Vertebral Column Movements, Joints, and Ligaments
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
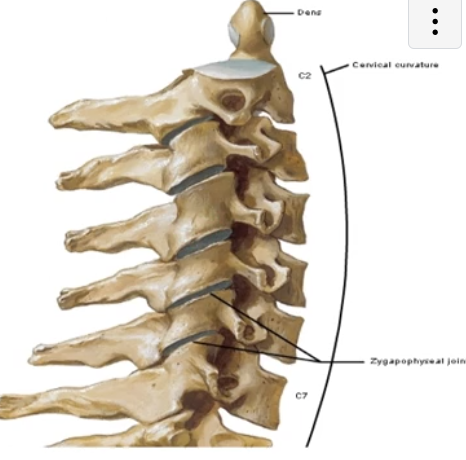
Zygapophysial Joint
-synovial plane joint between the superior and inferior articular processes of the vertebra
also called facet joints
plane joint = the surfaces of the joint are flat and “glide” over each other
-surrounded by a joint capsule due to it being a synovial joint
-cervical articular facets are oriented relatively horizontally and less tightly interlocked than other regions, making them more mobile and subject to dislocation
superior articular facet faces posteriorly and the inferior faces anteriorly
-specific angle and direction of the facets vary regionally and influence the motion available
-can be visualized on radiograph imaging
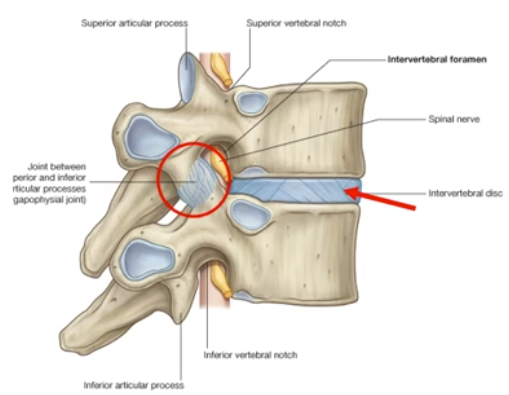
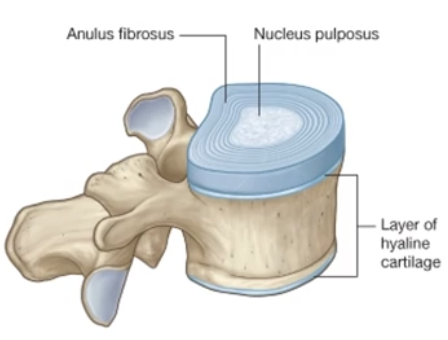
Intervertebral Disc
-symphysis joint sitting between adjacent vertebral bodies
-permits movement and absorbs shock
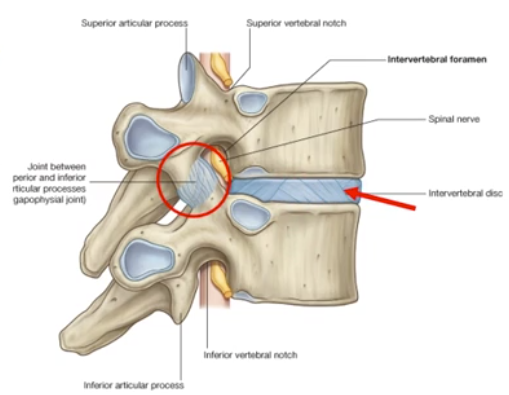
Intervertebral Disc Symphysis
-symphysis between adjacent vertebral bodies is formed by a layer of hyaline cartilage AND an intervertebral disc lying between those cartilage layers
-intervertebral disc is made up of: an outer anulus fibrosus and an inner nucleus pulposus
nucleus pulposus is gelatinous early in life, then becomes harder with age
Which type of imaging best shows details of the intervertebral discs?
-MRI
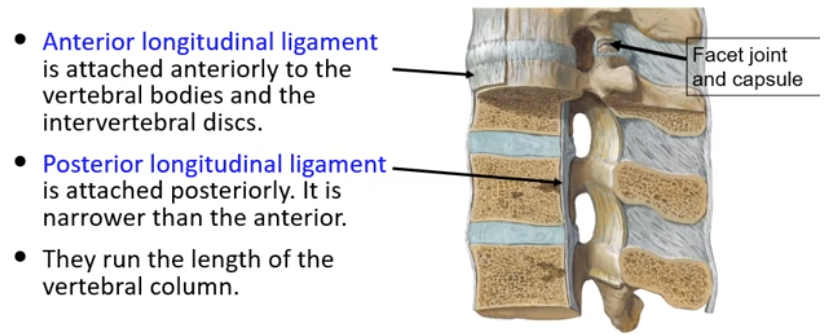
Anterior and Posterior Longitudinal Ligaments
-anterior longitudinal ligament is attached anteriorly to the vertebral bodies and the intervertebral discs
-posterior longitudinal ligament is attached posteriorly to the vertebral bodies; narrower than the interior
-both anterior and posterior longitudinal ligaments run the entire length of the vertebral column
Whiplash and the Anterior Longitudinal Ligaments
-whiplash causes traumatic hyperextension of the neck and may cause strain/tears to the anterior longitudinal ligament
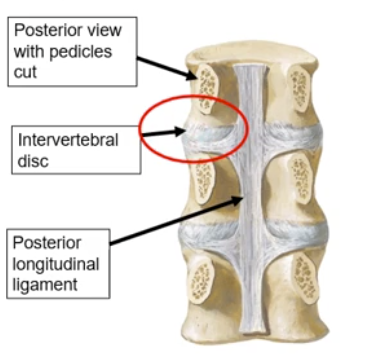
Disc Herniation and the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament
-the PLL is located within the vertebral canal, posterior to the vertebral bodies
-its structure being narrower than the ALL causes it to provide less support to the intervertebral discs → WEAKNESS
this weakness makes causes the risk of intervertebral disc herniation with posterolateral movement in the areas lacking PLL support
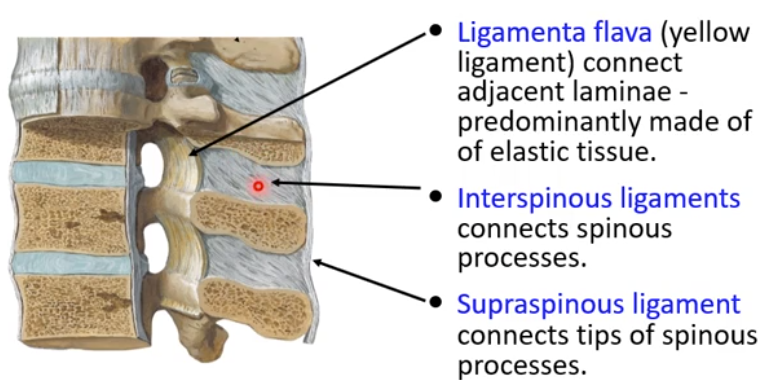
Ligamenta Flava
-yellow ligament
-connect adjacent laminae of the vertebral column
-made of many short ligamentous sections
-predominantly elastic tissue
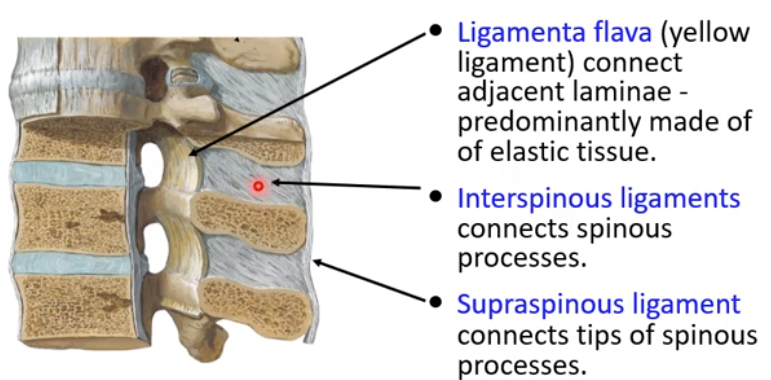
Interspinous Ligaments
-connect spinous processes of adjacent vertebra
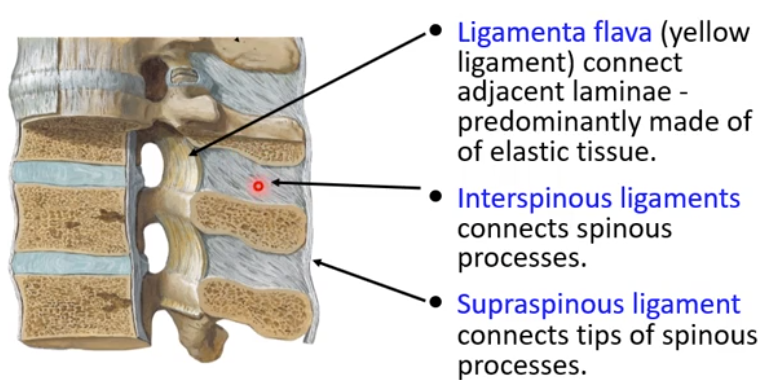
Supraspinous Ligament
-connects tips of spinous processes
-runs most of the length of the vertebral column
Nuchal Ligament
-also called ligamentum nuchae
“nuchal” = neck
-special ligament in the cervical spine that attaches from the external occipital protuberance over all 7 cervical spinous processes
-contains fibroelastic tissue
-resists flexion, aids returning head to anatomical position from flexion
-provides attachments for muscles on its lateral surface
Which ligaments become taught and limit the vertebral column in vertebral flexion?
-PLL
-Ligamentum flavum
-Interspinous ligaments
-Supraspinous ligaments
Which ligaments become taught and limit the vertebral column in vertebral extension?
-ALL
-anterior body musculature also limits extension under normal circumstances and is a source of pain during whiplash injury
Regional Variation in Spinal Motion
*the shape and thickness of intervertebral discs in the cervical and lumbar region also contribute to the curvatures found in this region

Atlantooccipital Joint (OA)
-occipital condyles of the skull articulate with the superior articular facets of “The Atlas” (C1)
-nodding the head (flexion and extension movement) and lateral flexion occur at this joint
Atlantoaxial Joint (AA)
-joint between “The Atlas” and “The Axis” (C1 and C2) vertebra
-rotation is the only motion available in this joint
-rotation is limited by the alar ligaments
-about half of all rotation in the cervical region occurs at the AA joint, while the rest occurs occurs as a composite motion between C2-C7
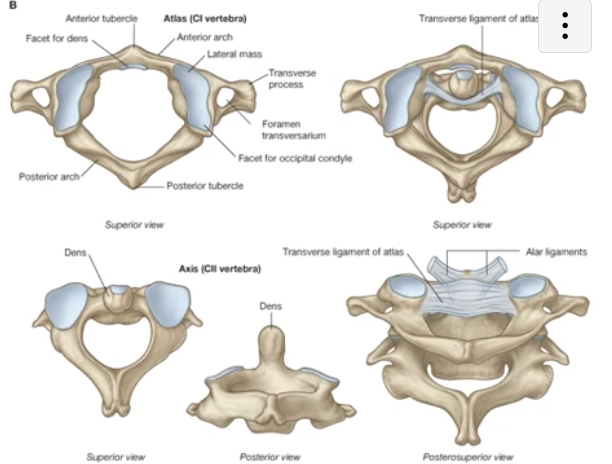
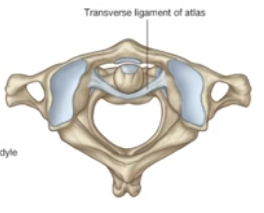
Transverse Ligament of “The Atlas”
-keeps the dens of the C2 vertebra from moving posterior and impinging upon the spinal cord