Biology 1 cells
1/30
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Protein
Long chain of amino acids coded for by genes.
The function depends on its shape.
some may contain nitrogen,hydrogen,carbon and oxygen
Carbohydrate
made from monosaccharides that form a chain of poly saccharides.
Starch, glycogen and cellulose are made from thousands of smaller glucose molecules.
Some contain only carbon,hydrogen and oxygen
Lipids
Made from 3 molecules of fatty acids and 1 molecule of glycerol.
They store energy.
Insoluble in water.
Some contain only carbon,hydrogen and oxygen
Nucleic Acid
Large molecules composed from nucleotides.
Carry information such as DNA and RNA.
some may contain nitrogen,sulfur and phosphorus.
Protein test
biuret test blue to purple
Lipids test
Emulsion test(using ethanol) from clear to a milky substance on the top.
Carbohydrates test
Iodine test from brown to blue black
reducing sugars test
benedict test from blue to red(hot water bath)
mitochondria
give energy to cell from glucose during respiration
+ where repiration takes place
cell membrane
controls what goes in and out of the cell
cell wall
keeps the structure of the cell and protects cell
ribosomes
make protein for the cell
nucleus
controls the cell (brain of cell)
cyptoplasm
a jelly like substance that makes up the inside of the cell except for the nucleus
vacuole
stores the cells waste and helps get rid of waste
chloroplast
green pigment found in chlorophyll
turns light into chemical energy for the synthesis of carbohydrates
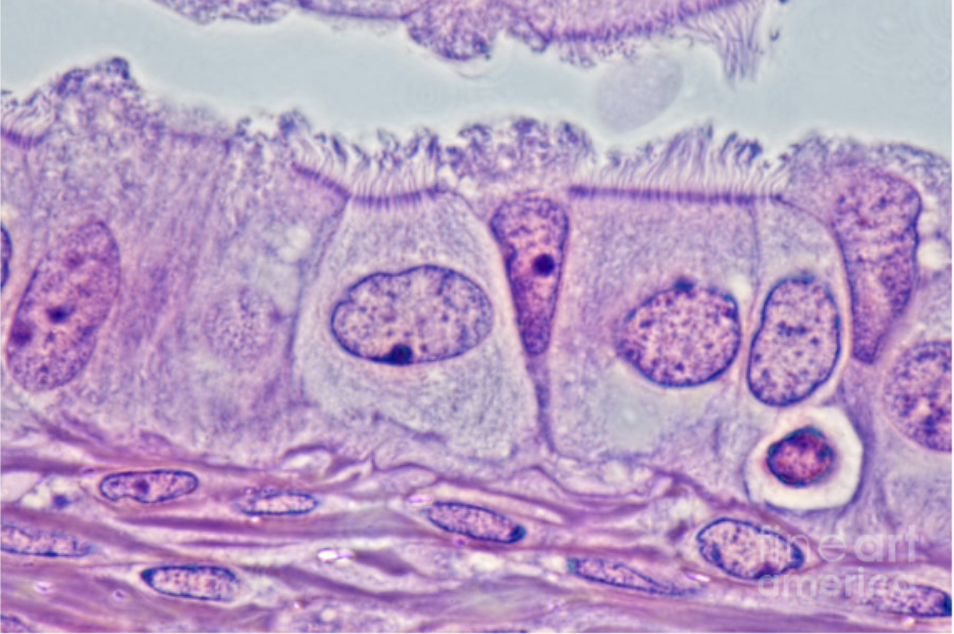
ciliated cells
have tiny hairs that move mucus out of the body.
Found in airways and oviducts.
In oviducts the cilia move the egg from the ovaries to the uterus
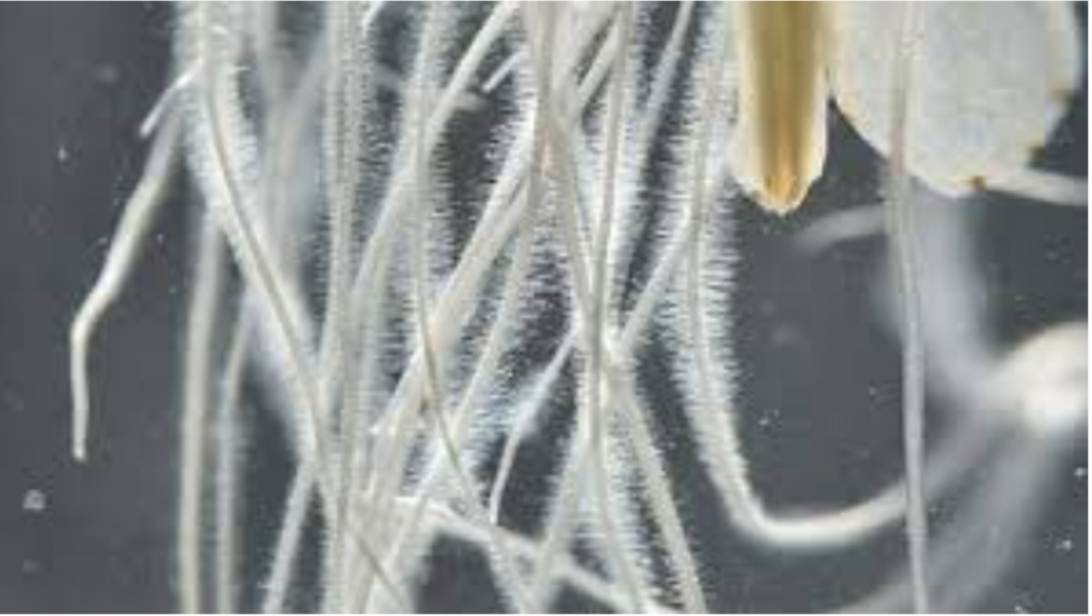

Roothair cells
Have a large surface area that help them take up water and mineral ions.
Contain mitochondria that release energy from glucose during respiration to give energy to the cell.
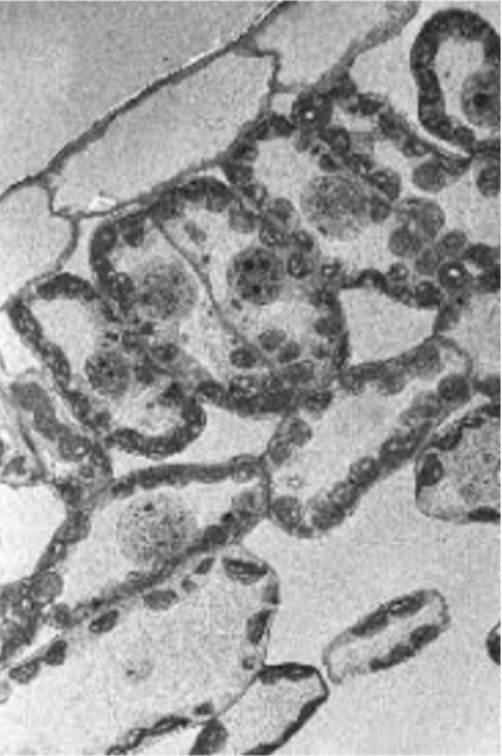
Palisade cells
Adapted for photosynthesis.
Column shaped and densely packed with chloroplast allowing them to absorb the maximum amount of energy.
One layer away from surface area.
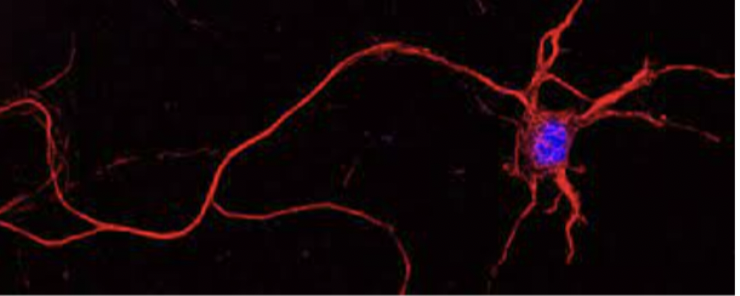
Neurons
transmit electrical signals across the nervous system.
Thin and over one metre long in your spinal cord.
Branched connections at each end —> join to other nerve cells.
Have a fatty sheath around —> increases speed they send messages
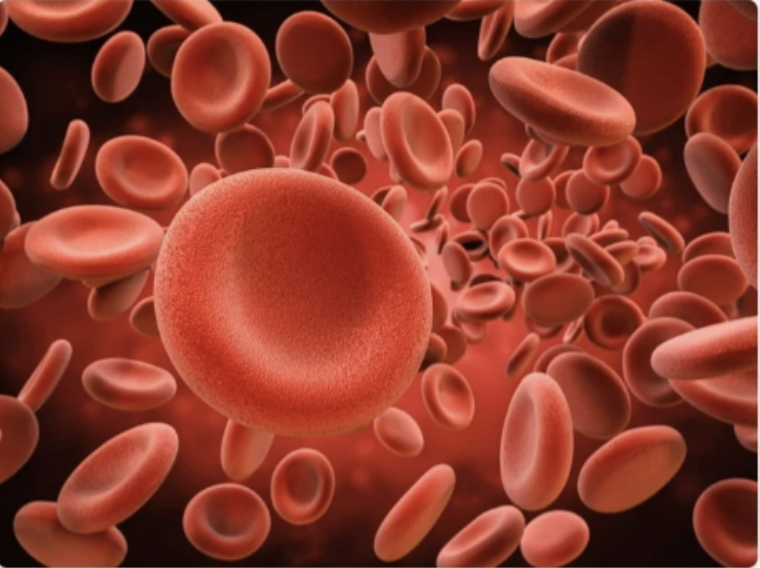
Red blood cells
contain haemoglobin that carry oxygen.
No nucleus —> more space to carry oxygen.
Flat disc shape with dips on -each side —> large surface area —> absorb more oxygen
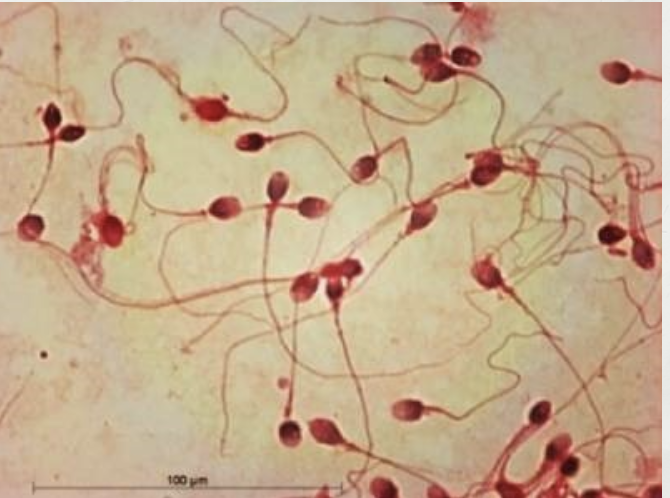
sperm
Tails —> move towards egg.
Mitochondria —> energy.
Tip of sperm( acrosome ) releases enzymes to get into egg.
Membrane —> for fertilisation to take place.
Haploid nucleus —> contains genetic information.
Produced in large amount of numbers to increase chance of fertilisation
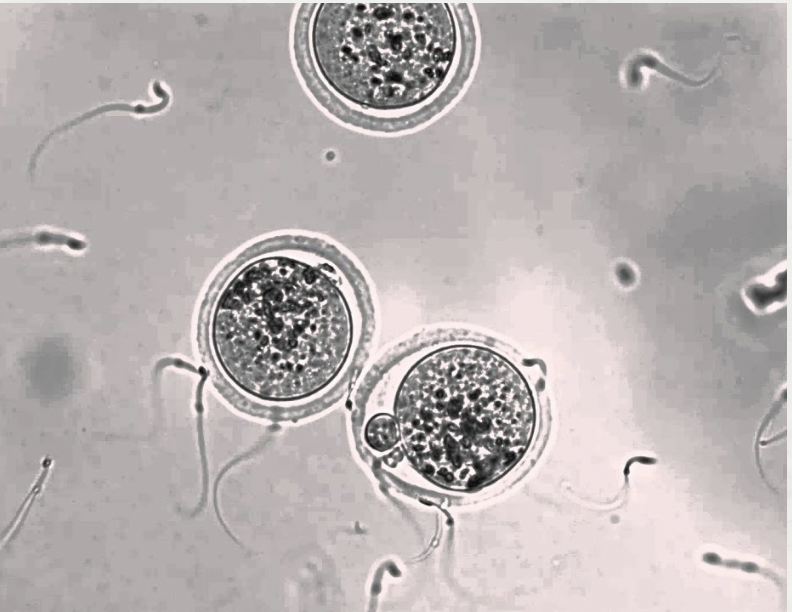
egg
cytoplasm contains nutrients to help growth of cell.
Haploid contain genetic information.
Cell membrane changes after fertilisation.
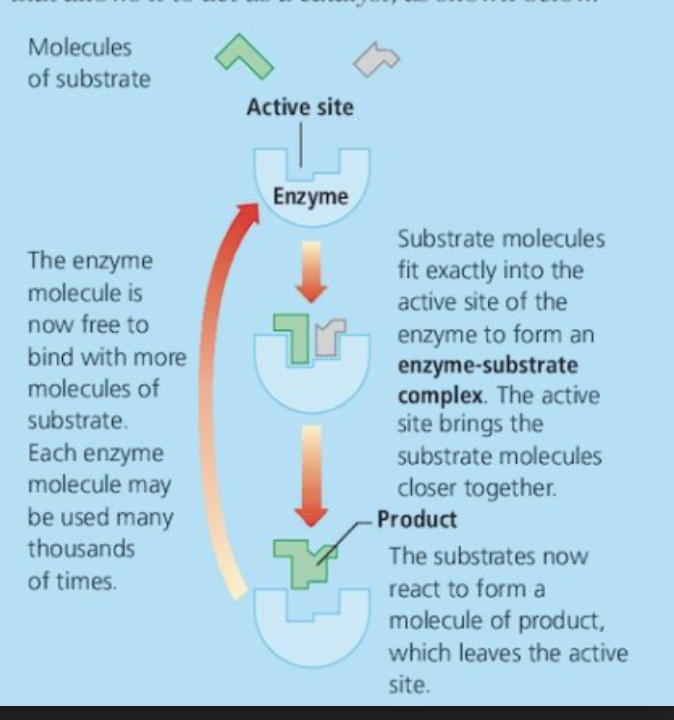
Enzymes
A protein folded into a three dimensional shape.
It is used to speed up chemical reactions by combining substrate molecules and create an enzyme-substrate complex.
An enzyme can be reused multiple times.
optimum pH - 7
characteristics of living organisms
movement, respiration, sensitivity, growth, reproduction, excretion, nutrition
magnification formula
size of image / actual size of object
actual size of object formula
size of image / magnification
mm to micro meter
1mm =1000 micro meters (µm)
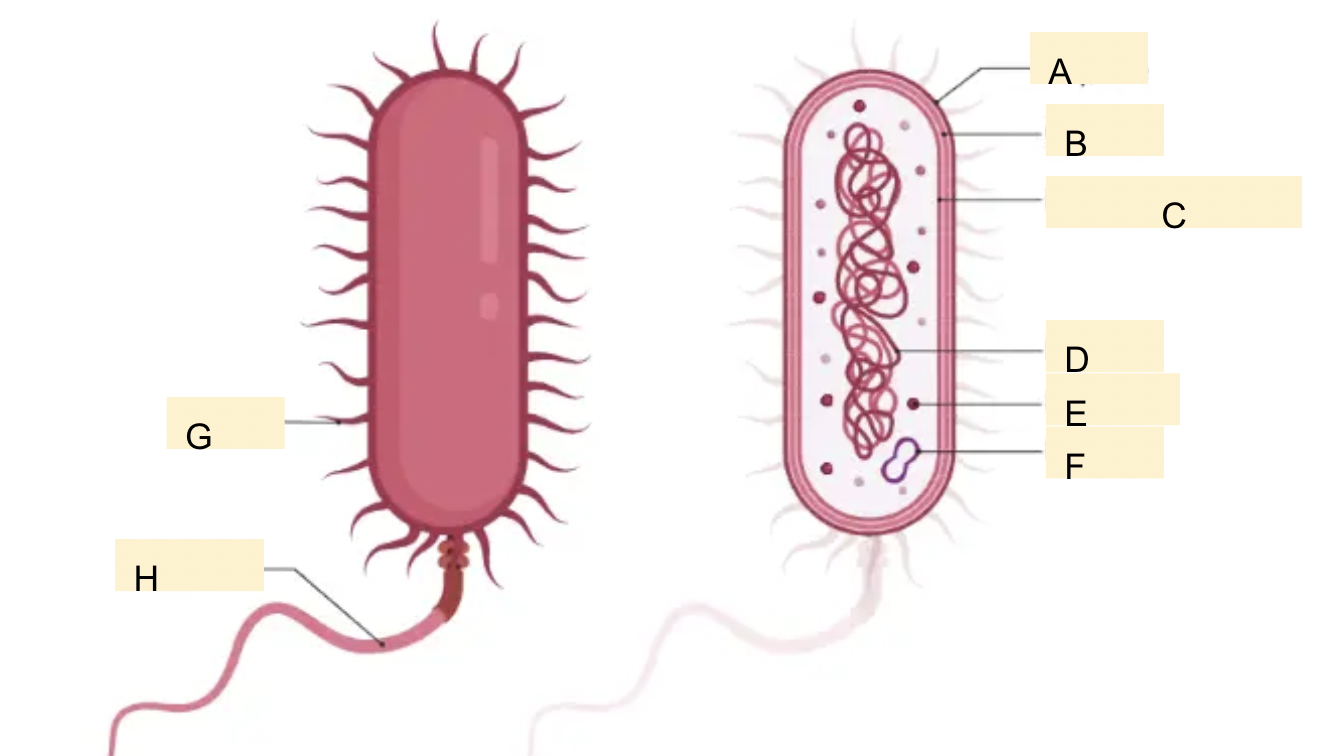
structure of bacteria cell label
(A - capsule)
B - cell wall
C - plasma membrane
D - nucleoid
E - ribosome
F - plasmid- (small circular dna molecule. transfer themselves from one host cell to another)
G - Pilus /Pili
H - flagella
role of goblet cells
produce mucus
codominance definition
when both alleles for a gene in a heterozygous organism equally contribute to the phenotype