Ch.1 Cell Structure
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Wavelength - 400-700 nm
Resolution - 200 nm
Specimen - alive
Image - colored
Light Microscope
Wavelength - 0.1 nm
Resolution - 0.05 nm
Specimen - dead
Image - monochrome
Electron Microscope
Cytoplasm
living material of the cell excluding the nucleus where metabolic reactions take place
Cell Surface Membrane
7 nm with three layers (phospholipid bilayer)
partially permeable and controls exchange between the cell and its environment
Microvilli
finger-like extensions of a cell which increases its surface area for more efficient absorption or secretion
Nucleus
Largest organelle (10 nm) containing genetic material
Chromatin
mass of coiled threads made of DNA, proteins (histones), and RNA
DNA contains the genes which controls cell activity
forms chromosomes during cell division
Nucleolus
made of loops of DNA from several chromosomes and makes ribosomes
densely staining and variable quantity
Nuclear Envelope & Pores
double-membraned with the outer membrane continuous with the RER
perforated by pores which control the exchange of materials between the nucleus and cytoplasm
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
covered with ribosomes
network of flattened sacs
molecules (particularly proteins) can be transported instead through the cell
continuous with the outer membrane of the nuclear envelope
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
makes lipids and steroids
storage site of calcium ions
Ribosomes
consists of two subunits
made of rRNA and protein
allow interacting molecules (mRNA, tRNA, amino acids, regulatory proteins) involved in protein synthesis to gather
70S (20 nm) in prokaryotes and mitochondria/chloroplasts and 80S (25 nm) in eukaryotes.
Golgi Apparatus
stack of flattened sacs called cisternae
formed at one end which bud off from the ER and broken down again at the other end to form the golgi vesicle
makes lysosomes, glycoproteins, glycolipids
processed molecules can be transported by the golgi vesicle
Lysosomes
simple sacs surrounded by a single membrane
contains digestive/hydrolytic enzymes(hydrolases) and performs destructive functions
Mitochondria
surrounded by an envelope (two membranes) with the inner membrane folding into cristae which project into the matrix
performs aerobic respiration
energy is transferred to molecules of ATP
energy is released from ATP by breaking down to ADP during hydrolysis
contains circular DNA and 70S ribosomes
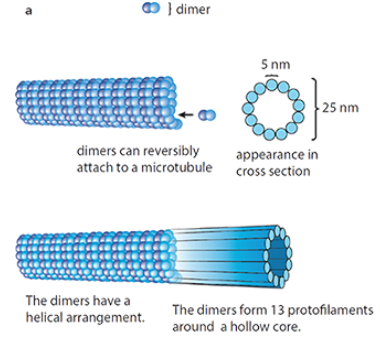
Microtubules
long, rigid, hollow tubes that make up the cytoskeleton
α- and β- tubulin combine to form dimers which are joined to make protofilaments. Thirteen protofilaments lines up to form microtubules
forms an intracellular transport system
forms a spindle during nuclear division
part of the structure of centrioles
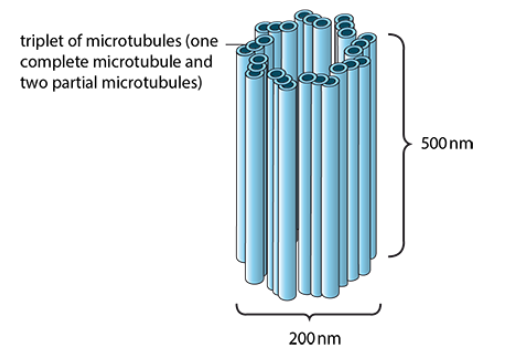
Centriole
cylindrical structures found outside the nucleus and at the bases of cilia and flagella
formed from a ring of nine triplets of microtubules
centrioles at the bases of cilia and flagella (basal bodies) act as MTOCs
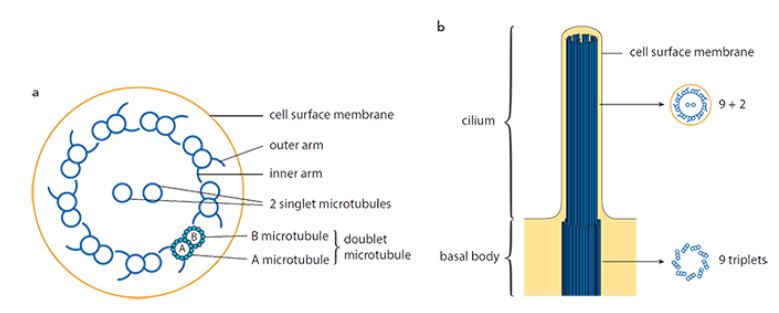
Cilia and Flagella
whip-like, beating extensions
two central microtubules and a ring of nine microtubule doublets (MTD)
MTD has an A microtubule with 13 protofilaments and a B microtubule with 10 protofilaments
has inner and outer arms made of the protein dynein which connect to the B microtubule of the neighboring MTD
used for locomotion
Chloroplasts
carries out photosynthesis
contains flattened sacs called thylakoids with chlorophyll embedded in there membranes
thylakoids are stacked to form grana
the energy converts carbon dioxide into sugars which are stored as starch grains in the stroma (matrix)
lipid droplets, 70S ribosomes, and circular DNA are found in the stroma
Cell Walls
rigid as they are made from polysaccharide cellulose which are inelastic and have high tensile strength
reinforced by lignin
provides mechanical strength, gives the cell a definite shape and prevents bursting by osmosis
Plasmodesmata
pore-like structure found in plant cell walls
forms passage between neighboring cells by fine threads of cytoplasm to allow exchange of materials
Vacuole
holds cells sap which contains pigments, enzymes, sugars, mineral salts, oxygen and carbon dioxide
surrounded by a partially permeable membrane (tonoplasts) which controls the exchange between the vacuole and cytoplasm
helps regulate the osmotic properties of the cell
Bacteria
prokaryotic and unicellular
1-5 µm diameter
circular DNA and plasmids
peptidoglycan cell walls
70S ribosomes
absence of organelles surrounded by double-membranes
Viruses
non-cellular structures with a nucleic acid core (DNA or RNA)
capsid (protein coat) made of the proteins molecules (capsomere)
some viruses have an outer layer made of phospholipids