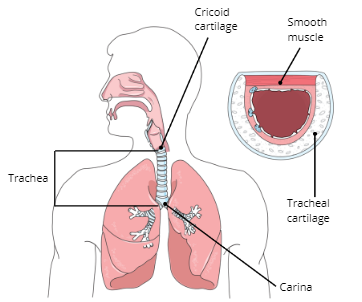
Carina
a ridge of cartilage at the base of the trachea that separates the openings of the main bronchi
45
New cards
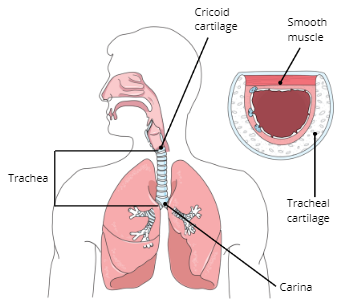
Function of Trachea
To warm and moisten the air before entering the lungs and serve as a passageway for air from the upper respiratory tract to the lungs
46
New cards
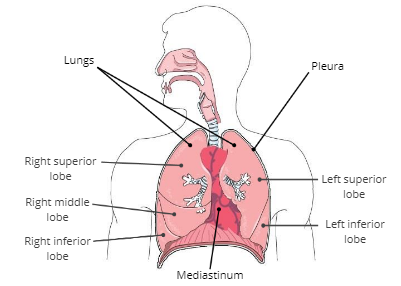
Lungs
soft, spongy organs in the thoracic cavity that are responsible for gas exchange
47
New cards
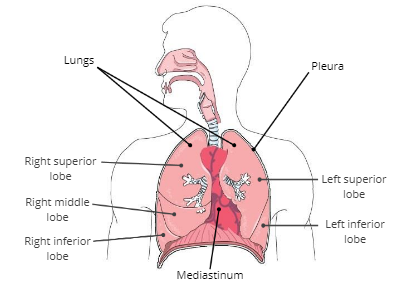
Mediastinum
a compartment in the center of the thoracic cavity that contains the heart, trachea, and esophagus.
48
New cards
Pleura
a thin, double membrane that surrounds each lung and lines inner surfaces of the thoracic cavity
49
New cards
Pleural fluid
fluid in between the pleura that reduces friction during breathing
50
New cards
Bronchi
larger airways in the lungs that are supported by cartilage rings
51
New cards
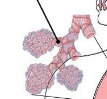
Bronchioles
narrow airways in the lungs (less than 1mm in diameter) that do not contain cartilage rings and connect bronchi to alveoli
52
New cards
Alveoli
small sacs of air
53
New cards
Surfectant
reduces surface tension of fluid in the wet surfaces of the alveoli; are produced by pneumocytes
54
New cards

What are PFTs, how are they used, and what is a common PFT?
Pulmonary function tests are tests that show how well the lungs are working. They are used to measure lung volume, capacity, rates of flow, and gas exchange. A common PFT is the Spirometry test
55
New cards
Tidal Volume (TV)
amount normally breathed in or out with each normal breath
56
New cards
Vital Capacity (VC)
largest amount of air one can breathe out in one expiration after the deepest inhalation possible
57
New cards
Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV)
amount of air that can be forcefully exhaled after a normal expiration
58
New cards
Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV)
amount of air that can be forcefully inhaled after a normal inspiration
59
New cards
Residual Volume (RV)
air that remains in the lungs after a forceful expiration
60
New cards
Total Lung Capacity
total amount of air the lungs can hold
61
New cards
Eupnea
normal breathing
62
New cards
Hyperventilation
rapid, deep respirations
63
New cards
Hypoventilation
slow, shallow respirations
64
New cards
Dyspnea
labored or difficult respirations
65
New cards
Orthopnea
dyspnea when lying down and is relieved when position is changed
66
New cards
Apnea
absence of breathing for more than 19 secs
67
New cards
Tachypnea
abnormal, rapid breathing
68
New cards
Cheyne-Stokes Syndrome (CSR)
a cycle of apnea and hyperventilation associated with critical conditions
69
New cards
Respiratory Arrest
failure to resume breathing after a period of apnea
70
New cards
Snoring
the vibration of soft tissues when muscles of the palate, tongue, and throat relax
71
New cards
Tuberculosis (TB)
a contagious infection that usually attacks your lungs
72
New cards

Asthma
a condition where the bronchial tubes become inflamed and as a result, restrict airflow
73
New cards

Atelectasis
the complete or partial collapse of the lung
74
New cards
Emphysema
a lung condition caused by damage to the alveoli, which eventually reduces the amount of oxygen that reaches the bloodstream
75
New cards
Lung Cancer (Lung Carcinoma)
a malignant tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in lung tissue
76
New cards
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
a term for chronic conditions that cause recurrent blockage of airflow in the lungs like emphysema, chronic bronchitis, and chronic obstructive asthma
77
New cards

Pneumonia
an infection that causes inflammation in the alveoli and can cause the alveoli to be filled with fluid or pus
78
New cards
COVID-19
a respiratory condition that has the greatest effect on the elderly and those with pre-existing conditions
79
New cards

Peak Expiratory Flow Rate (PEFR)
Peak expiratory flow rate is a measurement of air flow out of the lungs or a person's maximum speed of expiration. It's mostly done to measure the severity of asthma and the effectiveness of treatment. It is measured with a peak flow meter.