Integumentary System
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
integumentary system
skin, hair, nails
The two major regions of the integument
epidermis and dermis
epidermis
most superficial layer, made of keratinocytes
keratin
tough material that protects the lower layers of the epidermis from wear and tear
strata
numerous layers of the epidermis
stratum basale
deepest layer of the strata.
attached by basement membrane.
cells divide repeatedly and push up toward the superficial layers as the cells increase in age.
melanocytes
produce melanin
in stratum basale
melanin
protects the stratum basale from the damaging effects of ultraviolet radiation
granules
precursors of keratin found in the outermost layer of epidermis
stratum corneum
most superficial layer (closest to outside)
tough layer of dead cells flattened at the surface
rapid cell division
producing precursor molecules for waterproofing
completion of waterproofing the cell
three major phases cells go through in epidermis
every 5-6 weeks
the epidermis renews itself every…
dermis
structural integrity of the integumentary system
superficial papillary layer
deeper reticular layer
two major regions of the dermis
papillary region
named for the papillae (bumps)
papillae
interdigitate with the epidermis
provides good adhesion between the layers
reticular layer
largest layer of the two regions in the dermis
blood vessels
bring nutrients to both the dermis and epidermis
occur only in dermis
dermal blood vessels
release heat to the external environment
nerves in the dermis
receive sensory inputs and transmits impulses to the central nervous system
light touch receptors
allow for the perception of very slight touch stimuli
tactile corpuscles
a form of light touch receptor that is in upper portion of the dermis
tactile discs
a form of light touch receptor that is in the upper dermis and lower EPIdermis
lamellar corpuscles
sense pressure
pain receptors
naked nerve endings in the dermis that respond to numerous environmental stimuli
hypodermis
attaches itself to the dermis by collagenous and elastic fibers
also known as subcutaneous tissue
sweat glands and sebaceous (oil) glands
two broadly distributed glands in the dermis and hypodermis
eccrine glands
most common gland
type of sweat gland
produce normal body perspiration
apocrine sweat glands
gland that secretes water and a higher concentration of organic acids
perspiration
reducing of temperature of body by evaporative cooling
hair
accessory structure of integumentary system
hair follicles
projections of the epidermal layers into the dermis
shaft
part of your hair that erupts from the head
hair ROOT
part of hair that is embedded/enclosed by the follicle
hair bulb
the actively growing portion of hair
dermal papilla
center of bulb
contains blood vessels and nerves that reach the hair bulb
root sheath
outer dermal layer of connective tissue and an inner epithelial layer create the …
arrector muscles
connects the hair follicle to the upper regions of the dermis
reason for hair “standing on end”
medulla
central portion of the hair
cortex
contains pigments that gives hair its color
cuticle of the hair
superficial to the cortex
looks rough in microscopic sections
nails
second type of accessory structure of the integumentary system
free edge
part of the nail you clip
eponychium
another name for the cuticle of the nail
nail root
portion of nail that is under the eponychium
nail bed
layer deep to the nail body
lunule
small white crescent that occurs at the base of the nail
hyponychium
region under the free edge of a nail
dark pigmentation
people who produce more melanin
lighter pigmentation
people who produce less melanin
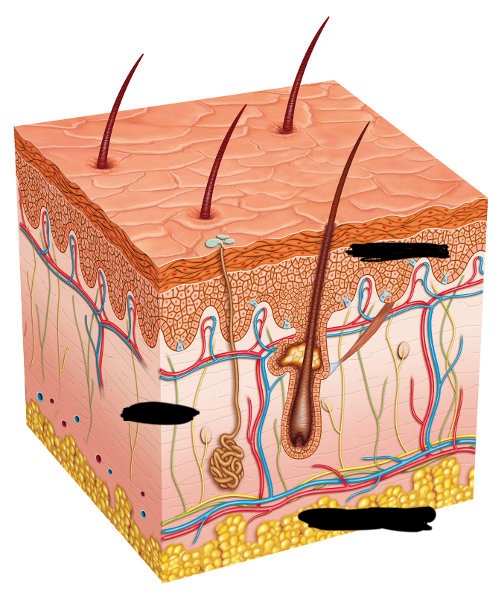
epidermis
top layer is called the
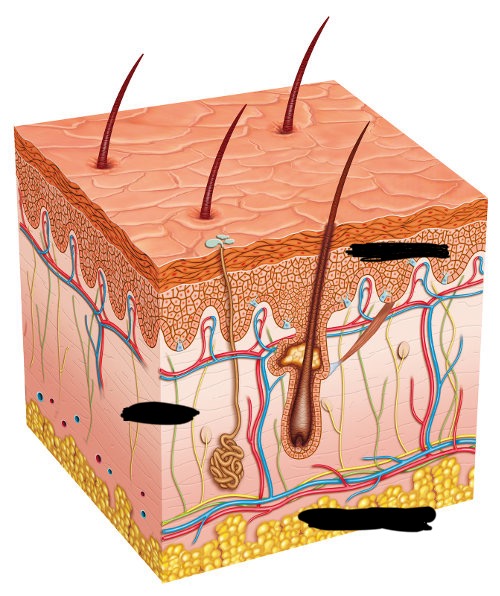
dermis
middle layer is called the
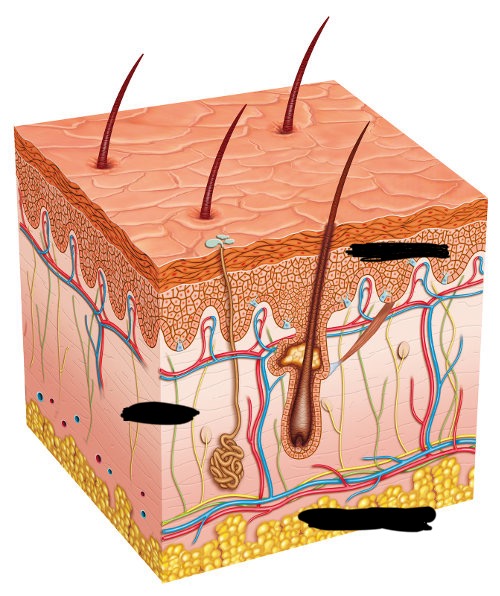
hypodermis
bottom layer is called the
stratum corneum
#1
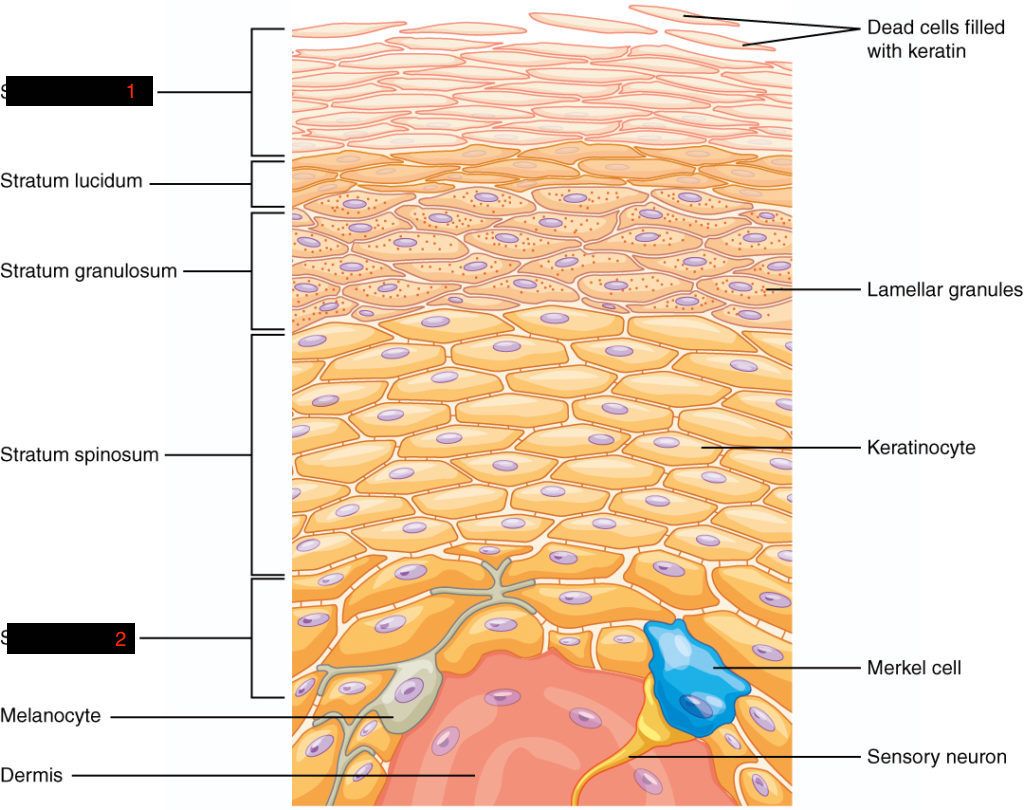
stratum basale
#2
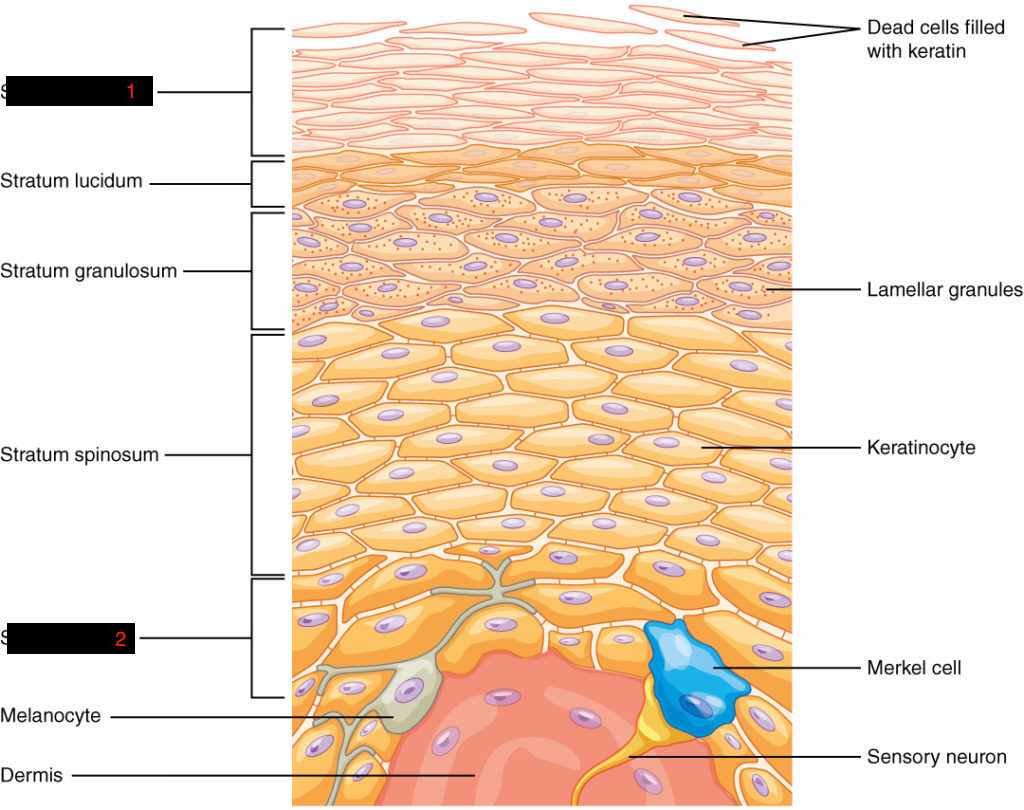
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
what kind of tissue is stratum corneum
areolar loose connective tissue
what kind of tissue makes up the papillary layer of the dermis?
perception of very slight touch stimuli
function of tactile corpuscle
sense pressure
function of lamellar corpuscle
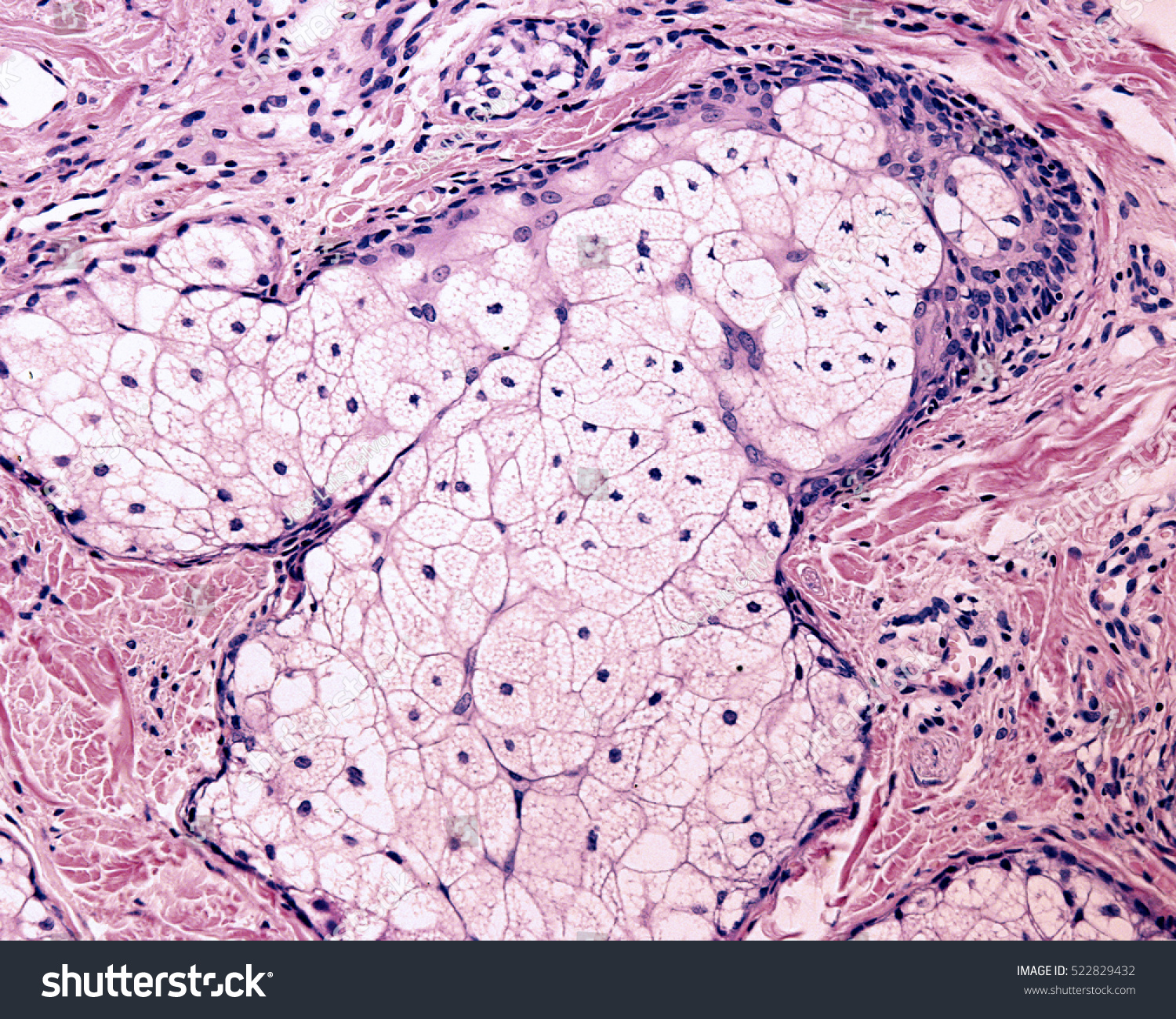
sebaceous gland
what gland does this represent?
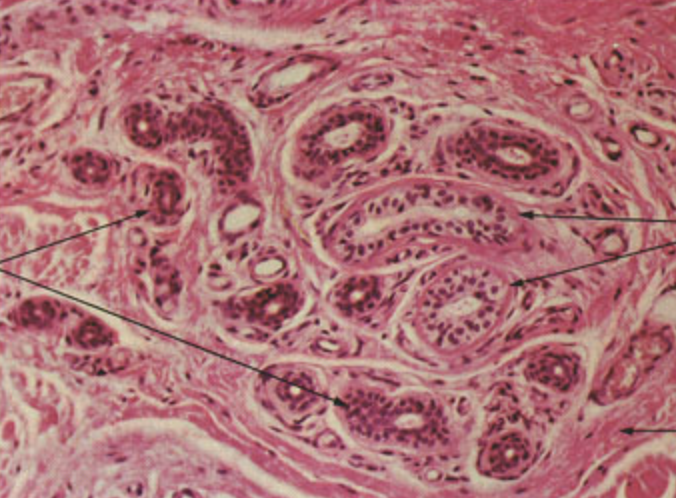
sweat gland
what gland does this represent?
dense irregular connective tissue
what kind of tissue makes up the reticular layer of the dermis?
adipose connective tissue
what kind of tissue makes up the hypodermis? (subcutaneous layer)
first degree burn
superficial burn where the epidermis is still intact and functional
second degree burns
burn that destroys the epidermis and damage extends into the dermis
victim looses heat and fluid
most painful burn
third degree burn
both epidermis and dermis are destroyed, with damage extending into the hypodermis
most likely will not have pain due to nerve cells being destroyed in that area
9% (4.5% front and back)
burn percentage for head
9% (4.5% front and back)
burn percentage for one arm
9%
burn percentage for chest
9%
burn percentage for upper back
9%
burn percentage for lower back
9%
burn percentage for abdomin
1%
burn percentage for genitals
9% (4.5% front and back)
burn percentage for one leg
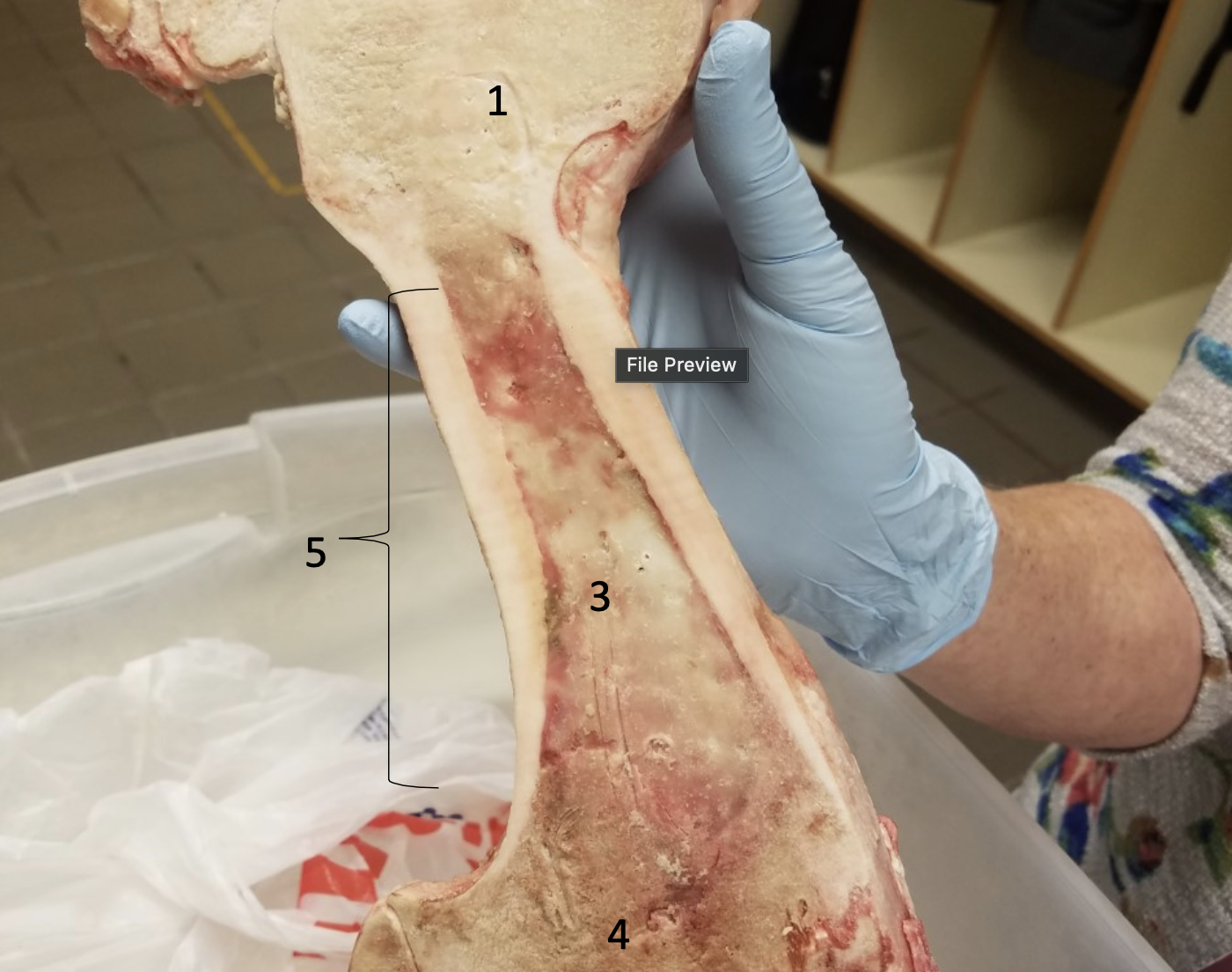
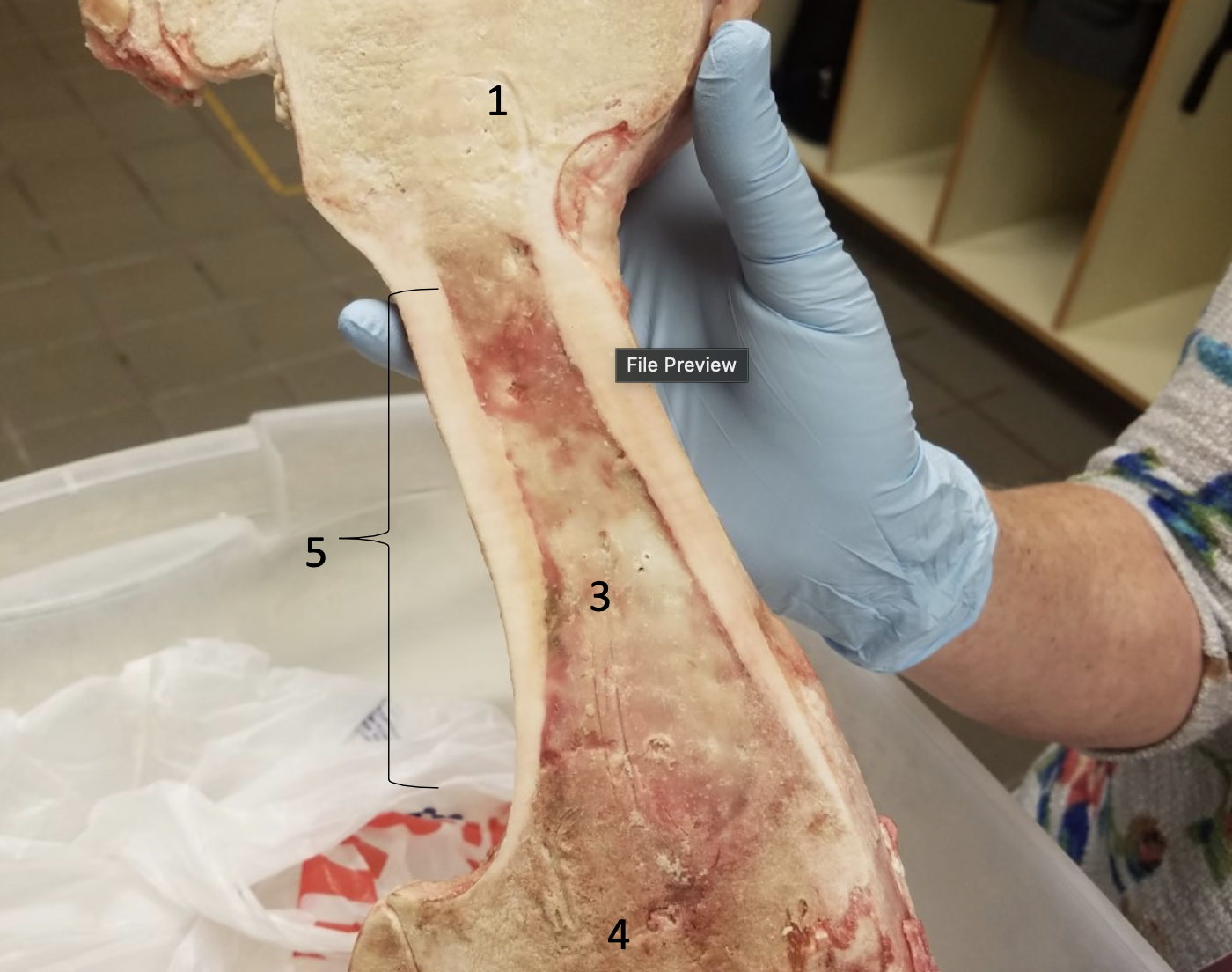
Epiphyseal line
#1
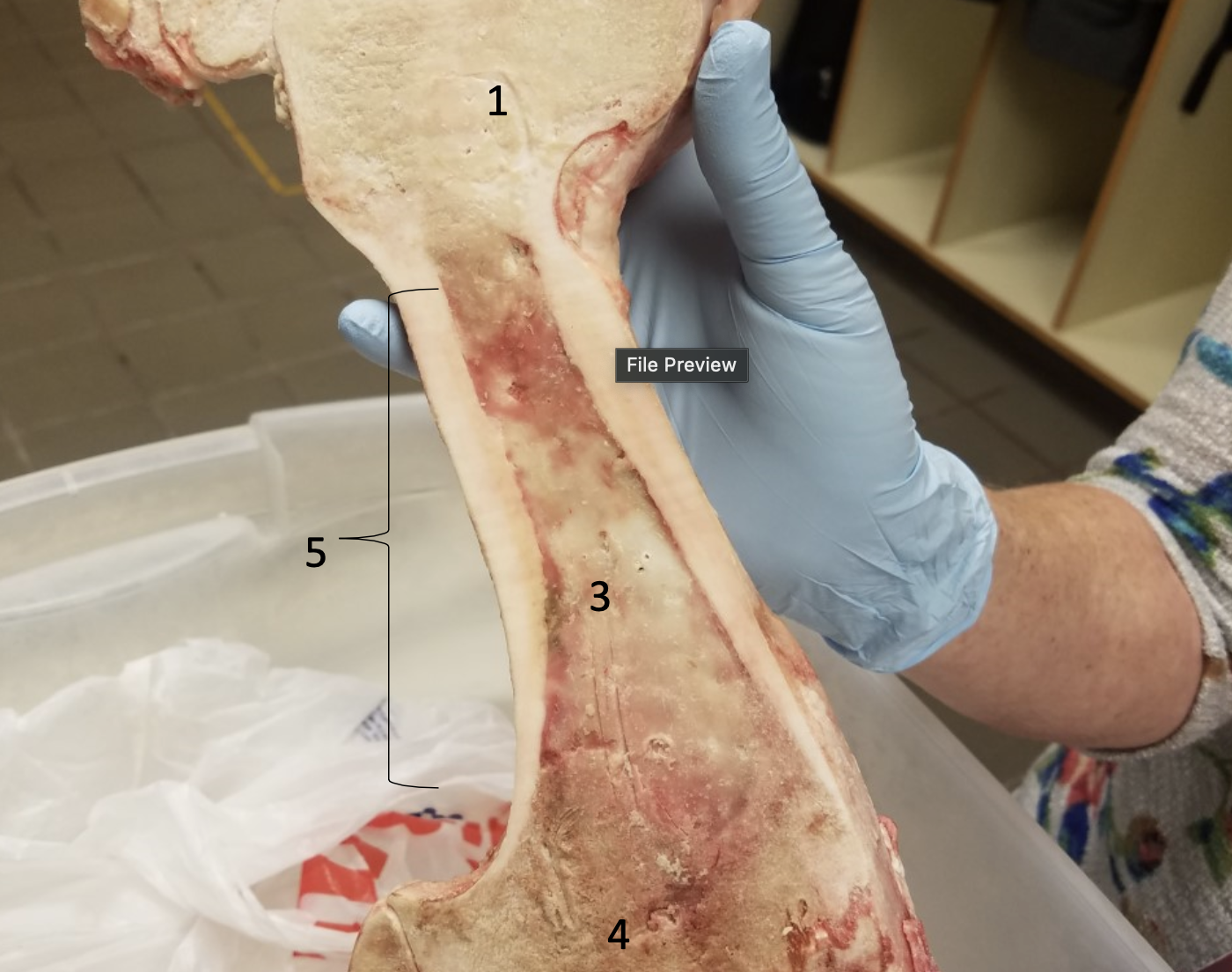
Compact bone
#2
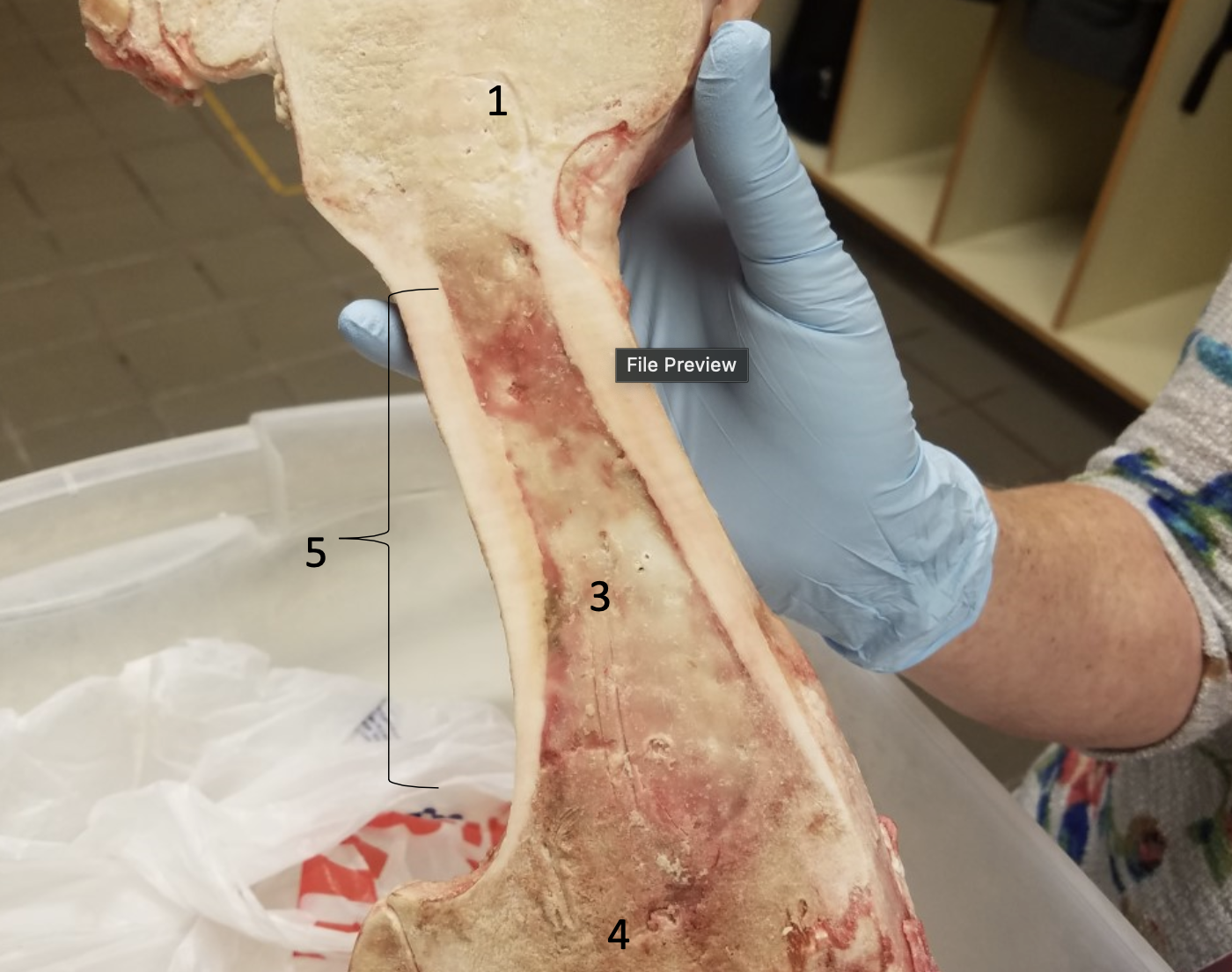
Medullary cavity filled with yellow bone
marrow
#3
Spongy bone
#4
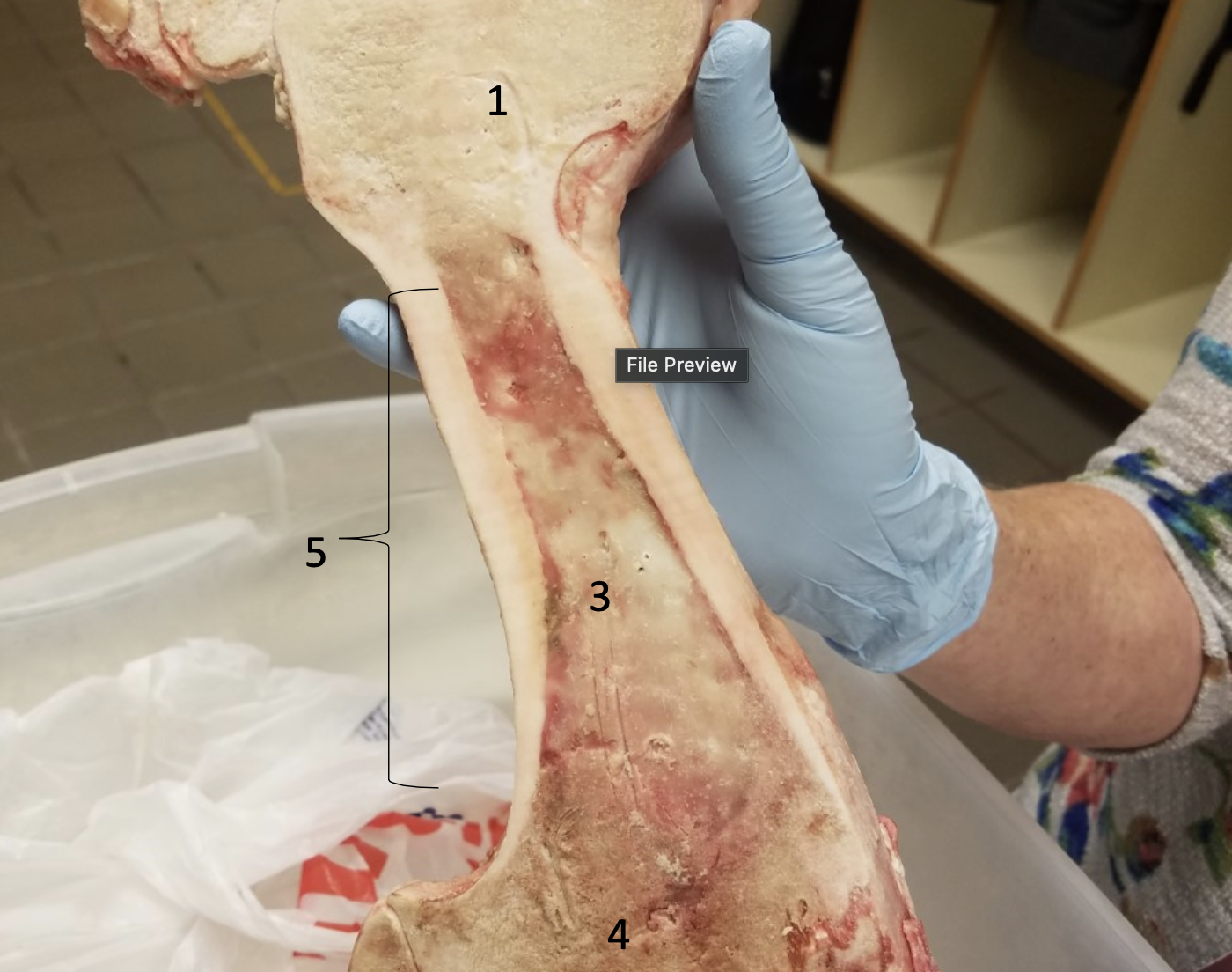
Diaphysis
#5